NASA chief to scientists on budget cuts: “I feel your pain”
Nelson as Senator Administrator —
“I can’t go and print the dollars.”
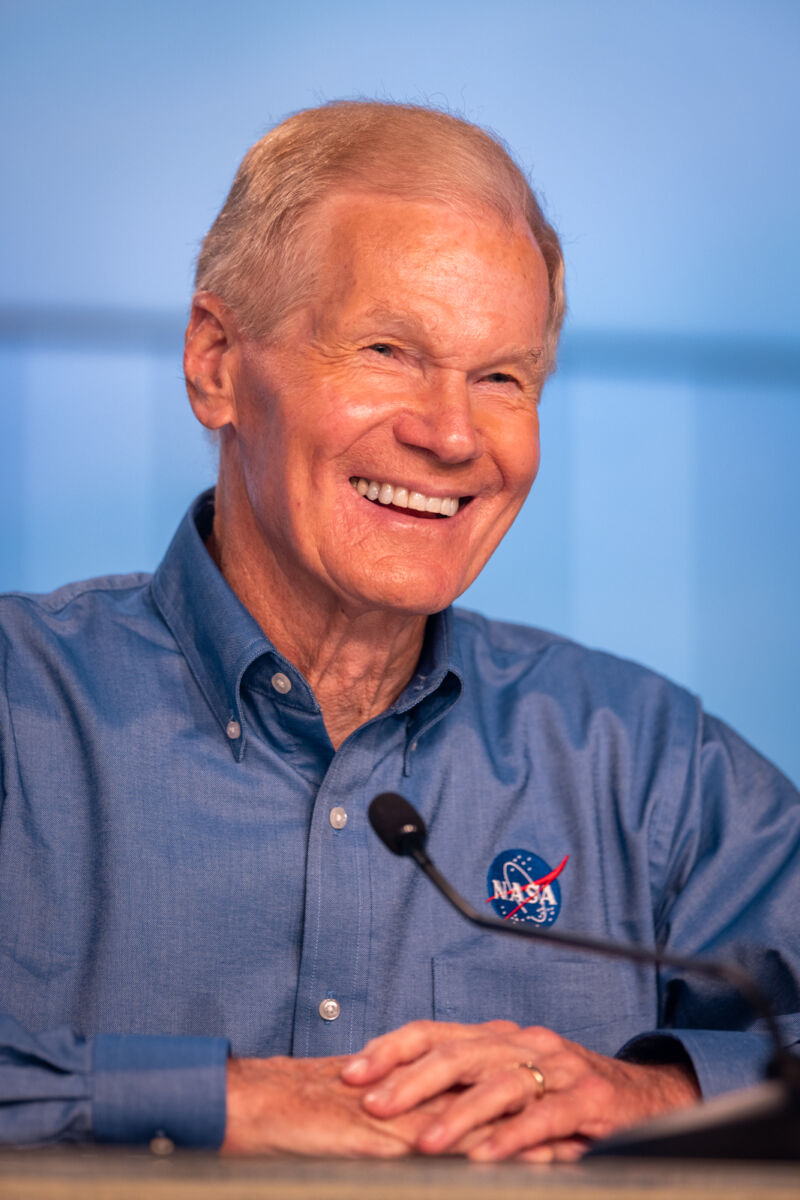

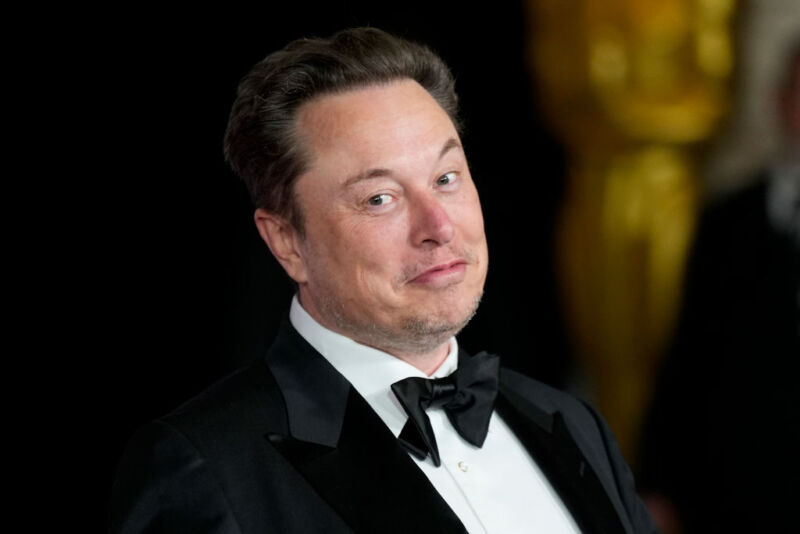
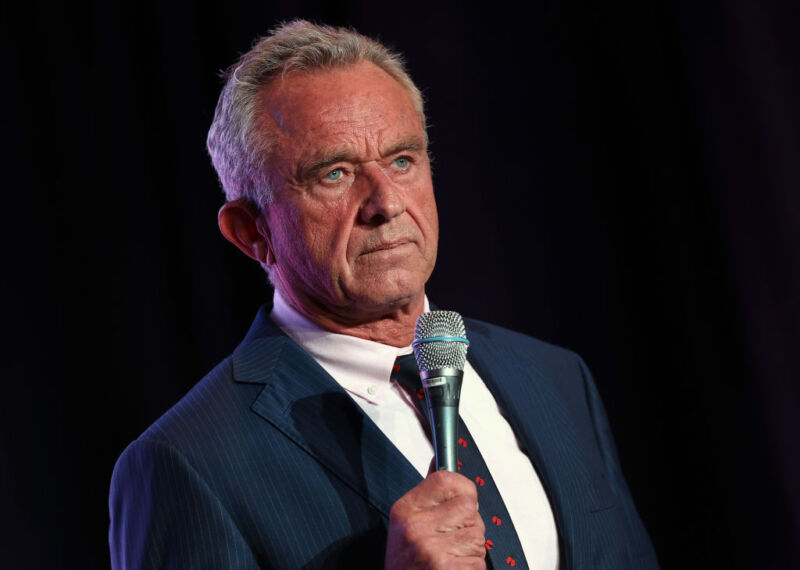
Enlarge / Administrator Bill Nelson delivering remarks and answering questions from the media at the OFT-2 prelaunch press conference.
Trevor Mahlmann
Ars Technica recently had the opportunity to speak with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, who has now led the US space agency for more than three years. We spoke about budget issues, Artemis Program timelines, and NASA’s role as a soft power in global diplomacy. What follows is a very lightly edited transcript of the conversation between Senior Space Editor Eric Berger and Nelson.
Ars Technica: I wanted to start with NASA’s budget for next year. We’ve now seen the numbers from the House of Senate, and NASA is once again facing some cuts. And I’m just wondering, what are your big concerns as we get into the final budgeting process this fall?
Administrator Bill Nelson: Well, the big concern is that you can’t put 10 pounds of potatoes in a five-pound sack. When you get cut $4.7 billion over two years, and when $2 billion of that over two years is just in science, then you have to start making some hard choices. Now, I understand the reasons for the cuts. Had I still been a member of the Senate I would’ve voted for it simply because they were held hostage by a small group in the House to get what they wanted. Which was reduced appropriations in order to raise the artificial, statutory budget debt ceiling in order for the government not to go into default. That’s part of the legislative process. It’s part of the compromises that go on. It happened over a year ago, and it was called the Fiscal Responsibility Act. The price for doing that wasn’t cuts across the entire budget. Remember, two-thirds of the budget is entitlement programs like Social Security and Medicare, and it certainly wasn’t in defense. So, all the cuts came out of everything left over, including NASA. I’m hoping that we’re going to get a reprieve come fiscal year ’26 when we will not be in the budgetary constraints of the Fiscal Responsibility Act. But who knows? Because lo and behold, they’ve got another artificial debt ceiling they’re going to have to raise next January.
Ars: What would you say to scientists who are concerned about Chandra, the cancellation of Viper, and Mars Sample Return, who see the budget for Artemis Program holding steady or even going up? It seems to me those of us who lived through Constellation saw this unfolding 15 to 20 years ago. Is the same thing happening with Artemis, is science being cannibalized to pay for human exploration?
Nelson: My response to the scientists is, I feel your pain. But, when I am faced with $2 billion of cuts over two years just in Science, I can’t go and print the dollars. And so, we have to make hard choices. Now, let’s go through those ones that you mentioned. Mars Sample Return. This was getting way out of control. It was going up to $11 billion, and we weren’t even going to get a sample return until 2040. And that’s the decade that when we’re going to land astronauts on Mars. So, something had to be done.
I convinced the budget director, Shalanda Young (director of the US Office of Management and Budget), and she was a partner in this, that we need to get those samples back. And so we pulled the plug on it. We said, “We’re going to start over, and we’re going to go out to all the NASA centers and to private industry, and we’re going to solicit and give some incentive money for their studies. And those studies will come back in, and by the end of the year, we will make a decision.” I’m hopeful that we are going to find such creativity and fiscal discipline that we’re going to end up with a much cheaper Mars sample return that will come back in the mid-30s, instead of all the way to 2040. So, if that’s what happens, and every indication I get is we’re getting some really creative proposals, if that’s what happens, then it’s a win-win. It’s a win for the taxpayer clearly. It’s a win for NASA because we didn’t have the money to spend $11 billion on it.
So, that’s one example. Another one that you used is Viper. Viper was running 40 percent over budget. Now, there comes a limit, and when you have to take a $2 billion hit just to science, you have to make tough choices. And so, that decision was made. We’re still getting (to the Moon) with Intuitive Machines at the end of the year. We are getting a lander that is going to drill to see if there is water underneath the surface. Understand that Viper was a much bigger rover, and it was going to rove around, but it was also 40 percent over budget. And so, these are the choices that you have to make.
You mentioned Chandra. By the way, I think we’ve worked Chandra out. Although it’s not going to have the funding way up there at the top funding. What we have worked out is, we are going to from what we requested, which was $41 million, it’s going to be some amount in excess of that. Although there will be some layoffs, not nearly as many, and all of the science will be protected. There will not be any diminution of the science.
NASA chief to scientists on budget cuts: “I feel your pain” Read More »