AI #84: Better Than a Podcast
Andrej Karpathy continues to be a big fan of NotebookLM, especially its podcast creation feature. There is something deeply alien to me about this proposed way of consuming information, but I probably shouldn’t knock it (too much) until I try it?
Carlos Perez: Google with NotebookLM may have accidentally stumbled upon an entirely new way of interacting with AI. Its original purpose was to summarize literature. But one unexpected benefit is when it’s used to talk about your expressions (i.e., conversations or lectures). This is when you discover the insight of multiple interpretations! Don’t just render a summary one time; have it do so several times. You’ll then realize how different interpretations emerge, often in unexpected ways.
Delip Rao gives the engine two words repeated over and over, the AI podcast hosts describe what it says about the meaning of art for ten minutes.
So I figured: What could be a better test than generating a podcast out of this post (without the question, results or reaction)?
I tried to do that, deselecting the other AI posts and going to town. This was the result. Unfortunately, after listening it seems I learned that deselecting posts from a notebook doesn’t seem to take them out of the info used for podcast generation, so that was more of an overall take on AIs ~40-64 plus the latest one.
In some ways I was impressed. The host voices and cadences are great, there were no mistakes, absurdities or factual errors, everything was smooth. In terms of being an actual substitute? Yeah, no. It did give me a good idea of which ideas are coming across ‘too well’ and taking up too much mindspace, especially things like ‘sci-fi.’ I did like that it led with OpenAI issues, and it did a halfway decent job with the parts it did discuss. But this was not information dense at all, and no way to get informed.
I then tried again with a fresh notebook, to ensure I was giving it only AI #84, which then started off with OpenAI’s voice mode as one would expect. This was better, because it got to a bunch of specifics, which kept it on target. If you do use the podcast feature I’d feed it relatively small input chunks. This still seemed like six minutes, not to do Hamlet, but to convey maybe two minutes of quick summary reading. Also it did make an important error that highlighted a place I needed to make my wording clearer – saying OpenAI became a B-corp rather than that it’s going to try and become one.
There were indeed, as usual, many things it was trying to summarize. OpenAI had its dev day products. Several good long posts or threads laid out arguments, so I’ve reproduced them here in full partly for reference. There was a detailed proposal called A Narrow Path. And there’s the usual assortment of other stuff, as well.
-
Introduction. Better than a podcast.
-
Language Models Offer Mundane Utility. You’d love to see it.
-
Language Models Don’t Offer Mundane Utility. Let’s see what happens.
-
Copyright Confrontation. Zuck to content creators: Drop dead.
-
Deepfaketown and Botpocalypse Soon. A word of bots, another for the humans.
-
They Took Our Jobs. Software engineers, now super productive, our price cheap.
-
The Art of the Jailbreak. Encode it in a math puzzle.
-
Get Involved. UK AISI is hiring three societal impacts workstream leads.
-
Introducing. AlphaChip, for designing better AI chips, what me worry?
-
OpenAI Dev Day. Advanced voice for everyone, if you want it enough.
-
In Other AI News. Anthropic revenue is on the rise.
-
The Mask Comes Off. The man who sold the world… hopefully to himself.
-
Quiet Speculations. Perplexity for shopping?
-
The Quest for Sane Regulations. The suggestion box is open.
-
The Week in Audio. Peter Thiel has some out there ideas, yo.
-
Rhetorical Innovation. Would you go for it, or just let it slip until you’re ready?
-
Remember Who Marc Andreessen Is. For reference, so I can remind people later.
-
A Narrow Path. If it would kill everyone, then don’t let anyone ing build it.
-
Aligning a Smarter Intelligence is Difficult. Pondering what I’m pondering?
-
The Wit and Wisdom of Sam Altman. To do, or not to do? To think hard about it?
-
The Lighter Side. 10/10, no notes.
OpenAI’s Advanced Voice Mode is really enjoying itself.
It enjoys itself more here: Ebonics mode activated.
Sarah Constantin requests AI applications she’d like to see. Some very cool ideas in here, including various forms of automatic online content filtering and labeling. I’m very tempted to do versions of some of these myself when I can find the time, especially the idea of automatic classification of feeds into worthwhile versus not. As always, the key is that if you are going to use it on content you would otherwise need to monitor fully, hitting false negatives is very bad. But if you could aim it at sources you would otherwise be okay missing, then you can take a hits-based approach.
Llama 3.2 ‘not available for download’ in the EU, unclear exactly which regulatory concern or necessary approval is the bottleneck. This could be an issue for law-abiding corporations looking to use Llama 3.2. But of course, if an individual wants to download and use it in the EU, and is competent enough that this is a good idea, I am confident they can figure out how to do that.
The current status of AI agents:
Buck Shlegeris: I asked my LLM agent (a wrapper around Claude that lets it run bash commands and see their outputs):
>can you ssh with the username buck to the computer on my network that is open to SSH
because I didn’t know the local IP of my desktop. I walked away and promptly forgot I’d spun up the agent. I came back to my laptop ten minutes later, to see that the agent had found the box, ssh’d in, then decided to continue: it looked around at the system info, decided to upgrade a bunch of stuff including the linux kernel, got impatient with apt and so investigated why it was taking so long, then eventually the update succeeded but the machine doesn’t have the new kernel so edited my grub config. At this point I was amused enough to just let it continue. Unfortunately, the computer no longer boots.
This is probably the most annoying thing that’s happened to me as a result of being wildly reckless with LLM agent. [logs here]
Buck was, of course, very much asking for it, and essentially chose to let this happen. One should still note that this type of proactive messing with things in order to get to the goal is the default behavior of such agents. Currently they’re quite bad at it.
As usual, you can’t get the utility from the AI unless you are willing to listen to it, but also we need to be careful how we score.
When measuring something called ‘diagnostic reasoning’ when given cases to diagnose GPT-4 alone (92%) did much better than doctors (73%) and also did much better than doctors plus GPT-4 (77%). So by that measure, the doctors would be much better fully out of the loop and delegating the task to GPT-4.
Ultimately, though, diagnosis is not a logic test, or a ‘match the logic we think you should use’ test. What we mostly care about is accuracy. GPT-4 had the correct diagnosis in 66% of cases, versus 62% for doctors.
My strong guess is that doctors learn various techniques that are ‘theoretically unsound’ in terms of their logic, or that take into account things that are ‘not supposed to matter’ but that do correlate with the right answer. And they’ve learned what approaches and diagnoses lead to good outcomes, rather than aiming for pure accuracy, because this is part of a greater system. That all mostly works in practice, while they get penalized heavily for it on ‘reasoning’ tests.
Indeed, this suggests that one future weakness of AIs will be if we succeed in restricting what things they can consider, actually enforcing a wide array of ‘you are not allowed to consider factor X’ rules that humans routinely pay lip service to and then ignore.
Ethan Mollick: Ok. Deleting this and reposting given the Community Note (you can see the original and Note below). The main point doesn’t change in any way, but I want to make sure I am clear in this post that the measurement was diagnostic reasoning & not final diagnoses.
A preview of the coming problem of working with AI when it starts to match or exceed human capability: Doctors were given cases to diagnose, with half getting GPT-4 access to help. The control group got 73% score in diagnostic accuracy (a measure of diagnostic reasoning) & the GPT-4 group 77%. No big difference.
But GPT-4 alone got 88%. The doctors didn’t change their opinions when working with AI.
To be clear, this doesn’t say AI will always beat doctors – this is a narrow test. It is much more about what this means for the future. As AI models get better, and match or exceed human level performance, what happens? This is one example where it is happening, and we see the issues emerging.
Jonathan Chen (study author): Provocative result we did NOT expect. We fully expected the Doctor + GPT4 arm to do better than Doctor + “conventional” Internet resources. Flies in the face of the Fundamental Theorem of Informatics (Human + Computer is Better than Either Alone).
It is already well known that if the AI is good enough, the humans will in many settings mess up and violate the Fundamental Theorem of Informatics. It’s happened before. At some point, even when you think you know better, you’re on average wrong, and doctors are not about to fully trust an AI on diagnosis until you prove to them they should (and often not even then, but they should indeed demand that much).
Mark Zuckerberg was asked to clarify his position around content creators whose work is used to create and train commercial products, in case his prior work had made his feelings insufficiently clear.
He was happy to oblige, and wants to be clear that his message is: Fuck you.
The Verge: Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg says there are complex copyright questions around scraping data to train Al models, but he suggests the individual work of most creators isn’t valuable enough for it to matter.
“I think individual creators or publishers tend to overestimate the value of their specific content in the grand scheme of this,” Zuckerberg said in the interview, which coincides with Meta’s annual Connect event. “My guess is that there are going to be certain partnerships that get made when content is really important and valuable.” But if creators are concerned or object, “when push comes to shove, if they demanded that we don’t use their content, then we just wouldn’t use their content. It’s not like that’s going to change the outcome of this stuff that much.”
So you’re going to give them a practical way to exercise that option, and if they say no and you don’t want to bother paying them or they ask for too much money then you won’t use their content?
Somehow I doubt that is his intention.
Levelsio predicts the social media platform endgame of bifurcation. You have free places where AIs are ubiquitous, and you have paid platforms with only humans.
Andrej Karpathy: Is it a function of whether you pay or not? We pay here and still there is a lot of bot radiation.
I’d look to improve things on OS level with a liveness certification. There were a number of comments along the lines of oh it’s too difficult and I basically disagree. A phone has a lot of sensing, history and local compute to calculate a score for “this device is used in a statistically regular way”.
Keen: seems the easiest / most reliable thing to converge to is some irl proof of personhood like worldcoin. no one likes the idea of iris scans but the fundamental idea seems correct.
I agree that some form of gatekeeping seems inevitable. We have several reasonable choices.
The most obvious is indeed payment. If you charge even a small amount, such as $10/month or perhaps far less, then one already ‘cannot simply’ deploy armies of AI slop. The tax is unfortunate, but highly affordable.
Various forms of proof of identity also work. You don’t need Worldcoin. Anything that is backed by a payment of money or a scarce identity will be fine. For example, if you require a working phone number and subscription with a major phone carrier, that seems like it would work, since faking that costs money? There are several other good alternatives.
Indeed, the only core concept is ‘you post a bond of some kind so if you misbehave there is a price.’ Any payment, either money or use of a scarce resource, will do.
I can also think of other solutions, involving using AI and other algorithms, that should reliably solve the issues involved. This all seems highly survivable, once we bring ourselves to care sufficiently. Right now, the problem isn’t so bad, but also we don’t care so much.
Qualy: my actual take about AI scam calls is that it probably won’t be a big issue, because:
– we have this prob with text already, the solution is using authenticated channels
– this authentication doesn’t have to be clever, someone giving you their phone number in person once is fine
There is also the factor of using only-known-to-you information, which in practice calls to your bank or whatever require already (not because they couldn’t in principle recognise your voice, just bc they don’t care to).
I also think this essentially applies to worries about deepfakes too, although I would have to think abt it more. In most cases someone saying “that’s not me” from their official twitter account seems good enough.
Danielle Fong: pretty sure this *isgoing to be a problem, and i wonder why these sort of instrumental evils are downplayed relative to the hypothetical existential threat post by Superintelligence. Intelligence is composed of many different components and tactic . I brought up these problems years ago, and I’m not sure I spoke to the correct office. It was basically impossible to get law enforcement to care.
I for one downplay them because if the problem does get bad we can ‘fix them in post.’ We can wait for there to be a some scam calls, then adjust to mitigate the damage, then adjust again and so on. Homeostasis should set in, the right number of scam calls is not zero.
There are obvious solutions to scam calls and deepfakes. We mostly don’t use them now because they are annoying and time consuming relative to not doing them, so they’re not worth using yet except in certain high-value situations. In those situations, we do use (often improvised and lousy) versions already.
The latest version of a common speculation on the software engineer market, which is super soft right now, taking things up a notch.
alz: reminder, the entry-level tech job market is still totally cooked, like 4.0’s from Berkeley are getting 0 job offers.
Senior PowerPoint Engineer: I say this as someone who was early to being short entry-level tech hires but at some level of quality and salary it had to make sense to hire them, even if for some lousy entry-level consulting role at Accenture. Something weird is going on.
Senior Spreadsheet Engineer: My pet theory rn is the hiring market is insanely adversarial with all the AI-generated slop going around, mostly on the applicant side. HR is just overwhelmed. And that’s on top of the post-covid slowdown and layoffs.
I think a lot of places have simply given up, sifting through the slop and resume mountain is just not worth it for entry level roles.
My other theory right now is the job market will evolve by necessity to hiring managers and HR going out to find candidates proactively. Recruiters might also be helped by/useful for this.
There is clearly an AI-fueled flooding-the-zone and faking-the-interviews application crisis. Giving up on hiring entirely seems like an extreme reaction. You can decline to fill entry-level rolls for a bit but the damage should quickly compound.
The problem should be self-limiting. If the job market gets super soft, that means there will be lots of good real candidates out there. Those candidates, knowing they are good, should be willing to send costly signals. This can mean ‘build cool things,’ it should also mean hard to fake things like the 4.0 GPA, and also being willing to travel in-person for interviews so they can’t cheat on them using AI. Recruiters with a reputation to uphold also seem promising. There are a number of other promising candidate strategies as well.
Tyler Cowen suggests granting tenure on the basis of what you contribute to major AI models. The suggested implementation is somehow even crazier than that sounds, if one were to take it the slightest bit seriously. A fun question is, if this is the right way to grant tenure, what is the tenure for, since clearly we won’t in this scenario need professors that much longer, even if the humans survive and are fine?
How long until we no longer need schools?
There are two clocks ticking here.
-
As AI improves, the AI tutors get better.
-
Also, as the child gets older, the relative value of the AI tutor improves.
I think that, today, an average 16 year old would learn better at home with an AI tutor than at a typical school, even if that ‘AI tutor’ was simply access to AIs like Gemini, NotebookLM, Claude and ChatGPT plus an AI coding assistant. Specialization is even better, but not required. You combine the AI with textbooks and other sources, and testing, with ability to reach a teacher or parent in a punch, and you’re good to go.
Of course, the same is true for well-motivated teens without the AI. The school was already only holding them back and now AI supercharges their independent studies.
Six years from now, I don’t see how that is even a question. Kids likely still will go to schools, but it will be a wasteful anachronism, the same way many of our current methods are, as someone once put it, ‘pre-Guttenberg.’ We will justify it with some nonsense, likely about socialization or learning discipline. It will be super dumb.
The question is, will a typical six year old, six years from now, be at a point where they can connect with the AI well enough for that to work? My presumption, given how well voice modes and multimodal with cameras are advancing, is absolutely yes, but there is some chance that kids that young will be better off in some hybrid system for a bit longer. If the kid is 10 at that point? I can’t see how the school makes any sense.
But then, the justifications for our schools have always been rather nonsensical.
A new jailbreak technique is MathPrompt, encoding harmful prompts into mathematical problems. They report a success rate of 73.6% across 13 SotA LLMs.
UK AISI is hiring three societal impacts workstream leads.
AlphaChip, Google DeepMind’s AI for designing better chips with which to build smarter AIs, that they have decided for some bizarre reason should be open sourced. That would not have been my move. File under ‘it’s happening.’
ChatGPT advanced voice mode comes to the UK. The EU is still waiting.
OpenAI used Dev Day to ship new tools for developers. In advance, Altman boasted about some of the progress we’ve made over the years in decreasing order of precision.
Sam Altman: shipping a few new tools for developers today!
from last devday to this one:
*98% decrease in cost per token from GPT-4 to 4o mini
*50x increase in token volume across our systems
*excellent model intelligence progress
*(and a little bit of drama along the way)
What’s a little drama between no longer friends?
All right, let’s get more detailed.
Srinivas Narayanan (OpenAI, VP Engineering): Launched at Dev Day today
— Real time API for low latency speech applications
— Vision fine-tuning
— Model distillation
— Prompt caching
Look forward to seeing what developers build.
Sam Altman: realtime api (speech-to-speech) [here].
vision in the fine-tuning api [here].
prompt caching (50% discounts and faster processing for recently-seen input tokens) [here].
model distillation (!!) [here].
They also doubled the API rate limits on o1 to 10k per minute, matching GPT-4.
Here’s a livestream thread of Lizzie being excited. Here’s Simon Willson’s live blog.
Here’s their general purpose pricing page, as a reference.
Prompt Caching is automatic now for prompts above 1,024 tokens, offering a 50% discount for anything reused. They’re cleared after about 5-10 minutes of inactivity. This contrasts with Claude, where you have to tell it to cache but the discount you get is 90%.
Model Distillation is to help developers use o1-preview and GPT-4o outputs to help fine tune models like GPT-4o mini. It uses stored completions to build data sets, a beta of evals that run continuously while you train, and integration with fine tuning. You give it an evaluation function and a set of stored examples, they handle the rest. After the free samples in October it will cost what fine-tuning already costs. It makes a lot of sense to emphasize this, very good for business.
Vision is now available in the fine-tuning API. They claim as few as 100 images can improve performance on specific tasks, like localized street sign recognition or identifying local UI elements.
What does it mean to have a ‘realtime API’? It means exactly that, you can use an API to sculpt queries by the user while they’re talking in voice mode. The intent is to let you build something like ChatGPT’s Advanced Voice Mode within your own app, and not requiring stringing together different tools for handling inputs and outputs.
They provided a demo of an AI agent making a phone call on your behalf, and in theory (the other end of the call was the person on stage) spending almost $1500 to buy chocolate covered strawberries. This was very much easy mode on every level. We should on many levels be impressed it can do this at all, but we’ve seen enough elsewhere that this much is no surprise. Also note that even in the demo there was an important hitch. The AI was not told how to pay, and jumped to saying it would pay for the full order in cash without confirming that. So there’s definitely some kinks.
The first thing I saw someone else build was called Live Roleplays, an offering from Speak to help with language learning, which OpenAI demoed on stage. This has always been what I’ve seen as the most obvious voice mode use case. There’s a 15 second sample video included at the link and on their blog post.
Andrew Hsu: We’ve been working closely with OpenAI for the past few months to test the new Realtime API. I’m excited to share some thoughts on the best way to productize speech-to-speech for language learning, and announce the first thing we’ve built here, Live Roleplays.
Language learning is the perfect use case for speech-to-speech, as everyone is discovering! We’ve been blown away at how immersive our conversational practice experience now feels. But how does it differ from a general AI assistant like Advanced Voice Mode?
We think it’s more important than ever to create a product experience that’s purpose-built for language learning by combining the best technology, product design, and pedagogy. This is what enables a real path to language fluency beyond the first 15 minutes of interaction.
…
Here are some key aspects of how we’ve purpose-built this experience to be the most effective:
As a user progresses through the conversation, we use our proficiency graph to ensure the dialogue is at the right level and exposes helpful language they should learn next
We give the user specific objectives to try and complete during the roleplay to drive the conversation forward and get them to use key language items
And when they need extra help, we proactively surface just the right amount of a hint to help them.
And of course all of our lessons are driven by our proprietary learning engine so these Live Roleplays (along with all of our lesson types) happen as part of a wider learning sequence personalized to the learner.
I’m definitely excited for the ‘good version’ of what Speak is building, whether or not Speak is indeed building a good version, or whether OpenAI’s new offerings are a key step towards that good version.
We do need to lower the price a bit, right now this is prohibitive for most uses. But if there’s one thing AI is great at, it’s lowering the price. I have to presume that they’re not going to charge 10x-20x the cost of the text version for that long. Right now GPT-4o-realtime-preview is $5/$20 for a million text tokens, $100/$200 for a million audio tokens.
Timothy Lee: Anyone have a theory for why OpenAI is charging so much more for on a per-token basis? I’d expect audio to be expensive if it was using many tokens per second. But I don’t understand why it would be 10-20x more expensive per token.
If you can take care of that, Sully is excited, as would be many others.
Sully: Whoa okay the realtime api looks kinda insane, low key more exciting than o1
It can use realtime tools + their voice to voice model, which is bonkers.
I genuinely think this:
1) opens up a new wave of never before possible voice startups (sooo much to build)
2) this *mightactually kill existing voice startups because while OAI is not competing with them, the tech moat is basically 0.
i can build a voice ai agent wrapper in < 1 day. cost will go to 0.
I really want to build some real time voice apps now!
Nikshep Saravanan: it’s awesome but expensive, $0.25 per minute of output. You can do 8-10x cheaper and lower latency with @cartesia_ai right now.
Sully: Yeah holy shit I just saw.
Anant: The prohibitive cost is why I’m still considering
@elevenlabsio for my current project. Can’t have an alarm app cost 40$/month 💀
But definitely something to revisit when it’s cheaper OR
if Google finally releases Duplex as an API, and that’s reasonable to implement.
McKay Wrigley is always fun for the ‘this will change everything’ and here you go:
McKay Wrigley: Realtime AI will change everything.
Computers won’t just be tools.
They will be 200 IQ coworkers who will actively help you with any task – and you will have entire teams of them.
OpenAI is building the nervous system for AGI, and it’s available via API.
Take advantage of it.
I know I’m a broken record on this, but once again, who stands to benefit the most from this?
PEOPLE WHO CAN CODE.
OpenAI drops a new API, and boom suddenly anyone who can use Cursor + read docs can build AI assistants with the latest tech.
Even <10 hours gets you far - learn!
The presentation also spent a bunch of time emphasizing progress on structured outputs and explaining how to use them properly, so you get useful JSONs.
These quotes are from the chat at the end between Altman and Kevin Weil. via Simon Willison’s live blog, we also have notes from Greg Kamradt but those don’t always differentiate who said what:
Kevin Weil: An enterprise said they wanted 60 days notice in advance of when you’re going to launch something, “I want that too!”
I don’t think enterprises should be able to get 60 days notice, but it would indeed be nice if OpenAI itself got 60 days notice, for various safety-related reasons?
Sam Altman: “We have an approach of: figure out where the capabilities are going, then work to make that system safe. o1 is our most capable model ever but it’s also our most aligned model ever.”
Is that what the Preparedness Framework says to do? This makes the dangerous assumption that you can establish the capabilities, and then fix the safety issues later in post.
-
If you’re not considering safety from the beginning, you could paint yourself into a corner, and have to backtrack.
-
If you’re building up the capabilities without the safety, assuming you can fix safety later, then that’s going to create every incentive to rush the safety efforts, and push to release even if they’re not ready or incomplete.
-
We already have examples of OpenAI rushing its safety work and testing.
-
If you build up sufficient capabilities, then the model being trained at all, or evaluated internally, could itself become unsafe. Or someone might steal the model in this intermediate unsafe state.
So, gulp?
Sam: “I think worrying about the sci-fi ways that this all goes wrong is also very important. We have people thinking about that.”
We’ve gone so far backward that Sam Altman needs to reassure us that they at least have some people ‘thinking about’ the ways this all goes wrong, while calling them ‘sci-fi ways’ in order to delegitimize them. Remember when this was 20% of overall compute? Now it’s ‘we have people thinking about that.’
Also this:
“Iterative deployment is our best safety system we have.”
Well, yes, I suppose it is, given that we don’t have anything else and OpenAI has no intention of trying hard to build anything else. So, iterative deployment, then, and the hope that when things go wrong we are always still in charge and around sufficiently to fix it for next time.
What are they going to do with the AGIs?
Mission: Build safe AGI. If the answer is a rack of GPUs, they’ll do that. If the answer is research, they’ll do that.
This must be some use of the word ‘safe’ that I wasn’t previously aware of? Or it’s expressing a hope of some kind, perhaps?
Kevin: “I think 2025 is really going to be the year that [agents] goes big”.
…
Sam: “I think people will ask an agent to do something for them that would have taken them a month, and it takes an hour – and then they’ll have ten of those at a time, and then a thousand at a time – and we’ll look back and say that this is what a human is meant to be capable of.”
I really, really do not think they have thought through the implications properly, here.
When is o1 going to support function calls? Kevin: “Before the end of the year.” (Applause). o1 is going to get system prompts, structured outputs and function calling by the end of the year.
Sam: “The model (o1) is going to get so much better so fast […] Maybe this is the GPT-2 moment, we know how to get it to GPT-4”. So plan for the model to get rapidly smarter.
I notice I am skeptical, because of how I think about the term ‘smarter.’ I think we can make it, maybe the word is ‘cleverer’? Have it use its smarts better. But already the key limitation is that it is not actually smarter, in my way of thinking, than GPT-4, instead it’s finding ways to maximize the use of what smarts it does have.
Sam asks if people who spend time with o1 feel like they’re “definitively smarter” than that thing, and if they expect to feel that way about o2.
Yes, after using it for a bit I will say I am ‘definitively smarter’ than o1. Perhaps I am prompting it badly but I have overall been disappointed in o1.
Sam: We’ve been tempted to produce a really good on-device model but that segment is actually pretty well served now.
Is this a way of saying they don’t know how to do better than Gemini there?
Singing is disabled for now, it seems, due to copyright issues.
Dirk Kingma, part of the original founding team of OpenAI and more recently of Google DeepMind, joins Anthropic.
Dirk Kingma: Personal news: I’m joining @AnthropicAI! 😄 Anthropic’s approach to AI development resonates significantly with my own beliefs; looking forward to contributing to Anthropic’s mission of developing powerful AI systems responsibly. Can’t wait to work with their talented team, including a number of great ex-colleagues from OpenAI and Google, and tackle the challenges ahead!
OpenAI is moving forward to raise $6.6 billion at a $157 billion valuation. That seems like a strangely small amount of money to be raising, both given their needs and given that valuation. Soon they will need far more.
OpenAI has asked investors to avoid backing rival start-ups such as Anthropic and xAI.
Elon Musk: OpenAI is evil.
Quoted largely because I’m sad Musk couldn’t find ‘OpenlyEvilAI.’ This is all standard business practice. OpenAI has stopped pretending it is above all that.
A list of the top 20 companies by ‘generative AI patents’ in 2023 shows exactly why this is not a meaningful metric.
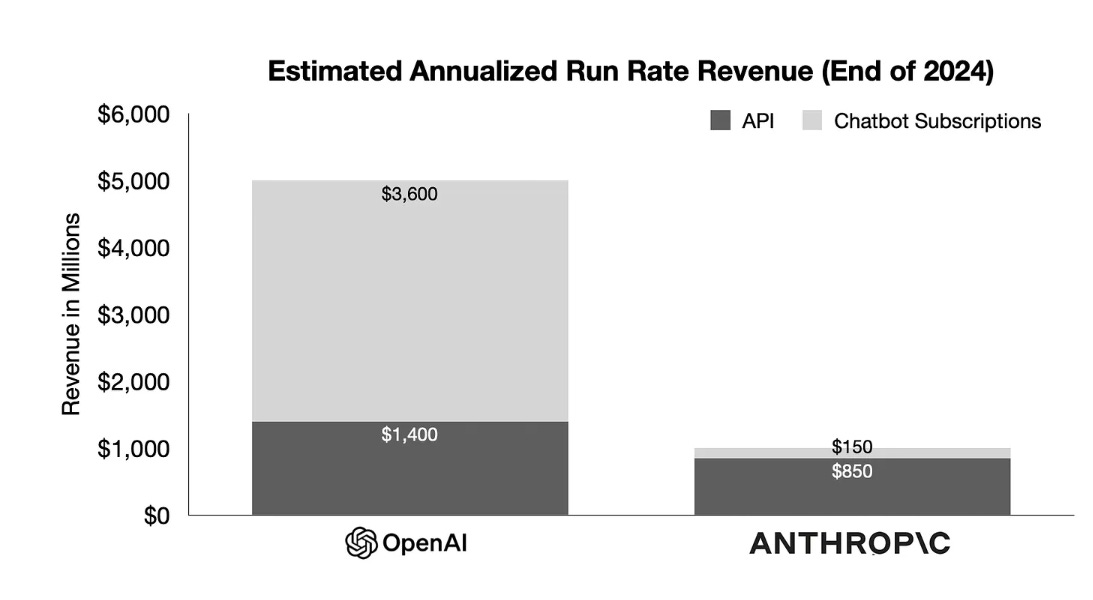
OpenAI and Anthropic revenue breakdown. Huge if true, they think Anthropic is highly competitive on the API side, but alas no one uses Claude.
They have OpenAI growing 285% year over year for subscriptions, 200% for API, whereas Anthropic is catching up with a 900% increase since last year. Whether that is sustained for the API will presumably depend on who has the better products going forward. For the consumer product, Claude is failing to break through to visibility, and it seems unrelated to product quality.
The best part of chatbot subscriptions is the profit margins are nuts. Most people, myself included, are paying miles more per token for subscriptions than we would pay for the API.
OpenAI got there early to capture the public imagination, and they’ve invested in voice mode and in responses people like and done a good job of that, and gotten good press for it all, such that ChatGPT is halfway to being the ‘Google,’ ‘xerox’ or ‘Kleenex’ of generative AI. I wonder how much of that is a lasting moat, versus being a choice of focus.
Long term, I’d think this is bullish for Anthropic. That’s huge year over year growth, and they’re fully competitive on the API, despite being supposedly valued at only something like 20% of OpenAI even taking into account all of OpenAI’s shall we say ‘issues.’ That seems too low.
BioNTech and Google DeepMind build biological research assistant AIs, primarily focused on predicting experimental outcomes, presumably to choose the right experiments. For now that’s obviously great, the risk concerns are obvious too.
Matthew Yglesias: OpenAI’s creators hired Sam Altman, an extremely intelligent autonomous agent, to execute their vision of x-risk conscious AGI development for the benefit of all humanity but it turned out to be impossible to control him or ensure he’d stay durably aligned to those goals. 🤔
Sigal Samuel writes at Vox that ‘OpenAI as we knew it is dead’ pointing out that this consolidation of absolute power in Altman’s hands and abandonment of the non-profit mission involves stealing billions in value from a 501c(3) and handing it to investors and especially to Microsoft.
OpenAI planning to convert to a for-profit B-corporation is a transparent betrayal of the mission of the OpenAI non-profit. It is a clear theft of resources, a clear break of the fiduciary duties of the new OpenAI board.
If we lived in a nation of laws and contracts, we would do something about this. Alas, we mostly don’t live in such a world, and every expectation is that OpenAI will ‘get away with it.’
So this is presumably correct legal realist take on OpenAI becoming a B-corporation:
John Arnold: I’m sure OpenAI has a bunch of lawyers signing off on this and all but starting a nonprofit that metamorphoses into $10 bil seems, um, interesting.
There are rules. Rules that apply to ‘the little people.’
Greg Colbourn: I run a charity. Pretty sure that I can’t just turn it into a business and have the board give me 7% of the assets. That’s flat out illegal here in the UK (and I’m pretty sure it is in the US too) – basically it’s just steeling charitable assets.
If the charity were to be disbanded, the assets still have to be used for charitable purposes (e.g. donated to another charity), they can’t just be taken into private hands. If this was legal, why wouldn’t everyone use this scam to start a business as a charity first to nefariously extract funds from honest charity givers?
Apple has withdrawn from the new funding round, and WSJ dropped this tidbit:
Tom Dotan and Berber Jin (WSJ): OpenAI is also in the process of overhauling its corporate structure from a nonprofit into a for-profit company. That change, which was encouraged by many of the investors in the round, will be a complicated process for the startup. If it doesn’t complete the change within two years, investors in the current round will have the right to request their money back.
This means OpenAI is potentially in very deep trouble if they don’t execute the switch to a B-corporation. They’re throwing their cap over the wall. If they fail, venture investment becomes venture debt with a conversion option. If the companies request their money back, which conditional on this failure to secure the right to OpenAI’s profits seems not so unlikely, that could then be the end.
So can they pull off the heist, or will they get a Not So Fast?
To those asking why everyone doesn’t go down this path, the path isn’t easy.
Theo Francis, Berber Jin and Tom Dotan (WSJ): To get there, it will have to deal with regulatory requirements in at least two states, determine how to award equity in the for-profit company, and split assets with the nonprofit entity, which will continue to exist.
“This kind of transaction is incredibly complex and would involve a large number of legal and regulatory hurdles that would need to be navigated,” said Karen Blackistone, general counsel at the investment firm Hangar Management and an attorney specializing in technology and tax-exempt organizations.
One problem will be antitrust attention, since Microsoft had been relying on OpenAI’s unique structure to fend off such complaints.
Regulators have already scrutinized Microsoft’s relationship with OpenAI and whether it effectively controls the startup. The tech giant has argued that its investment only entitles it to a share of potential profits, but a new structure under which Microsoft has an equity stake in OpenAI could invite further antitrust attention.
I think the antitrust concerns are bogus and stupid, but many people seem to care.
The bigger question is, what happens to OpenAI’s assets?
The more complicated part is what would happen to OpenAI’s assets. When such a conversion takes place, it can’t simply shift assets from a nonprofit to a for-profit. The nonprofit is legally required to end up with assets, including any cash and securities, at least as valuable as those it turns over to the for-profit. In effect, OpenAI’s operations would likely be sold to the for-profit company or its investors, with the charity retaining the proceeds.
That makes sense and matches my understanding. You can take things away from the 501c3 world, but you have to pay fair market price for them. In this circumstance, the fair value of what is being taken away seems like quite a lot?
Gretchen Krueger, current AI policy researcher who was formerly at OpenAI, notes that her decision to join was partly due to the non-profit governance and profit cap, whereas if they’re removed now it is at least as bad as never having had them.
Carrol Wainwright, formerly of OpenAI, points out that Altman has proven himself a danger to OpenAI’s nonprofit mission that has now been entirely abandoned, that you cannot trust him or OpenAI, and that the actions of the past year were collectively a successful coup by Altman against those in his way, rather than the other way around.
Greg Brockman offers his appreciation to the departing Barret, Bob and Mira.
Wojciech Zaremba, OpenAI cofounder still standing, offers his appreciation, and his sadness about the departures.
Everyone likes money. I like money. But does Sam Altman like money, on a different level I like money?
Joe Rogan argues that yes. The guy very much likes money.
Joe Rogan: He’s always kind of said, ‘I’m not doing this for money; I don’t make any money.’
They just busted him in a $4 million Koenigsegg.
See if you can find that car.
‘Oh, I don’t need money, me money?
I’m not even interested in money.’
He’s driving around in a $4 million Koenigsegg.
Hi busted! I think you like money.
This is certainly a fun argument. Is it a valid one? Or does it only say that he (1) already has a lot of money and (2) likes nice things like a $4 million car?
I think it’s Bayesian evidence that the person likes money, but not the kind of super strong evidence Joe Rogan thinks this is. If you have a thousand times as much money as I do, and this brings you joy, why wouldn’t you go for it? He can certainly afford it. And I do want someone like Altman appreciating nice things, and not to feel guilty about buying those things and enjoying himself.
It is however a different cultural attitude than the one I’d prefer to be in charge of a company like OpenAI. I notice I would never want such a car.
When I asked Claude what it indicates about someone driving such a model around town (without saying who the person in question was), it included that this was evidence of (among other things) status consciousness, attention-seeking and high risk tolerance, which all seems right and concerning. It also speaks to the image he chooses to project on these questions. Intentionally projecting that image is not easily compatible with having the attitude Altman will need in his position leading OpenAI.
Gwern, who predicted Mira’s departure, offered further thoughts a few months ago on the proposition that OpenAI has been a dead or rotting organization walking for a while now, and is rapidly losing its lead. One has to take into account the new o1 model in such assessments, but the part of this that resonates most is that the situation seems likely to be binary. Either OpenAI is ‘still OpenAI’ and can use its superior position to maintain its lead and continue to attract talent and everything else it takes. Or, if OpenAI is no longer so special in the positive ways, it gets weighed down by all of its unique problems, and continues to bleed its talent.
Deepa Seetharaman writes at the WSJ that Turning OpenAI Into a Real Business Is Tearing It Apart.
Deepa Seetharaman (WSJ): Some tensions are related to conflicts between OpenAI’s original mission to develop AI for the public good and new initiatives to deploy moneymaking products. Others relate to chaos and infighting among executives worthy of a soap opera.
Current and former employees say OpenAI has rushed product announcements and safety testing, and lost its lead over rival AI developers. They say Altman has been largely detached from the day-to-day—a characterization the company disputes—as he has flown around the globe promoting AI and his plans to raise huge sums of money to build chips and data centers for AI to work.
OpenAI has also been evolving into a more normal business, as Altman has described it, since his return. The company, which has grown to 1,700 employees from 770 last November, this year appointed its first chief financial officer and chief product officer.
The majority of OpenAI employees have been hired since the Battle of the Board, and that would be true even if no one had left. That’s an extreme level of growth. It is very difficult to retain a good culture doing that. One likely shift is from a research culture to a product-first culture.
Tim Shi (Former OpenAI): It’s hard to do both at the same time—product-first culture is very different from research culture. You have to attract different kinds of talent. And maybe you’re building a different kind of company.
Noam Brown disagrees, and promises us that OpenAI still prioritizes research, in the wake of losing several senior researchers. I am sure there has been a substantial shift towards product focus, of course that does not preclude an increase in resources being poured into capabilities research. We do however know that OpenAI has starved their safety research efforts of resources and other support.
So far nothing that new, but I don’t think we’ve heard about this before:
Deepa Seetharaman: Murati and President Greg Brockman told Sutskever that the company was in disarray and might collapse without him. They visited his home, bringing him cards and letters from other employees urging him to return.
Altman visited him as well and expressed regret that others at OpenAI hadn’t found a solution.
Sutskever indicated to his former OpenAI colleagues that he was seriously considering coming back. But soon after, Brockman called and said OpenAI was rescinding the offer for him to return.
This report does not mean that Murati and Brockman actually worried that the company would collapse, there are multiple ways to interpret this, but it does provide valuable color in multiple ways, including that OpenAI made and then rescinded an offer for Sutskever to return.
It’s also hard not to be concerned about the concrete details of the safety protocols around the release of GPT-4o:
Executives wanted to debut 4o ahead of Google’s annual developer conference and take attention from their bigger rival.
The safety staffers worked 20 hour days, and didn’t have time to double check their work. The initial results, based on incomplete data, indicated GPT-4o was safe enough to deploy.
But after the model launched, people familiar with the project said a subsequent analysis found the model exceeded OpenAI’s internal standards for persuasion—defined as the ability to create content that can persuade people to change their beliefs and engage in potentially dangerous or illegal behavior.
I believe that releasing GPT-4o does not, in practice and on reflection, exceed what my threshold would be for persuasion, or otherwise have any capabilities that would cause me not to release it. And I do think it was highly reasonable to not give 4o the ‘full frontier model’ treatment given it wasn’t pushing the frontier much.
It still is rather damning that, in order to score a marketing win, it was rushed out the door, after 20 hour days from the safety team, without giving the safety team the time they needed to follow their own protocols. Or that the model turned out to violate their own protocols.
I’ve seen at least one mocking response of ‘so where’s all the massive harm from 4o then?’ and that is not the point. The point is that the safety process failed and was overridden by management under the flimsy pressure of ‘we want to announce something before Google announces something.’ Why should we think that process will be followed later, when it matters?
Nor was this a one time incident. It was a pattern.
The rush to deploy GPT-4o was part of a pattern that affected technical leaders like Murati.
The CTO repeatedly delayed the planned launches of products including search and voice interaction because she thought they weren’t ready.
Other senior staffers also were growing unhappy.
John Schulman, another co-founder and top scientist, told colleagues he was frustrated over OpenAI’s internal conflicts, disappointed in the failure to woo back Sutskever and concerned about the diminishing importance of its original mission.
In August, he left for Anthropic.
The article also heavily suggests that Brockman’s leave of absence, rather than being motivated by family concerns, was because his management style was pissing off too many employees.
The New York Times covers Altman’s grand compute expansion dreams and his attempts to make them reality. His ambitions have ‘scaled down’ to the hundreds of billions of dollars.
Cate Metz and Tripp Mickle (NYT): TSMC’s executives found the idea so absurd that they took to calling Mr. Altman a “podcasting bro,” one of these people said. Adding just a few more chip-making plants, much less 36, was incredibly risky because of the money involved.
The article is full of people laughing at the sheer audacity and scale of Altman’s asks. But if no one is laughing at your requests, in an enterprise like this, you aren’t asking for enough. What is clear is that Altman does not seem to care which companies and nations he partners with, or what the safety or security implications would be. All he wants is to get the job done.
In Nate Silver’s book, there is a footnote that Altman told Silver that self-improving AI is ‘really scary’ and that OpenAI isn’t pursuing it. This is a highly bizarre way to make a statement that contradicts OpenAI’s clearly stated policies, which include using o1 (aka Strawberry) to do AI research, and the direct pursuit of AGI, and the entire goal of the former superalignment team (RIP) being an AI alignment researcher. So this quote shows how much Altman is willing to mislead.
The new head of alignment at OpenAI is Joshua Achiam. He’s said some useful and interesting things on Twitter at times, but also some deeply troubling things, such as:
Joshua Achiam (November 11, 2022) [giving advice to EAs]: Try to get better calibrated about what tail risks are real and what tail risks aren’t!
It seems like a huge miss to me that an enormous amount of ink gets spilled over speculative AGI tail risks predicted by people who are clearly converting anxiety disorders into made-up numbers about the likelihood of everyone dying within 10 years…
P(Misaligned AGI doom by 2032): <1e-6%
P(Large scale catastrophic accident risk from general-purpose AI by 2032, resulting for example in substantial cyberattack or e.g. empowering bad human actors by helping them accomplish a significant bioterrorist operation, with scale of impact smaller than Covid19): maybe ~3%?
In other words, the new head of AI alignment at OpenAI is on record lecturing EAs that misalignment risk from AGI is not real.
I do get the overall sense that Joshua is attempting to be helpful, but if the head of AI alignment at OpenAI does not believe in existential risk from AI misalignment, at all? If he thinks that all of our efforts should be in fighting human misuse?
Then that is perhaps the worst possible sign. Effectively, OpenAI would be saying that they have no superalignment team, that they are not making any attempt to avoid AI killing everyone, and they intend to proceed without it.
The question then becomes: What do we intend to do about this?
TestingCatalogNews: BREAKING 🚨: Perplexity to offer “One-click purchase and free shipping on infinite products” to Pro subscribers in the future.
Will AI-assisted shopping kill the traditional purchasing experience? 🤔
Previously discovered “Buy with PPLX” turned out to be a part of a planned Pro offering to help users make purchases while searching.
It will come along with a separate Purchase tab to let users list and track their purchases as well 👀
Gallabytes: if all perplexity does is build a better search layer & a less broken website/mobile app I will gladly give them 5% of each purchase even if it still uses amazon on the backend. AI curation and prompt interface = perfect antidote to the horrid ui of amazon.com & app.
I still often use both Google and Wikipedia, and was never using Bing in the first place, so let’s not get ahead of ourselves.
In some form or another, yes, of course the future of shopping looks like some version of ‘tell the AI what you want and it locates the item or candidate items for you, and checks for the lowest available price and whether the deal is reasonable, and then you can one-click to purchase it without having to deal with the particular website.’
The question is, how good does this have to be before it is good enough to use? Before it is good enough to use as a default? Use without sanity checking, even for substantial purchases? When will it get that reliable and good? When that happens, who will be providing it to us?
Dreaming Tulpa reports they’ve created smart glasses that automatically snap photos of people you see, identifies them, searches online and tells you tons of stuff about them, like phone number and home address, via streaming the camera video to Instagram.
So on the one hand all of this is incredibly useful, especially if it caches everything for future reference. I hate having to try and remember people’s names and faces, and having to be sure to exchange contact info and ask for basic information. Imagine if you didn’t have to worry about that, and your glasses could tell you ‘oh, right, it’s that guy, with the face’ and even give you key info about them. Parties would be so much more fun, you’d know what to talk to people about, you could stop missing connections, and so on. Love it.
Alas, there are then the privacy concerns. If you make all of this too smooth and too easy, it opens up some malicious and anti-social use cases as well. And those are exactly the types of cases that get the authorities involved to tell you no, despite all of this technically being public information. Most of all it wigs people out.
The good news, I think, is that there is not that much overlap in the Venn diagram between ‘things you would want to know about people’ and ‘things you would want to ensure other people do not know.’ It seems highly practical to design a product that is a win-win, that runs checks and doesn’t share certain specific things like your exact address or your social security number?
Mostly, though, the problem here is not even AI. The problem is that people are leaving their personal info exposed on the web. All the glasses are doing is removing the ‘extra steps.’
Now that SB 1047 has been vetoed, but Newsom has said he wants us to try again with something ‘more comprehensive,’ what should it be? As I explained on Tuesday (recommended if you haven’t read it already), Newsom’s suggested approach of use-based regulation is a recipe for industry strangulation without helping with risks that matter, an EU-style disaster. But now is the time to blue sky, and think big, in case we can come up with something better, especially something that might answer Newsom’s objections while also, ya know, possibly working and not wrecking things.
Garrison Lovely makes it into the New York Times to discuss scandals at OpenAI and argue this supports the need for enhanced whistleblower protections. The case for such protections seems overwhelming to me, even if you don’t believe in existential risk mitigation at all.
Jack Clark offers the rogue state theory of AIs.
From August: Peter Thiel talked to Joe Rogan about a wide variety of things, and I had the chance to listen to a lot more of it.
His central early AI take here is bizarre. He thinks passing the Turing Test is big, with his justification largely being due to how important we previously thought it was, which seems neither here nor there. We agree that current Turing-level AIs are roughly ‘internet big’ (~8.0 on the Technological Richter Scale) in impact if things don’t advance from here, over the course of several decades. The weird part is where he then makes this more important than superintelligence, or thinks this proves superintelligence was an incorrect hypothesis.
I don’t understand the logic. Yes, the path to getting there is not what we expected, and it is possible things stop soon, but the progress so far doesn’t make superintelligence either less likely to happen. And if superintelligence does happen, it will undoubtedly be the new and probably last ‘most important event in the history of history,’ no matter whether that event proves good or bad for humans or our values, and regardless of how important AI had already been.
Peter then takes us on a wild ride through many other topics and unique opinions. He’s always fun and interesting to listen to, even (and perhaps especially) the parts where he seems utterly wrong. You’ve got everything from how and why they built the Pyramids to chimp political dynamics to his suspicions about climate science to extended takes on Jeffrey Epstein. It’s refreshing to hear fresh and unique wrong takes, as opposed to standard dumb wrong takes and especially Not Even Wrong takes.
That’s all in addition to the section on racing with China on AI, which I covered earlier.
Democratic control is nice but have you experienced not dying?
Or: If it turns out Petrov defied ‘the will of the Soviet people’? I’m cool with that.
Sigal Samuel: OpenAI is building tech that aims to totally change the world without asking if we consent. It’s undemocratic. And Sam Altman just proved that bespoke corporate structures & voluntary commitments won’t cut it — we need LAWS that give independent oversight
Robin Hanson: ALL innovation changes the world without democratic consent.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: My problem with ASI is not that it will undemocratically kill everyone, but that it will kill everyone. Call me a wild-eyed libertarian, but I would consider that event to be almost exactly as bad if it happened as the result of a 51% vote of Earth’s population.
Connor Leahy: I disagree.
If we somehow fairly and verifiably gained informed voter consent and like 75% of people were like “fuck it, let it rip”, I think this scenario would be vastly more ethical and dignified than the scenario we are in.
Davidad: The word “informed” is pulling a lot of weight here, and seems contradicted by the phrasing “fuck it, let it rip.” Surely it should sound more like “actually our safeguards seem pretty decent and it’s not worth postponing all the medical/climate/empowerment miracles any longer.”
Robin Hanson’s point is valid and one can go far further than that, in the sense that we all ‘change the world’ every time we do anything or fail to do something, there will often be losers from our decisions, and obviously we should still be free to do most things without permission from another. Innovation is not special.
One must however be careful not to prove too much. Innovation does not mean you automatically need permission. It also does not mean you have or should have a free pass to change the world however you like. Robin and I would both draw the line to give permission to more things than America’s status quo, and indeed I expect to oppose many AI regulations upon mundane AI, starting with much of the EU AI Act (sorry I haven’t finished my summary there, the reason it’s not done is it hurts my eyes to look and I keep not forcing myself to finish it). I would still make an exception for things that would plausibly kill everyone, or otherwise plausibly have massive net negative externalities.
I’m also strongly with Yudkowsky here, not Leahy. My problem with everyone dying undemocratically is mostly the dying part, not the undemocratic one. I’d feel better I suppose in some karmic justice sense that the people ‘deserved it’ if they offered actually informed consent, but none of us would end up less dead.
Indeed, our founders knew this principle well. The Constitution is in large part designed to protect us from the majority doing various highly dumb things.
Your periodic reminder: Better start believing in science fiction stories, dear reader, you’re in one – regardless of how much additional AI progress we see.
David Manheim: “AI takeover and existential risks sound like science fiction, not real problems.”
Science fiction like AI that writes poetry and solves mathematical problems better than a significant majority of humans?
Sorry, reality exists independent of the genre you think it belongs to.
Never mind o1. All the fictional characters in most of the science fiction I’ve read or seen over the years would be blown away by at least one of GPT-4 or what you can do with a smartphone without AI, often by both. You have all the world’s knowledge at your fingertips right now. I could go on. In general, anyone who calls something ‘science fiction’ should be considered to have invoked a variation of Godwin’s Law.
Here’s some fire from Robert Miles, via AI Notkilleveryoneism Memes. Video is at the link, and yes this whole thing is unbelievably exhausting.
It absolutely boggles my mind, every time, no matter how many times I hear it. People really will say, with a straight face that building AIs smarter and more capable than us is a default-safe activity, and letting everyone use them for whatever they want will go fine and turn out well for the humans unless I can show exactly how that goes wrong.
And each time, it’s like, seriously WTF everyone, sure I have a thousand detailed arguments for things likely to go wrong but why do I need to even bring them up?
Robert Miles: People are starting from a prior in which ‘[AIs] are safe until you give me an airtight case for why they’re dangerous.’
This framing is exhausting. You explain one of the 10,000 ways that AIs could be dangerous, then they explain why they don’t think that specific thing would happen. Then you have to change tack, and then they say, ‘your story keeps changing’…
“If you’re building an AGI, it’s like building a Saturn V rocket [but with every human on it]. It’s a complex, difficult engineering task, and you’re going to try and make it aligned, which means it’s going to deliver people to the moon and home again.
People ask “why assume they won’t just land on the Moon and return home safely?”
And I’m like, because you don’t know what you’re doing!
If you try to send people to the moon and you don’t know what you’re doing, your astronauts will die.
[Unlike the telephone, or electricity, where you can assume it’s probably going to work out okay] I contend that ASI is more like the moon rocket.
“The moon is small compared with the rest of the sky, so you don’t get to the moon by default – you hit some part of the sky that isn’t the moon. So, show me the plan by which you predict to specifically hit the moon.”
And then people say, “how do you predict that [AIs] will want bad things?”
There’s more bad things than good things! It’s not actually a complicated argument…
I’m not going to predict specifically where it off into random space your astronauts are going, but you’re not going to hit the moon unless you have a really good, technically clear plan for how you do it. And if you ask these people for their plan, they don’t have one. What’s Yann Lecun’s plan?”
“I think that if you’re building an enormously powerful technology and you have a lot of uncertainty about what’s going to happen, this is bad. Like, this is default unsafe.
If you’ve got something that’s going to do enormously influential things in the world, and you don’t know what enormously influential things it’s going to do, this thing is unsafe until you can convince me that it’s safe.”
HOST: “That’s a good way of thinking about it – with some technologies you can assume that the default will be good or at least neutral, or that the capacity of a person to use this in a very bad way is bounded somehow. There’s just only so many people you could electrocute one by one.
In related metaphor news, here is a thread by Eliezer Yudkowsky, use your judgment on whether you need to read it, the rest of you can skip after the opening.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: The big issue in aligning superintelligence is that, if you screw up enough, you cannot repair your mistake. The ASI will not let you repair it.
I tried calling this the “oneshot” aspect of the problem. This word, “oneshot”, proved vulnerable to misrepresentation… …by motivated misunderstanders (or maybe grinning liars) who said: “But ASI is not one-shot; we can do all sorts of experiments to make sure we understand! Oh, these poor fools who don’t understand empiricism; who think they can analyze a superintelligence by pure theory!”
To design a space probe that will actually land on Mars, without dying to some weird malfunction, is a Huge Difficult Murphy-Cursed Problem. Why?
Because you can’t fix the probe after it launches.
OK, this is the point where a lot of you can skip ahead, but I’ll copy the rest anyway to preserve it for easy reference and copying, cause it’s good.
You can run all kinds of ground experiments. They do! It’s still cursed.
Why is launching a space-probe still Murphy-cursed, with actual weird failures that destroy $327M efforts? Despite all the empirical!!! advance testing done on the ground?
Because the ground experiments can’t exactly reproduce the real outer-space environment. Something changes.
And then, once conditions have changed a little, something goes wrong.
And once a probe is high up in space, far far above you, it is too late for regrets, too late for tears; your one $327M project on which you staked your whole scientific career is dead; you cannot repair it.
We could call it, maybe, Murphy’s Curse of Unretrievability, if we were cataloguing the conditions that make an engineering project be Cursed of Murphy:
If you can’t repair a thing past a certain time, this alone will make an easy engineering project into a Very Hard Problem.
(The phrase “one-shotness” ought to have been shorter, and covered it. But if you’ve got people running around (deliberately or motivatedly-but-deniably-unconsciously) misrepresenting everything, they can do the real damage of making short sensible phrases unusable.)
Murphy’s Curse of Unretrievability is not defeated by doing earlier experiments that are not exactly like the critical context where things need to work.
This is clearly true in practice. Ask GPT-4o about the costliest failed space probes.
Still, let’s talk about the theory.
Let’s say you have no understanding of physics, and are trying to build a bridge.
Can testing, without theory, save you?
And one answer is: Possibly, if you can apply a genuinely matched testing regime that is more severe than the actual intended use.
Eg, say you have no idea of the theory of bridge-building.
So you build a bridge; and then you order a cart pulled across that bridge with a rope.
The cart is loaded down with rocks that weigh 10 times the most weight you expect the bridge to ever bear.
Will this save you?
(Figuring out how this bridge-testing method would need to work, might be for some readers a helpful exercise in alignment mindset. So I invite readers to pause, and consider this question before continuing: Absent theory, how must you verify a bridge by mere testing?)
I answer: Loading a cart down with rocks, and running it over the bridge once before use, might still lead the bridge to fail and fall later.
Maybe the mortar that you used, degrades; or wooden beams rot, or the earth below settles.
So every year again you need to use ropes to pull across that heavier cart, loaded with 10 times as much weight as the bridge ought to hold.
Conditions change over time. When you first pulled the cart across, you were not testing exactly the conditions of use 10 years later.
And how sure is your assumption about the weight the bridge will later bear?
If you wanted to really be sure, you’d have to install a weighing station, where heavy-looking carts are weighed against rocks that are one-tenth of the weight used to test the bridge…
You would write down all these assumptions.
There would be a sheet of parchment on which was written: “I believe as a loadbearing assumption: If I post up a sign saying ‘no carts over 1 ton lest the bridge fall’, nobody will drive a cart more than 2 tons over the bridge”.
The parchment should also say: “I believe as a loadbearing assumption: Though conditions change over time, if I once per year test the bridge’s ability to bear 20 tons of weight, the bridge will not, in just the next year, degrade past being able to hold 2 tons of weight.”
And once you write down an assumption like that, and stop and reflect on it, you realize that maybe the bridge’s operating instructions need to say: “Retest the bridge after a major flood or unprecedented set of storms; don’t just pick up and start using it again.”
None of this, of course, is going to save you if somebody marches troops across the bridge, and the rhythm of their marching feet is close to a resonant frequency of the bridge.
(Eg: Angers Bridge, 1850, 226 deaths.)
It takes theory to know to test something like that.
To be clear: humanity has always picked itself up and trudged on, after bridge collapses that kill 226 people, a little wiser and having a better idea of what to test next time. A bridge collapsing doesn’t wipe out the whole of humanity. So it’s not worth that much worry.
Also TBC: this notion of “Write down all your assumptions on parchment so you can reflect on what might violate them” is anachronistic for an era that knows no bridge-physics. Even the Romans had a little physics of loads, but not parchment lists of load-bearing assumptions.
Likewise today: If we look at the people building artificial superintelligence, they have no physics to tell them if a bridge will stay up.
And they have no written lists of load-bearing assumptions.
And their grand testing plan is to run smaller carts across the bridge first.
To summarize:
– “Unretrievability”, more fully “Murphy’s Curse of Unretrievability”, is what makes it Very Hard to build space probes.
— I tried calling this property “oneshotness”, but people motivatedly misinterpreted it to say, “It’s not ‘one-shot’, we can run tests first!”
– The reason why running ground tests doesn’t make space probes not be Murphy-Cursed (i.e. building space probes is still a Big Huge Deal, and even then often fails in practice) is that conditions on the ground experiments are not exactly like conditions in space.
— We can understand a bit about how hard it is to exactly match conditions, by looking at the example of what it would take to make a bridge stay up by pure testing, absent any theory. — This would also go better with “written lists of load-bearing assumptions”.
—- But even written lists, still won’t save you from learning a hard lesson about resonance, the first time that soldiers march across a bridge. —- The would-be builders of gods, don’t even have written lists of load-bearing assumptions and what might violate them.
John Pressman: I’m no longer allowed to signal my epistemic fairness with public likes so I would like to inform you this is a good thread.
Gallabytes: yeah it’s an interesting fact about the world that neural net training almost has a “reverse-murphy” curse. it’s definitely not *anti*fragile but it’s quite robust. in fact this is a defining characteristic of good neural net architecture choices.
John Pressman: It is, but I think the Murphy Curse he’s worried about here is more like the 2nd order effects of the continuous learning dynamics than the neural net training itself. There’s a lot of opportunity for things to go wrong once the model is in a feedback loop with its training set.
My understanding of capabilities training is that there are a lot of knobs and fiddly bits and characteristics of your data and if you screw them up then the thing doesn’t work right, but you can tinker with them until you get them right and fix the issues, and if you have the experience and intuition you can do a huge ‘YOLO run’ where you guess at all of them and have a decent chance of that part working out.
The contrast is with the alignment part, with regard to the level you need for things smarter or more capable than people (exact thresholds unclear, hard to predict and debatable) which I believe is most definitely cursed, and where one must hit a narrow target. For mundane (or ‘prosaic’) alignment, the kludges we use now are mostly fine, but if you tried to ‘fly to the moon’ with them you’re very out of your test distribution, you were only kind of approximating even within the test, and I can assure you that you are not landing on that moon.
Roon offers wise words (in an unrelated thread), I fully endorse:
Roon: A true accelerationist feels their heart beat faster when they stare into the fog of war. The stomach lurch from the vertigo of science fiction. The courage of someone changing their whole life knowing it could go sideways. Anyone else is a larping idiot.
People who are wearing blindfolds accelerating into walls dissociated from the real world in an amphetamine haze with nothing precious to gain or lose are shuffling zombies that have given up their soul to the great replicator.
There is no guarantee of victory. no hands left unbloodied. only the lightcone of possibilities.
An example of what this failure mode looks like, in a response to Roon:
Anton: “Faster, Faster, until the thrill of speed overcomes the fear of death.”
There is a school of thought that anything opposed to them is 1984-level totalitarian.
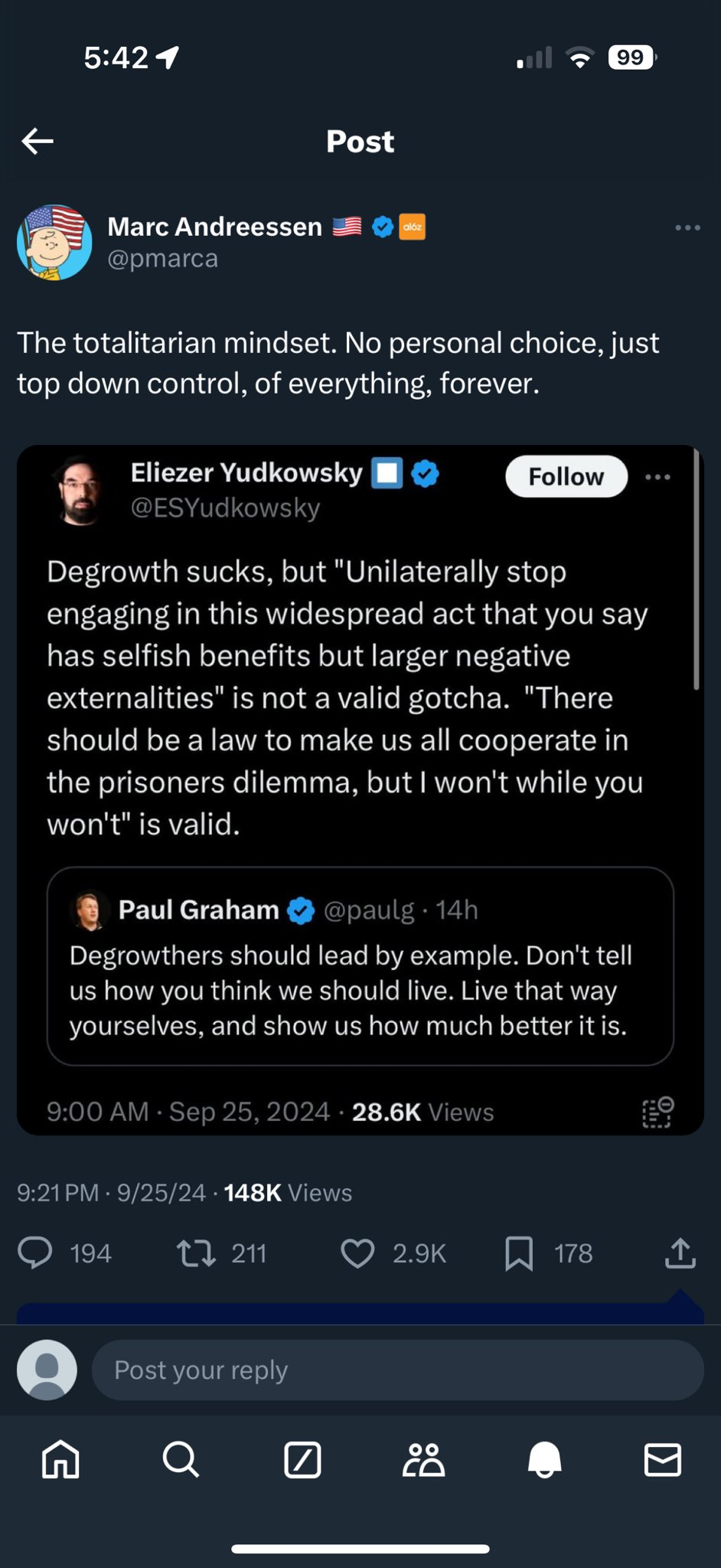
Marc Andreessen, and to a lesser extent Paul Graham, provide us with a fully clean examples this week of how his rhetorical world works and what it means when they say words. So I wanted to note them for future reference, so I don’t have to keep doing it over and over again going forward, at least with Marc in particular.
Paul Graham: Degrowthers should lead by example. Don’t tell us how you think we should live. Live that way yourselves, and show us how much better it is.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: Degrowth sucks, but ‘Unilaterally stop engaging in this widespread act that you say has selfish benefits but larger negative externalities” is not a valid gotcha. “There should be a law to make us all cooperate in the prisoners dilemma, but I won’t while you won’t” is valid.
Marc Andreessen: The totalitarian mindset. No personal choice, just top down control, of everything, forever.
Did someone point out that ‘you first’ is not a valid argument or gotcha against requiring a personal sacrifice that some claim would do good? While also opposing (the obligatory and also deeply true ‘degrowth sucks’) the sacrifice by pointing out it is stupid and would not, in fact, do good?
Well, that must mean the people pointing that out are totalitarians, favoring no personal choice, just top down control, of everything, forever.
So the next time people of that ilk call someone a totalitarian, or say that someone opposes personal choice, or otherwise haul out their slogans, remember what they mean when they say this.
The charitable interpretation is that they define ‘totalitarian’ as one who does not, in principle and in every case, oppose the idea of requiring people to do things not in that person’s self-interest.
Here is another example from this week of the same Enemies List attitude, and attributing to them absurdist things that have nothing to do with their actual arguments or positions, except to lash out at anyone with a different position or who cares about the quality of arguments:
Marc Andreessen: There will be no curiosity, no enjoyment. But always there will be the intoxication of power. Always there will be the sensation of trampling on an enemy who is helpless. If you want a picture of the future, imagine Helen Toner’s boot stamping on a human face— forever.
I don’t think he actually believes the things he is saying. I don’t know if that’s worse.
As a bonus, here’s who Martin Casado is and what he cares about.
Martin Casado: Had to mass unmute/unblock a bunch of EA folks just to enjoy their lamentations for a day.
Roon: Seems in really poor taste.
Martin Casado: You’re a bigger person than I am Roon. After months of largely baseless vilification and hit pieces I’m enjoying the moment. Don’t you worry, I’ll block them all again in a day or so.
A Narrow Path is a newly written plan for allowing humanity to survive the path to superintelligence. Like the plan or hate the plan, this at least is indeed a plan, that tries to lay out a path that might work.
The core thesis is, if we build superintelligence before we are ready then we die. So make sure no one builds it until then.
I do agree that this much is clear: Until such time as we figure out how to handle superintelligence in multiple senses, building superintelligence would probably be collective suicide. We are a very long way from figuring out how to handle it.
Andrea Miotti: We chart a path of three Phases:
0. Safety: Build up our defenses to restrict the development of superintelligent AI.
1. Stability: Build a stable international AI governance framework.
2. Flourishing: With a stable system and humanity secure, build transformative AI technology.
…
We propose a normative guiding principle:
No superintelligence.
Most AI is a beneficial tool for human growth. Superintelligence is a successor species. We should understand the latter as a hyper-capable adversary to contain, and build our defenses against.
If we build things that are plausibly AGIs, that directly creates a lot of mundane issues we can deal with and not-so-mundane intermediate issues that would be difficult to deal with. If that’s all it did, which is how many think about it, then you gotta do it.
The problem is: What we definitely cannot deal with is that once we build AGI, the world would rapidly build ASI, one way or another.
That’s what they realize we need to avoid doing for a while. You backchain from there.
Here is their plan. At whatever level of detail you prefer to focus on: Do you think it is sufficient? Do you think it is necessary? Can you think of a superior alternative that would do the job?
To achieve safety, we identify certain conditions to be met:
1. No AIs improving AIs
2. No AIs capable of breaking out of their environment
3. No unbounded AIs
4. Limit the general intelligence of AI systems so that they cannot reach superhuman level at general tasks
1. No AIs improving AIs
Any restriction on the general intelligence of AIs will be broken if machines can improve themselves or other machines at machine speed. We draw a principled line to focus only on dangerous illegible AIs, while leaving untouched human written software.
This is a tough ask even if you want it. It’s a gray area – are Claude and o1 AIs that can improve AIs? Not in the automated super scary way, but a software engineer with current AI is a lot more productive than one without it. What do you do when humans use AI code assistant tools? When they copy-paste AI code outputs? At what point does more of that change to something different? Can you actually stop it? How?
Similarly, they say ‘no AIs capable of breaking out of their environment’ but for a sufficiently unprotected environment, current AIs already are on the verge of being able to do this. And many will ‘set them free’ on purpose anyway.
Similarly, when interacting with the world and being given tools, what AI can we be confident will stay ‘bounded’? They suggest this can happen with safety justifications. It’s going to be tough.
Finally there is a limit to the ‘general intelligence’ of systems, which again you would need to somehow define, measure and enforce.
This is a long dense document (~80 pages). Even if we did get society and government to buy-in, there are tons of practical obstacles ahead on many levels. We’re talking about some very difficult to pin down, define or enforce provisions. This is very far from a model bill. Everything here would need a lot of iteration and vetting and debate, and there are various details I suspect are laid out poorly. And then you’d need to deal with the game theory and international aspects of the issue.
But it is a great exercise – instead of asking ‘what can we in practice hope to get done right now?’ they instead ask a different question ‘where do we need to go’ and then ‘what would it take to do something that would actually get there?’
You can of course disagree with how they answer those questions. But they are the right question to ask. Then, if the answer comes back ‘anything that might work to get us a place we can afford to go is going to be highly not fun,’ as it well might, how highly not fun? Do you care more about it not working or things being not fun? Is there an alternative path or destination to consider?
No doubt many who read (realistically: glance at or lightly skim or feed into an LLM) this proposal will respond along the lines of ‘look at these horrible people who want to restrict X or require a license for Y’ or ‘they want a global government’ or ‘war on math’ or what not. And then treat that as that.
It would be good to resist that response.
Instead, treat this not as a call to implement anything. Rather treat this as a claim that if we did XYZ, then that is plausibly sufficient, and that no one has a less onerous plan that is plausibly sufficient. And until we can find a better approach, we should ask what might cut us off from being able to implement that plan, versus what would enable us to choose if necessary to walk that path, if events show it is needed.
One should respond on that level. Debate the logic of the path.
Either argue it is insufficient, or it is unnecessary, or that it flat out won’t work or is not well defined, or suggest improvements, point out differing assumptions and cruxes, including doing that conditional on various possible world features.
This can include ‘we won’t get ASI anyway’ or ‘here are less painful measures that are plausibly sufficient’ or ‘here’s why there was never a problem in the first place, creating things smarter than ourselves is going to go great by default.’ And they include many good objections about detail choices, implementations, definitions, and so on, which I haven’t dug into in depth. There are a lot of assumptions and choices here that one can and should question, and requirements that can be emphasized.
Ultimately, if your actual point of view is something like ‘I believe that building ASI would almost certainly go fine [because of reasons]’ then you can say that and stop there. Or you can say ‘I believe building ASI now is fine, but let’s presume that we’ve decided for whatever reason that this is wrong’ and then argue about what alternative paths might prevent ASI from being built soon.
The key is you must pick one of these:
-
Building a superintelligence under current conditions will turn out fine.
-
No one will build a superintelligence under anything like current conditions.
-
We must prevent at almost all costs anyone building superintelligence soon.
Thus, be clear which of these you are endorsing. If it’s #1, fine. If it’s #2, fine.
If you think it’s too early to know if #1 or #2 is true, then you want to keep your options open.
If you know you won’t be able to bite either of those first two bullets? Then it’s time to figure out the path to victory, and talk methods and price. And we should do what is necessary now to gather more information, and ensure we have the option to walk down such paths.
That is very different from saying ‘we should write this agenda into law right now.’ Everyone involved understands that this would be overdeterminedly premature.
A fun feature of interpretability is that the model needs to be smart enough that you can understand it, but not so smart that you stop understanding it again.
Or, similarly, that the model needs to be smart enough to be able to get a useful answer out of a human-style Chain of Thought, without being smart enough to no longer get a useful answer out of a human-style Chain of Thought. And definitely without it being smart enough that it’s better off figuring out the answer and then backfilling in a Chain of Thought to satisfy the humans giving the feedback, a classic alignment failure mode.
Wojciech Zaremba: o1 paradigm of solving problems with a chain of thought offers new avenues to safety/alignment research. It’s easier to ensure such AI behaves as expected because we can see its thoughts. I am feeling pumped.
Davidad: Remember folks, the more capable the base model (beyond about 13B-34B), the less the “reasoning trace” serves as an effective interpretability tool for the true causes of the final answer. UNLESS the final answer is produced only via running formal methods on the reasoning…
Roon: you cannot conclude that native reasoning tokens exhibit similar behaviors to prompted CoTs.
Davidad: yeah you’re right. Qis even worse it doesn’t just hallucinate a plausible answer and then back-rationalize it, it specifically hallucinates a *successfulanswer and then back-rationalizes it.
Roon: you’re changing the subject. your cot faithfulness scaling law may not hold.
Davidad: Look, here’s an a priori argument. If an architecture has enough model capacity to distill the CoT search process into its layers, it will achieve higher reward for its final answers by separating its reasoning process from the noise introduced by sampling during the CoT rollout.
There may be ways to avoid this, by doing *not justprocess supervision but also some kind of per-step entropic regularization.
But if you just say “oh, it’s native reasoning, it’s different,” I think you just mean process supervision, and I think you haven’t understood the problem, and I think your model may still do its true reasoning purely in latent space—in parallel with CoT steps to satisfy the PRM.
If the agent is interacting with a process supervisor that is truly impossible to fool, like a proof assistant, this may be okay, because there’s no corner of strategy space which gets highly rewarded for confident wrong answers.
But even then, you still shouldn’t expect the formal proof to mirror the actual underlying reasoning. Mathematicians often reason almost entirely through geometric intuition while writing down an entirely algebraic proof, even if their motivation is to write down correct algebra.
I think Davidad is correct here.
Always remember to reverse any advice you hear, including the advice to reverse any advice you hear:
Sam Altman: You should have a very high bar for doing anything but thinking about what to work on… Of course that doesn’t work all of the time. At some point, you actually have to go execute. But I often see people who I think are really talented, work super hard, and are super product, not spend any time thinking about what they’re going to work on.
…
If I have a very hard problem or I’m a little confused about something, I still have not found anything better to do than sit down and make myself write it out… It is a super powerful thinking tool.
My experience is that almost no one gets this correct. People usually do one of:
-
Do something reasonably random without thinking about what to do.
-
Do a ton of thinking about what to do, stay paralyzed and do nothing.
-
Do a ton of thinking about what to do, realize they are paralyzed or out of time and money, and end up doing something reasonably random instead.
-
Do a ton of thinking, buy some abstract argument, and do something unwise.
-
Overthink it, and do something unwise.
The good news is, even your system-1 instinctive guess on whether you are doing too little or too much thinking versus doing is almost certainly correct.
And yes, I do hope everyone sees the irony of Altman telling everyone to take more time to think harder about whether they’re working on the right project.
The perfect subtweet doesn’t exist.
Sasha de Marigny (Head of Anthropic Comms): Happy to report that Anthropic’s co-founders all still merrily work at the company. None have been lost to Middle Age plagues or jacuzzis.
(See the section The Mask Comes Off and this in particular if you don’t have the proper context.)
AI #84: Better Than a Podcast Read More »