Lego announces NASA Artemis SLS rocket set to lift off (literally) in 2026
How do you top a highly detailed scale model of NASA’s new moon-bound rocket and its support tower? If you’re Lego, you make it so it can actually lift off.
Lego’s NASA Artemis Space Launch System Rocket, part of its Technic line of advanced building sets, will land on store shelves for $60 on January 1, 2026, and then “blast off” from kitchen tables, office desks and living room floors. The 632-piece set climbs skyward, separating from its expendable stages along the way, until the Orion crew spacecraft and its European Service Module top out the motion on their way to the moon—or wherever your imagination carries it.
“The educational LEGO Technic set shows the moment a rocket launches, in three distinct stages,” reads the product description on Lego’s website. “Turn the crank to see the solid rocket boosters separate from the core stage, which then also detaches. Continue turning to watch the upper stage with its engine module, Orion spacecraft and launch abort system separate.”
Crank it up
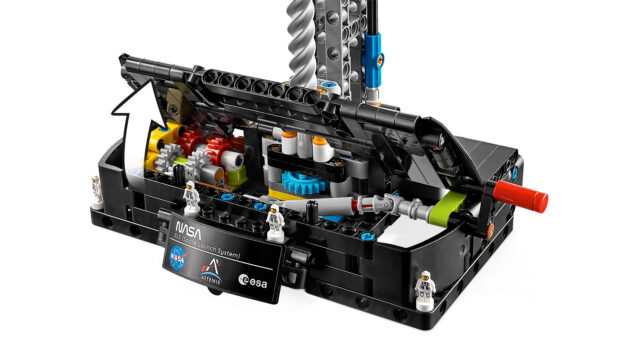
The lid of the mobile launcher opens to reveal the gears that set the Lego Technic NASA Artemis Space Launch System Rocket into motion. Credit: LEGO
The new set captures all the major milestones of the first eight and a half minutes of an Artemis mission (with the exception of the jettison of the abort system tower, which on the real rocket occurs before the Orion separates from the core stage). Lego worked with NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) to ensure the overall accuracy of the display.
“On the way up, there is sound. You can hear it—it is really noisy, the rocket,” said Olaf Kegger, the set’s designer at Lego, at an unveiling of his creation. He added that there is no sound when the motion is reversed, as the real SLS, “of course, does not go [back] down like this.”
Lego announces NASA Artemis SLS rocket set to lift off (literally) in 2026 Read More »