Childhood and Education #14: The War On Education
The purported main purpose of school, and even of childhood, is educating children.
Many people are actively opposed to this idea.
Either they have other priorities that matter more, or sometimes they outright think that your child learning things is bad and you should feel bad for wanting that.
Some even say it openly. They actively and openly want to stop your child from learning things, and want to put your child into settings where they will not learn things. And they say that this is good.
Or they simply assert that the primary point of education is as a positional good, where what matters is your relative standing. And then they pretend this doesn’t imply they both should and are going around preventing children from learning.
In other places, we simply epicly fail at education and don’t seem to care. Or education ‘experts’ claim that things that obviously work don’t work, or things that obviously don’t work, do work.
Consider this section some combination of peek into this alternative universe of thought and the fun of multiple meta levels of shooting fish in a barrel?
I present, HT to Pamela Hobart who makes many of the same points: Freddie DeBoer writes the long ‘Education Doesn’t Work 3.0’ which is ‘a comprehensive argument that education cannot close academic gaps.’
What? Was it supposed to do that? Would you want it to?
Very obviously the only way to close academic gaps fully is to go all handicapper general and ban bright kids from getting educations. Thus, The War on Education.
Freddie starts off saying we can’t admit some kids aren’t smart, and some kids will naturally do better at school than others, to which I say you just admitted it, and I’m happy to admit it, and everyone I talk to is willing to admit it, so who is this mysterious we. It is, presumably, a Certain Type of Guy who is an ‘education expert’ of some kind and presumably has a maximum of one child who has gone to school.
Freddie DeBoer: Our educational debates are largely useless because most people engaged in those debates assume out of hand that, absent unusual circumstances like severe neglect or abuse or the presence of developmental or cognitive disabilities, any student can be taught to any level of academic success, and any failure to induce academic success in students is the result of some sort of unfortunate error.
Well, it depends.
If you mean ‘those debates’ as in those between those ‘education experts’? Then perhaps yes, they make these types of absurdly stupid assumptions. If you mean ‘debates among actual regular humans,’ then no. Obviously not. One would question whether Freddie has met such people.
Education can raise the absolute performance of most students modestly, but it almost never meaningfully reshuffles the relative distribution of ability and achievement.
Um, again, what exactly were we trying to do? Educate the children? Or make sure we don’t educate the children? Half and half?
I mean, I guess Freddie then does a job repeatedly exposing ‘the contradictions’ as it were in the entire equality project, but the barrel already has a lot of bullet holes, the water is leaking and the fish are dead.
So we get more fun lines like this:
We have spent an immense amount of effort, manpower, time, and treasure on forcing students to meet procrustean academic standards, despite the fact that we have overwhelming evidence that their relative performance is largely fixed.
Yes, obviously, also yes the extra money is mostly being wasted but even if it wasn’t the whole point was presumably to (drum roll) educate the children.
Why in the world would we spend tons of resources and time on relative education, which by definition is zero sum and a red queen’s race? That doesn’t make sense. There’s a fixed amount of relative education.
At the end of this essay, I will argue that education is important, does matter, and is worth funding – but that what’s now assumed to be its primary purpose, moving students around in quantitative educational metrics, is actually what education does worst.
Who thought that was its primary purpose, either the metrics or the thing itself?
Meanwhile, the reason this was brought to my attention is that his ‘absolute learning has value’ t-shirt is raising questions supposedly answered by the shirt:
What This Essay Does Not Argue:
That absolute learning (that is, learning as measured against a standard or benchmark or criterion) has no value; rather, relative learning is practically and morally dominant in these discussions because only relative learning (sometimes discussed in terms of educational mobility) can better one’s economic fortunes, and it is that potential that underlies our entire modern educational debates and the reason for obsession with achievement gaps.
The next section is ‘I Assure You, You Do Care About Relative Learning.’
I assure him that I don’t.
His first argument is that relative learning indicates absolute learning. That is true but saying this means therefore you care about relative learning (checkmate, liberals?) is not how logic or words work. Caring about the territory does not mean you care about the (not very accurate) map.
Second, while I am happy to concede that absolute learning happens all the time, this should not be mistaken for saying that absolute learning is easily achieved, reliable, or consistent.
I don’t understand why this is supposed to be a relevant argument here. It seems like he’s saying I care about [X], but actually [X] is hard, so instead I care about [Y]?
Most importantly, though, is a simple reality: the consequences of education are derived from relative performance, not absolute.
…
In the vast majority of scenarios where education is relevant, applicants of whatever type are being evaluated relative to peers.
There’s saying the quiet part out loud, and then there’s this.
The purpose of education is… to do well on applications?
He concedes that one might learn to drive and then use this skill to usefully operate a moving vehicle, but says this type of education is rare – that most education has no actual use whatsoever, other than as a positional good to grab a larger share of stuff.
Then he goes through that schools are ‘not guilty’ because improving educational outcomes is impossible anyway. Transferring does nothing. Charter schools don’t work. Interventions don’t work (literally “Nothing “Works””), full null hypothesis.
All right, so now we have a section ‘So What Should We Do?’
Very obviously, if you actually believed all that, you would want to dramatically reduce spending, both in money and in the time of children, on school, since school is almost entirely about relative position. Spending more on school, trying to achieve more or improve performance, in this model, is a defection against everyone else. So we should ban attempts to educate children, beyond some basic skills, and focus on practical stuff like learning to drive. Completely reorient childhood.
So having pre registered that, let’s see what he recommends.
-
Improve air quality. Okay, sure, that is one of the somethings that work, although again I don’t understand why he thinks improving performance is good.
-
Lower our educational standards. Don’t make kids learn (for example) abstract math. Yes, that makes perfect sense for Freddie, if the learning is useless, you shouldn’t require it. Again, if he is right then we should go farther, and ban such learning. Why are we letting kids engage in a zero sum competition?
-
Soft tracking. Again, good idea, not sure what it has to do with the post.
-
Invest in a robust safety net. Maybe? That’s a different department.
Then he tries to pivot back to ‘actually education matters.’
Education creates the conditions for children and young adults to discover ideas, literature, science, and art that might otherwise remain inaccessible.
It provides the structured time and social environment where curiosity can blossom, where students can learn how to think about problems that don’t have easy answers, and where they can build lasting relationships with peers and mentors.
The point of school, then, is not to guarantee that every child climbs into the top decile of performance but to offer each student the chance to cultivate knowledge, resilience, and imagination in ways that enrich their lives.
So absolute learning of something does matter after all, then. I mean, this description does not match what I know about actual schools, nor would I design anything like a current school if those were the goals. And he doesn’t seem interested in a redesign or asking how to maximize the things that he thinks matter. But hey.
Meanwhile, here’s the top comment, so yes things do get pretty insane:
James K: This is what I pay you for, Freddie, thank you for being so clear-headed about this topic.
I’ve been teaching for 16 years now and it boggles my mind that the band teacher can literally get on stage and say “We have the beginner, intermediate, and advanced band for you” and of course the baseball team can be divided into Varsity and JV, but I am not allowed to say that some kids are not smart enough to handle my AP classes because this means I don’t BELIEVE IN THEM or am supporting TRACKING (always said in the tones people reserve for the words ‘eugenics’ or ‘segregation’).
I mean, yes. It means you support tracking because tracking is good. It means you don’t believe in them in the sense that you don’t believe in things that aren’t real.
So no, in that sense Freddie isn’t arguing with a strawman. Which means that the entire system of education is being run by people who are at war with education.
A Tennessee teen is suing his school for ‘compensatory education’ after graduating with a 3.4 GPA, but being unable to read, or even spell his own name, and the school system has the audacity to defend against that lawsuit.
But the school took no action, the suit says, other than giving him 24 hours to complete his assignments.
But even this “solution” was a problem. Because when William was at home with his schoolwork, he relied on AI programs like ChatGPT and Grammarly to complete his assignments for him, according to the judge who ruled on his suit last week. As a result, William continued to achieve high marks on his classwork throughout his entire four years of high school, even though teachers knew he was illiterate.
If you can’t read, using ChatGPT is kind of crazy – you’re presumably scanning or copy pasting in text you don’t understand, then copying out text you don’t understand and hoping for the best.
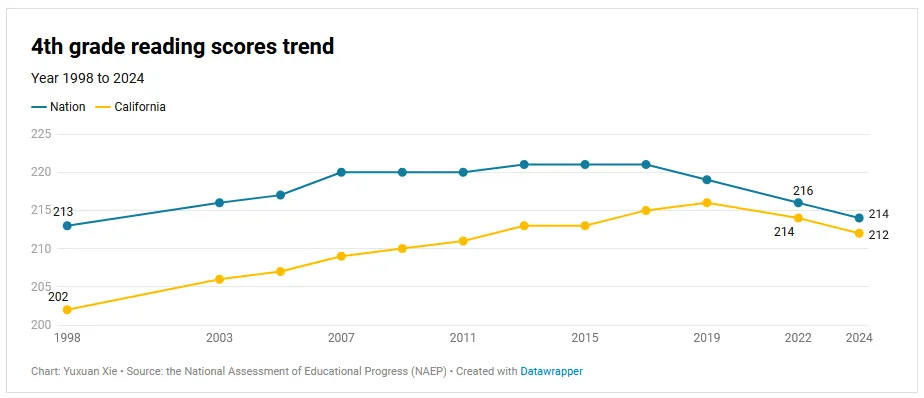
Scott Alexander asks: What happened to NAEP Scores? He says they are ‘not good’:
Well, they’re not great obviously, to the extent you can trust the scores to map to Reality, but they are still above the start of the graph in 1998, and we’re talking about a seven point difference. That’s less than a fifth of a standard deviation. This is nothing, if anything this shows that Covid didn’t change things much?
The comments section of Scott’s post is full of despair about classroom conditions getting worse, shifts to teaching strategies that don’t work (see the Mississippi reforms but in reverse), discipline collapsing and teachers having no tools if kids don’t play along, many teachers quitting, chronic absenteeism happening and being accepted and tolerated, and many families not prioritizing education, on top of the continuing trends involving smartphones. That’s on top of the obvious ‘Covid took away a lot of schooling’ concern that Scott starts with.
What seems more meaningful than the overall smaller drop is the widening gap between low and high performers, another trend predating Covid. Scott has several graphs showing this, and I am convinced this is real, with a variety of causes. If you are properly equipped and motivated, you can avoid the pitfalls described above, and you have access to the entire web and world and a lot of new resources, now even including AI. Whereas when the bottom falls out, the bottom falls out.
Meanwhile in 12th grade, nearly half scored below ‘the basic level,’ which involves things like ‘using percentages to solve real-world problems,’ and reading scores hit a new low. What we are doing, including adding funding, is clearly not working. Or rather, it is working hard, only not at the goal of children learning academic skills.
The War on Algebra in particular is still perhaps the craziest thing I’ve ever seen, actively preventing children from learning math out of spite. In the sense that it both very clearly purely destructive and evil, and also horribly unpopular across the board, and also high salience to a lot of voters. Yes, I do know what their arguments are for doing it, and they very much do not make it any better.
And yet it still happened, and it happens across the board, straight up Handicapper General style.
Ro Khanna: It is absurd that Palo Alto School district just voted to remove honors biology for all students & already removed honors English. They call it de-laning. I call it an assault on excellence. I took many honors classes at Council Rock High in PA.
Autumn Looijen: I ran the campaign to bring algebra back to SF’s middle schools.
It was the most popular thing I ever worked on. Voters don’t want to take away opportunities for kids who can’t afford private school.
If anyone wants to put this on the ballot in Palo Alto, happy to advise.
Maud Maron: We are trying to do a version of this in NYC! Would love to have you speak to NYC parents who want to have algebra & geometry options in Middle School.
Meanwhile in San Francisco, the war rages on. It seems the city has not yet been retaken by sanity on all fronts yet, although there are some promising signs. All of this seems like it has to be beyond unpopular, in a ‘cause families to move out’ way, yet here we were again not too long ago (it got better, for now):
Garry Tan: San Francisco schools is trying its absolute hardest to make sure all middle income families who could move out of the city do so right away.
“Grading for Equity” is going to be a real disaster and I guess this is a boon for SF private schools and Burlingame housing prices.
For education bureaucrats who ruin our public schools with the most unfair and anti-merit polices: BUSINESS IS BOOMING.
Someone needs to investigate the Schools of Education that spawn these policies because it is a real danger to public schools everywhere.
Basically this scam is Idiocracy in real life.
Mike Solana: the san francisco board of education must immediately fire the superintendent. if they do not, they must all be removed from power.
I don’t get how this falls under ‘you can just do things’ but it seems it did, at least until people sounded the alarm?
John Trasvina (The Voice of SF): Without seeking approval of the San Francisco Board of Education, Superintendent of Schools Maria Su plans to unveil a new Grading for Equity plan on Tuesday that will go into effect this fall at 14 high schools and cover over 10,000 students.
The school district is already negotiating with an outside consultant to train teachers in August in a system that awards a passing C grade to as low as a score of 41 on a 100-point exam.
Were it not for an intrepid school board member, the drastic change in grading with implications for college admissions and career readiness would have gone unnoticed and unexplained. It is buried in a three-word phrase on the last page of a PowerPoint presentation embedded in the school board meeting’s 25-page agenda.
…
Grading for Equity eliminates homework or weekly tests from being counted in a student’s final semester grade. All that matters is how the student scores on a final examination, which can be taken multiple times.
Under the San Leandro Unified School District’s grading for equity system touted by the San Francisco Unified School District and its consultant, a student with a score as low as 80 can attain an A and as low as 21 can pass with a D.
Derek Thompson: New SF public school plan would
– eliminate homework and weekly tests from counting toward semester grade
– allow students to take the final exam multiple times
– convert all B grades into As, and all Fs into Cs
It’s hard to see the difference between this policy and what you’d get if a bunch of 10yos locked the teachers in a closet and rewrote the rules.
Karen Vaites: More media attention here, please! 🚩🚩🚩
Jared Walczak: The sad irony is that Grading for Equity is virtually the opposite of Teaching for Equity, because under this system, the only kids who might get a real education are those from families that take more into their own hands, bringing higher expectations and resources to bear.
So, effectively no grading, then. You can do whatever you want all semester, no homework (so perhaps there’s some upside here?), phone out in class every day, whatever, all you have to do to pass is get 21% on an exam you can take multiple times. That was going to be it.
And Maria Su could just do this on her own? What?
It turns out that enough backlash does matter, and this combination of graft and civilizational suicide took the loss on this one.
SF Standard: Just in: SFUSD is delaying a planned “grading for equity” initiative after the proposal sparked furious backlash.
Kelsey Piper: SF superintendent backed off immediately after the flood of negative feedback. This strikes me as a pretty dramatic change from how previous standards erosions were received, and a really good sign.
Most politicians want to make their constituents happy, and often their information environment is kind of terrible for that. It’s worth advocating for the stuff that matters to you. Don’t be an asshole, but be clear and outspoken.
San Francisco’s turnaround happened very fast. The Bay Area could become one of the best-governed parts of the United States inside a few years if we work to make it happen.
Well, maybe. They say they are ‘delaying’ the initiative. Which means they’re presumably going to keep paying the consultants, and they are going to try again to destroy all the incentives and measurements involved in education.
Fighting against algebra and grading is bad enough, but reading?
As in, people who want to ban teaching kids to read until age 6. No. Seriously.
Because they’re ‘not ready.’
Erik Hoel: 62% of American kids have a tablet at age 6.
They spend 3.5 hours every day on screens (increasingly, TikTok).
And because our school system waits so long to teach reading, they never get a chance to become readers.
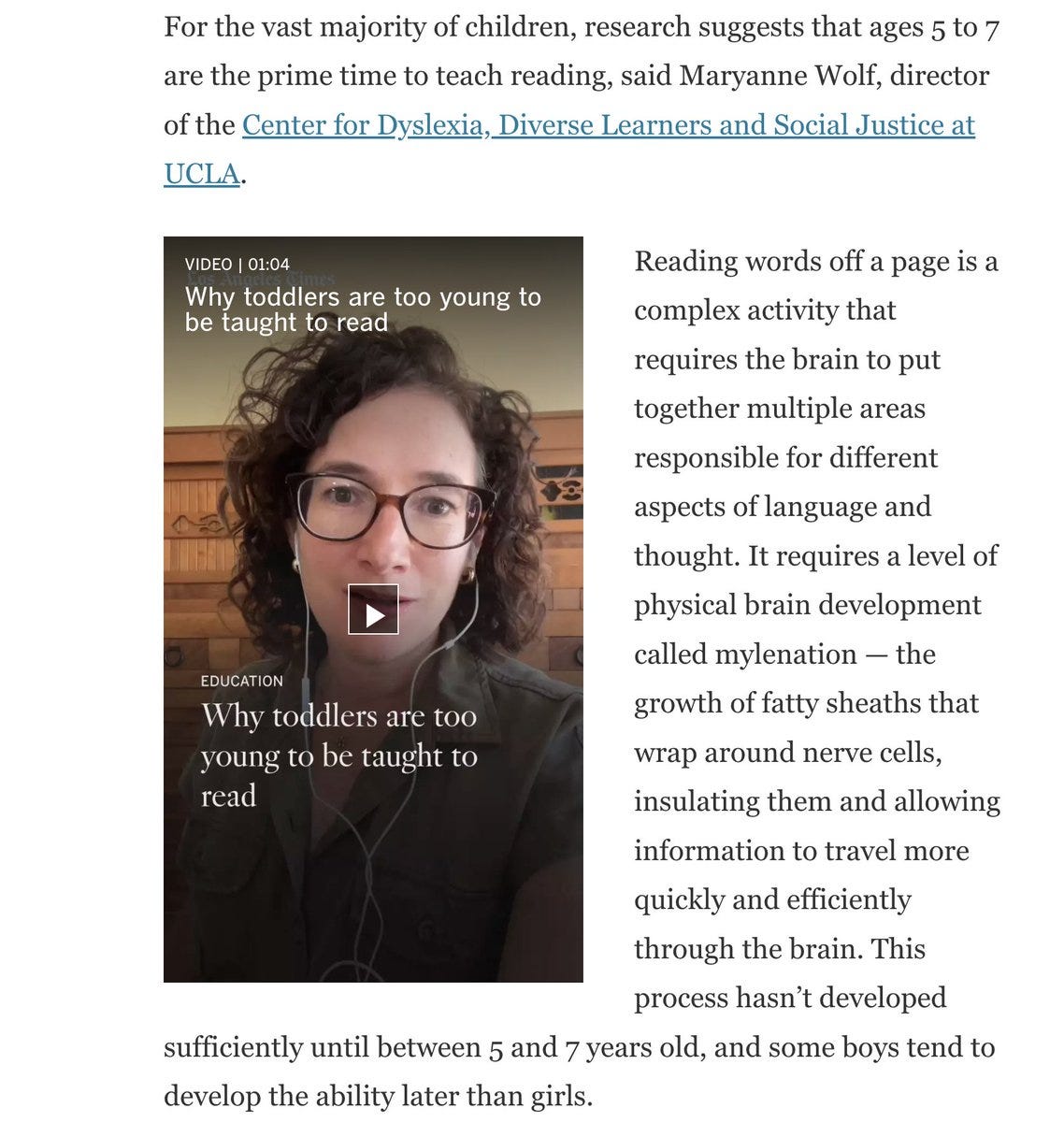
“Education experts” have been saying for decades that we must wait to start teaching reading until 6-7 for neuroscientific reasons. These reasons appear, as far as I can tell, to be basically made up. Consider this recent article, which quotes a bunch of experts on this.
E.g., Maryanne Wolf says that brain myelination needs to reach a certain stage, and that teaching reading prior to 5 is “really wrong” and that she would ban teaching reading prior to 6 nationwide if she could.
Siberian Fox: what in the fuck
I was playing Pokémon before 6 if I recall correctly, if not, other games that require reading
good to know that there are people in the US that think this should be super illegal
In a good school, a 1st grader will be reading quite a lot, actually.
I’m not going to bother quoting more of the evidence because this is so utterly Obvious Nonsense as to be beyond belief. Frankly, if I had a child that was 6 years old and couldn’t read I would not be thinking ‘good it is finally time,’ I would be debating exactly how much to panic and reassuring my wife not to panic far more.
The 3 year old I am currently supervising can somewhat read. I could read before my first memory (which was at 5 and involves reading books) so I don’t know exactly when it happened, and I learned without anyone trying to teach me.
I am going maximum opposite. There is no higher priority than teaching a child to read as early as they can handle it, and every actual parent knows this. There is a reason why the advice is constantly read to them, read with them, push reading. Reading enables everything else. The entire ‘education’ establishment really does need to flat out join the delenda est club.
In the name of them developing empathy for the people you force them to teach? As long as they pass a certain threshold of knowledge, the rest of their childhood, and indeed life, belongs to the people, and they’re a horrible person if they think otherwise, and the purpose of school is to teach them this?
No, seriously, this is something quite a lot of people, especially those in education, actually believe.
Setting all ethical or moral considerations aside, and even assuming that is the goal, what in the world makes you think this is going to work in the direction you want?
Tracing Woods: If a child is in a class, they should be there because it is the best environment to help them learn, not so they can act as an unpaid tutor to provide vague “peer effects” to others A system that abuses children as resources instead of teaching them to their level is unethical.
Joe McReynolds (3.4m views): That’s what life *is*, though! If you’re unusually smart/talented, your primary purpose in life is to help lift up others who weren’t born/raised as lucky as you were. Learning that sooner rather than later is important for developing a sense of altruism and communitarianism.
“With great power comes great responsibility” is a simple, true statement. To the extent being born with unusual (intellectual) power is an “innate characteristic,” that good luck means that you owe the universe hard work. You’re born with a debt that takes a lifetime to repay.
There it is, very explicitly. These people actually believe this. If you’re talented, your purpose in life is to be enslaved, to be forced to help others. Your life does not belong to you. Your labor does not belong to you. Your time does not belong to you. Who cares whether that benefits you? You belong to the people, from each according to their ability, at the barrel of a gun.
Kelsey Piper: If I were actively trying to extinguish my children’s sense of altruism, compassion and responsibility I can’t think of a better plan than forcing them to spend all of their time doing random ‘altruistic’ chores they didn’t choose, and aren’t equipped to succeed at.
If you say to your kid “I’m going to volunteer this weekend to help socialize cats”, they’ll probably come along and they may discover a lifelong love of helping animals! if you force them to spend all their time on it, guess what, they’re gonna hate it.
if you want your children to be people who give generously to their communities and their broader world, be that kind of person yourself and let them witness the ways in which this is part of the good for you and for your community.
SteelBlaidd: Why do they need to go to college to learn to be teachers if kids can be expected to do it in elementary school?
Kelsey Piper: some people out here believe that homeschooling is immoral since you don’t know enough to teach your kids and also that a smart 9 yo can do it.
Ben Hoffman: The important thing is that the 9yo is forced to do it without pay to teach them that being educated means going along with nonsense dramas, which qualifies them to get paid to go along with nonsense dramas when old enough that that’s dramatically appropriate.
Not only that the smart 9you can do it, that they should be forced to do it without pay. While the parent is forbidden to do it, because they are unqualified.
Ryan Moulton (QTing Joe above): Everybody is dunking on this, and I get why, but I’m a little more sympathetic. Particularly in lower grades, developing empathy for people different from you or dumber than you is a really important thing to get out of school, comparably important to getting through math faster.
Sarah Constantin: t is super common for kids to openly taunt anyone who’s not as good as them (at anything!) and i do think it’s important for them to learn manners, grace, and sportsmanship…
but it doesn’t deserve as much time in the day as math class.
Gallabytes: I would add that these kinds of assignments don’t necessarily breed empathy it’s pretty easy for it to create contempt instead.
Sarah Constantin: yeahhh.
Gallabytes: feels like people talk about school in far mode as some inscrutable thing.
if I put *youin a room with people you had 4 sigma on and told you to teach them math Or Else, how would you feel? how would this make you feel about them?
I believe we should treat Joe’s perspective the same way we would treat others who would force people with certain characteristics to labor for no compensation.
See my discussion of Alpha School for extensive previous discussions.
Tracing Woods (reference documents and more details in thread): in 1930, researchers studied ability grouping and concluded you needed to adjust the curriculum to make it work
in 1960, more confidently so
then in 1990, they studied grouping without changing curriculum, concluded it was useless, and advocated to get rid of ability grouping
over time the field got better and better at studying the form of ability grouping that everybody had known was pointless for sixty years while just sorta disregarding the form that kept getting results
I get so mad every time I read this stupid study
the field of education set itself back generations because it kept listening to people who thought ability grouping was “antidemocratic and antiegalitarian” and as such badly wanted it not to work
we had it figured out in 1936 and then we threw it away for kicks.
I am not a fan of the idea of educating children in 2025 primary via traditional classes. Traditional classes feel like learning a lot more than they actually cause learning.
But I accept that we are going to keep doing this for a while.
Given you are going to have traditionally shaped classes on various subjects, very obviously you want to track their progress and group those children by ability.
Grouping children into classes by ability has the advantages that it, as covered in Education #11:
-
Helps almost all children learn more, whether they are behind, ahead or neither. There are some corner cases where kids are ‘on the bubble’ between tracks, or get tracked wrong, but mostly this is opportunity cost, that they missed benefits.
-
Is universally popular with parents, to the extent that ‘ending tracking’ is the least popular serious policy proposal we have ever seen. As in David Shor says ‘removing advanced classes from schools’ is literally the single most unpopular policy Blue Rose has ever polled (yet there goes Palo Alto doing exactly this.)
Ability grouping, done wisely, so utterly obviously works as to make the alternate hypothesis absurd.
Tracing Woods: will someone struggling with basic arithmetic and someone who knows calculus benefit from the same instruction? no.
would selective schools and the students in them benefit from opening their doors to everyone? they certainly don’t seem to think so!
do athletics orgs advocate grouping young LeBron into his local mixed-ability rec league so he can trarin and progress? no.
do gifted kids who accelerate learn more advanced material when they’re presented with it? yes.
if people see school as a democratic equalizer where everyone should learn the same things, they find ability grouping doesn’t work (doesn’t accomplish that goal). if people see school as a place where people should learn specific subjects and progess to whatever level they can, they find it does work (does accomplish that goal). and because education research is dominated by the former, onlookers glance at its output and say “huh, the results are mixed. guess we’ll never know!”
there is no substitute for understanding what is going on at a ground level.
The question is how to make it work best, not whether it works. Very obviously, as the next section discusses, it is possible to massively screw it up if you try hard enough.
Jordan Michelson: Why would *teacher’s unionsoppose ability grouping? It makes no sense.
Matthew Yglesias: Ideology.
Karen Vaites: The average American would be shocked by the degree to which K-12 education is ruled by ideology. Beliefs about teaching and how we want learning to work often trump evidence about what does, in fact, work.
Tracing Woods: “Trace, why are you making such a big deal out of something everybody already agrees with?”
Because the people we trust to direct society on this topic at every level oppose it.
And I hope that maybe if I shout enough about that people will really internalize what that means.
Exactly. Everyone agrees we want [X], where [X] is tracking. We keep talking about it because [~X] keeps actually happening.
I presume opposition is mostly ideology. Full stop. They want to prevent the wrong kids learning too much. They are sacrificing the kids on their alter.
Academics and education ‘experts,’ despite the literature and all actual observations and everyone involved saying that tracking helps all kids learn better, keep lamenting that parents want tracking, and work to destroy it, often in the name of ‘equity.’
It is common to see people claim ‘the research’ says that ‘downstreamed’ kids who are grouped at lower ability do worse rather than better as a result and that ‘the research’ supports this. As far as I can tell this is simply not true, these people simply think it ‘should’ be true, and seek out ways to say it anyway.
Tracing Woods: what happens when academics study parental perception of ability grouping?
They lament that parents of students at all levels favor it even though it’s BAD.
Virtually no parents support ending ability grouping.
Parents of kids in both remedial and G/T programs agreed that their kids should be grouped with kids of equal ability
80% of special-ed parents, 90% of parents with kids in remedial courses, and 98% of parents with kids in advanced programs agreed that their kids were helped by it.
This was all very disappointing to the authors.
Why do the authors here, like many other academics and education experts and many school principals who somehow end up actually destroying such programs, say that this is bad, despite everyone involved in the actual schools agreeing it helps all of the students?
Because the ‘educators’ who determine policy (as opposed to the teachers whose job is to actually educate children) consistently have decided that they do not care about the life experiences of families and children or helping children learn.
What they care about, other than money, is preventing learning rather than causing learning. Or, as they call it, ‘equality’ or ‘equity.’ Never mind that this ‘equity’ directly hurts the students who are otherwise being ‘denied’ it, what matters is that they be given ‘opportunity to learn and equality of educational opportunity.’ Educational opportunity shall be destroyed until this is achieved. If that leads to everyone getting a worse education, even the worst off kids, well, that’s not their department’s KPI.
I don’t quite agree with Anton that these people ‘hate you and your children.’ They only hate that you and your children might do better than other children, and want to prevent this from happening. They only hate you if you oppose this goal.
Garry Tan: Ability grouping in school (honors/AP) depends on your frame. If school’s job is to equalize, grouping looks like a fail. If it’s to let kids sprint ahead, it works.
Academia worships equalizing— so the School of Education bureaucrats become anti-education, ruining schools.
When you examine the list of nonprofits and academics that want to remove advanced math from classrooms and water down the standards for all students it will leave you shaken.
It’s not a fringe movement. It is School of Education Orthodoxy.
Tracing Woods: This is a fair question! Opposition to ability grouping is a fringe idea opposed by the great majority of parents. So which obscure, fringe organizations are pushing it?
Let’s ask the National Council of Teachers of English what they think:
Or what about the most prominent law casebook publishers?
Or consider the National Association of Secondary School Principals.
How about the Association of State
Supervisors of Mathematics, NCSM: Leadership in
Mathematics Education, and the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM)?
You know it.
If it is a choice between the form of academia that wants to prevent children from learning, and the form of academia that helps teach useful things, and one or the other must be destroyed?
The choice seems clear.
Tracing Woods: my modest proposal to every university that has published research claiming ability grouping (with paired curricular modification) doesn’t work:
detrack. remove your admissions standards. remove course prerequisites.
if detracking works, let’s create Harvard Community College.
However, you do have to choose a reasonable implementation. Is it possible we also in some ways are screwing implementation up so badly that adding what we call ability grouping to the mix, as implemented in practice, could make things worse?
North Carolina excluded half its qualified students from advanced math. They tried to pass a law to fix some of this. The schools fought back.
Tracing Woods: What happened when North Carolina changed its laws to require top-scoring students to be placed in advanced math?
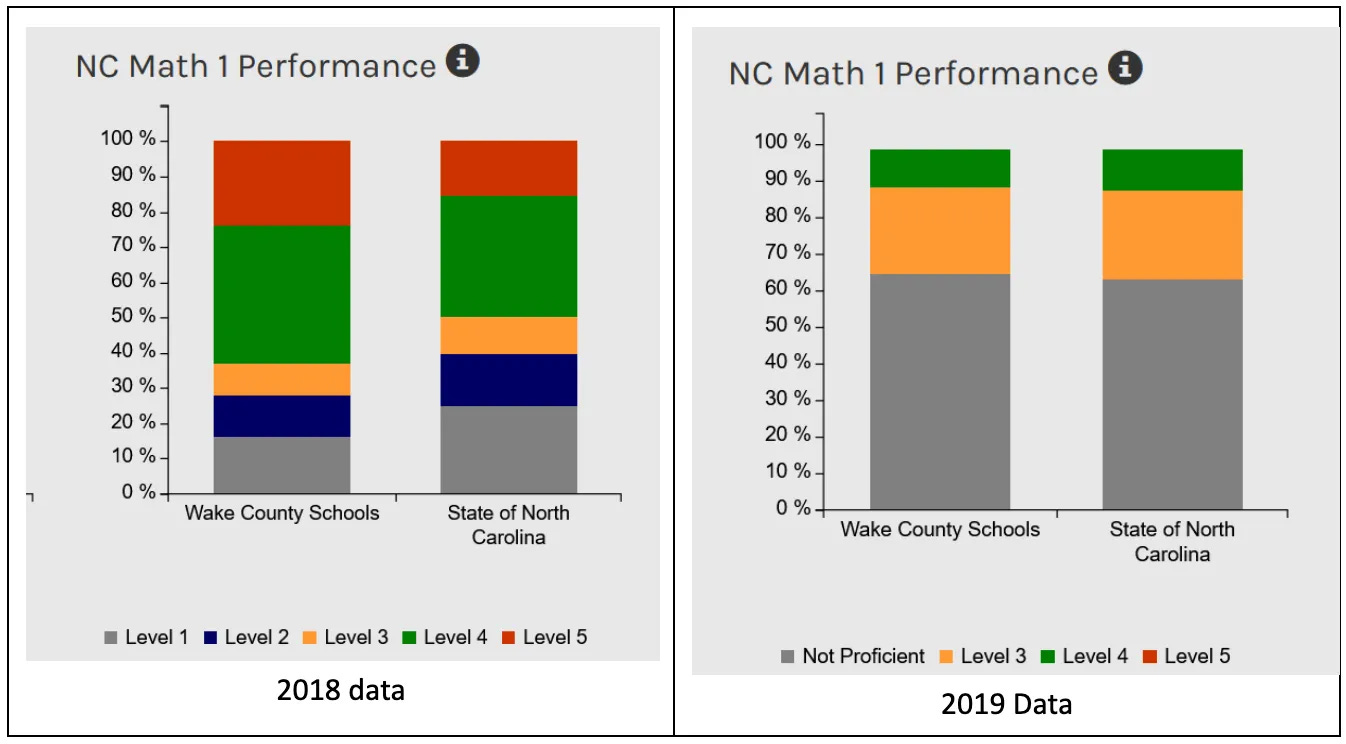
The state board of education changed the test cutoffs, subverting the intent of the law by dropping almost all students from the top-scoring category.
Janet Johnson and John Wittle: The law was intended to help high school students who excelled in their math classes move into the advanced track. Before the scoring change, 11% of high school students statewide scored at Level 5, the highest level, with some districts seeing rates as high as 25%. The EVAAS Prediction vs. Performance table (above) showed that in 2009, 42,144 students were predicted to be successful in 8th-grade algebra, and only 18,670 students were enrolled. Using EVAAS prediction as the metric would have given 23,474 more students access to advanced math.
After the law passed, which required schools to admit all Level 5 students to advanced classes, and the state changed the scoring scale, fewer than 1,500 (too few to report) high school students in the entire state achieved Level 5.
The schools had technically complied with the law while completely subverting its intent. These charts are from the NC School Report Cards.14 After 2019, the Math 1 Performance charts show no Level 5 and very little Level 4, similar to this.
The full post on ‘the Algebra gatekeepers’ keeps outlining all the tactics used to ensure that kids do not learn algebra, especially disadvantaged kids. As you read it, it keeps getting worse.
For example, we attended a meeting with the parents of a middle school girl who had earned an A in 7th-grade pre-algebra but was denied enrollment in 8th-grade algebra despite her and her parents’ wishes. The teachers argued that her formative assessments didn’t align with her summative performance, suggesting her previous success didn’t guarantee future outcomes.
The language arts teacher claimed the student had “appeared to struggle” during benchmark activities and that earning an A seemed “harder for her than for other students who achieved similar summative data results.” The math teacher who had given her an A pointed to C grades on some earlier formative assessments, arguing that despite her subsequent A performance on chapter tests and other summative data points, these initial benchmark scores indicated she “sometimes struggles with foundational concepts during the formative assessment process.”
The administrators nodded knowingly as teachers referenced “inconsistent performance across benchmark measures” and “concerns about the gap between formative and summative data trends.” They suggested that while her final grades represented solid summative data, the formative assessment patterns revealed “areas of concern” that made advanced placement inadvisable, regardless of what the summative data actually showed about her mastery of the subject matter. This is just an example of the kind of talk the parents encountered, so the church advocacy group started bringing someone from our staff to the meetings to help them cut through this.
This type of circular reasoning, where success was reframed as evidence of potential failure, was typical of how schools justified excluding qualified students from advanced courses.
Administrators would routinely promise that students could move to advanced tracks “later, in high school,” but our analyses and other research we found indicate students rarely moved to the advanced track after the 8th grade.
The tracking system created rigid pathways where missing 8th-grade algebra typically meant students couldn’t reach calculus by graduation, limiting their college and career options.
…
One fifth grader exemplified the problem. He had scored at the highest level on every test, had a 98% EVAAS prediction for success, and straight As on his report card. He was also officially classified as Academically Gifted by the school. When a new advanced math class was created, he wasn’t invited. When he asked to join, his parents were told no, he needed to be “recommended.” School officials told us, with straight faces, that his consistent past success was no indication he could succeed in advanced math, that they were keeping him out for his own good.
What North Carolina is doing here, excluding lots of qualified students, does at least seem better than ending algebra entirely for everyone, I suppose.
Pamela Hobart also looked into the same writeup and offers her own thread, notes that this steps fully into cartoon villainy.
The true teaching of algebra to kids who are ready for it is almost impossible to find. Even if you send your child to a ‘gifted’ school, they mostly won’t let kids get more than a year or two ahead of ‘schedule.’ Schools instead think it is better kids be bored for five years, for their own good you see.
Raymond Arnold points to the best objection I have seen, which is that if a more advanced option exists then many parents will push for it even when it is inappropriate for their particular child, or use it to push their child way too hard, and while this means some kids are bored it is saving a lot of families from being forced into a red queen’s race.
This is a real cost, but the prior should be rather extremely stacked against ‘if we let kids learn more then parents would try to have their kids learn too much and this would be bad,’ especially when you can gate the advanced classes with objective tests. Yes, parents can push their kids to study harder to try and pass those tests, but that’s a risk I am willing to take.
What is the steelman case that ‘ability grouping doesn’t work’ or ‘ability grouping has been tried and didn’t work’ in some particular context?
This by Karen Vaites is perhaps the closest, in particular on early reading grouping, convinced me that in practice you really can mess it up badly enough to make things actively worse. This was convincing that we’re messing up badly enough that this is a real possibility.
As in, what happens in practice is that you group kids by a measurement of abstract ‘reading level’ and then focus on ‘achievement’ of ‘reading level,’ forbid them to read anything beyond ‘reading level,’ and don’t ask what actual skills they need, don’t move them between groupings as their skills change, and then wonder why it isn’t working.
One could almost say, if you look at the details, that the teachers are using ‘reading groups’ as a substitute for actually teaching the children to read. You put them in a group and then you did your job. Again, yeah, I can see how that wouldn’t work. Indeed, if you are outsourcing the teaching job to other kids, then at that point you actively want uneven groups, because you want to group students with student teachers.
Whereas once students get to ‘escape velocity’ on reading, which the better students have relatively early, they no longer need a teacher, they just need motivation and permission to read books. Whereas the system seems designed to stop kids from reading books they want to read if they are deemed ‘too hard’? A kid can tell you if a book is too hard, they won’t want to read it.
One big complaint is that it is ‘hard to measure reading level.’ I don’t think it is hard. You can observe a lot just by watching. The problem is that you’re measuring a set of distinct reading skills as if it was one number, and then treating that one number as real, and also abdicating all the real work.
Sarah Sparks: But evidence suggests that the practice may be less beneficial than teachers think: It can exacerbate achievement gaps and even slow reading growth for some children unless the groups are fluid and focused on skills rather than overall achievement.
…
“What we’ve discovered is that it’s fine to have a group of students of different levels, as long as they all are working on the same learning needs,” said Carol Connor, an education professor at the University of California, Irvine, who developed the program. “You can have students of different reading abilities who all need to work on decoding. … What doesn’t work is if you put your kids who already know how to code in a group to learn how to code, again. You receive more behavior problems because they’re really bored, … and our research suggests that it has a negative effect on their growth.”
Karen Vaites: Tim Shanahan breaks down key research and its instructional implications in The Instructional Level Concept Revisited: Teaching with Complex Text. As researchers looked into the effectiveness working at reading level, studies found that it “has made no difference—that is the kids taught from grade level materials do as well as those at an instructional level—or the instructional level placements have led to less learning.”
More recently, he highlights additional new evidence from a study of third graders: “Results indicate that weaker readers, using texts at two, three, and four grade levels above their instructional levels with the assistance of lead readers [other, better reading, third graders], outscored both proficient and less proficient students in the control group across multiple measures of reading achievement.”
From a question: My daughter is in first grade. Her classroom teachers have all the books in the classroom library leveled, and students are not allowed to go beyond their reading level during “Independent” reading.
From the answer: Your daughter’s aspirations as a reader are the problem here. Some kids are allowed to read the red-dot books and others are stuck with the baby books with the blue dots. She wants to be a red dot kid, to hang with the red dot kids, to be seen as a red dot kid … but her teacher can only see her as a blue dot kid and she must learn to stay to her own bookshelf with her own kind if she is going to succeed in this classroom.
…
In the meantime, explain to your daughter that the teacher is trying to help her but that we teachers sometimes don’t get it right, and that you can’t always “fight city hall.”
So yes, you group primarily by what aspects the kids need to work on most, and that works better. Sure. I can totally believe that is a better strategy. Skill issue.
Instead of using it to figure out what kids need to do to learn to read and putting them in position to learn that, it sounds like grouping is being used to prevent kids from meaningfully reading? The purpose is to gate reading behind general tests? To spread ‘equality’ to progress on different reading aspects?
Sarah Sparks: It sounds like good sense. “Kids should be reading just-right texts as they grow as readers.” That just sounds sensible, doesn’t it? Many urban legends do… until you know better.
I can see why that might actively backfire. This isn’t about ‘ability grouping’ not working. It’s about failing to actually group by the relevant ability, and it’s about the ‘just-right text’ theory that seems to me obviously wrong.
Sarah Sparks: During Tier 1 instruction, you want all kids working with grade level texts; students reading below grade level will need scaffolding and support (as well as targeted Tier 2 and/or 3 intervention).
This promotes equity, for it’s the best mechanism for helping below-benchmark students to catch up.
It also honors the fact that a fifth grader who reads at second grade level is still thinking at the level of a fifth grader, and he or she will remain engaged and motivated by learning content and vocabulary at his or her developmental level. (No more baby books for big kids, y’all!)
For details on how to do this, check out:
Eight Ways to Help Kids Read Complex Text by Tim Shanahan
Supporting All Learners with Complex Text, a resource collection from Achieve the Core.
The Rethinking Reading Levels webinar.
Ignore the ‘this promotes equity’ framing, since you could simply say ‘this promotes learning to read.’ Equity via catching up those lagging is good, and you call it learning.
The theory here is that age matters a lot. That if you are a fifth grader, your ability to learn is inherently much stronger than that of a second grader, whereas the ability of different second graders is alike? Equality (of those at the same age) for me, inequality (of those at different ages) for thee. Whereas the correct model is that each kid has a different ability to learn different things, that usually improves steadily with age.
But also note that this is saying that the best way for many students at second grade reading level to learn reading is to assign them to read fifth grade level books, indeed to mandate it. Yes, I can believe that. So why are we so often telling kids at second grade reading level or literally in second grade or both that they can’t read the fifth grade books even when they want to?
The other theory present in this proposal is, how about using techniques that actually teach kids reading. And yeah, I agree, that would be great.
Tracing Woods (replying to Vaites): This is an extremely useful article that deserves a full, thorough response.
My short response is that I agree narrowly (most leveled readers seem quite bad, training specific skills matters, in-class grouping for reading is quite popular and often pretty uninspired) and disagree broadly (there is pretty strong evidence for the value of several forms of ability grouping, drawing from eg Direct Instruction, Success for All, acceleration/gifted literature; ability grouping has acquired a bad reputation for reasons mostly unrelated to its performance; “grade level” is the wrong measure) in a way that would be productive to hash out more fully.
I agree fully that the real question is cultural.
In case you didn’t realize that there is a war. There has been for a while.
Discussion about this post
Childhood and Education #14: The War On Education Read More »