New experiments focused on understanding the enigmatic neutrino may offer insights.
An artist’s composition of the Milky Way seen with a neutrino lens (blue). Credit: IceCube Collaboration/NSF/ESO
Everything we see around us, from the ground beneath our feet to the most remote galaxies, is made of matter. For scientists, that has long posed a problem: According to physicists’ best current theories, matter and its counterpart, antimatter, ought to have been created in equal amounts at the time of the Big Bang. But antimatter is vanishingly rare in the universe. So what happened?
Physicists don’t know the answer to that question yet, but many think the solution must involve some subtle difference in the way that matter and antimatter behave. And right now, the most promising path into that unexplored territory centers on new experiments involving the mysterious subatomic particle known as the neutrino.
“It’s not to say that neutrinos are definitely the explanation of the matter-antimatter asymmetry, but a very large class of models that can explain this asymmetry are connected to neutrinos,” says Jessica Turner, a theoretical physicist at Durham University in the United Kingdom.
Let’s back up for a moment: When physicists talk about matter, that’s just the ordinary stuff that the universe is made of—mainly protons and neutrons (which make up the nuclei of atoms), along with lighter particles like electrons. Although the term “antimatter” has a sci-fi ring to it, antimatter is not all that different from ordinary matter. Typically, the only difference is electric charge: For example, the positron—the first antimatter particle to be discovered—matches an electron in its mass but carries a positive rather than a negative charge. (Things are a bit more complicated with electrically neutral particles. For example, a photon is considered to be its own antiparticle, but an antineutron is distinct from a neutron in that it’s made up of antiquarks rather than ordinary quarks.)
Various antimatter particles can exist in nature; they occur in cosmic rays and in thunderclouds, and are produced by certain kinds of radioactive decay. (Because people—and bananas—contain a small amount of radioactive potassium, they emit minuscule amounts of antimatter in the form of positrons.)
Small amounts of antimatter have also been created by scientists in particle accelerators and other experiments, at great effort and expense—putting a damper on science fiction dreams of rockets propelled by antimatter or planet-destroying weapons energized by it.
When matter and antimatter meet, they annihilate, releasing energy in the form of radiation. Such encounters are governed by Einstein’s famous equation, E=mc2—energy equals mass times the square of the speed of light — which says you can convert a little bit of matter into a lot of energy, or vice versa. (The positrons emitted by bananas and bodies have so little mass that we don’t notice the teeny amounts of energy released when they annihilate.) Because matter and antimatter annihilate so readily, it’s hard to make a chunk of antimatter much bigger than an atom, though in theory you could have everything from antimatter molecules to antimatter planets and stars.
But there’s a puzzle: If matter and antimatter were created in equal amounts at the time of the Big Bang, as theory suggests, shouldn’t they have annihilated, leaving a universe made up of pure energy? Why is there any matter left?
Physicists’ best guess is that some process in the early universe favored the production of matter compared to the production of antimatter — but exactly what that process was is a mystery, and the question of why we live in a matter-dominated universe is one of the most vexing problems in all of physics.
Crucially, physicists haven’t been able to think of any such process that would mesh with today’s leading theory of matter and energy, known as the Standard Model of particle physics. That leaves theorists seeking new ideas, some as-yet-unknown physics that goes beyond the Standard Model. This is where neutrinos come in.
A neutral answer
Neutrinos are tiny particles without any electric charge. (The name translates as “little neutral one.”) According to the Standard Model, they ought to be massless, like photons, but experiments beginning in the 1990s showed that they do in fact have a tiny mass. (They’re at least a million times lighter than electrons, the extreme lightweights among normal matter.) Since physicists already know that neutrinos violate the Standard Model by having mass, their hope is that learning more about these diminutive particles might yield insights into whatever lies beyond.
Neutrinos have been slow to yield their secrets, however, because they barely interact with other particles. About 60 billion neutrinos from the Sun pass through every square centimeter of your skin each second. If those neutrinos interacted with the atoms in our bodies, they would probably destroy us. Instead, they pass right through. “You most likely will not interact with a single neutrino in your lifetime,” says Pedro Machado, a physicist at Fermilab near Chicago. “It’s just so unlikely.”
Experiments, however, have shown that neutrinos “oscillate” as they travel, switching among three different identities—physicists call them “flavors”: electron neutrino, muon neutrino, and tau neutrino. Oscillation measurements have also revealed that different-flavored neutrinos have slightly different masses.
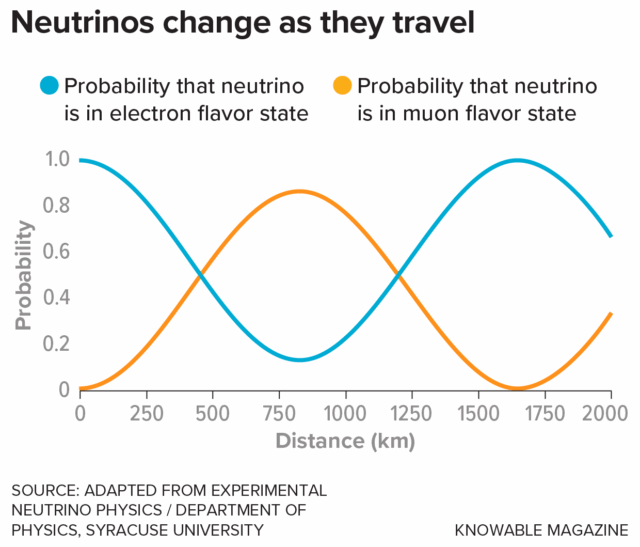
Neutrinos are known to oscillate, switching between three varieties or “flavors.” Exactly how they oscillate is governed by the laws of quantum mechanics, and the probability of finding that an electron neutrino has transformed into a muon neutrino, for example, varies as a function of the distance traveled. (The third flavor state, the tau neutrino, is very rare.) Credit: Knowable Magazine
Neutrino oscillation is weird, but it may be weird in a useful way, because it might allow physicists to probe certain fundamental symmetries in nature—and these in turn may illuminate the most troubling of asymmetries, namely the universe’s matter-antimatter imbalance.
For neutrino researchers, a key symmetry is called charge-parity or CP symmetry. It’s actually a combination of two distinct symmetries: Changing a particle’s charge flips matter into antimatter (or vice versa), while changing a particle’s parity flips a particle into its mirror image (like turning a right-handed glove into a left-handed glove). So the CP-opposite version of a particle of ordinary matter is a mirror image of the corresponding antiparticle. But does this opposite particle behave exactly the same as the original one? If not, physicists say that CP symmetry is violated—a fancy way of saying that matter and antimatter behave slightly differently from one another. So any examples of CP symmetry violation in nature could help to explain the matter-antimatter imbalance.
In fact, CP violation has already been observed in some mesons, a type of subatomic particle typically made up of one quark and one antiquark, a surprising result first found in the 1960s. But it’s an extremely small effect, and it falls far short of being able to account for the universe’s matter-antimatter asymmetry.
In July 2025, scientists working at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN near Geneva reported clear evidence for a similar violation by one type of particle from a different family of subatomic particles known as baryons—but this newly observed CP violation is similarly believed to be much too small to account for the matter-antimatter imbalance.
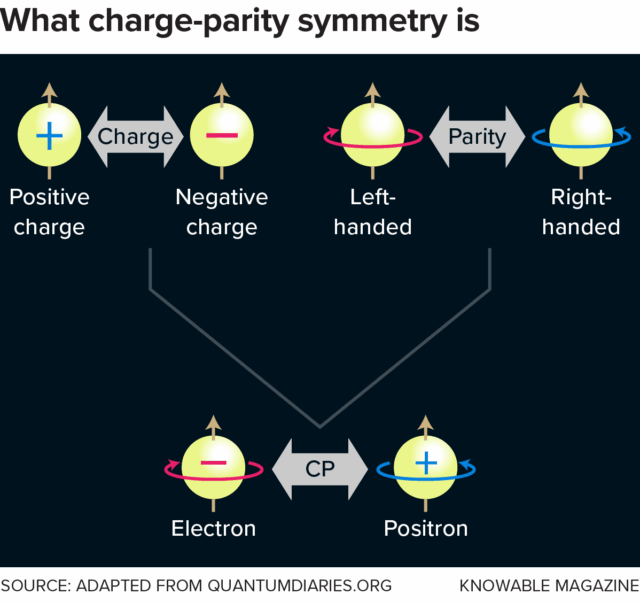
Charge-parity or CP symmetry is a combination of two distinct symmetries: Changing a particle’s charge from positive to negative, for example, flips matter into antimatter (or vice versa), while changing a particle’s parity flips a particle into its mirror image (like turning a right-handed glove into a left-handed glove). Consider an electron: Flip its charge and you end up with a positron; flip its “handedness”—in particle physics, this is actually a quantum-mechanical property known as spin—and you get an electron with opposite spin. Flip both properties, and you get a positron that’s like a mirror image of the original electron. Whether this CP-flipped particle behaves the same way as the original electron is a key question: If it doesn’t, physicists say that CP symmetry is “violated.” Any examples of CP symmetry violation in nature could help to explain the matter-antimatter imbalance observed in the universe today. Credit: Knowable Magazine
Experiments on the horizon
So what about neutrinos? Do they violate CP symmetry—and if so, do they do it in a big enough way to explain why we live in a matter-dominated universe? This is precisely the question being addressed by a new generation of particle physics experiments. Most ambitious among them is the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE), which is now under construction in the United States; data collection could begin as early as 2029.
DUNE will employ the world’s most intense neutrino beam, which will fire both neutrinos and antineutrinos from Fermilab to the Sanford Underground Research Facility, located 800 miles away in South Dakota. (There’s no tunnel; the neutrinos and antineutrinos simply zip through the earth, for the most part hardly noticing that it’s there.) Detectors at each end of the beam will reveal how the particles oscillate as they traverse the distance between the two labs—and whether the behavior of the neutrinos differs from that of the antineutrinos.
DUNE won’t pin down the precise amount of neutrinos’ CP symmetry violation (if there is any), but it will set an upper limit on it. The larger the possible effect, the greater the discrepancy in the behavior of neutrinos versus antineutrinos, and the greater the likelihood that neutrinos could be responsible for the matter-antimatter asymmetry in the early universe.
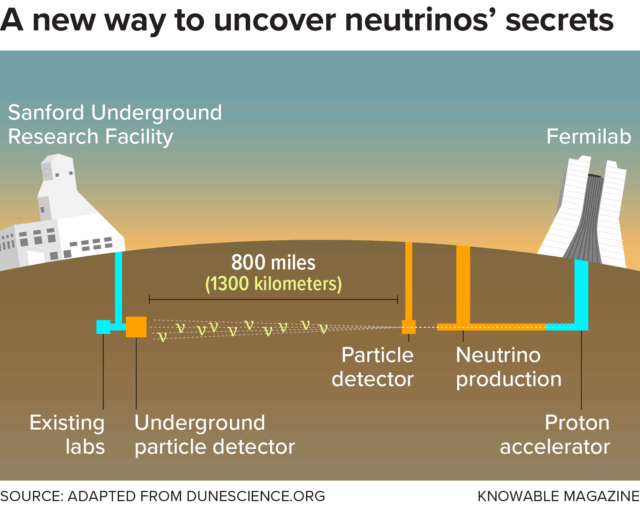
The Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE), now under construction, will see both neutrinos and antineutrinos fired from below Fermilab near Chicago to the Sanford Underground Research Facility some 800 miles away in South Dakota. Neutrinos can pass through earth unaltered, with no need of a tunnel. The ambitious experiment may reveal how the behavior of neutrinos differs from that of their antimatter counterparts, antineutrinos. Credit: Knowable Magazine
For Shirley Li, a physicist at the University of California, Irvine, the issue of neutrino CP violation is an urgent question, one that could point the way to a major rethink of particle physics. “If I could have one question answered by the end of my lifetime, I would want to know what that’s about,” she says.
Aside from being a major discovery in its own right, CP symmetry violation in neutrinos could challenge the Standard Model by pointing the way to other novel physics. For example, theorists say it would mean there could be two kinds of neutrinos—left-handed ones (the normal lightweight ones observed to date) and much heavier right-handed neutrinos, which are so far just a theoretical possibility. (The particles’ “handedness” refers to their quantum properties.)
These right-handed neutrinos could be as much as 1015 times heavier than protons, and they’d be unstable, decaying almost instantly after coming into existence. Although they’re not found in today’s universe, physicists suspect that right-handed neutrinos may have existed in the moments after the Big Bang — possibly decaying via a process that mimicked CP violation and favored the creation of matter over antimatter.
It’s even possible that neutrinos can act as their own antiparticles—that is, that neutrinos could turn into antineutrinos and vice versa. This scenario, which the discovery of right-handed neutrinos would support, would make neutrinos fundamentally different from more familiar particles like quarks and electrons. If antineutrinos can turn into neutrinos, that could help explain where the antimatter went during the universe’s earliest moments.
One way to test this idea is to look for an unusual type of radioactive decay — theorized but thus far never observed—known as “neutrinoless double-beta decay.” In regular double-beta decay, two neutrons in a nucleus simultaneously decay into protons, releasing two electrons and two antineutrinos in the process. But if neutrinos can act as their own antiparticles, then the two neutrinos could annihilate each other, leaving only the two electrons and a burst of energy.
A number of experiments are underway or planned to look for this decay process, including the KamLAND-Zen experiment, at the Kamioka neutrino detection facility in Japan; the nEXO experiment at the SNOLAB facility in Ontario, Canada; the NEXT experiment at the Canfranc Underground Laboratory in Spain; and the LEGEND experiment at the Gran Sasso laboratory in Italy. KamLAND-Zen, NEXT, and LEGEND are already up and running.
While these experiments differ in the details, they all employ the same general strategy: They use a giant vat of dense, radioactive material with arrays of detectors that look for the emission of unusually energetic electrons. (The electrons’ expected neutrino companions would be missing, with the energy they would have had instead carried by the electrons.)
While the neutrino remains one of the most mysterious of the known particles, it is slowly but steadily giving up its secrets. As it does so, it may crack the puzzle of our matter-dominated universe — a universe that happens to allow inquisitive creatures like us to flourish. The neutrinos that zip silently through your body every second are gradually revealing the universe in a new light.
“I think we’re entering a very exciting era,” says Turner.
This article originally appeared in Knowable Magazine, a nonprofit publication dedicated to making scientific knowledge accessible to all. Sign up for Knowable Magazine’s newsletter.
