The assassination of a Hungarian duke, why woodpeckers grunt when they peck, and more.
Skull of remains found in a 13th century Dominican monastery on Margaret Island, Budapest, Hungary Credit: Eötvös Loránd University
It’s a regrettable reality that there is never enough time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. In the past, we’ve featured year-end roundups of cool science stories we (almost) missed. This year, we’re experimenting with a monthly collection. November’s list includes forensic details of the medieval assassination of a Hungarian duke, why woodpeckers grunt when they peck, and more evidence that X’s much-maligned community notes might actually help combat the spread of misinformation after all.
An assassinated medieval Hungarian duke
Credit: Tamás Hajdu et al., 2026
Back in 1915, archaeologists discovered the skeletal remains of a young man in a Dominican monastery on Margaret Island in Budapest, Hungary. The remains were believed to be those of Duke Bela of Masco, grandson of the medieval Hungarian King Bela IV. Per historical records, the young duke was brutally assassinated in 1272 by a rival faction and his mutilated remains were recovered by the duke’s sister and niece and buried in the monastery.
The identification of the remains was based on a contemporary osteological analysis, but they were subsequently lost and only rediscovered in 2018. A paper published in the journal Forensic Science International: Genetics has now confirmed that identification and shed more light on precisely how the duke died. (A preprint is available on bioRxiv.]
An interdisciplinary team of researchers performed various kinds of bioarchaeological analysis on the remains. including genetic testing, proteomics, 3D modeling, and radiocarbon dating. The resulting data definitively proves that the skeleton is indeed that of Duke Bela of Masco.
The authors were also able to reconstruct the manner of the duke’s death, concluding that this was a coordinated attack by three people. One attacked from the front while the other two attacked from the left and right sides, and the duke was facing his assassins and tried to defend himself. The weapons used were most likely a saber and a long sword, and the assassins kept raining down blows even after the duke had fallen to the ground. The authors concluded that while the attack was clearly planned, it was also personal and fueled by rage or hate.
DOI: Forensic Science International: Genetics, 2025. 10.1016/j.fsigen.2025.103381 (About DOIs).
Why woodpeckers grunt when they peck
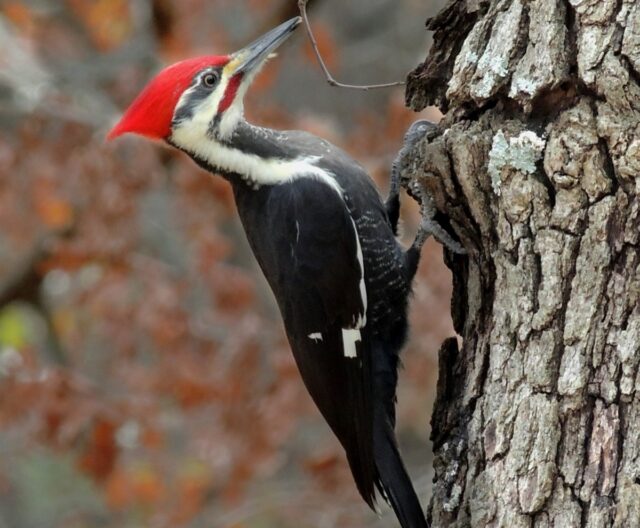

Woodpeckers energetically drum away at tree trunks all day long with their beaks and yet somehow never seem to get concussions, despite the fact that such drumming can produce deceleration forces as high as 1,200 g’s. (Humans suffer concussions with a sudden deceleration of just 100 g’s.) While popular myth holds that woodpecker heads are structured in such a way to absorb the shock, and there has been some science to back that up, more recent research found that their heads act more like hammers than shock absorbers. A paper published in the Journal of Experimental Biology sheds further light on the biomechanics of how woodpeckers essentially turn themselves into hammers and reveals that the birds actually grunt as they strike wood.
The authors caught eight wild downy woodpeckers and recorded them drilling and tapping on pieces of hardwood in the lab for three days, while also measuring electrical signals in their heads, necks, abdomens, tails, and leg muscles. Analyzing the footage, they found that woodpeckers use their hip flexors and front neck muscles to propel themselves forward as they peck while tipping their heads back and bracing themselves using muscles at the base of the skull and back of the neck. The birds use abdominal muscles for stability and brace for impact using their tail muscles to anchor their bodies against a tree. As for the grunting, the authors noted that it’s a type of breathing pattern used by tennis players (and martial artists) to boost the power of a strike.
DOI: Journal of Experimental Biology, 2025. 10.1242/jeb.251167 (About DOIs).
Raisins turn water into wine

Credit: Kyoto University
Fermentation has been around in some form for millennia, relying on alcohol-producing yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae; cultured S. cerevisiae is still used by winemakers today. It’s long been thought that winemakers in ancient times stored fresh crushed grapes in jars and relied on natural fermentation to work its magic, but recent studies have called this into question by demonstrating that S. cerevisiae colonies usually don’t form on fresh grape skins. But the yeast does like raisins, as Kyoto University researchers recently discovered. They’ve followed up that earlier work with a paper published in Scientific Reports, demonstrating that it’s possible to use raisins to turn water into wine.
The authors harvested fresh grapes and dried them for 28 days. Some were dried using an incubator, some were sun-dried, and a third batch was dried using a combination of the two methods. The researchers then added the resulting raisins to bottles of water—three samples for each type of drying process—sealed the bottles, and stored them at room temperature for two weeks. One incubator-dried sample and two combo samples successfully fermented, but all three of the sun-dried samples did so, and at higher ethanol concentrations. Future research will focus on identifying the underlying molecular mechanisms. And for those interested in trying this at home, the authors warn that it only works with naturally sun-dried raisins, since store-bought varieties have oil coatings that block fermentation.
DOI: Scientific Reports, 2025. 10.1038/s41598-025-23715-3 (About DOIs).
An octopus-inspired pigment

Credit: Charlotte Seid
Octopuses, cuttlefish, and several other cephalopods can rapidly shift the colors in their skin thanks to that skin’s unique complex structure, including layers of chromatophores, iridophores, and leucophores. A color-shifting natural pigment called xanthommatin also plays a key role, but it’s been difficult to study because it’s hard to harvest enough directly from animals, and lab-based methods of making the pigment are labor-intensive and don’t yield much. Scientists at the University of San Diego have developed a new method for making xanthommatin in substantially larger quantities, according to a paper published in Nature Biotechnology.
The issue is that trying to get microbes to make foreign compounds creates a metabolic burden, and the microbes hence resist the process, hindering yields. The USD team figured out how to trick the cells into producing more xanthommatin by genetically engineering them in such a way that making the pigment was essential to a cell’s survival. They achieved yields of between 1 and 3 grams per liter, compared to just five milligrams of pigment per liter using traditional approaches. While this work is proof of principle, the authors foresee such future applications as photoelectronic devices and thermal coatings, dyes, natural sunscreens, color-changing paints, and environmental sensors. It could also be used to make other kinds of chemicals and help industries shift away from older methods that rely on fossil fuel-based materials.
DOI: Nature Biotechnology, 2025. 10.1038/s41587-025-02867-7 (About DOIs).
A body-swap robot

Credit: Sachi Wickramasinghe/UBC Media Relations
Among the most serious risks facing older adults is falling. According to the authors of a paper published in Science Robotics, standing upright requires the brain to coordinate signals from the eyes, inner ears, and feet to counter gravity, and there’s a natural lag in how fast this information travels back and forth between brain and muscles. Aging and certain diseases like diabetic neuropathy and multiple sclerosis can further delay that vital communication; the authors liken it to steering a car with a wheel that responds half a second late. And it’s a challenge to directly study the brain under such conditions.
That’s why researchers at the University of British Columbia built a large “body swap” robotic platform. Subjects stood on force plates attached to a motor-driven backboard to reproduce the physical forces at play when standing upright: gravity, inertia, and “viscosity,” which in this case describes the damping effect of muscles and joints that allow us to lean without falling. The platform is designed to subtly alter those forces and also add a 200-millisecond delay.
The authors tested 20 participants and found that lowering inertia and making the viscosity negative resulted in similar instability to that which resulted from a signal delay. They then brought in ten new subjects to study whether adjusting body mechanics could compensate for information delays. They found that adding inertia and viscosity could at least partially counter the instability that arose from signal delay—essentially giving the body a small mechanical boost to help the brain maintain balance. The eventual goal is to design wearables that offer gentle resistance when an older person starts to lose their balance, and/or help patients with MS, for example, adjust to slower signal feedback.
DOI: Science Robotics, 2025. 10.1126/scirobotics.adv0496 (About DOIs).
X community notes might actually work
Credit: Huaxia Rui
Earlier this year, Elon Musk claimed that X’s community notes feature needed tweaking because it was being gamed by “government & legacy media” to contradict Trump—despite vigorously defending the robustness of the feature against such manipulation in the past. A growing body of research seems to back Musk’s earlier stance.
For instance, last year Bloomberg pointed to several studies suggesting that crowdsourcing worked just as well as using professional fact-checkers when assessing the accuracy of news stories. The latest evidence that crowd-sourcing fact checks can be effective at curbing misinformation comes from a paper published in the journal Information Systems Research, which found that X posts with public corrections were 32 percent more likely to be deleted by authors.
Co-author Huaxia Rui of the University of Rochester pointed out that community notes must meet a threshold before they will appear publicly on posts, while those that do not remain hidden from public view. Seeing a prime opportunity in the arrangement, Rui et al. analyzed 264,600 X posts that had received at least one community note and compared those just above and just below that threshold. The posts were collected from two different periods: June through August 2024, right before the US presidential election (when misinformation typically surges), and the post-election period of January and February 2025.
The fact that roughly one-third of authors responded to public community notes by deleting the post suggests that the built-in dynamics of social media (e.g., status, visibility, peer feedback) might actually help improve the spread of misinformation as intended. The authors concluded that crowd-checking “strikes a balance between First Amendment rights and the urgent need to curb misinformation.” Letting AI write the community notes, however, is probably still a bad idea.
DOI: Information Systems Research, 2025. 10.1287/isre.2024.1609 (About DOIs).
Jennifer is a senior writer at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
