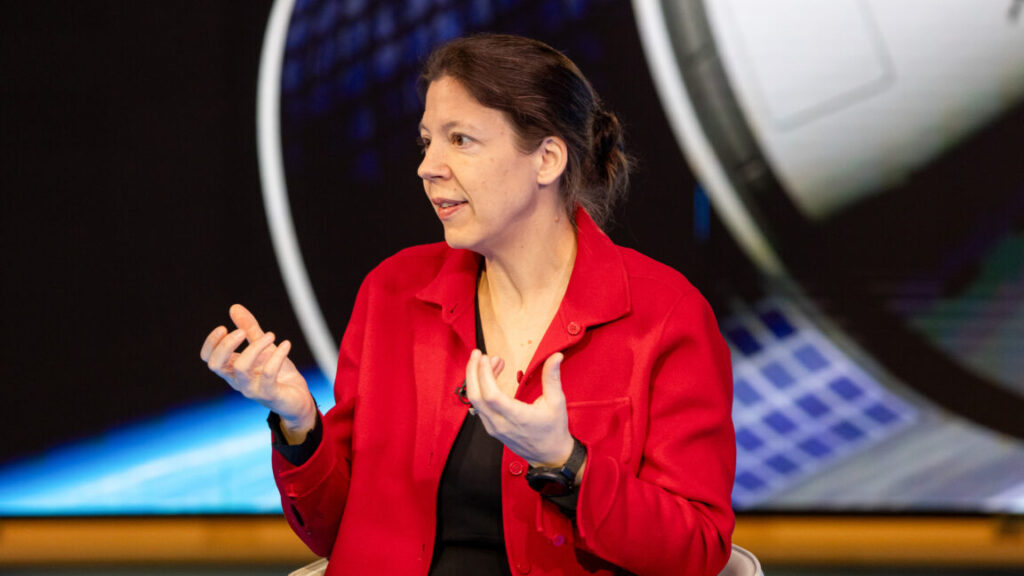
A former Orion manager has surprisingly credible plans to fly European astronauts
She found herself wanting to build something more modern. Looking across the Atlantic, she drew inspiration from what SpaceX was doing with its reusable Falcon 9 rocket. She watched humans launch into space aboard Crew Dragon and saw that same vehicle fly again and again. “I have a huge admiration for what SpaceX has done,” she said.
Huby also saw opportunity in that company’s success. SpaceX is the only provider of crew transportation in the Western world. It’s likely that Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft will never become a serious competitor. India’s human spaceflight program is making some progress, but it’s unclear whether the Gaganyaan vehicle will serve non-Indian customers.
The opportunity she saw was to provide an alternative to SpaceX based in Europe. This would yield 100 percent of the market in Europe and offer an option to countries like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Australia, and other nations interested in going to space.
“I know it’s super hard, and I know it was crazy,” Huby said. “But I wanted to try.”
Starting small
She founded The Exploration Company in August 2021 with $50,000 in the bank and a small team of four people. Three years later, the company has 200 employees and recently announced that it had raised $160 million in Series B funding. It marked the first time that two European sovereign funds, French Tech and Germany-based DTCF, invested together. The news even scored a congratulatory post on LinkedIn from French President Emmanuel Macron, who wrote, “The history of space continues to be written in Europeans.”
To date, then, Huby has raised nearly $230 million. Her company has already flown a mission, the “Bikini” reentry demonstrator, on the debut flight of the Ariane 6 rocket this last summer. The small capsule was intended to demonstrate the company’s reentry technology. Unfortunately, the rocket’s upper stage failed on its deorbit burn, so the Bikini capsule remains stuck in space.
Still, the company is already hard at work on a second demonstration vehicle, about 2.5 meters in diameter, that will have more than a dozen customers on board. The spacecraft for this demonstration flight, named Mission Possible, is fully assembled, Huby said, and it will launch on SpaceX’s Transporter 14 mission next summer, likely in July. This mission was developed in 2.5 years at a cost of $20 million, plus $10 million for the launch.
A former Orion manager has surprisingly credible plans to fly European astronauts Read More »