A history of the Internet, part 2: The high-tech gold rush begins
Welcome to the second article in our three-part series on the history of the Internet. If you haven’t already, read part one here.
As a refresher, here’s the story so far:
The ARPANET was a project started by the Defense Department’s Advanced Research Project Agency in 1969 to network different mainframe computers together across the country. Later, it evolved into the Internet, connecting multiple global networks together using a common TCP/IP protocol.
By the late 1980s, investments from the National Science Foundation (NSF) had established an “Internet backbone” supporting hundreds of thousands of users worldwide. These users were mostly professors, researchers, and graduate students.
In the meantime, commercial online services like CompuServe were growing rapidly. These systems connected personal computer users, using dial-up modems, to a mainframe running proprietary software. Once online, people could read news articles and message other users. In 1989, CompuServe added the ability to send email to anyone on the Internet.
In 1965, Ted Nelson submitted a paper to the Association for Computing Machinery. He wrote: “Let me introduce the word ‘hypertext’ to mean a body of written or pictorial material interconnected in such a complex way that it could not conveniently be presented or represented on paper.” The paper was part of a grand vision he called Xanadu, after the poem by Samuel Coleridge.
A decade later, in his book “Dream Machines/Computer Lib,” he described Xanadu thusly: “To give you a screen in your home from which you can see into the world’s hypertext libraries.” He admitted that the world didn’t have any hypertext libraries yet, but that wasn’t the point. One day, maybe soon, it would. And he was going to dedicate his life to making it happen.
As the Internet grew, it became more and more difficult to find things on it. There were lots of cool documents like the Hitchhiker’s Guide To The Internet, but to read them, you first had to know where they were.
The community of helpful programmers on the Internet leapt to the challenge. Alan Emtage at McGill University in Montreal wrote a tool called Archie. It searched a list of public file transfer protocol (FTP) servers. You still had to know the file name you were looking for, but Archie would let you download it no matter what server it was on.
An improved search engine was Gopher, written by a team headed by Mark McCahill at the University of Minnesota. It used a text-based menu system so that users didn’t have to remember file names or locations. Gopher servers could display a customized collection of links inside nested menus, and they integrated with other services like Archie and Veronica to help users search for more resources.
Gopher is a text-based Internet search and retrieval system. It’s still running in 2025! Jeremy Reimer
A Gopher server could provide many of the things we take for granted today: search engines, personal pages that could contain links, and downloadable files. But this wasn’t enough for a British computer scientist who was working at CERN, an intergovernmental institute that operated the world’s largest particle physics lab.
The World Wide Web
Hypertext had come a long way since Ted Nelson had coined the word in 1965. Bill Atkinson, a member of the original Macintosh development team, released HyperCard in 1987. It used the Mac’s graphical interface to let anyone develop “stacks,” collections of text, graphics, and sounds that could be connected together with clickable links. There was no networking, but stacks could be shared with other users by sending the files on a floppy disk.
The home screen of HyperCard 1.0 for Macintosh. Jeremy Reimer
Hypertext was so big that conferences were held just to discuss it in 1987 and 1988. Even Ted Nelson had finally found a sponsor for his personal dream: Autodesk founder John Walker had agreed to spin up a subsidiary to create a commercial version of Xanadu.
It was in this environment that CERN fellow Tim Berners-Lee drew up his own proposal in March 1989 for a new hypertext environment. His goal was to make it easier for researchers at CERN to collaborate and share information about new projects.
The proposal (which he called “Mesh”) had several objectives. It would provide a system for connecting information about people, projects, documents, and hardware being developed at CERN. It would be decentralized and distributed over many computers. Not all the computers at CERN were the same—there were Digital Equipment minis running VMS, some Macintoshes, and an increasing number of Unix workstations. Each of them should be able to view the information in the same way.
As Berners-Lee described it, “There are few products which take Ted Nelson’s idea of a wide ‘docuverse’ literally by allowing links between nodes in different databases. In order to do this, some standardization would be necessary.”
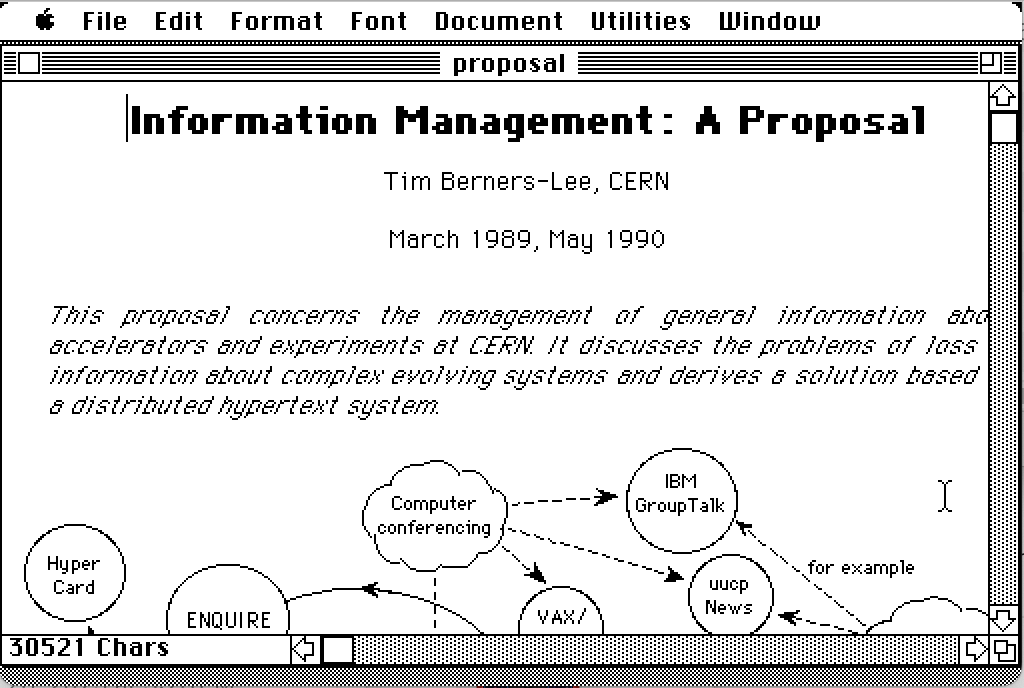
The original proposal document for the web, written in Microsoft Word for Macintosh 4.0, downloaded from Tim Berners-Lee’s website. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
The document ended by describing the project as “practical” and estimating that it might take two people six to 12 months to complete. Berners-Lee’s manager called it “vague, but exciting.” Robert Cailliau, who had independently proposed a hypertext system for CERN, joined Berners-Lee to start designing the project.
The computer Berners-Lee used was a NeXT cube, from the company Steve Jobs started after he was kicked out of Apple. NeXT workstations were expensive, but they came with a software development environment that was years ahead of its time. If you could afford one, it was like a coding accelerator. John Carmack would later write DOOM on a NeXT.
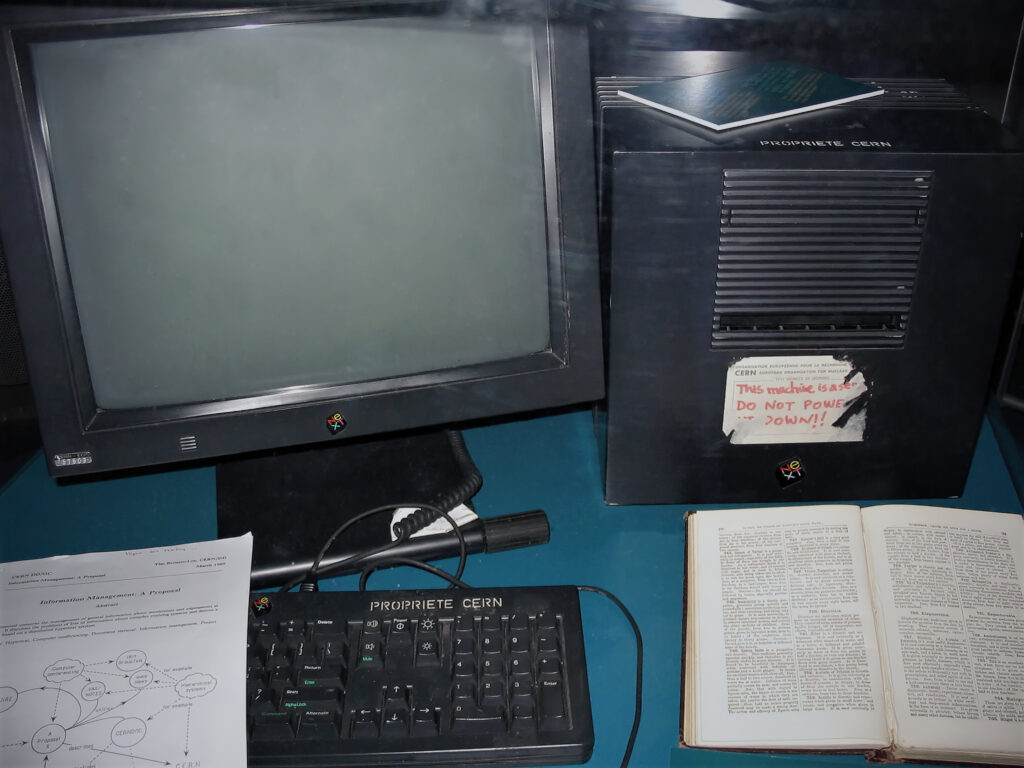

The NeXT workstation that Tim Berners-Lee used to create the World Wide Web. Please do not power down the World Wide Web. Credit: Coolcaesar (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Berners-Lee called his application “WorldWideWeb.” The software consisted of a server, which delivered pages of text over a new protocol called “Hypertext Transport Protocol,” or HTTP, and a browser that rendered the text. The browser translated markup code like “h1” to indicate a larger header font or “a” to indicate a link. There was also a graphical webpage editor, but it didn’t work very well and was abandoned.
The very first website was published, running on the development NeXT cube, on December 20, 1990. Anyone who had a NeXT machine and access to the Internet could view the site in all its glory.
The original WorldWideWeb browser running on NeXTstep 3, browsing the world’s first webpage. Jeremy Reimer
Because NeXT only sold 50,000 computers in total, that intersection did not represent a lot of people. Eight months later, Berners-Lee posted a reply to a question about interesting projects on the alt.hypertext Usenet newsgroup. He described the World Wide Web project and included links to all the software and documentation.
That one post changed the world forever.
Mosaic
On December 9, 1991, President George H.W. Bush signed into law the High Performance Computing Act, also known as the Gore Bill. The bill paid for an upgrade of the NSFNET backbone, as well as a separate funding initiative for the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA).
NCSA, based out of the University of Illinois, became a dream location for computing research. “NCSA was heaven,” recalled Alex Totic, who was a student there. “They had all the toys, from Thinking Machines to Crays to Macs to beautiful networks. It was awesome.” As is often the case in academia, the professors came up with research ideas but assigned most of the actual work to their grad students.
One of those students was Marc Andreessen, who joined NCSA as a part-time programmer for $6.85 an hour. Andreessen was fascinated by the World Wide Web, especially browsers. A new browser for Unix computers, ViolaWWW, was making the rounds at NCSA. No longer confined to the NeXT workstation, the web had caught the attention of the Unix community. But that community was still too small for Andreessen.
“To use the Net, you had to understand Unix,” he said in an interview with Forbes. “And the current users had no interest in making it easier. In fact, there was a definite element of not wanting to make it easier, of actually wanting to keep the riffraff out.”
Andreessen enlisted the help of his colleague, programmer Eric Bina, and started developing a new web browser in December 1992. In a little over a month, they released version 0.5 of “NCSA X Mosaic”—so called because it was designed to work with Unix’s X Window System. Ports for the Macintosh and Windows followed shortly thereafter.
Being available on the most popular graphical computers changed the trajectory of the web. In just 18 months, millions of copies of Mosaic were downloaded, and the rate was accelerating. The riffraff was here to stay.
Netscape
The instant popularity of Mosaic caused the management at NCSA to take a deeper interest in the project. Jon Mittelhauser, who co-wrote the Windows version, recalled that the small team “suddenly found ourselves in meetings with forty people planning our next features, as opposed to the five of us making plans at 2 am over pizzas and Cokes.”
Andreessen was told to step aside and let more experienced managers take over. Instead, he left NCSA and moved to California, looking for his next opportunity. “I thought I had missed the whole thing,” Andreessen said. “The overwhelming mood in the Valley when I arrived was that the PC was done, and by the way, the Valley was probably done because there was nothing else to do.”
But his reputation had preceded him. Jim Clark, the founder of Silicon Graphics, was also looking to start something new. A friend had shown him a demo of Mosaic, and Clark reached out to meet with Andreessen.
At a meeting, Andreessen pitched the idea of building a “Mosaic killer.” He showed Clark a graph that showed web users doubling every five months. Excited by the possibilities, the two men founded Mosaic Communications Corporation on April 4, 1994. Andreessen quickly recruited programmers from his former team, and they got to work. They codenamed their new browser “Mozilla” since it was going to be a monster that would devour Mosaic. Beta versions were titled “Mosaic Netscape,” but the University of Illinois threatened to sue the new company. To avoid litigation, the name of the company and browser were changed to Netscape, and the programmers audited their code to ensure none of it had been copied from NCSA.
Netscape became the model for all Internet startups to follow. Programmers were given unlimited free sodas and encouraged to basically never leave the office. “Netscape Time” accelerated software development schedules, and because updates could be delivered over the Internet, old principles of quality assurance went out the window. And the business model? It was simply to “get big fast,” and profits could be figured out later.
Work proceeded quickly, and the 1.0 version of Netscape Navigator and the Netsite web server were released on December 15, 1994, for Windows, Macintosh, and Unix systems running X Windows. The browser was priced at $39 for commercial users, but there was no charge for “academic and non-profit use, as well as for free evaluation purposes.”
Version 0.9 was called “Mosaic Netscape,” and the logo and company were still Mosaic. Jeremy Reimer
Netscape quickly became the standard. Within six months, it captured over 70 percent of the market share for web browsers. On August 9, 1995, only 16 months after the founding of the company, Netscape filed for an Initial Public Offering. A last-minute decision doubled the offering price to $28 per share, and on the first day of trading, the stock soared to $75 and closed at $58.25. The Web Era had officially arrived.
The web battles proprietary solutions
The excitement over a new way to transmit text and images to the public over phone lines wasn’t confined to the World Wide Web. Commercial online systems like CompuServe were also evolving to meet the graphical age. These companies released attractive new front-ends for their services that ran on DOS, Windows, and Macintosh computers. There were also new services that were graphics-only, like Prodigy, a cooperation between IBM and Sears, and an upstart that had sprung from the ashes of a Commodore 64 service called Quantum Link. This was America Online, or AOL.
Even Microsoft was getting into the act. Bill Gates believed that the “Information Superhighway” was the future of computing, and he wanted to make sure that all roads went through his company’s toll booth. The highly anticipated Windows 95 was scheduled to ship with a bundled dial-up online service called the Microsoft Network, or MSN.
At first, it wasn’t clear which of these online services would emerge as the winner. But people assumed that at least one of them would beat the complicated, nerdy Internet. CompuServe was the oldest, but AOL was nimbler and found success by sending out millions of free “starter” disks (and later, CDs) to potential customers. Microsoft was sure that bundling MSN with the upcoming Windows 95 would ensure victory.
Most of these services decided to hedge their bets by adding a sort of “side access” to the World Wide Web. After all, if they didn’t, their competitors would. At the same time, smaller companies (many of them former bulletin board services) started becoming Internet service providers. These smaller “ISPs” could charge less money than the big services because they didn’t have to create any content themselves. Thousands of new websites were appearing on the Internet every day, much faster than new sections could be added to AOL or CompuServe.
The tipping point happened very quickly. Before Windows 95 had even shipped, Bill Gates wrote his famous “Internet Tidal Wave” memo, where he assigned the Internet the “highest level of importance.” MSN was quickly changed to become more of a standard ISP and moved all of its content to the web. Microsoft rushed to release its own web browser, Internet Explorer, and bundled it with the Windows 95 Plus Pack.
The hype and momentum were entirely with the web now. It was the most exciting, most transformative technology of its time. The decade-long battle to control the Internet by forcing a shift to a new OSI standards model was forgotten. The web was all anyone cared about, and the web ran on TCP/IP.
The browser wars
Netscape had never expected to make a lot of money from its browser, as it was assumed that most people would continue to download new “evaluation” versions for free. Executives were pleasantly surprised when businesses started sending Netscape huge checks. The company went from $17 million in revenue in 1995 to $346 million the following year, and the press started calling Marc Andreessen “the new Bill Gates.”
The old Bill Gates wasn’t having any of that. Following his 1995 memo, Microsoft worked hard to improve Internet Explorer and made it available for free, including to business users. Netscape tried to fight back. It added groundbreaking new features like JavaScript, which was inspired by LISP but with a syntax similar to Java, the hot new programming language from Sun Microsystems. But it was hard to compete with free, and Netscape’s market share started to fall. By 1996, both browsers had reached version 3.0 and were roughly equal in terms of features. The battle continued, but when the Apache Software Foundation released its free web server, Netscape’s other source of revenue dried up as well. The writing was on the wall.

There was no better way to declare your allegiance to a web browser in 1996 than adding “Best Viewed In” above one of these icons. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
The dot-com boom
In 1989, the NSF lifted the restrictions on providing commercial access to the Internet, and by 1991, it had removed all barriers to commercial trade on the network. With the sudden ascent of the web, thanks to Mosaic, Netscape, and Internet Explorer, new companies jumped into this high-tech gold rush. But at first, it wasn’t clear what the best business strategy was. Users expected everything on the web to be free, so how could you make money?
Many early web companies started as hobby projects. In 1994, Jerry Yang and David Filo were electrical engineering PhD students at Stanford University. After Mosaic started popping off, they began collecting and trading links to new websites. Thus, “Jerry’s Guide to the World Wide Web” was born, running on Yang’s Sun workstation. Renamed Yahoo! (Yet Another Hierarchical, Officious Oracle), the site exploded in popularity. Netscape put multiple links to Yahoo on its main navigation bar, which further accelerated growth. “We weren’t really sure if you could make a business out of it, though,” Yang told Fortune. Nevertheless, venture capital companies came calling. Sequoia, which had made millions investing in Apple, put in $1 million for 25 percent of Yahoo.
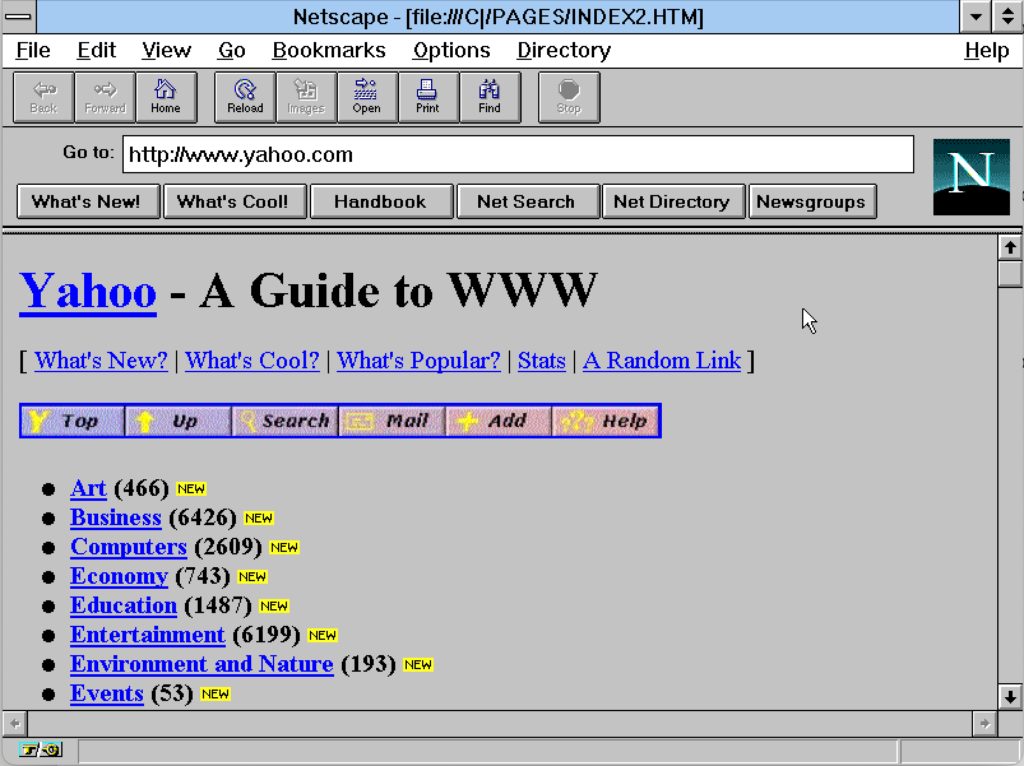
Yahoo.com as it would have appeared in 1995. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
Another hobby site, AuctionWeb, was started in 1995 by Pierre Omidyar. Running on his own home server using the regular $30 per month service from his ISP, the site let people buy and sell items of almost any kind. When traffic started growing, his ISP told him it was increasing his Internet fees to $250 per month, as befitting a commercial enterprise. Omidyar decided he would try to make it a real business, even though he didn’t have a merchant account for credit cards or even a way to enforce the new 5 percent or 2.5 percent royalty charges. That didn’t matter, as the checks started rolling in. He found a business partner, changed the name to eBay, and the rest was history.
AuctionWeb (later eBay) as it would have appeared in 1995. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
In 1993, Jeff Bezos, a senior vice president at a hedge fund company, was tasked with investigating business opportunities on the Internet. He decided to create a proof of concept for what he described as an “everything store.” He chose books as an ideal commodity to sell online, since a book in one store was identical to one in another, and a website could offer access to obscure titles that might not get stocked in physical bookstores.
He left the hedge fund company, gathered investors and software development talent, and moved to Seattle. There, he started Amazon. At first, the site wasn’t much more than an online version of an existing bookseller catalog called Books In Print. But over time, Bezos added inventory data from the two major book distributors, Ingram and Baker & Taylor. The promise of access to every book in the world was exciting for people, and the company grew quickly.
Amazon.com as it would have appeared in 1995. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
The explosive growth of these startups fueled a self-perpetuating cycle. As publications like Wired experimented with online versions of their magazines, they invented and sold banner ads to fund their websites. The best customers for these ads were other web startups. These companies wanted more traffic, and they knew ads on sites like Yahoo were the best way to get it. Yahoo salespeople could then turn around and point to their exponential ad sales curves, which caused Yahoo stock to rise. This encouraged people to fund more web startups, which would all need to advertise on Yahoo. These new startups also needed to buy servers from companies like Sun Microsystems, causing those stocks to rise as well.
The crash
In the latter half of the 1990s, it looked like everything was going great. The economy was booming, thanks in part to the rise of the World Wide Web and the huge boost it gave to computer hardware and software companies. The NASDAQ index of tech-focused stocks painted a clear picture of the boom.
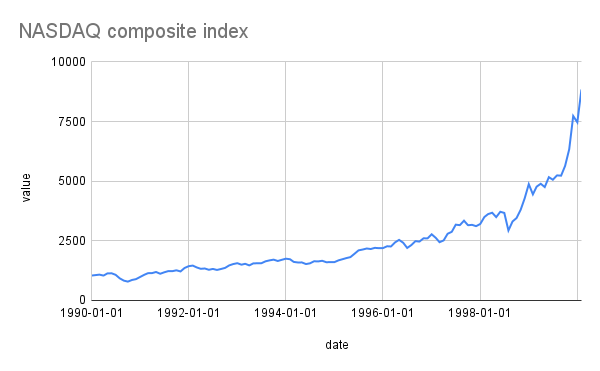
The NASDAQ composite index in the 1990s. Credit: Jeremy Reimer
Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan called this phenomenon “irrational exuberance” but didn’t seem to be in a hurry to stop it. The fact that most new web startups didn’t have a realistic business model didn’t seem to bother investors. Sure, WebVan might have been paying more to deliver groceries than they earned from customers, but look at that growth curve!
The exuberance couldn’t last forever. The NASDAQ peaked at 8,843.87 in February 2000 and started to go down. In one month, it lost 34 percent of its value, and by August 2001, it was down to 3,253.38. Web companies laid off employees or went out of business completely. The party was over.
Andreessen said that the tech crash scarred him. “The overwhelming message to our generation in the early nineties was ‘You’re dirty, you’re all about grunge—you guys are fucking losers!’ Then the tech boom hit, and it was ‘We are going to do amazing things!’ And then the roof caved in, and the wisdom was that the Internet was a mirage. I 100 percent believed that because the rejection was so personal—both what everybody thought of me and what I thought of myself.”
But while some companies quietly celebrated the end of the whole Internet thing, others would rise from the ashes of the dot-com collapse. That’s the subject of our third and final article.
A history of the Internet, part 2: The high-tech gold rush begins Read More »