Yes, Rocket Lab is blowing up engines. No, it’s not a big deal, CEO says.
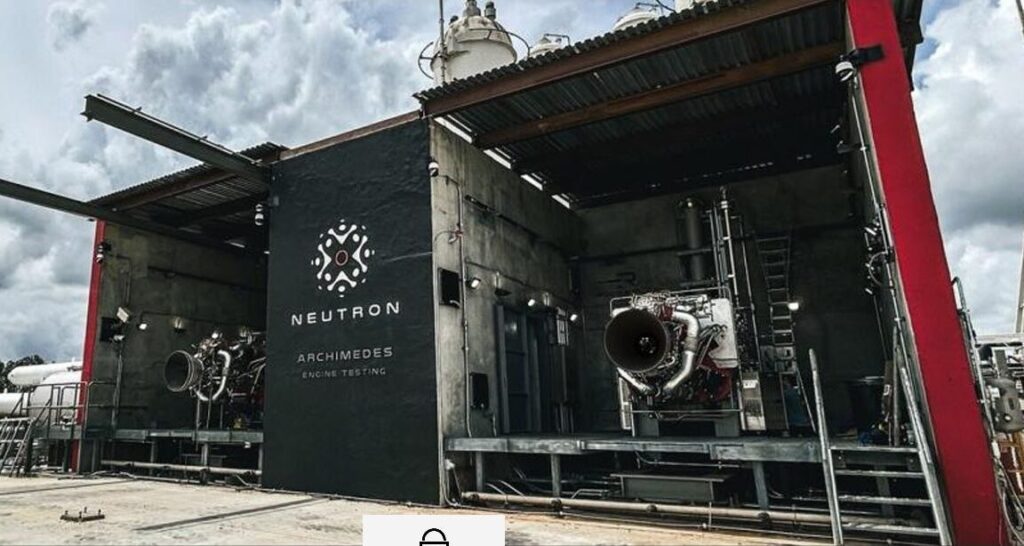
A little more than two months ago, a Rocket Lab employee called the Stennis Space Center Fire Department from the nearby A3 test stand. There was a grass fire where Archimedes engines undergo testing. Could they please send personnel over?
According to the fire station’s November 30 dispatcher log, the employee said, “The fire started during a test when an anomaly caused an electrical box to catch fire.”
Satellite imagery from before and after the anomaly appears to show that the roof had been blown off the left test cell, one of two at the test stand at the historic NASA facility in southern Mississippi. One person with knowledge of the anomaly said, “The characterization of this as an electrical fire doesn’t reflect what actually occurred. This was a catastrophic engine explosion that resulted in significant infrastructure damage.”
According to two sources, this is one of at least two Archimedes engine tests that have failed in the past three months.
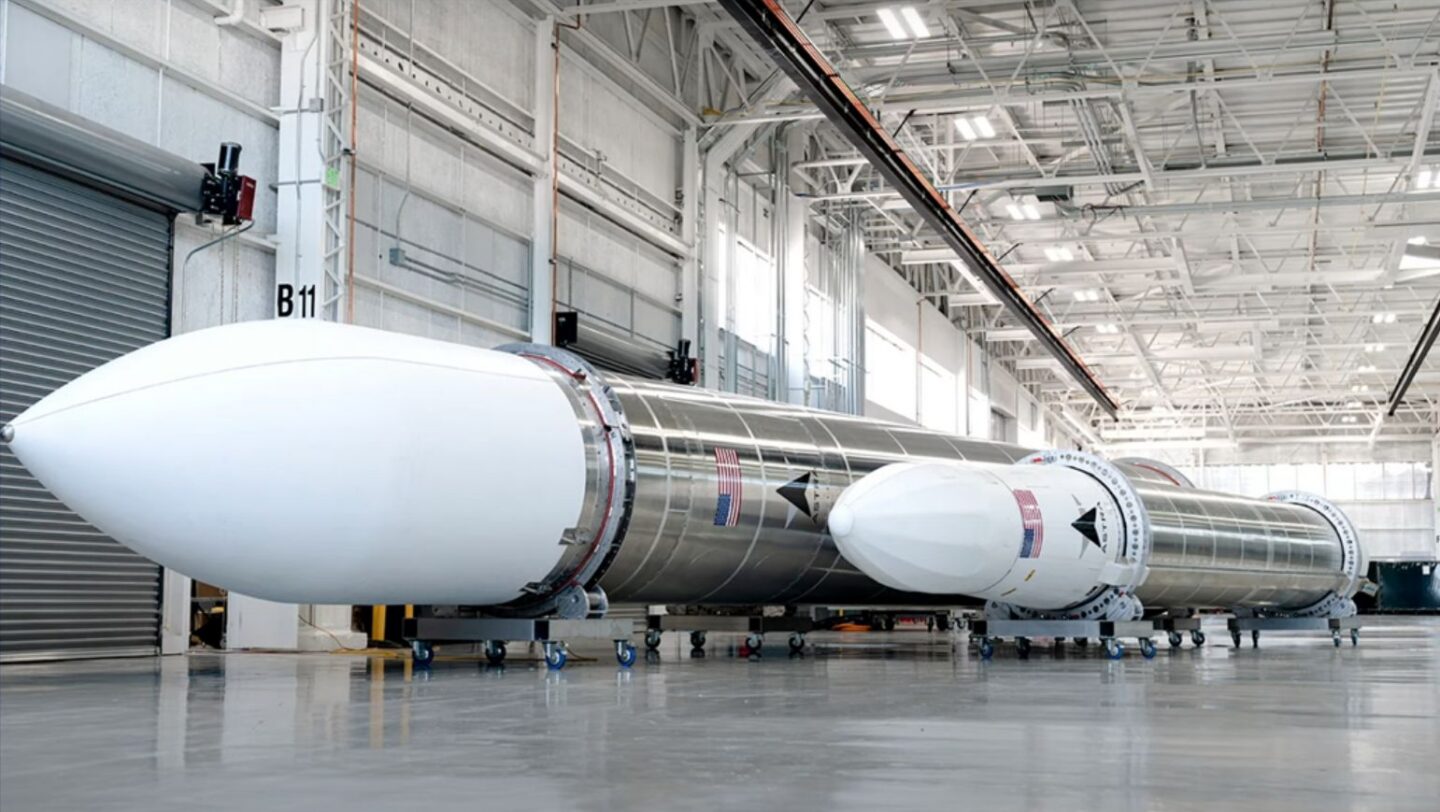
The engine test anomalies come at a critical time for Rocket Lab, as it is attempting to finalize development of a flight version of the Archimedes engine, which burns liquid oxygen and methane and has a sea-level thrust of 165,000 pounds. Nine of these engines will power the company’s much-anticipated Neutron rocket, which is aiming for a debut launch later this year.
Making mountains out of molehills?
In response to a query from Ars about the engine test anomalies, Rocket Lab Chief Executive Officer Pete Beck downplayed concerns.
Yes, Rocket Lab is blowing up engines. No, it’s not a big deal, CEO says. Read More »