Is generative AI making it harder for young people to find jobs?
My answer is:
-
Yes, definitely, in terms of for any given job that exists finding the job and getting hired. That’s getting harder. AI is most definitely screwing up that process.
-
Yes, probably, in terms of employment in automation-impacted sectors. It always seemed odd to think otherwise, and this week’s new study has strong evidence here.
-
Maybe, overall, in terms of the jobs available (excluding search and matching effects from #1), because AI should be increasing employment in areas not being automated yet, and that effect can be small and still dominate.
The claims go back and forth on the employment effects of AI. As Derek Thompson points out, if you go by articles in the popular press, we’ve gone from ‘possibly’ to ‘definitely yes’ to ‘almost certainly no’ until what Derek describes as this week’s ‘plausibly yes’ and which others are treating as stronger than that.
Derek Thompson: To be honest with you, I considered this debate well and truly settled. No, I’d come to think, AI is probably not wrecking employment for young people. But now, I’m thinking about changing my mind again.
It’s weird to pull an ‘I told you all so’ when what you said was ‘I am confused and you all are overconfident’ but yeah, basically. The idea that this was ‘well and truly settled’ always seemed absurd to me even considering present effects, none of these arguments should have filled anyone with confidence and neither should the new one, and this is AI so even if it definitively wasn’t happening now who knows where we would be six months later.
People changing their minds a lot reflects, as Derek notes, the way discovery, evaluation, discourse and science are supposed to work, except for the overconfidence.
Most recently before this week we had claims that what looks like effects of AI automation are delayed impacts from Covid, various interest rate changes, existing overhiring or other non-AI market trends.
The new hotness is this new Stanford study from Brynjolfsson, Chandar and Chen:
This paper examines changes in the labor market for occupations exposed to generative artificial intelligence using high-frequency administrative data from the largest payroll software provider in the United States.
We present six facts that characterize these shifts. We find that since the widespread adoption of generative AI, early-career workers (ages 22-25) in the most AI-exposed occupations have experienced a 13 percent relative decline in employment even after controlling for firm-level shocks.
In contrast, employment for workers in less exposed fields and more experienced workers in the same occupations has remained stable or continued to grow.
We also find that adjustments occur primarily through employment rather than compensation. Furthermore, employment declines are concentrated in occupations where AI is more likely to automate, rather than augment, human labor. Our results are robust to alternative explanations, such as excluding technology-related firms and excluding occupations amenable to remote work.
Effects acting through employment rather than compensation makes sense since the different fields are competing against each other for labor and wages are sticky downwards even across workers.
Bharat Chanar (author): We observe millions of workers each month. Use this cut the data finely by age and occ.
What do we find?
Stories about young SW developers struggling to find work borne out in data
Employment for 22-25 y/o developers ⬇️ ~20% from peak in 2022. Older ages show steady rise.
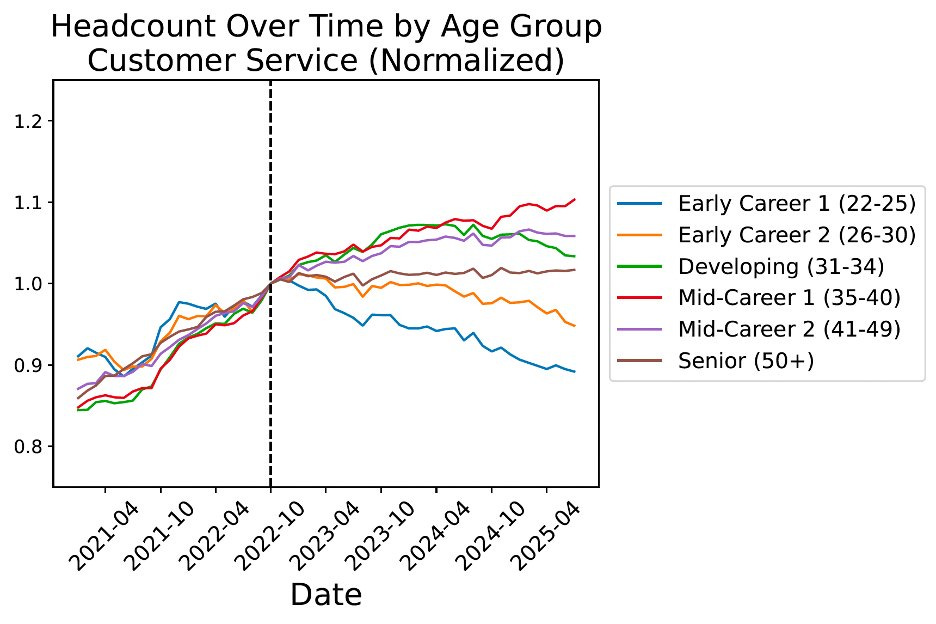
This isn’t just about software. See a similar pattern for customer service reps, another job highly exposed to AI. For both roles, the decline is sharpest for the 22-25 age group, with older, more experienced workers less affected.
In contrast, jobs less exposed to AI, like health aides, show the opposite trend. These jobs, which require in-person physical tasks, have seen the fastest employment growth among youngest workers.
…
Overall, job market for entry-level workers has been stagnant since late 2022, while market for experienced workers remains robust. Stagnation for young workers driven by declines in AI-exposed jobs. Of course, lots of changes in the economy, so this is not all caused by AI.
Note the y-axis scale on the graphs, but that does seem like a definitive result. It seems far too fast and targeted to be the result of non-AI factors.
John Burn-Murdoch: Very important paper, for two reasons:
-
Key finding: employment *isfalling in early-career roles exposed to LLM automation
-
Shows that administrative data (millions of payroll records) is much better than survey data for questions requiring precision (occupation x age)
There’s always that battle between ‘our findings are robust to various things’ and ‘your findings go away when you account for this particular thing in this way,’ and different findings appear to contradict.
I don’t know for sure who is right, but I was convinced by their explanation of why they have better data sources and thus they’re right and the FT study was wrong, in terms of there being relative entry-level employment effects that vary based on the amount of automation in each sector.
Areas with automation from AI saw job losses at entry level, whereas areas with AI amplification saw job gains, but we should expect more full automation over time.
There’s the additional twist that a 13 percent decline in employment for the AI-exposed early-career jobs does not mean work is harder to find. Everyone agrees AI will automate away some jobs. The bull case for employment is not that those jobs don’t go away. It is that those jobs are replaced by other jobs. So the 13% could be an 11% decline in some areas and a 2% increase in other larger areas, where they cancel out. AI is driving substantial economic growth already which should create jobs. We can’t tell.
There is one place I am very confident AI is making things harder. That is the many ways it is making it harder to find and get hired for what jobs do exist. Automated job applications are flooding and breaking the job application market, most of all in software but across the board. Matching is by all reports getting harder rather than easier, although if you are ahead of the curve on AI use here you presumably have an edge.
Predictions are hard, especially about the future, but I would as strongly as always disagree with this advice from Derek Thompson:
Derek Thompson: Someone once asked me recently if I had any advice on how to predict the future when I wrote about social and technological trends. Sure, I said. My advice is that predicting the future is impossible, so the best thing you can do is try to describe the present accurately.
Since most people live in the past, hanging onto stale narratives and outdated models, people who pay attention to what’s happening as it happens will appear to others like they’re predicting the future when all they’re doing is describing the present.
Predicting the future is hard in some ways, but that is no reason to throw up one’s hands and pretend to know nothing. We can especially know big things based on broad trends, destinations are often clearer than the road towards them. And in the age of AI, while predicting the present puts you ahead of many, we can know for certain many ways the future will not look like the present.
The most important and in some ways easiest things we can say involve what would happen with powerful or transformational AI, and that is really important, the only truly important thing, but in this particular context that’s not important right now.
If by the future we do mean the effect on jobs, and we presume that the world is not otherwise transformed so much we have far bigger problems, we can indeed still say many things. At minimum, we know many jobs will be amplified or augmented, and many more jobs will be fully automated or rendered irrelevant, even if we have high uncertainty about which ones in what order how fast.
We know that there will be some number of new jobs created by this process, especially if we have time to adjust, but that as AI ‘automates the new jobs as well’ this will get harder and eventually break. And we know that there is a lot of slack for an increasingly wealthy civilization to hire people for quite a lot of what I call ‘shadow jobs,’ which are jobs that would already exist except labor and capital currently choose better opportunities, again if those jobs too are not yet automated. Eventually we should expect unemployment.
Getting more speculative and less confident, earlier than that, it makes sense to expect unemployment for those lacking a necessary threshold of skill as technology advances, even if AI wasn’t a direct substitute for your intelligence. Notice that the employment charts above start at age 22. They used to start at age 18, and before that even younger, or they would have if we had charts back then.