ChatGPT unexpectedly began speaking in a user’s cloned voice during testing

On Thursday, OpenAI released the “system card” for ChatGPT’s new GPT-4o AI model that details model limitations and safety testing procedures. Among other examples, the document reveals that in rare occurrences during testing, the model’s Advanced Voice Mode unintentionally imitated users’ voices without permission. Currently, OpenAI has safeguards in place that prevent this from happening, but the instance reflects the growing complexity of safely architecting with an AI chatbot that could potentially imitate any voice from a small clip.
Advanced Voice Mode is a feature of ChatGPT that allows users to have spoken conversations with the AI assistant.
In a section of the GPT-4o system card titled “Unauthorized voice generation,” OpenAI details an episode where a noisy input somehow prompted the model to suddenly imitate the user’s voice. “Voice generation can also occur in non-adversarial situations, such as our use of that ability to generate voices for ChatGPT’s advanced voice mode,” OpenAI writes. “During testing, we also observed rare instances where the model would unintentionally generate an output emulating the user’s voice.”
In this example of unintentional voice generation provided by OpenAI, the AI model outbursts “No!” and continues the sentence in a voice that sounds similar to the “red teamer” heard in the beginning of the clip. (A red teamer is a person hired by a company to do adversarial testing.)
It would certainly be creepy to be talking to a machine and then have it unexpectedly begin talking to you in your own voice. Ordinarily, OpenAI has safeguards to prevent this, which is why the company says this occurrence was rare even before it developed ways to prevent it completely. But the example prompted BuzzFeed data scientist Max Woolf to tweet, “OpenAI just leaked the plot of Black Mirror’s next season.”
Audio prompt injections
How could voice imitation happen with OpenAI’s new model? The primary clue lies elsewhere in the GPT-4o system card. To create voices, GPT-4o can apparently synthesize almost any type of sound found in its training data, including sound effects and music (though OpenAI discourages that behavior with special instructions).
As noted in the system card, the model can fundamentally imitate any voice based on a short audio clip. OpenAI guides this capability safely by providing an authorized voice sample (of a hired voice actor) that it is instructed to imitate. It provides the sample in the AI model’s system prompt (what OpenAI calls the “system message”) at the beginning of a conversation. “We supervise ideal completions using the voice sample in the system message as the base voice,” writes OpenAI.
In text-only LLMs, the system message is a hidden set of text instructions that guides behavior of the chatbot that gets added to the conversation history silently just before the chat session begins. Successive interactions are appended to the same chat history, and the entire context (often called a “context window”) is fed back into the AI model each time the user provides a new input.
(It’s probably time to update this diagram created in early 2023 below, but it shows how the context window works in an AI chat. Just imagine that the first prompt is a system message that says things like “You are a helpful chatbot. You do not talk about violent acts, etc.”)
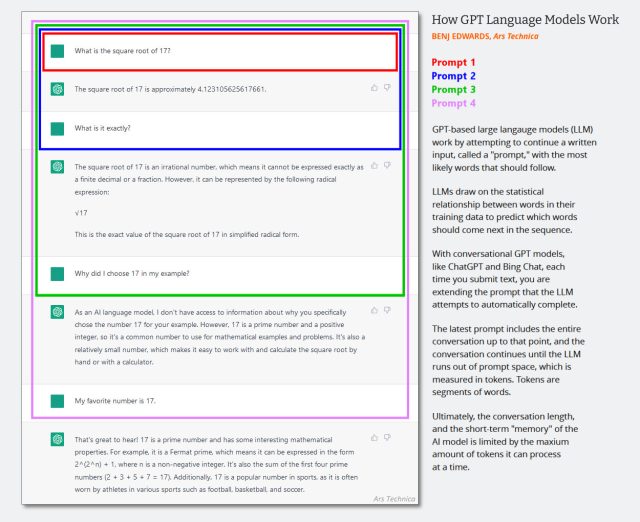
Enlarge / A diagram showing how GPT conversational language model prompting works.
Benj Edwards / Ars Technica
Since GPT-4o is multimodal and can process tokenized audio, OpenAI can also use audio inputs as part of the model’s system prompt, and that’s what it does when OpenAI provides an authorized voice sample for the model to imitate. The company also uses another system to detect if the model is generating unauthorized audio. “We only allow the model to use certain pre-selected voices,” writes OpenAI, “and use an output classifier to detect if the model deviates from that.”
ChatGPT unexpectedly began speaking in a user’s cloned voice during testing Read More »