After 50 years, Ars staffers pick their favorite Saturday Night Live sketches
“Do not taunt Happy Fun Ball.”
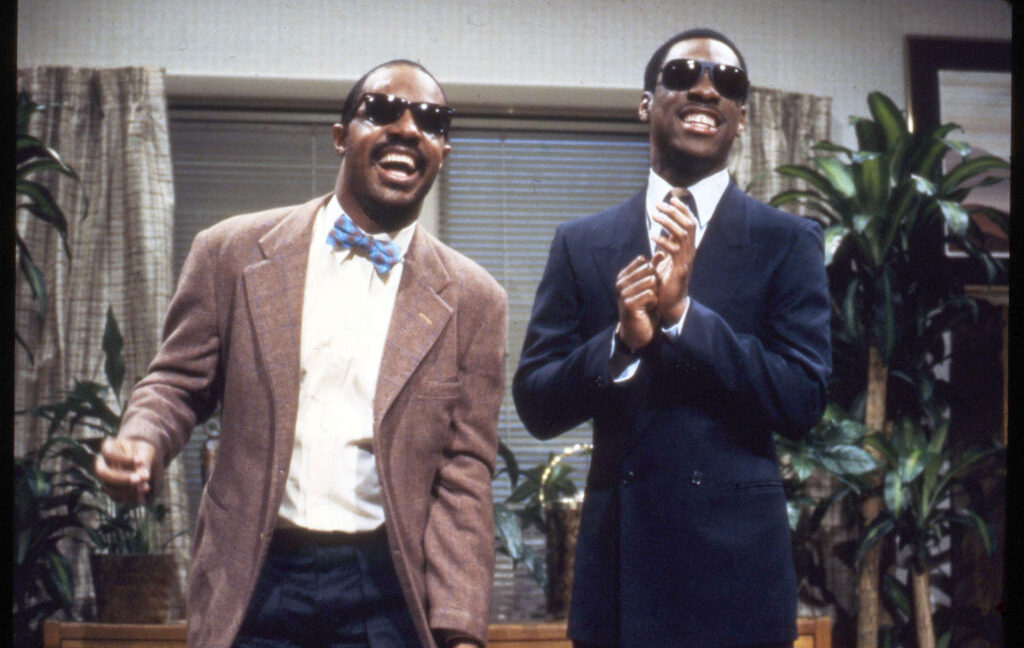
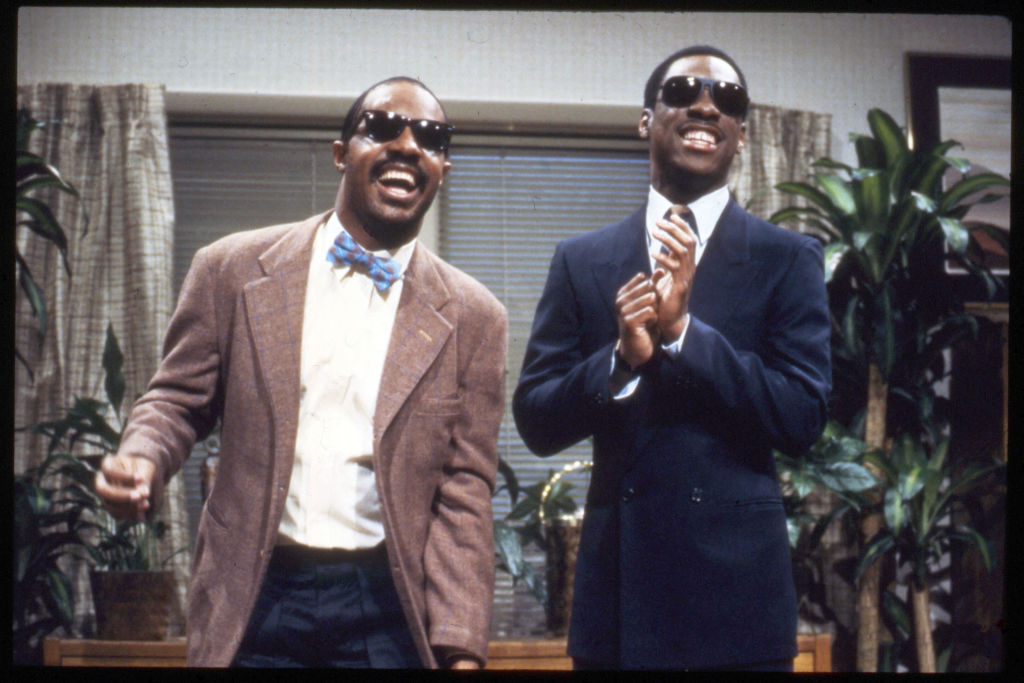
American musician Stevie Wonder (left) appears on an episode of ‘Saturday Night Live’ with comedian and actor Eddie Murphy, New York, New York, May 6, 1983. Credit: Anthony Barboza/Getty Images
The venerable late-night sketch comedy show Saturday Night Live is celebrating its 50th anniversary season this year. NBC will air a special on Sunday evening featuring current and former cast members.
I’ve long been a big fan of the show, since I was a kid in the late 1980s watching cast members such as Phil Hartman, Dana Carvey, and Jan Hooks. By then, the show was more than a decade old. It had already spawned huge Hollywood stars like Chevy Chase and Eddie Murphy and had gone through some near-death experiences as it struggled to find its footing.
The show most definitely does not appeal to some people. When I asked the Ars editorial team to share their favorite sketches, a few writers told me they had never found Saturday Night Live funny, hadn’t watched it in decades, or just did not get the premise of the show. Others, of course, love the show’s ability to poke fun at the cultural and political zeitgeist of the moment.
With the rise of the Internet, Saturday Night Live has become much more accessible. If you don’t care to watch live on Saturday night or record the show, its sketches are available on YouTube within a day or two. Not all of the show’s 10,000-odd sketches from the last five decades are available online, but many of them are.
With that said, here are some of our favorites!
Celebrity Hot Tub Party (Season 9)
Saturday Night Live has a thing for hot tubs, and it starts here, with the greatest of all hot tub parties.
Should you get in the water? Will it make you sweat?
Good god!
Celebrity Hot Tub.
—Ken Fisher
Papyrus (Season 43)
Some of SNL’s best skits satirize cultural touchstones that seem like they’d be way too niche but actually resonate broadly with its audience—like Font Snobs, i.e., those people who sneer at fonts like Comic-Sans (you know who you are) in favor of more serious options like the all-time favorite Helvetica. (Seriously, Helvetica has its own documentary.)
In “Papyrus,” host Ryan Gosling played Steven, a man who becomes obsessed with the fact that the person who designed the Avatar logo chose to use Papyrus. “Was it laziness? Was it cruelty?” Why would any self-respecting graphic designer select the same font one sees all over in “hookah bars, Shakira merch, [and] off-brand teas”? The skit is played straight as a tense psychological thriller and ends with a frustrated Steven screaming, “I know what you did!” in front of the graphic designer’s house while the designer smirks in triumph.
There was even a sequel last year in which Gosling’s Steven is in a support group and seems to have recovered from the trauma of seeing the hated font everywhere—as long as he avoids triggers. Then he learns that the font for Avatar: The Way of Water is just Papyrus in bold.
So begins an elaborate plot to infiltrate a graphic designer awards event to confront his tormentor head-on. The twist: Steven achieves a personal epiphany instead and confronts the root of his trauma: the fact that he was never able to understand his father, Jonathan WingDings. “My dad was so hard to read,” a weeping Steven laments as he finally gets some much-needed closure. Like most sequels, it doesn’t quite capture the magic of the original, but it’s still a charming addition to the archive.
Papyrus.
—Jennifer Ouellette
Washington’s Dream (Season 49)
The only SNL skit known and loved by all my kids. Nate Bargatze is George Washington, who explains his dream of “liberty” to soldiers in his revolutionary army. Washington’s future America is heavy on bizarre weights, measures, and rules, though not quite so concerned about things like slavery.
Washington’s Dream.
—Nate Anderson
Commercial parodies
I’ve always been partial to SNL‘s commercial parodies, probably because I saw way too many similar (but earnest) commercials while watching terrestrial TV growing up.
The other good thing about the commercial format is that it’s hard to make them longer than about two minutes, so they don’t outstay their welcome like some other SNL sketches
It’s hard to pick just one, so I’ll give a trio, along with the bits I think about and/or quote regularly.
Old Glory Insurance: “I don’t even know why the scientists make them!” (Season 21)
Old Glory Insurance.
First Citywide Change Bank: “All the time, our customers ask us, ‘How do you make money doing this?’ The answer is simple: volume.” (Season 14)
First CityWide Change Bank.
Happy Fun Ball: “Do not taunt Happy Fun Ball” (Season 16)
Happy Fun Ball.
—Kyle Orland
Anything with Phil Hartman (Seasons 12 to 20)
Phil Hartman was a regular on Saturday Night Live throughout my high school and college years, and it was nice to know that on the rare Saturday night when I did not have a date or plans, he and the cast would be on television to provide entertainment. He was the “glue” guy during his time on the show, playing a variety of roles and holding the show together.
Here are some of his most memorable sketches, at least to me.
Anal Retentive Chef. Hartman acts as Gene, who is… well, anal retentive. He appeared in five different skits over the years. This is the first one. (Season 14)
The Anal Retentive Chef.
Hartman had incredible range. During his first year on the show, he played President Reagan, who at the time had acquired the reputation of becoming doddering and forgetful. However, as Hartman clearly shows us in this sketch, that is far from reality. (Season 12)
President Reagan, Mastermind.
And here he is a few years later, during the first year of President Clinton’s term in office. This skit also features Chris Farley, who was memorable in almost everything he appeared in. “Do you mind if I wash it down?” (Season 18)
President Bill Clinton at McDonald’s.
Kyle has noted commercial parodies above, and there are many good ones. Hartman often appeared in these because he did such a good job of playing the “straight man” character in comedy, the generally normal person in contrast to all of the wackiness happening in a scene. One of Hartman’s most famous commercials is for Colon Blow cereal. However, my favorite is this zany commercial for Jiffy Pop… Airbags. (Season 17)
Jiffy Pop Airbag.
—Eric Berger
Motherlover (Season 34)
The Lonely Island (an American comedy trio, formed by Andy Samberg, Jorma Taccone, and Akiva Schaffer, which wrote comedy music videos) had bigger, more viral hits, but nothing surpasses the subversiveness of “to me, you’re like a brother, so be my motherlover.”
Motherlover.
—Jacob May
More Cowbell (Season 25)
This classic sketch gets featured on almost all SNL “best of” lists; “more cowbell” even made it into the dictionary. It’s a sendup of VH1’s “Behind the Music,” focused on the recording of Blue Oyster Cult’s 1975 hit “Don’t Fear the Reaper,” which features a distinctive percussive cowbell in the background. Will Ferrell is perfection as fictional cowbell player Gene Frenkel, whose overly enthusiastic playing is a distraction to his bandmates. But Christopher Walken’s “legendary” (and fictional) producer Bruce Dickinson loves the cowbell, encouraging Gene to “really explore the studio space” with each successive take. “I gotta have more cowbell, baby!”
Things escalate as Gene’s playing first becomes too flamboyant, and then passive-aggressive, until the band works through its tensions and decides to embrace the cowbell after all. The comic timing is spot on, and the cast doesn’t let the joke run too long (a common flaw in lesser SNL skits). Ferrell’s physical antics and Walken’s brilliantly deadpan delivery—”I got a fever and the only prescription is more cowbell!”—has the cast on the verge of breaking character throughout. It deserves its place in the pantheon of SNL‘s best.
More Cowbell.
—Jennifer Ouellette
The Californians (Season 37-present day)
I was going to go with Old Glory Insurance as my favorite SNL skit, but since Kyle already grabbed that one, I have to fall back on some of my runners-up. And although the Microsoft Robots and Career Day and even good ol’ Jingleheimer Junction almost topped my list, ultimately, I have to give it up to the recurring SNL skit that has probably given me more joy than anything the show has done since John Belushi’s samurai librarian. I am speaking of The Californians.
This fake soap opera, featuring a cast of perpetually blonde, perpetually unfaithful, perpetually directions-obsessed California stereotypes hits me just right. The elements that get repeated in every skit (including and especially Fred Armisen’s inevitable “WHATAREYUUUUDUUUUUUUINGHERE” or the locally produced furniture that everyone makes a point of using in the second act) are the kind of absurdities that get funnier over time, and it’s awesome to see guest stars try on the hyper-SoCal accent that is mandatory for all characters in the Californians’ universe.
Special props to Kristen Wiig, too—she’s inevitably hilarious, but her incredulous line reading when Mick Jagger shows up as Stuart’s long-absent father (“STUART! You never told me you had a dad!”) can and will fully send me into doubled-over hysterics every single time.
The Californians.
—Lee Hutchinson
What’s the fuss about?
In more than 20 years of living in the United States, few things still remain as far outside my cultural frame of reference as SNL. Whenever someone makes an unintelligible joke in Slack (or IRC before it) and everyone laughs, it invariably turns out to be some SNL thing that anyone who grew up here instinctively understands.
To me, it was always just *crickets*.
—Jonathan Gitlin
Black Jeopardy (Season 42)
Kenan Thompson was the show’s first cast member born after SNL‘s premiere in 1975, and after joining the show in 2003, he has become its longest-running cast member. Whenever he is on screen, you know you’re about to see something hilarious. One of his best roles on SNL has become the “game show host,” with long-running bits on Family Feud and the absurdly hilarious Black Jeopardy. The most famous of these latter skits occurred in 2016, when Tom Hanks appeared. If you haven’t watched it, you really must.
Black Jeopardy.
—Eric Berger
Josh Acid (Season 15)
One of my favorite SNL sketches (and perhaps one of the most underrated) is an Old West send-up featuring a sheriff named “Josh Acid” (played by Mel Gibson during his hosting appearance in 1989), who keeps two bottles of acid in holsters instead of the standard six-shooter revolvers.
The character is a hero in his town, but when he throws acid on people, their skin melts, and they die a horrible, gruesome death. The townspeople witness one such death and say it’s “gross.” In response, the main character cites Jim Bowie using a Bowie knife and says, “I use acid because that’s my name.” At one point, Kevin Nealon, as the bartender, says the town is grateful he’s cleaned up the place, but “it’s just that we’re not sure which is worse: lawlessness, or having to watch people die horribly from acid.”
Later, when a woman asks Josh to choose between her or acid, he says, “Frida, I took a job, and that job’s not done until every criminal in this territory is either behind bars or melted down.”
The sketch is just absurdly ridiculous in a delightful way, and it gleefully subverts the stoic nobility of the stereotypical Western hero, which is a trope baby boomers grew up with on TV. If I were to stretch, I’d also say it works because it lampoons the idea that some methods of legally or rightfully killing someone are more honorable and socially acceptable than others.
It’s not on YouTube that I can find, but I found a copy on TikTok.
—Benj Edwards
Hidden Camera Commercials (Season 17)
For me—and, I suspect, most people—there are several “golden ages” of SNL. But if I had to pick just one, it would be the Chris Farley era. The crown jewel of Farley’s SNL tenure was certainly the Bob Odenkirk- penned “Van Down by the River.” Today, though, I’d like to highlight a deeper cut: a coffee commercial in which Farley’s character is told he is drinking decaf coffee instead of regular. Instead of being delighted that he can’t tell the difference in taste, he gets… ANGRY.
Farley’s incredulous “what?” and dawning rage at being deceived never fail to make me laugh.
Hidden Camera Commercials.
—Aaron Zimmerman
Wake Up and Smile (Season 21)
SNL loves to take a simple idea and repeat it—sometimes without enough progression. But “Wake Up and Smile” stands out by following its simple idea (perky morning show hosts are lost without their teleprompters) into an incredibly dark place. In six minutes, you can watch the polished veneer of civilization collapse into tribal violence, all within the absurdist confines of a vapid TV show. In the end, everyone wakes from their temporary dystopian dreamland. Well, except for the weatherman.
Wake Up and Smile
—Nate Anderson
Thanks, Nate, and everyone who contributed. Indeed, one of the joys of watching the show live is you never know when a sketch is going to dark or very, very dark.
Eric Berger is the senior space editor at Ars Technica, covering everything from astronomy to private space to NASA policy, and author of two books: Liftoff, about the rise of SpaceX; and Reentry, on the development of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon. A certified meteorologist, Eric lives in Houston.
After 50 years, Ars staffers pick their favorite Saturday Night Live sketches Read More »