Trump orders cull of regulations governing commercial rocket launches
The head of the FAA’s commercial spaceflight division will become a political appointee.
Birds take flight at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in this 2010 photo. Credit: NASA
President Donald Trump signed an executive order Wednesday directing government agencies to “eliminate or expedite” environmental reviews for commercial launch and reentry licenses.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), part of the Department of Transportation (DOT), grants licenses for commercial launch and reentry operations. The FAA is charged with ensuring launch and reentries comply with environmental laws, comport with US national interests, and don’t endanger the public.
The drive toward deregulation will be welcome news for companies like SpaceX, led by onetime Trump ally Elon Musk; SpaceX conducts nearly all of the commercial launches and reentries licensed by the FAA.
Deregulation time
Trump ordered Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy, who also serves as the acting administrator of NASA, to “use all available authorities to eliminate or expedite… environmental reviews for… launch and reentry licenses and permits.” In the order signed by Trump, White House officials wrote that Duffy should consult with the chair of the Council on Environmental Quality and follow “applicable law” in the regulatory cull.
The executive order also includes a clause directing Duffy to reevaluate, amend, or rescind a slate of launch-safety regulations written during the first Trump administration. The FAA published the new regulations, known as Part 450, in 2020, and they went into effect in 2021, but space companies have complained they are too cumbersome and have slowed down the license approval process.
And there’s more. Trump ordered NASA, the military, and DOT to eliminate duplicative reviews for spaceport development. This is particularly pertinent at federally owned launch ranges like those at Cape Canaveral, Florida; Vandenberg Space Force Base, California; and Wallops Island, Virginia.
The Trump administration also plans to make the head of the FAA’s Office of Commercial Space Transportation a political appointee. This office oversees commercial launch and reentry licensing and was previously led by a career civil servant. Duffy will also hire an advisor on deregulation in the commercial spaceflight industry to join DOT, and the Office of Space Commerce will be elevated to a more prominent position within the Commerce Department.
“It is the policy of the United States to enhance American greatness in space by enabling a competitive launch marketplace and substantially increasing commercial space launch cadence and novel space activities by 2030,” Trump’s executive order reads. “To accomplish this, the federal government will streamline commercial license and permit approvals for United States-based operators.”
News of the executive order was reported last month by ProPublica, which wrote that the Trump administration was circulating draft language among federal agencies to slash rules to protect the environment and the public from the dangers of rocket launches. The executive order signed by Trump and released by the White House on Wednesday confirms ProPublica’s reporting.
Jared Margolis, a senior attorney for the Center for Biological Diversity, criticized the Trump administration’s move.
“This reckless order puts people and wildlife at risk from private companies launching giant rockets that often explode and wreak devastation on surrounding areas,” Margolis said in a statement. “Bending the knee to powerful corporations by allowing federal agencies to ignore bedrock environmental laws is incredibly dangerous and puts all of us in harm’s way. This is clearly not in the public interest.”
Duffy, the first person to lead NASA and another federal department at the same time, argued the order is important to sustain economic growth in the space industry.
“By slashing red tape tying up spaceport construction, streamlining launch licenses so they can occur at scale, and creating high-level space positions in government, we can unleash the next wave of innovation,” Duffy said in a statement. “At NASA, this means continuing to work with commercial space companies and improving our spaceports’ ability to launch.”
Nipping NEPA
The executive order is emblematic of the Trump administration’s broader push to curtail environmental reviews for large infrastructure projects.
The White House has already directed federal agencies to repeal regulations enforcing the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), a 1969 law that requires the feds prepare environmental assessments and environmental impact statements to evaluate the effects of government actions—such as licensing approvals—on the environment.
Regarding commercial spaceflight, the White House ordered the Transportation Department to create a list of activities officials there believe are not subject to NEPA and establish exclusions under NEPA for launch and reentry licenses.
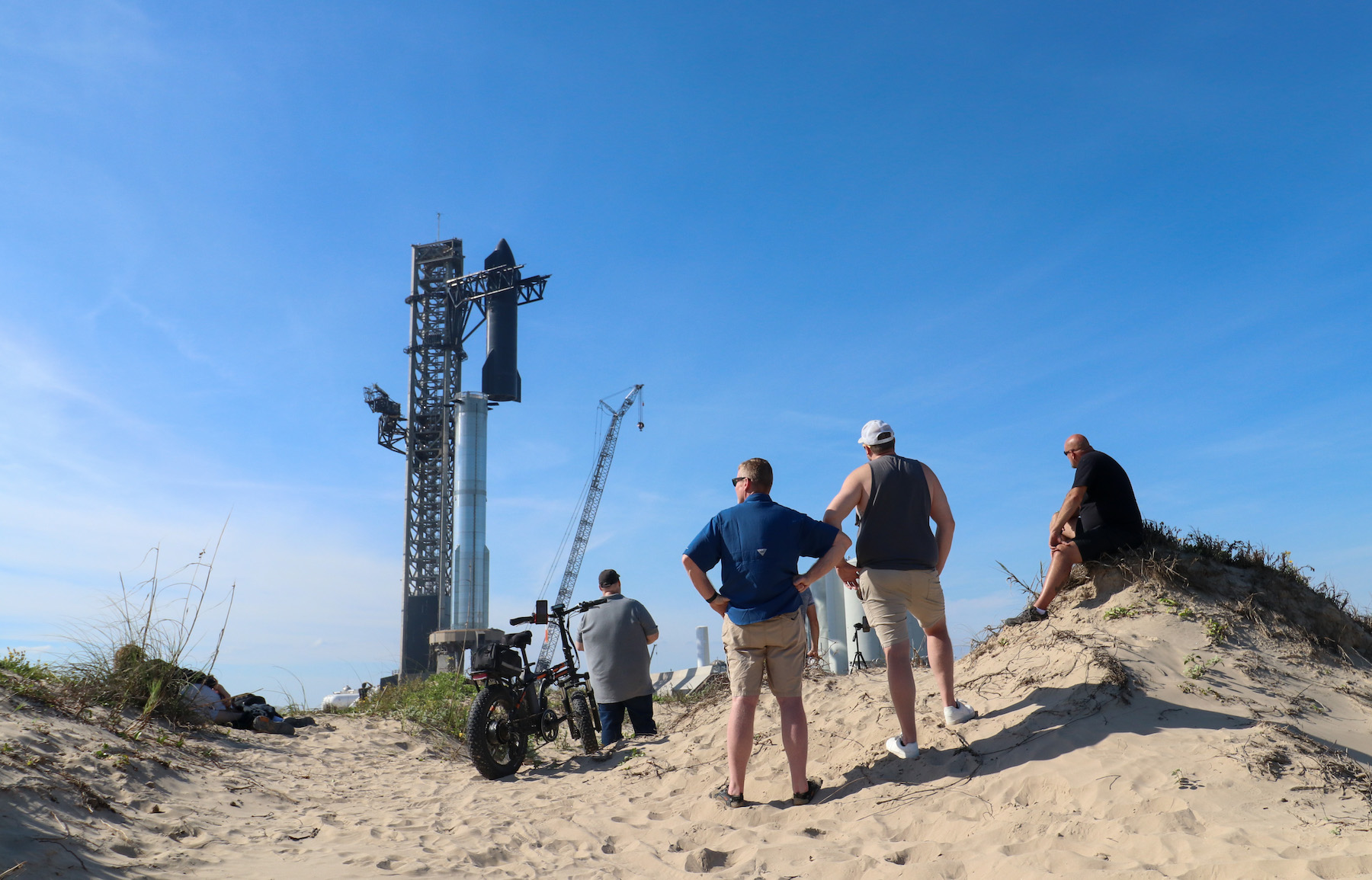

Onlookers watch from nearby sand dunes as SpaceX prepares a Starship rocket for launch from Starbase, Texas. Credit: Stephen Clark/Ars Technica
The changes to the environmental review process might be the most controversial part of Trump’s new executive order. Another section of the order—the attempt to reform or rescind the so-called Part 450 launch and reentry regulations—appears to have bipartisan support in Congress.
The FAA started implementing its new Part 450 commercial launch and reentry regulations less than five years ago after writing the rules in response to another Trump executive order signed in 2018. Part 450 was intended to streamline the launch approval process by allowing companies to submit applications for a series of launches or reentries, rather than requiring a new license for each mission.
But industry officials quickly criticized the new regulations, which they said didn’t account for rapid iteration of rockets and spacecraft like SpaceX’s enormous Starship/Super Heavy launch vehicle. The FAA approved a SpaceX request in May to increase the number of approved Starship launches from five to 25 per year from the company’s base in Starship, Texas, near the US-Mexico border.
Last year, the FAA’s leadership under the Biden administration established a committee to examine the shortcomings of Part 450. The Republican and Democratic leaders of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee submitted a joint request in February for the Government Accountability Office to conduct an independent review of the FAA’s Part 450 regulations.
“Reforming and streamlining commercial launch regulations and licensing is an area the Biden administration knew needed reform,” wrote Laura Forczyk, founder and executive director of the space consulting firm Astralytical, in a post on X. “However, little was done. Will more be done with this executive order? I hope so. This was needed years ago.”
Dave Cavossa, president of the Commercial Spaceflight Federation, applauded the Trump administration’s regulatory policy.
“This executive order will strengthen and grow the US commercial space industry by cutting red tape while maintaining a commitment to public safety, benefitting the American people and the US government that are increasingly reliant on space for our national and economic security,” Cavossa said in a statement.
Specific language in the new Trump executive order calls for the FAA to evaluate which regulations should be waived for hybrid launch or reentry vehicles that hold FAA airworthiness certificates, and which requirements should be remitted for rockets with a flight termination system, an explosive charge designed to destroy a launch vehicle if it veers off its pre-approved course after liftoff. These are similar to the topics the Biden-era FAA was looking at last year.
The new Trump administration policy also seeks to limit the authority of state officials in enforcing their own environmental rules related to the construction or operation of spaceports.
This is especially relevant after the California Coastal Commission rejected a proposal by SpaceX to double its launch cadence at Vandenberg Space Force Base, a spaceport located roughly 140 miles (225 kilometers) northwest of Los Angeles. The Space Force, which owns Vandenberg and is one of SpaceX’s primary customers, backs SpaceX’s push for more launches.
Finally, the order gives the Department of Commerce responsibility for authorizing “novel space activities” such as in-space assembly and manufacturing, asteroid and planetary mining, and missions to remove space debris from orbit.
This story was updated at 12: 30 am EDT on August 14 with statements from the Center for Biological Diversity and the Commercial Spaceflight Federation.
Trump orders cull of regulations governing commercial rocket launches Read More »