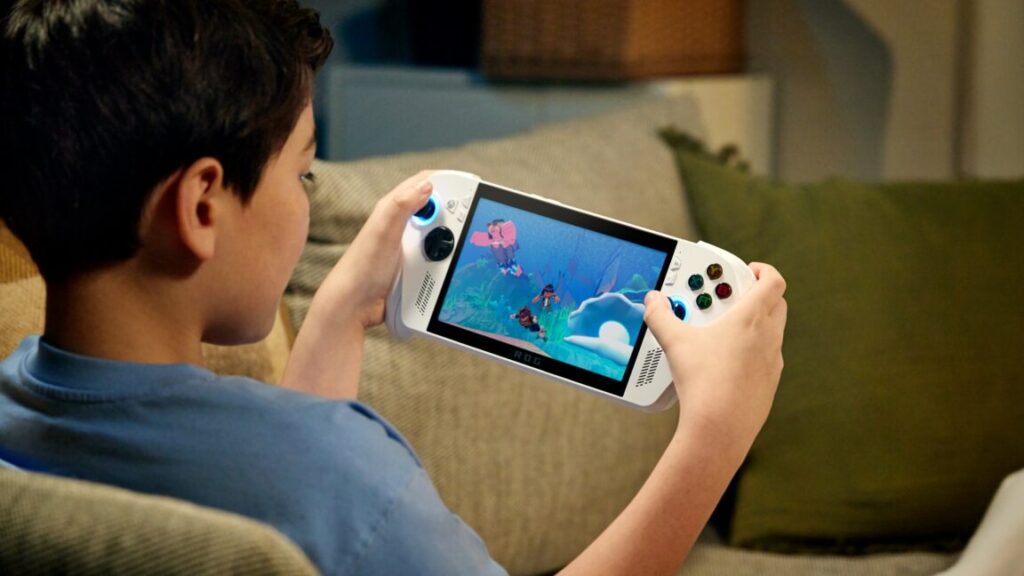
Asus’ new ROG Xbox Ally X set to break the bank at $999.99
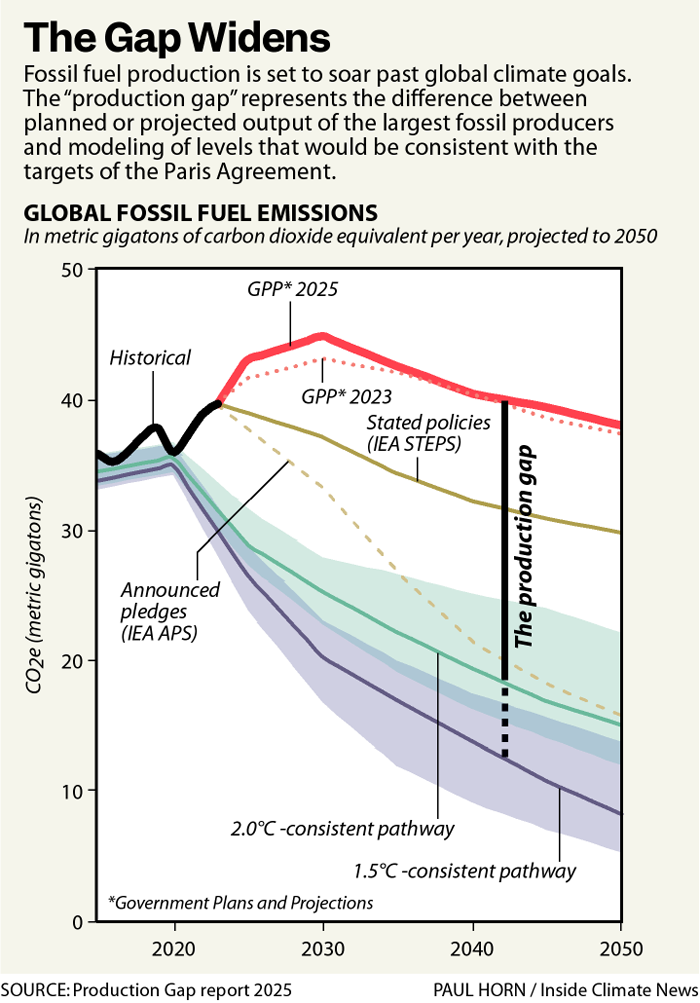
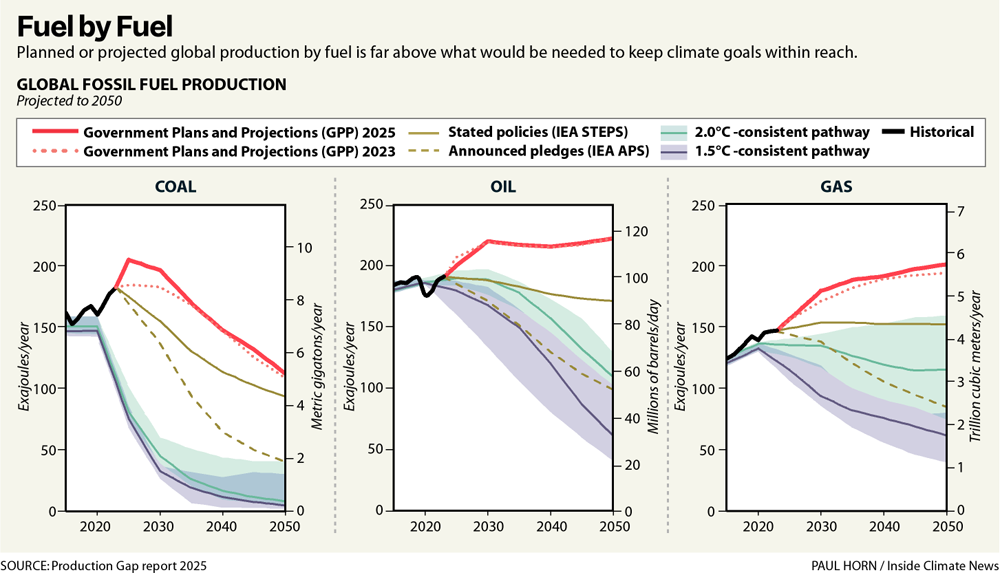
Microsoft and Asus revealed the ROG Xbox Ally handheld PC gaming line in June and promised an October 16 launch date in August. But they waited all the way until Thursday night to reveal preorder pricing set at $599.99 for the base ROG Xbox Ally hardware and a whopping $999.99 for the souped-up ROG Xbox Ally X.
Those prices put the baseline ROG Xbox Ally units in the same general price tier as competition like Valve’s Steam Deck OLED, Lenovo’s Legion Go S, and even Nintendo’s Switch 2. But the higher-grade ROG Xbox Ally X is significantly more expensive than almost all competing gaming handhelds, thanks in part to components like a Ryzen Z2 Extreme processor and an NPU that Asus says will ensure it is ready for a future when “AI enhancements” are rolling out in new games.
That may seem like overkill when Steam Deck users seem content using their handheld mainly for low-end games like Vampire Survivors and Hades. But Asus said that, in pre-release hardware tests, the ROG Xbox Ally X gets “up to a 30% performance boost” over 2024’s ROG Ally X on high-end games like Indiana Jones and the Great Circle. The newer hardware also gets “up to twice the battery life” over the ROG Ally X on a game like Hollow Knight Silksong, Asus said.
The new Xbox Ally line keeps the same 7-inch 1080p screens and starting RAM and storage capacity as the regular ROG Ally units from years past. But in addition to upgraded processors, Asus’ new handhelds also sport branded Xbox-style controls and logos and promise easy access to “all of the games available on Windows” through the new “Xbox experience for handhelds” that can handle games from various storefronts and manage launchers.
We’ll have to wait until we get our hands on our own testing units to see how that extra power and new interface compare to the competition. For now, the ROG Xbox Ally can be preordered directly from the Asus shop or retailers like Microsoft and Best Buy.
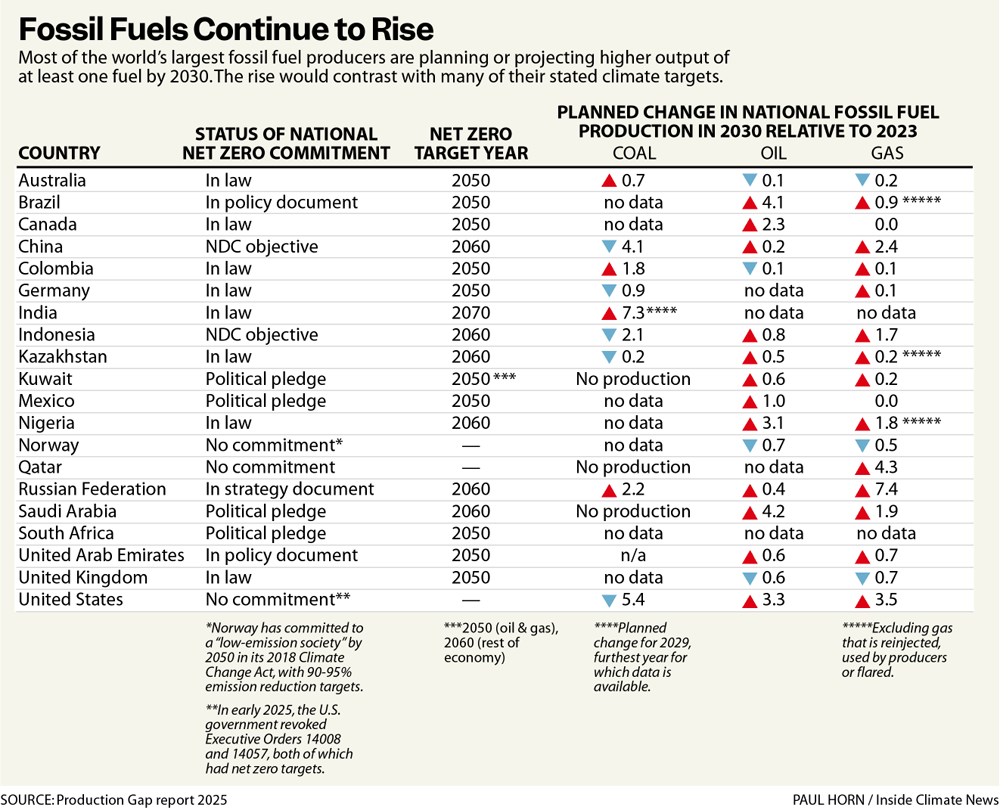
| Company | Name | Release year | Current starting price | Processor | Starting storage | RAM | Screen size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valve | Steam Deck LCD | 2022 | $399.00 | AMD Zen 2 | 256GB | 16GB | 7 inches |
| Asus | ROG Ally | 2023 | $499.99 | Ryzen Z1 | 512GB | 16GB | 7 inches |
| Valve | Steam Deck OLED | 2023 | $549.00 | AMD Zen 2 | 512GB | 16GB | 7.4 inches |
| Asus | ROG Xbox Ally | 2025 | $599.99 | Ryzen Z2 A | 512GB | 16GB | 7 inches |
| Lenovo | Legion Go S | 2025 | $649.99 | Ryzen Z2 Go | 512GB | 16GB | 8 inches |
| Lenovo | Legion Go | 2023 | $749.99 | Ryzen Z1 Extreme | 1TB | 16GB | 8.8 inches |
| Asus | ROG Ally X | 2024 | $799.99 | Ryzen Z1 Extreme | 1TB | 24GB | 7 inches |
| Asus | ROG Xbox Ally X | 2025 | $999.99 | Ryzen Z2 Extreme | 1TB | 24GB | 7 inches |
Asus’ new ROG Xbox Ally X set to break the bank at $999.99 Read More »