FTC bans noncompete clauses, declares vast majority unenforceable
No more noncompetes —
Chamber of Commerce vows to sue FTC, will try to block ban on noncompetes.

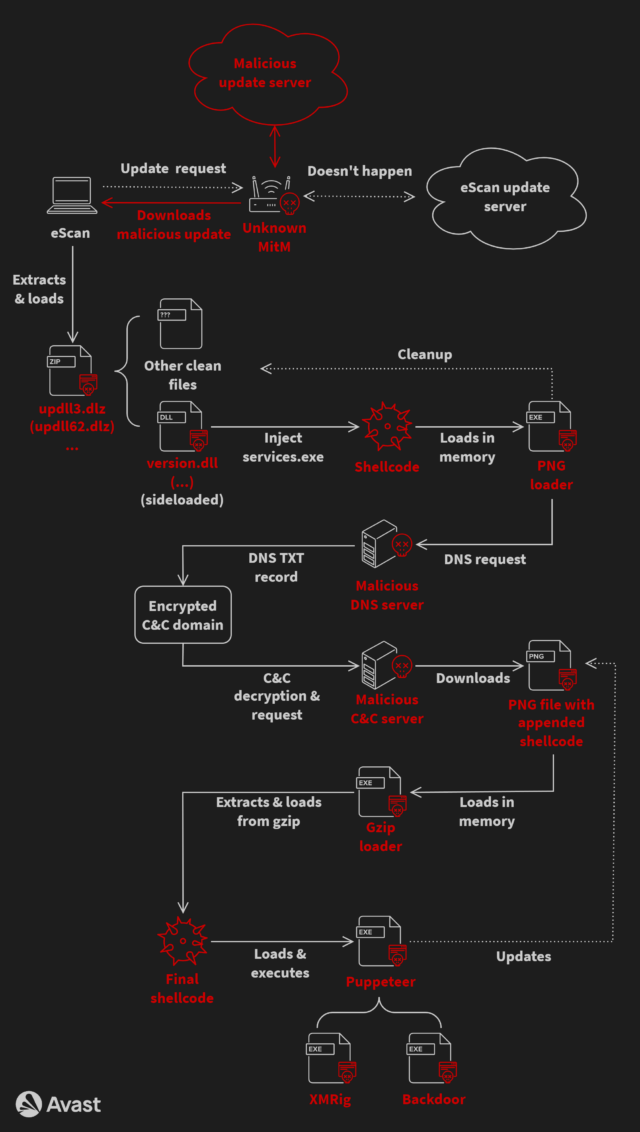
Enlarge / Federal Trade Commission Chair Lina Khan talks with guests during an event in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on April 03, 2024
Getty Images | Chip Somodevilla
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) today announced that it has issued a final rule banning noncompete clauses. The rule will render the vast majority of current noncompete clauses unenforceable, according to the agency.
“In the final rule, the Commission has determined that it is an unfair method of competition and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act, for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers and to enforce certain noncompetes,” the FTC said.
The US Chamber of Commerce said it will sue the FTC in an effort to block the rule, claiming the ban is “a blatant power grab that will undermine American businesses’ ability to remain competitive.”
The FTC proposed the rule in January 2023 and received over 26,000 public comments on its proposal. Over 25,000 of the comments supported the proposed ban, the FTC said. The final rule announced today will take effect 120 days after it is published in the Federal Register, unless opponents of the rule secure a court order blocking it.
The FTC said that “noncompetes are a widespread and often exploitative practice imposing contractual conditions that prevent workers from taking a new job or starting a new business. Noncompetes often force workers to either stay in a job they want to leave or bear other significant harms and costs, such as being forced to switch to a lower-paying field, being forced to relocate, being forced to leave the workforce altogether, or being forced to defend against expensive litigation.”
Noncompete clauses currently bind about 30 million workers in the US, the agency said. “Under the FTC’s new rule, existing noncompetes for the vast majority of workers will no longer be enforceable after the rule’s effective date,” the FTC said.
FTC: “Noncompete clauses keep wages low”
The only existing noncompetes that won’t be nullified are those for senior executives, who represent less than 0.75 percent of workers, the FTC said. The rule defines senior executives as people earning more than $151,164 a year and who are in policy-making positions.
“The final rule allows existing noncompetes with senior executives to remain in force because this subset of workers is less likely to be subject to the kind of acute, ongoing harms currently being suffered by other workers subject to existing noncompetes and because commenters raised credible concerns about the practical impacts of extinguishing existing noncompetes for senior executives,” the FTC said.
Senior executives will be protected from new noncompete clauses after the rule takes effect. Employers will be “banned from entering into or attempting to enforce any new noncompetes, even if they involve senior executives,” the FTC said. “Employers will be required to provide notice to workers other than senior executives who are bound by an existing noncompete that they will not be enforcing any noncompetes against them.”
The FTC vote was 3-2, with Democrats supporting the noncompete ban and Republicans opposing.
“Noncompete clauses keep wages low, suppress new ideas, and rob the American economy of dynamism, including from the more than 8,500 new startups that would be created a year once noncompetes are banned,” FTC Chair Lina Khan said. “The FTC’s final rule to ban noncompetes will ensure Americans have the freedom to pursue a new job, start a new business, or bring a new idea to market.”
Chamber of Commerce CEO Suzanne Clark argued that “the FTC has never been granted the constitutional and statutory authority to write its own competition rules… The Chamber will sue the FTC to block this unnecessary and unlawful rule and put other agencies on notice that such overreach will not go unchecked.”
FTC cites authority, urges businesses to raise wages
The FTC argues that it can impose the rule using authority under sections 5 and 6(g) of the FTC Act:
Alongside section 5, Congress adopted section 6(g) of the Act, in which it authorized the Commission to “make rules and regulations for the purpose of carrying out the provisions of” the FTC Act, which include the Act’s prohibition of unfair methods of competition. The plain text of section 5 and section 6(g), taken together, empower the Commission to promulgate rules for the purpose of preventing unfair methods of competition. That includes legislative rules defining certain conduct as an unfair method of competition.
The FTC said it found evidence that “noncompetes tend to negatively affect competitive conditions in product and service markets, inhibiting new business formation and innovation” and “lead to increased market concentration and higher prices for consumers.”
Businesses can protect trade secrets without noncompetes, the agency said:
Trade secret laws and nondisclosure agreements (NDAs) both provide employers with well-established means to protect proprietary and other sensitive information. Researchers estimate that over 95 percent of workers with a noncompete already have an NDA.
The Commission also finds that instead of using noncompetes to lock in workers, employers that wish to retain employees can compete on the merits for the worker’s labor services by improving wages and working conditions.
FTC bans noncompete clauses, declares vast majority unenforceable Read More »