Rocket Report: SpaceX focused on Starship reentry; Firefly may be for sale
Fiery news —
“Teams are in the process of completing a follow-on propulsion system assessment.”
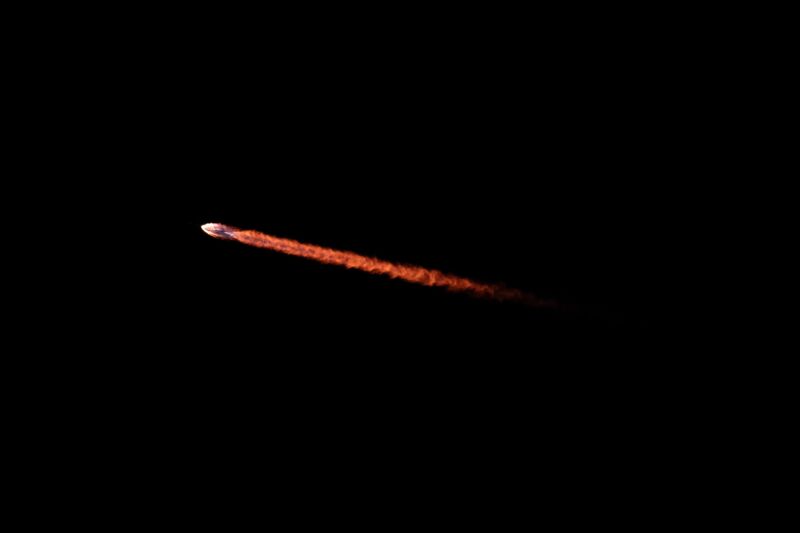

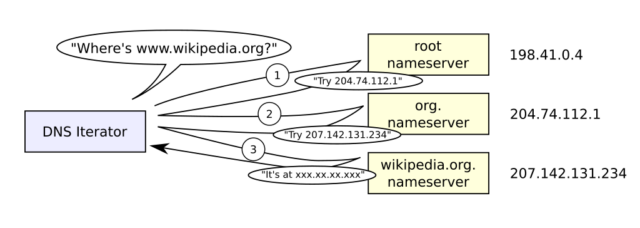
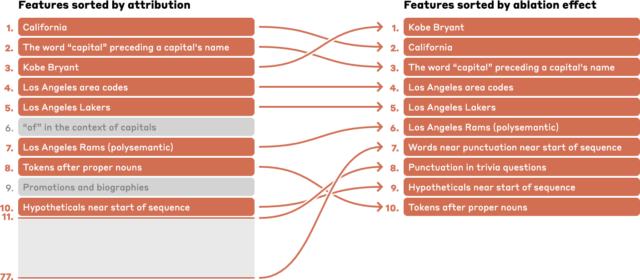
Enlarge / A Falcon 9 rocket launches the NROL-146 mission from California this week.
SpaceX
Welcome to Edition 6.45 of the Rocket Report! The most interesting news in launch this week, to me, is that Firefly is potentially up for sale. That makes two of the handful of US companies with operational rockets, Firefly and United Launch Alliance, actively on offer. I’ll be fascinated to see what the valuations of each end up being if/when sales go through.
As always, we welcome reader submissions, and if you don’t want to miss an issue, please subscribe using the box below (the form will not appear on AMP-enabled versions of the site). Each report will include information on small-, medium-, and heavy-lift rockets as well as a quick look ahead at the next three launches on the calendar.

Firefly may be up for sale. Firefly Aerospace investors are considering a sale that could value the closely held rocket and Moon lander maker at about $1.5 billion, Bloomberg reports. The rocket company’s primary owner, AE Industrial Partners, is working with an adviser on “strategic options” for Firefly. Neither AE nor Firefly commented to Bloomberg about the potential sale. AE invested $75 million into Texas-based Firefly as part of a series B financing round in 2022. The firm made a subsequent investment in its Series C round in November 2023.
Launches and landers … Now more than a decade old and with a history of financial struggles, Firefly has emerged as one of the apparent winners in the small launch race in the United States. The company’s Alpha rocket has now launched four times since its unsuccessful debut in September 2021, and it is due to fly a Venture Class Launch Services 2 mission for NASA in the coming weeks. Firefly also aims to launch its Blue Ghost spacecraft to the moon later this year and is working on an orbital transfer vehicle.
Blue Origin makes successful return to flight. With retired Air Force captain and test pilot Ed Dwight as the headline passenger, Blue Origin’s New Shepard spacecraft returned to flight on Sunday morning. An African American, Dwight was one of 26 pilots the Air Force recommended to NASA for the third class of astronauts in 1963, but the agency didn’t select him. It took another 20 years for America’s first Black astronaut, Guion Bluford, to fly in space in 1983. At the age of 90, Dwight finally entered the record books Sunday, becoming the oldest person to reach space. “I thought I didn’t need it in my life,” Dwight said after Sunday’s fight. “But I lied!”
One chute down … This was the seventh time Blue Origin, the space company owned by billionaire Jeff Bezos, has flown people to suborbital space, and the 25th flight overall of the company’s fleet of New Shepard rockets. It was the first time Blue Origin had launched people in nearly two years, resuming suborbital service after a rocket failure on an uncrewed research flight in September 2022. In December, Blue Origin launched another uncrewed suborbital research mission to set the stage for the resumption of human missions Sunday. There was one issue with the flight, as only two of the capsule’s three parachutes deployed. It’s unclear how long it will take to address this problem.
The easiest way to keep up with Eric Berger’s space reporting is to sign up for his newsletter, we’ll collect his stories in your inbox.
RFA tests first stage of its rocket. German launch startup Rocket Factory Augsburg announced Sunday that it had begun the hot-fire campaign for the first stage of its RFA One rocket. “We hot-fired a total of four Helix engines, igniting one by one at four-second intervals,” the company said on the social media site X. “All engines ran simultaneously for 8 seconds with a total hot-fire duration of 20 seconds. The test ran flawlessly through start-up, steady-state, and shutdown.” It’s a great step forward for the launch company.
Targeting a test flight this year, but … The test occurred at the SaxaVord Spaceport in the United Kingdom. The RFA One vehicle is powered by nine Helix engines and will have a payload capacity of 1.6 metric tons to low-Earth orbit. The company is targeting a debut launch later this year, but I’m fairly skeptical of that. By way of comparison, SpaceX began test firing its Falcon 9 first stage in 2008, with a full-duration test firing of all nine engines in November of that year. But the rocket did not make its debut flight until June 2010.
China expanding commercial spaceport. China is planning new phases of expansion for its new commercial spaceport to support an expected surge in launch and commercial space activity, Space News reports. Construction of the second of two launch pads at Hainan Commercial Launch Site could be completed by the end of May. The first, completed in December and dedicated to the Long March 8 rocket, could host its first launch before the end of June.
Fulfilling a mega-need … However this appears to be just the beginning, as the spaceport could have a total of 10 pads serving both liquid and solid rockets. The reason for the dramatic expansion appears to be increasing access to space and allowing China to achieve a launch rate needed to build a pair of low-Earth orbit megaconstellations, each over 10,000 satellites strong. It is also a further sign of China’s commitment to establishing a thriving commercial space sector. (submitted by Ken the Bin)
Rocket Report: SpaceX focused on Starship reentry; Firefly may be for sale Read More »