or, “the impatient person’s guide to buying a Steam Machine”
With a little know-how, you can get yourself a Steam Machine right this minute.
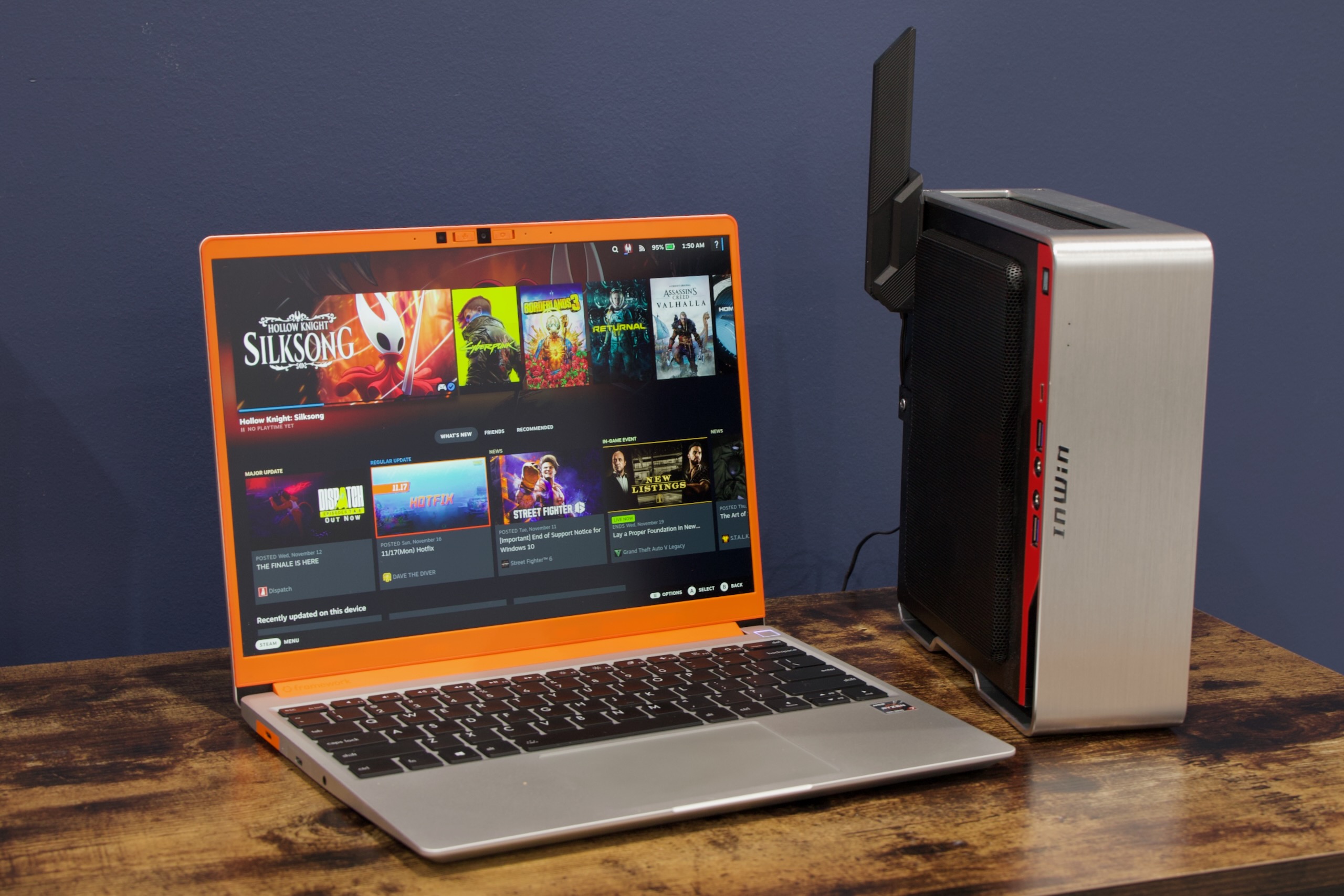
I started trying to install SteamOS on other PCs basically as soon as Valve made it possible. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Valve’s second big foray into first-party PC hardware isn’t a sequel to the much-imitated Steam Deck portable, but rather a desktop computer called the Steam Machine. And while it could go on your desk, Valve clearly intends for it to fit in an entertainment center under a TV—next to, or perhaps even instead of, a game console like the Xbox or PlayStation 5.
I am pretty sure this idea could work, and it’s because I’ve already been experimenting with what is essentially a “Steam Machine” underneath my own TV for months, starting in May when Valve began making it possible to install SteamOS on certain kinds of generic PC hardware.
Depending on what it costs—and we can only guess what it will cost—the Steam Machine could be a good fit for people who just want to plug a more powerful version of the Steam Deck experience into their TVs. But for people who like tinkering or who, like me, have been messing with miniature TV-connecting gaming PCs for years and are simply tired of trying to make Windows workable, the future promised by the Steam Machine is already here.
My TV PC setup
I had always been sort of TV PC-curious, but I can trace my current setup to December 2018, when, according to a Micro Center receipt in my inbox, I built a $504.51 PC in a tiny InWin Chopin case centered on an AMD Ryzen 5 2400G processor.
At the time, the Ryzen brand was only a couple of years old, and the 2400G had impressed reviewers by combining a competent-enough quad-core CPU with a usably performant integrated GPU. And the good news was: It worked! It was nowhere near as good as the graphical experience that, say, a PlayStation 4 could provide, but it worked well for older and indie games, while also giving me access to a TV-connected computer for the occasions when I wanted to stream things from a browser, or participate in a living room-scale Zoom call (something that would become the box’s main job during the pandemic-induced isolation of 2020 and early 2021).
(This PC evolved over time and currently uses a Ryzen 8700G processor, which includes AMD’s best CPU and integrated GPU for socketed desktop motherboards. I did this to get more stable 1080p performance in more games, but I would not recommend this build to most people right now—more on that in a bit.)
The main problem was Windows, which was not and still is not particularly well-optimized for controller-driven living room use. What I really wanted was a startup process that felt more or less like a game console: hit the power button, and automatically get launched into a gamepad-navigable interface that would let me launch and play things without touching a mouse or keyboard.
There are third-party apps like Launchbox that make a go of providing this functionality for people more interested in emulation or who own games from multiple PC storefronts. What I eventually settled on was a sort of hacky fix that allowed my user account to log in automatically, and then automatically launch Steam in Big Picture Mode.
This worked… fine—except when I needed to interact with a mouse and keyboard to install driver updates, or when some component of the Windows UI would steal focus from the Big Picture Mode window and make it impossible to use the controller to navigate.
So when reports indicated that Valve was working on a SteamOS version that would run on more hardware, I was immediately interested. SteamOS was designed to boot right into its gaming interface, and the desktop mode was its own separate thing that you needed to open up manually—ideal for my usage model, since I didn’t want to give up the desktop mode but also didn’t need to use it often. But I did run into some bumps during the installation process, which I’ll share here in case it helps you avoid them.
SteamOS or Bazzite

Bazzite’s desktop mode wallpaper. A community supported alternative to SteamOS, Bazzite offers much wider hardware compatibility but can have rough edges. Credit: Bazzite
I had trouble using Valve’s official restore image (SteamOS version 3.7.7, from this support page) to get newer hardware working, which may be one reason why that language was softened. It was no problem to install official first-party SteamOS on slightly older hardware, like the Ryzen 7040 version of the Framework Laptop 13 or an older Acer laptop with a Ryzen 6000-series processor installed. But trying to install the software on newer hardware failed no matter what I tried. Those systems included the Ryzen AI 300 version of the Framework Laptop; a socket AM5 testbed desktop with a dedicated Radeon RX 7800 XT GPU; and, to my great disappointment, my TV desktop’s Ryzen 7 8700G.
There’s very little information out there about installing or troubleshooting SteamOS on generic hardware, but if you poke around on Reddit about much of anything, you’ll quickly meet a specific Type of Guy who believes that anyone with hardware compatibility issues should just use Bazzite, a community-developed alternate operating system that attempts to provide a SteamOS-ish alternative with wider hardware support (including for Intel and Nvidia hardware, which isn’t likely to be supported by the official SteamOS any time soon).
And so Bazzite I tried! Indicating that I used an AMD GPU and wanted to boot into the SteamOS interface offered me the exact same image that Bazzite offers for the Steam Deck and other handhelds, and it installed on my Ryzen desktop with minimal fuss.
Bazzite also came painfully close to what I wanted it to be, in terms of user experience—a desktop mode to boot into on the occasions I needed one, but otherwise I could just fire up the Xbox controller I had paired to the PC and jump right into a game.
But Bazzite was sunk by the same kind of bugs and edge cases that often chase me away from Linux operating systems when I try them. The main issue was that periodically, the system would boot up into desktop mode without asking (usually this seemed to happen when the Steam client software needed an update, but I can’t say for sure). Restarting the system would usually boot it back into the SteamOS interface—but I’d need to log in all over again, and the OS would switch Bluetooth off by default. Not only am I having to dig out a keyboard and mouse to solve this problem, but I’m needing to use a wired keyboard until I could get Bluetooth turned back on.
By the time this had happened twice, I was sure it wasn’t a fluke; by the time it had happened four or five times, I was determined to blow the entire operating system away and try again. And I was particularly interested in trying actual, for-real SteamOS again, just in case a new Bazzite install would have the same problems as the one I was already using.
After some digging, I found this directory. If you look through those folders, you’ll see OS images for various versions of SteamOS, including newer versions of SteamOS 3.7 (the “stable” version you’ll find on the Deck) and builds of both SteamOS 3.8 and 3.9 (the Deck will pull these down if you switch from the “stable” OS channel to “main”). Not all of those folders include the repair image you need to wipe a device and install SteamOS, but a few do—this one, dated October 27, is the most recent as of this writing.
Those newer versions of the operating system include changes that expand SteamOS’s hardware support, most notably a step up from Linux kernel version 6.11 to version 6.16. And it was that steamdeck-repair-main-20251027.1000-3.8.0.img.zip file that I was finally able to flash to a USB drive and install on my TV desktop using Valve’s instructions.
It has only been a week or so since then, but at least so far I’m finally getting what I wanted: the same experience as on my Deck, just on my TV, with hardware that is somewhat better-suited for a larger and higher-resolution screen (and that’s the main reason to do this, rather than use a docked Steam Deck for everything).
The SteamOS experience
The “console-like experience” designed for the Steam Deck also works well with a TV and a gamepad. Credit: Valve
Once the OS is installed and is up and running, anyone who has used a Steam Deck will find it instantly familiar, and all you’ll need to do to get going is connect or pair a gamepad and/or a keyboard and mouse.
Most of the bugs and quirks I’ve run into stem from the fact that this software was developed for standalone handheld gaming consoles first and foremost. There are multiple settings toggles—including those for adaptive brightness and HDMI-CEC—that serve a purpose on the Steam Deck but just don’t function on a desktop, where these features usually aren’t present or aren’t supported.
SteamOS is also pretty hit or miss about selecting the correct resolution and refresh rate for a connected display. Navigate to the Settings, to Display, and then turn off the “Automatically Set Resolution” toggle, and you’ll see a full list of supported resolutions and refresh rates that you can pick from. You may also want to scroll down and change the “Maximum Game Resolution” from “Native” to the actual native resolution of your screen, since I occasionally encountered games that wouldn’t offer resolutions that were supported by the display I was using.
Similarly, you may need to navigate to the Audio settings and switch output devices if you’re sending audio over HDMI. I also needed to turn the audio output volume up to around 80 percent before the sound coming out of my Steam Machine would match the volume of all the other boxes connected to my TV.
And if you’ve never used SteamOS before, it’s worth reading up on some of its limitations. While its compatibility with Windows games is quite good, Valve’s Proton compatibility layer is in continuous development, and not every game will play perfectly or play at all. Games that use anti-cheat software are still broadly incompatible with SteamOS, since many anti-cheat programs hook into the Windows kernel in ways that are impossible to translate or emulate. And while it’s possible to run games from other storefronts like Epic or GOG, it’s best done with third-party software like the Heroic Games Launcher, adding an extra layer of complexity.
And although SteamOS includes a useful desktop mode, it’s really not meant to be used as a day-to-day workhorse operating system—security features like “using a password to log in” are off by default in the interest of expediency, and you need to open your system to bootloader tampering just to install it. It’s fine for installing and running the odd desktop app every once in a while, but I’d hesitate to trust it with anything sensitive.
Finally, while our tests have shown that SteamOS generally performs at least as well, if not better, than Windows running on the same hardware, the first-party version of SteamOS is still made with handhelds and other low-power hardware in mind. In my limited testing of SteamOS on desktops with both integrated and with more powerful dedicated GPUs, I’ve generally found that those observations hold up. But I’ve only tested on a narrow range of hardware, and you could easily encounter a setup where SteamOS just doesn’t run games as well as Windows does.
Rolling your own Steam Machine

A Ryzen 7 8700G-based “Steam Machine,” in an InWin Chopin Max case. I enjoy PC building, but the economics of this box aren’t great for most people. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Say you’re interested in having a Steam Machine, you don’t want to wait for Valve, and you don’t just happen to have a spare ideally configured AMD-based PC to sacrifice to the testing gods.
I am more or less happy with my custom-built mini ITX Steam Machine, but I find it difficult to recommend this hardware combination to basically anybody at this point. For me, it scratched a PC-building itch, and the potential for future upgradability is mildly interesting to me. But given the high cost of AMD’s Socket AM5 platform and spiking costs for RAM and SSDs, it’s going to be difficult to put together an 8700G-focused system in an InWin Chopin for less than $800. And that’s a whole lot to pay for a years-old Radeon 780M GPU.
For a more budget-friendly Steam Machine, consider the range of no-name mini PCs available on Amazon and some other places. We’ve dabbled with systems from manufacturers like Aoostar, Beelink, Bosgame, and GMKtec before and come away conditionally impressed by the ratio of utility-to-performance, and YouTubers like RetroGameCorps and ETA Prime periodically cover new ones and generally have positive things to say. You’re rolling the dice on long-term reliability and support, but it’s also tough to argue with the convenience of the form factor or the pricing compared to a custom-built system.
If you’re going this route, we have some general recommendations and performance numbers, based on testing of similar chips in other laptops and desktops. Note that the Ryzen 6800U/Radeon 680M system is an Acer Swift Edge 16 laptop with 16GB of soldered DDR5, while the Ryzen 7840U/Radeon 780M system is a Framework Laptop 13 with non-soldered DDR5. Performance may differ a few FPS in either direction depending on your hardware configuration. The Ryzen 7700X/Radeon RX 7600 system is a custom-built testbed desktop similar to the one we use for testing CPUs and GPUs; based on hardware alone, we’d expect the real Steam Machine to perform near or slightly below .
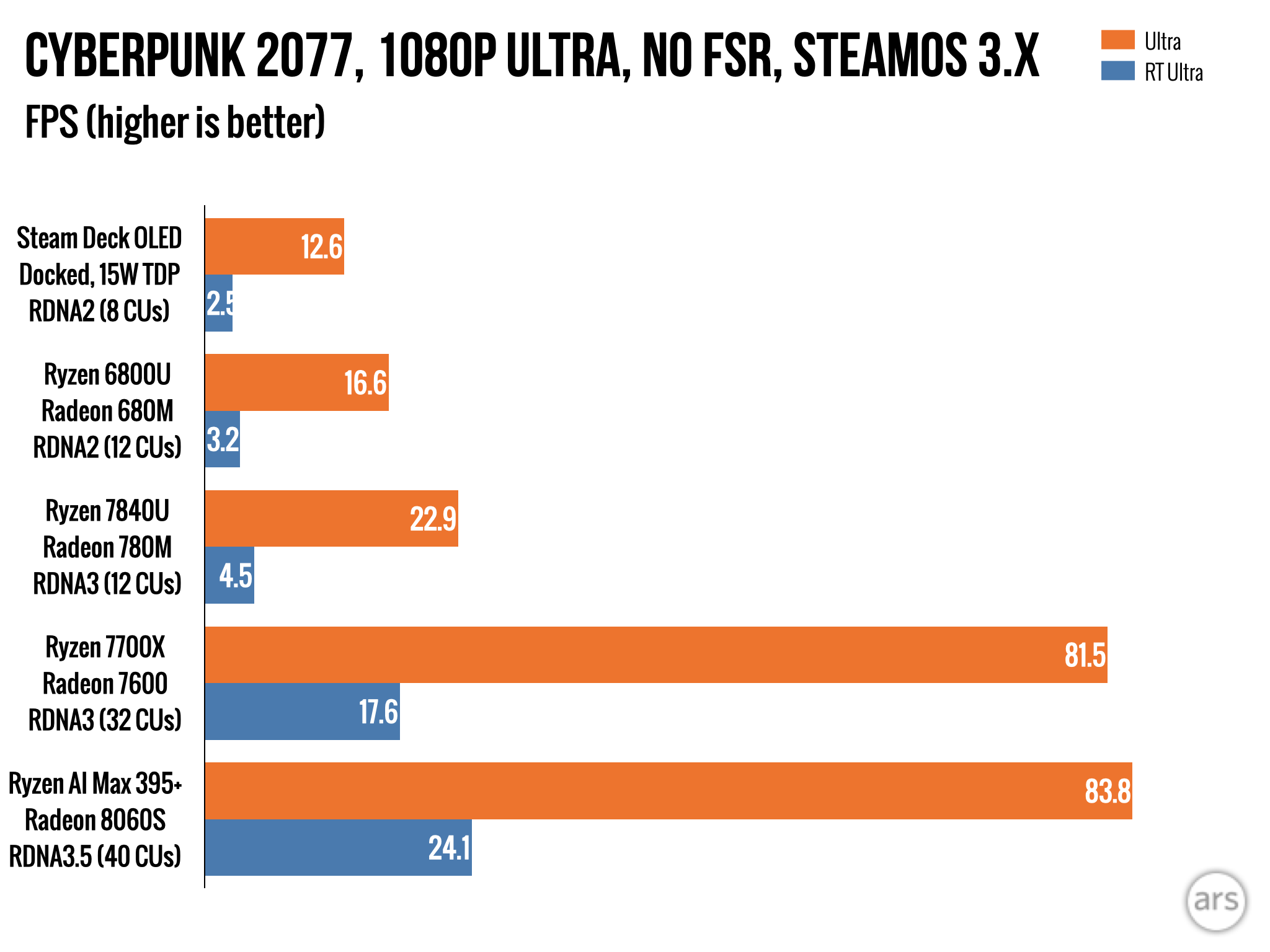
A handful of numbers from a single game, to show relative performance differences between some integrated and low-end dedicated AMD GPUs. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
In the $350 to $400 range, look for PCs with a Ryzen 6800-series chip in them, like the 6800H or 6850H (here’s one from GMKTec for $385, and one from Beelink for $379). These processors come with a Radeon 680M integrated GPU, with 12 compute units (CUs) based on the RDNA2 architecture. These boxes will offer performance slightly superior to the actual Steam Deck, which uses eight RDNA2 CUs and squeezes them into a system with a small power envelope.
If you can spend around $500, that generally seems to get you the best performance for the price right now. Look for processors in the Ryzen 7040 or 8040 series, or the Ryzen 250 series (here’s one for $$490 from GMKtec, one for $499 from Bosgame, and one for $449 from Aoostar). These chips all offer broadly similar combinations of eight Zen 4-based CPU cores, and a 12-core Radeon 780M GPU based on the RDNA3 architecture.
In a mini desktop, this GPU can come pretty close to doubling the performance of the Steam Deck, though it will still fall short of most dedicated graphics cards. It’s similar to the performance level of the non-Extreme version of the Ryzen Z2 chip for competing handhelds. The 780M is also the same GPU that comes with the Ryzen 8700G desktop chip I use, and I’ve found that it gets you decent 1080p performance in many games.
The GPU is the most important thing to focus on in these systems, since it’s going to have the most impact on the way games actually run. But keep an eye on RAM and storage, too; a 1TB SSD is obviously preferable to a 500GB SSD. And while most of these come with a healthy 32GB of RAM by default, pay attention to the type of RAM. If it just says “DDR5,” that’s most likely to be socketed RAM that’s a bit slower, but which you can upgrade yourself if you want. If it comes with LPDDR5X, that’s going to be soldered down, but also a bit faster, maximizing your graphics performance.
The Steam Deck is a useful benchmark here, because it’s a fixed hardware platform that’s popular enough that PC game developers sometimes go out of their way to target. Games often include Steam Deck-specific graphics presets, which are a useful starting point when you’re fiddling with settings.
I would generally try to avoid systems with Ryzen AI 300-series chips in them—their Radeon 890M GPUs are faster, but they can also be twice as expensive as the Radeon 780M boxes. I’d also stay away from anything with Ryzen 5000 or 3000-series chips, or Ryzen 7030-series chips. The price tags on these $200 to $300 systems are tempting, and they will probably run SteamOS, but their older Vega-based GPUs will fall far short of the Steam Deck’s GPU, let alone the Radeon 680M or 780M.

The Framework Desktop is a compelling alternative to the actual Steam Machine, if you don’t mind paying for it. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
OK, but what if you have more money to spend, and you’re more interested in 1440p or 4K gaming performance (roughly what Valve is targeting with the actual Steam Machine)? I think that the Framework Desktop is a surprisingly good fit here; $1,200 will get you a console-sized PC with an eight-core Zen 5 CPU, a Radeon 8050S GPU with 32 CUs based on the RDNA 3.5 architecture (the Steam Machine has 28 RDNA3 CUs), 32GB of RAM, and a 1TB SSD. I can confirm firsthand that SteamOS 3.8/3.9 installs and runs just fine.
This desktop is probably a bit more expensive than the Steam Machine will end up being, but it’s impossible to say how much more expensive before Valve actually puts out a price.
The TV PC is ready for its close-up
TV-connected PCs have historically been a niche thing. They’re expensive, they’re finicky, and purpose-built game consoles have always provided a more pleasant and seamless experience for people who just want to do everything with a controller from the couch.
But the TV PC could finally be ready for its moment. In SteamOS, Valve has created a pretty good, pretty widely compatible Windows substitute that buries a lot of the PC’s complexity (without totally removing it, for the people who want it sometimes). Like the Nintendo Switch, Valve has crafted a user interface that feels good to use on a handheld screen and on a TV from 10 feet away.
And this is happening at the same time as a weird detente in the console wars, where Sony seems to be embracing PC ports and easing up on exclusive releases at the same time as Microsoft seems, for all intents and purposes, to be winding down the Xbox hardware operation in favor of Windows. Valve is way out in front of Microsoft on its console-style PC interface at the same time as the PC is becoming a sort of universally compatible über-console.
I’m kind of the ideal audience for the Steam Machine; nearly all my PC games are on Steam, I play practically nothing that requires anti-cheat software, and I play mostly graphically undemanding indie games rather than GPU-bruising AAA titles. So, you know, take my enthusiasm for the concept with a grain of salt.
But as someone who has already functionally been living with a Steam Machine for months, I think that Valve’s new hardware could do for living room PCs what the Steam Deck has done for handhelds: defining and expanding a product category that others have tried and failed to crack. This year, my Steam Machine has ably kept up with me as I’ve played Silksong, UFO 50, Dave the Diver, both HD-2D Dragon Quest remakes, part of a bad-guy run through Baldur’s Gate III, some multiplayer Vampire Survivors experimentation, several Jackbox Party Pack sessions, and more besides. I’ve never been less tempted to buy a PlayStation 5.
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.

