It is increasingly often strange compiling the monthly roundup, because life comes at us fast. I look at various things I’ve written, and it feels like they are from a different time. Remember that whole debate over free speech? Yeah, that was a few weeks ago. Many such cases. Gives one a chance to reflect.
In any case, here we go.
-
Don’t Provide Bad Training Data.
-
Maybe Don’t Say Maybe.
-
Throwing Good Parties Means Throwing Parties.
-
Air Travel Gets Worse.
-
Bad News.
-
You Do Not Need To Constantly Acknowledge That There Is Bad News.
-
Prediction Market Madness.
-
No Reply Necessary.
-
While I Cannot Condone This.
-
Antisocial Media.
-
Government Working.
-
Tylenol Does Not Cause Autism.
-
Jones Act Watch.
-
For Science!.
-
Work Smart And Hard.
-
So Emotional.
-
Where Credit Is Due.
-
Good News, Everyone.
-
I Love New York.
-
For Your Entertainment.
-
Gamers Gonna Game Game Game Game Game.
-
I Was Promised Flying Self-Driving Cars.
-
Sports Go Sports.
-
Opportunity Knocks.
People should be free to squander their money, but when other people make bad choices, this tends to not go well for you either, even when talking about consumer choices, let alone things like ‘building superintelligence thus causing everyone to die.’
Bryan Caplan: If everyone but you squanders their money, everyone but you suffers.
If everyone but you votes for terrible policies, everyone including you suffers.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: Idiots with buying power have negative externalities, not just idiots with voting power. It means going on Amazon and seeing crap. It’s an easier problem to attack but not at all trivial.
Eg broken Amazon reviews won’t let you find one non-crappy product even if it exists.
Or to put it in another way: we live in an economy, not just a legal system. I too feel like there could and should be a libertarian solution rather than a tyrannical one, but I’m not in denial about the problem.
There are also times when you don’t want to compete for the good stuff. Or when this makes it easy for you to save money or turn a profit, and it goes well for you.
Most of the time, no, you want everyone to choose wisely. When others have good taste, and choose quality products, the market produces quality products. If not, not. When they rate things properly, you can find the good stuff. When we collectively make choices that enrich everyone, that too is good for everyone, and so on. It’s #NotOnlyPolicy.
Again, no, you shouldn’t coerce these choices, but you mostly don’t want to live in a world where everyone else is squandering their money in dumb ways.
Hosts don’t like it when you reply ‘maybe,’ they’d feel more respected if you said ‘no’ when invited to an event. Certainly by saying ‘maybe’ you are making life easier for you and harder for the host. Invitees told themselves the ‘maybe’ indicated interest, which it does, but it’s mainly annoying since you have to plan for both outcomes.
Thus, you should only reply ‘maybe’ if you get high value from the option, or you attending provides a lot of value to the host and you’re genuinely unsure. Assume that by doing so you are imposing a cost.
Uri gives us 21 Facts About Throwing Good Parties (via MR). Mostly seems like great advice starting with the ‘announce at a quarter-hour so people will only be 15 minutes late,’ especially if you are trying to optimize the party as a public service.
My biggest new takeaway is I was under considering the ‘know who else is going’ value of using apps like Partiful or Luma. I strongly endorse that if you want to leave a group at a party, you straight up walk away, don’t say anything (and if a group is bigger than ~5, strongly consider leaving it).
One thing I challenge is that he thinks if you are gender imbalanced, the sparse gender will stop attending. It’s definitely true that women become apprehensive if too outnumbered, but running the other way is probably symptomatic of party design that didn’t appeal to men in the first place. Men are not, in general, less likely to show up to a party when there’s going to be more women.
My biggest old takeaway, the first one on the list this time, that throwing a part at all is good, is you are not throwing enough parties, and you should not let the perfect be the enemy of the good. The MVP (minimum viable party) is inviting friends over, providing some food, and chilling. That’s a remarkably valuable public service. If obsessing over details would top you from throwing or enjoying it, skip those details.
One can compare this to Auren Hoffman’s advice for dinner parties, which I discussed in the January 2025 roundup, where again a central theme is not letting perfect be the enemy of the good. I stand by my disagreement there that it is important in a dinner party that the food be good. It is less important for other party formats, but also in a pinch not so difficult to make the food good because delivery services exist.
Also one can reiterate this thread from Kasay and my commentary on it from June 2024, especially that you only need 14 square feet per person, and that ultimately the most important decision is who to invite, with another key factor being engineering a space to create alcoves of conversation.
Airplanes seem to have a growing systemic problem with exposing passengers to fumes in a way that is importantly bad for their health, which they have handled badly and covered up in similar fashion to other industries with similar health issues.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: If it’s true, aircraft manufacturers and airlines are engaging in a classic denial-coverup in the style of cigarette companies, leaded gasoline makers, or AI builders. (At smaller scale.)
Patrick Collison: I’ve been tracking it for a few years (outside of MSM); I’m pretty sure it’s true in a way that does not reflect well on the sector.
My quick math says that this is not common enough you should worry much about it as a passenger, and that air travel remains far safer than other forms of travel even in the worst case. Claude did a worst-case scenario estimate based on the claims and came up with a cost per flight of 0.00003 QALY, which is still at least one order of magnitude lower than any alternative form of transportation.
But this is worth noticing.
The French left is being heavily influenced by a so-called ‘economist’ advocating for ultimately instituting an 8% annual wealth tax, also known as full confiscatory taxation of all wealth subject to such a tax, which can then serve as a warning to the next ten generations. Nine of which will presumably forget, but that’s the way it goes.
Halloween, a holiday so not deep that you don’t even get the day off of work or school, is out of control, complete with not only sales and banners but people who put intentional nightmare fuel (as in, items intentionally created to be scary especially to kids) on display for over a month.
Lady Nimby: Why would you want this at your doorstep for 10% of your life? Why are my kids seeing this?
Mason: Yeah, I love Halloween but I think you should be able to easily opt out of nightmare fuel. This is great decor for your indoor/backyard party.
I’m not saying we should ban you from displaying that stuff if you want to, it’s your house. I am definitely saying that you shouldn’t want to beyond a few days tops, because it is cool in the context of a party or active trick-or-treating, and totally not cool left in place for several days before or after that.
Halloween is of course only a secondary offender when compared to Christmas.
Broadway musicals are in deep trouble, since 2020 there have been 46 new musicals costing $800 million and 43 of them have lost money, including all 18 last season. One neglected explanation is that New York has de facto banned hotel construction and largely banned AirBnB, so hotel prices are way up. The good news is that would be easy to fix.
An article I suspect is itself slop (but in this case, fair!) says We Are The Slop, living our lives in order to generate entertainment slop for others. Certainly influencers do this, that is their job, but the basic math says that like rock stars there is a lot of aspiration to that job but there are not so many slots that pay real money. Most of us do indeed live our lives with the cameras off.
There is a lot of bad news in the world. There is also a lot of good news in the world.
I cannot emphasize enough that the existence of bad news, and especially of political bad news, should not be a constant preface to conversation or good news.
You do not need to continuously self-flagellate to show that you care about the bad news. If others do insist that you do this, that is no good, you need to push back.
This applies across all causes, across the political spectrum, and it especially applies to AI and the fact that it is likely that someone is going to build superintelligence and then everyone will die. Yes, And That’s Terrible, and we should spend some of the time trying to prevent it, but at other times the show must go on. Worry, but also at other times Be Happy.
Tyler Alterman: “Share your happiness with the world.” Duh, right? That’s some basic bh stuff. But recently a Buddhist nun said this to me in this sort of knowing way and it’s been changing my life
I realized that I am often not only hiding my happiness but actively turning it down. I’m doing this to fit in, to connect with the zeitgeist. And today’s zeitgeist has made it borderline offensive to be happy
“You’re happy? What about the war? And misaligned AI? And Tr*mp???”
Being happy is uncool right now in academia, amongst liberals, amongst humanitarians, and in art circles. It’s cringe in many locales of NYC and twitter. So I noticed that when I walk smiling through the streets, I start to feel like I’m Out Of Touch
This nun, however, was pointing out that if you don’t share your happiness, if you don’t let thy cup runneth over, you’re depriving other people of something that can light them up
No one wants to be seen as naive, spiritually bypassing, or brushing aside the horrors of the world. But a mature form of happiness, one that acknowledges these horrors, and which shines despite them…? that strikes me as exactly the sort of thing we need right now
Nick Cammarata: almost got attacked in a russian subway over this. someone was angrily like what the f are you smiling about bc you’re not supposed to smile there but i don’t speak russian so i ignored him and he freaked but it was okay
he was coming up behind me and someone I was with noticed I didn’t realize and grabbed me and pointed me towards him. door happened to be open so we hopped out and took the next one a min later, whole thing was like 15s
Chris Lakin: “I must suffer to show that I care” is a memetic virus.
Jake Eaton (again, this applies to a wide variety of groups): among a fraction of my leftiest friends, there appears to be an internalized norm that you cannot celebrate life if you don’t first acknowledge political reality. i’ve seen birth announcements that begin with the state of American politics, family photos captioned with “the world sucks but here’s this,” instagram carousels that begin with “this year has been hard,” so that i need to read on to figure out whether it’s cancer or trump
maybe it’s an expression of grief — fine. but my sense is that the most progressive environments demand an outward expression of despair before personal celebration, either as some sort of act of solidarity or otherwise guilt. this started in the workplace before moving into our personal lives
I wish I could find ways to explain how quietly corrosive that is, both socially, but more so personally. it makes me sad not for the world but for them! but my experience — having been in those environments for years — is that you have to find your own way out
Robin Hanson points out that if you are trying to do futarchy, you can avoid any non-causal correlation issues by creating enough different markets based on possible random decisions and decisions at different time points. I mean, yeah, okay, technically that works, but even if you can get clean definitions for all of this, how are you going to get price discovery on all of them? This is not a realistic ask.
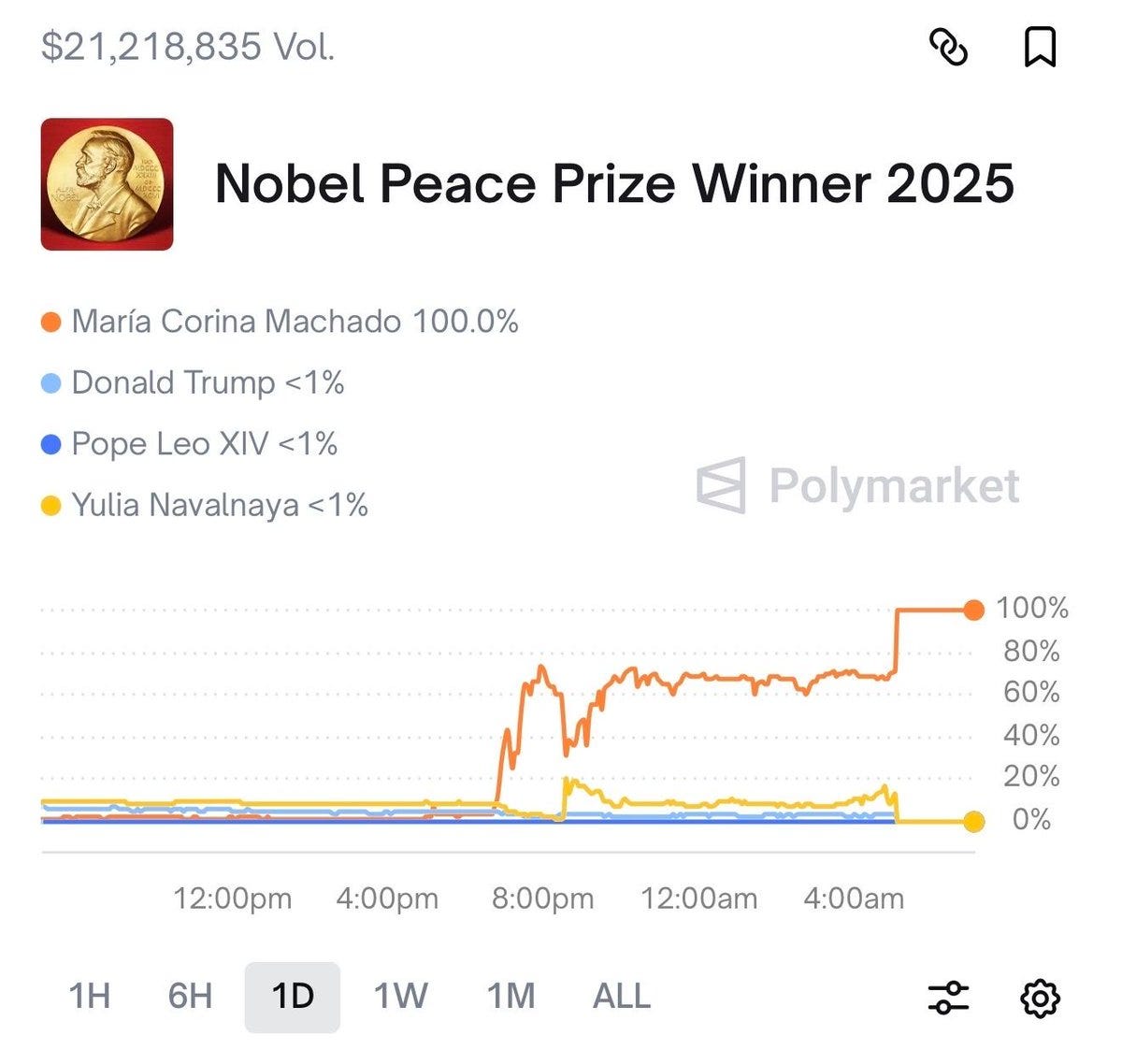
There was insider trading of the winner of the Nobel Peace Prize. Which is good.
Jason Furman: The other day a student asked me about the prevalence of insider trading in prediction markets. I now have an answer.
If I was asked to draw a graph of what insider trading on a prediction market looks like, I would draw this graph. At a time when the outcome could plausibly be known, a rapid shoot upwards of the winner, up to some upper limit that still allows substantial gains, then settling at that limit, until the jump to ~100%.
The even better news is that since insider trading mostly exhibits such obvious patterns, it is easy to avoid it. Here, there are two easy principles to learn.
-
Do not trade after the decision has already been made and could be known.
-
If you must trade, do not trade against this kind of sharp move up.
-
Definitely, absolutely do not have resting sell orders on the book this late.
The person buying is claiming to know the outcome, that the fair price is 100. You might choose to trade against that person if you think they’re often wrong, but understand that this is what you will be doing.
Should insider trading be allowed here, as it is on Polymarket? I say yes. It depends on your goal. Do you want to be able to trade at and know the non-insider price, or to know the insider price and info? You can get at most one of those two things.
Norwegian officials are predictably not amused by this particular bout of insider trading, and are investigating what they call a ‘criminal actor who wants to earn money on our information.’
Polymarket: JUST IN: It has been revealed only 5 people at the Nobel Peace Prize foundation knew the winner before they were announced.
Everyone checking Polymarket knew.
A good periodic reminder of one reason people often reject prediction markets:
Robin Hanson: Years ago a NYC based software firm ran some prediction markets, hoping in part to find & promote “diamonds in the rough” employees who predict especially well. They did find such, but then said “Oh, not them”; such folks didn’t have the polish & style they wanted.
Let that be a warning to those who think that being proven right will gain them more respect and inclusion.
Duncan Sabien notes that comments often create an obligation to respond, and suggests a new way of differentiating ask culture versus guess culture. I see what he’s trying to do to connect them and both are interesting, but I think mostly distinct.
The obligation to respond is that if others see a criticism [Z] to which you don’t respond, or others mischaracterize your [X] as if you said [Y] and respond to [Y], and especially if others then argue about [Y], then you’re in trouble. In the first case, your failure to respond will imply you don’t have a good response to [Z]. In the second case, they’ll start to believe you really did say [Y].
The ultimate source of this obligation to respond is, essentially, that your failure to respond would be Bayesian evidence of inability to respond, or to respond well.
As in, if I get a comment [C] that says [Z], and I had a good response [R] that answers [Z], then why didn’t I respond to [Z] with [R]? A conspicuous non-answer suggests I don’t know of any such [R]. A bad answer [B] also suggests I don’t have a good [R].
A non-conspicuous non-answer does not. One price of consistently engaging with critical comments or statements, in any context, is that an increasing share of non-answers become conspicuous.
Indeed, one of the reasons I rarely respond to comments these days is that I do not wish to create this obligation to respond to other comments, to avoid the time sink. When I do consider a comment worth responding to, because many would want to see that, I will often do so by quoting it in a full post.
The theory on guess versus ask culture is that the distinction is about how many ‘echoes’ you trace. As in, ask culture traces zero echoes, you simply ask for what you want, and they are responsible for saying no and not holding the ask against you. Whereas guess culture traces one echo, you think about how they would respond, and you can imagine sophisticated others (guess harder!) tracking many echoes.
I think this is an interesting idea but I don’t think it is right. In both guess and ask culture, you are responsible for an unlimited number of potential echoes. The difference is what consequences and thus echoes an action causes.
Technically speaking, I think the actual dial is either or both of these:
-
Narrowly: Ask culture is created by radically raising the penalty for imposing a penalty upon someone for refusing an explicit request. As you turn up that penalty, and turn it up under a broader set of circumstances, you get Ask culture.
-
Broadly: Guess culture is created by, in an increasing variety of circumstances, punishing fully generally the creation of common knowledge.
In case #1, I am less penalized for saying no, which means that there is far less reason to penalize you for asking, which in turn means you should ask, and indeed because you should ask I can then put the impetus upon you to ask, and impose various penalties upon you for instead trying to have me guess, and also my guess if you don’t ask is that you probably aren’t implicitly asking either.
Explanation #2 is more compete, more general, and cleaner, once you grok it.
Ask culture very much does not get you out of tracking social echoes in general.
The ultimate both guess and ask culture move here is the anti-ask, as in: No Reply Necessary, or saying (NRN) the way you would with an email. Duncan mentions less blunt ways to say this, but I prefer the classic version, the straight NRN, without further explanation. As in, here is some information, and it is 100% fine on all levels to simply ignore it if you do not find it useful.
John Wentworth advises us how to dress to improve our epistemics, the central thesis is that coolness is status countersignaling. This oversimplifies but is a helpful note.
Have you tried making any effort at all to talk to people in the industry you are studying or want to know about, including any of the many many free ways to request this? It seems very often the answer for PhD students is no. So you get papers where data is analyzed in detail but there has been zero contact with anyone in the real world. In general, remarkably many people are willing to talk to you if you ask.
Scott Sumner points to the concept of ‘defining deviancy up’ by extending words that refer to extremely wrong and bad things [X] (such as genocide, slave labor or pedophilia) to include related things [Y] that most people would agree are, at minimum, a lot less wrong or bad. If you try to respond that [Y] is less bad than [X], or that the new expansive definition covers things it shouldn’t, people respond by claiming you’re saying [X] is fine (or you’re condoning [Y]). Other times, or eventually, things loop around, and definitions are so expansive the word becomes meaningless or fine, the same way mere ‘speeding’ is now ignored so they invented ‘reckless driving.’
People are, according to a new study, ‘much more likely’ to purchase ‘stigmatized’ items like condoms and pregnancy tests at self-checkout counters.
Abstract: On the intensive margin, we show that stigmatized items are much more likely to be purchased at self-checkout than at cashier registers, especially condoms and pregnancy tests. We estimate that customers are willing to pay 8.5 cents in additional time cost for the privacy of purchasing stigmatized items at self-checkout.
I totally buy that if there is an open self-checkout line and an open cashier, and you are buying a pregnancy test, you are going to go for self-checkout on the intensive margin. Sure.
But if anything, this effect looks surprisingly tiny. Customers are only willing to pay 8.5 cents in additional time? That’s not a lot of stigma. If one values time at $20 per hour, then this is on the order of fifteen seconds. Do you have any idea what people will do in other contexts to avoid mild social awkwardness? If people had the opportunity to pay money to not have to look anyone in the eye, some would pay $0, but you could get some people for dollars, and also you can stimulate new demand.
Tyler Cowen: I even draw distinctions across automated models. For instance, if I have “a stupid question,” I am more likely to ask Grok, since I would rather GPT maintain a higher opinion of what I do and do not know.
Dismalist: Reminds me of a line in Mad About You when after hiring a cleaner to start coming the next day, Jamie starts cleaning the night before. Paul sees her, and says: We don’t need a cleaner. We need a credible threat of a cleaner!
If you worry about ChatGPT or Claude’s memory on this, which I wouldn’t, you can use a temporary chat, or delete the chat afterwards. Let’s not panic and use Grok.
Also, yeah, I absolutely hate the thing where you hire a person to do [X], and then you get pressure to do [X] for them in advance to avoid looking bad or being rude or what not. The whole point of hiring them is to get them to do [X] so you don’t have to, or so they can do it better.
Another commentator notes that the right amount of stigma is sometimes not zero, indeed one can see this because for some prosocial items we approve of the existing negative stigma (as in, you buy wisely and the cashier looks at you approvingly).
China cracks down on ‘negative emotional contagion’ and ‘excessively pessimistic’ social media users. I do agree with Tyler Cowen that if you are spreading negative emotional contagion, ‘there is a very good chance’ you are likely to be ‘part of the problem,’ but it is a hell of a thing to ‘crack down’ on it.
Lily Kuo (NYT): The authorities have punished two bloggers who advocated for a life of less work and less pressure; an influencer who said that it made financial sense not to marry and have children; and a commentator known for bluntly observing that China still lags behind Western countries in terms of quality of life.
… Beijing is concerned that such pessimism doesn’t just discourage citizens from being productive members of society. It could turn into criticism of the ruling Communist Party.
… In the city of Zhengzhou in central China, officials said two social media account owners were investigated for portraying the city in an unflattering light.
… Weibo, a popular microblog, said last week that it suspended more than 1,200 accounts that “spread rumors” about the economy and government welfare programs.
Banning not only political dissent but any and all pessimistic speech in this way is, shall we say, highly pessimistic speech, not a sign things are going well.
Lily Kuo: “The official message of positivity is contrasted by an economic reality that is just starkly different compared with the last decades,” said Katja Drinhausen, head of Chinese politics and society at the Mercator Institute for China Studies. “It will not be enough to keep online negative emotions in check.”
I do not expect this to end well.
Are you excited for this new method of sharing content on Twitter? I know I am.
Nikita Bier (Twitter): Starting next week we’ll be testing a new way to share and engage with web links on Twitter. The goal will be to ensure all content on the platform has equal visibility on Timeline.
Johnny v5: oh wow. hoping this is legit. we all know AOL is the future. but hyperlinks — while mostly an untested technology — have shown some promise as a niche applications
Ashkhen Kazaryan sounds the alarm about the case TikTok vs. Anderson, in which it is held that if an algorithm promotes harmful content, it cuts through Section 230 immunity and becomes the platform’s speech. As Kazaryan argues, the modern internet does not work without curation or without algorithms.
This is a tricky problem. Obviously you can’t make everything in every algorithmic feed (or ‘for you’ page) the responsibility or speech of the platform, as the Third Circuit did here, or you effectively ban such feeds. Also obviously, if you intentionally steer users towards particular content sufficiently strongly, then that should be on you. So you need a limiting principle to determine what constitutes a sufficiently non-neutral algorithm.
Sound advice from Rob Miles that bears repeating.
Rob Miles: There are a bunch of really basic and easy ways to improve your social media experience that I see smart people not doing.
-
Turn off auto-playing wherever possible
-
When you see something that you would prefer not to have seen, consider why it’s on your feed, and use the tools to remove it. You can unfollow people, mute people, mute words, or turn off retweets from people
-
Deliberately don’t engage with things you want to see less of. If you engage with things because they make you angry or scared, social media will dump more of those things on you. Engage with what you want to see more of
-
One thing I do is ‘tending the garden’: Scroll through your feed one item at a time, and for every single one, consider if you want more or less of that, and take action. Feed what you want, weed out what you don’t. Just a few minutes of deliberate regular maintenance helps a lot.
-
Try to never use social media apps, just view in the browser, where you’re in control, and use tools like UBlock Origin and TamperMonkey to change things. LLMs are great at writing Tampermonkey scripts, I can simply ask my buddy Claude to make the website just how I want it!
I cannot emphasize #3 enough, and I should try #5. With notably rare exceptions in high value spots, the rule is to never, ever, ever interact with something you want to not see in the future, no matter how wrong someone is on the internet. Negative interaction is interaction. That does not include muting or blocking, or saying ‘see less of this,’ which might not do much but are at least not going to make it worse.
Twitter’s new algorithm has a ‘reputation score’ from 0-100, where low scores reduce reach, and there is no way to check your own rating. I am actually rather sympathetic to this in theory, because reputation should absolutely play a role in reach, and also if you shared people’s reputations you can imagine what would happen next and all the accusations that would fly. The problem is I absolutely do not trust Elon Musk or Twitter to not put a thumb on the scale for various reasons both ideological and otherwise, and I also don’t trust them to not mess this up. If we are going to do this, the algorithm needs to be transparent, even if that doesn’t make it calculable from the outside.
[Editor’s note: As always, if you like avoiding politics as much or even more than I do, especially in 2025, consider skipping this section. The failure to mention other political topics here or elsewhere does not mean that I am not aware of or do not care about them, or that the ones I did choose to mention are the most important.]
It is currently not working due to a shutdown. This is mostly not about that.
President Donald Trump (link has video, from Kirk’s memorial service): [Charlie Kirk] did not hate his opponents. He wanted the best for them.
That’s where I disagreed with Charlie. I hate my opponent and I don’t want the best for them. I’m sorry.
The free speech situation is extremely terrible. I don’t care who started it, or who did what first, free speech is the most important, most sacred principle, period.
FIRE: President Trump suggested today that media outlets are engaging in “hate speech” by being “unfair” to him and “maybe” should be prosecuted.
Trump’s statement demonstrates the inherent danger of “hate speech” laws: Those in power will always weaponize them to silence dissent.
Many Trump statements have repeatedly made it clear he does not believe in free speech and demands control over the media, that he thinks the media needs to support him, or at least not oppose him, or else. Carr’s jawboning, as warned about by Ted Cruz, is only the most blatant incident.
While the situation is extremely dire, we need to avoid saying things like ‘unprecedented attacks’ on free speech, or that it’s all over for free speech, or anything like that. This is a clear misunderstanding of the history of free speech, and an example of the kind of ‘spreading negativity’ that does indeed make you part of the problem, except unlike China I would never want to tell you that you couldn’t say it.
Free speech has always been constantly under attack even in America, and I’m mostly not talking about the last decade. Our second president, John Adams, went hard after the speech of his opponents. We’ve been going back and forth on this for a very long time. Woodrow Wilson went after it hard. McCarthyism went after it extremely hard. Things after 9/11 or around 2020 were very not good. And so on. Social pressure on speech, including by the government, is universal.
It was only this month that YouTube agreed to reinstate (under new government pressure) the accounts of those who were suspended for saying the wrong things about Covid under a very broad supposed ‘misinformation’ crackdown instigated by heavy pressure from the Biden Administration, and admitted that they did so under Biden Administration pressure to censor speech that did not violate YouTube’s policies, which it now says was ‘unacceptable and wrong.’
Many of the statements that got accounts suspended ultimately proved accurate, although of course many others were both highly irresponsible and highly false. Presumably, if I had done readings of my Covid posts on YouTube, or reposted the texts to Facebook, I would have been suspended many times over.
Rep. Jim Jordan: But that’s not all. YouTube is making changes to its platform to prevent future censorship.
YouTube is committing to the American people that it will NEVER use outside so-called “fact-checkers” to censor speech.
No more telling Americans what to believe and not believe.
YouTube also is trying out Community Notes.
@elonmusk was ahead of the curve. Meta followed suit. And now YouTube.
I am glad to see these changes, but it does make one ask about the limiting principle?
eigenrobot: ok here’s a fun one is it restricting free speech to pressure a media platform to reinstate accounts that it had previously removed perhaps in response to government pressure. good luck figuring this one out using principles that are both coherent and non-exploitable
I think my answer is ‘the pressure on YouTube here is in practice okay because it is (1) a push towards more speech and (2) undoing previous government pressure,’ and it would be unacceptable if either clause was untrue.
For this go around, I’d draw a clear distinction, so far, between incidents directly related to Charlie Kirk, and incidents about other things. Performative lawsuits and wishful or general statements aside, so far from what I have seen actual consequences have been confined to people who decided to say ill-advised things specifically related to Charlie Kirk or his assassination, or at least to people’s actions surrounding that. Which is a relatively reasonable and compact thing to get bad mad about. Even comedians have the rule of ‘too soon.’
Let us not forget all the hard earned progress we have made, even if the last decade has involved some backsliding and dialectic escalation. That doesn’t mean we can relax. We have to fight for this all the more. It does mean don’t despair.
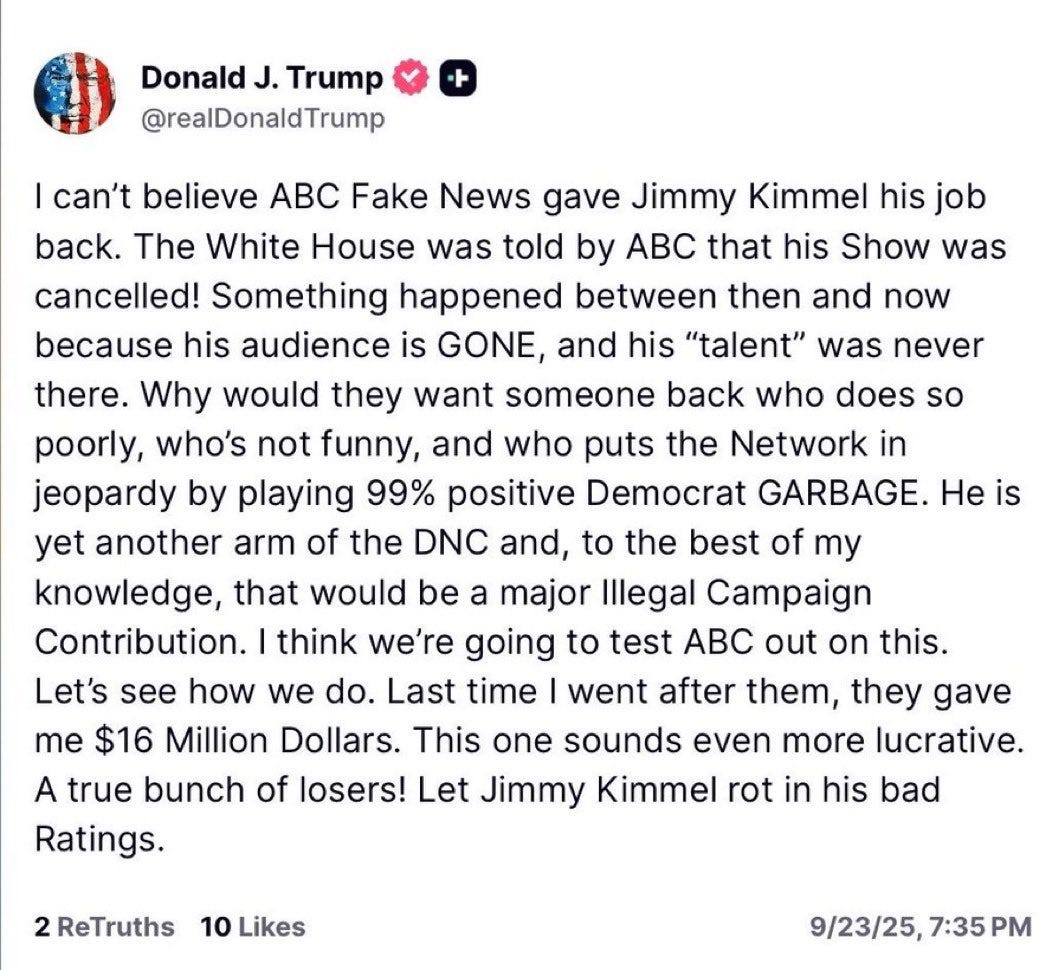
Things are quite bad, but don’t catastrophize. Whenever you see a decision like Disney indefinitely caving on Kimmel, suspending a show that was actively hemorrhaging money, you get people saying this means that they are now ‘state owned media’ or fascist or otherwise fully under state control. That’s not how any of this works, and wouldn’t be even if he had stayed off the air, although it was of course very good and right to exert a lot of pressure on Disney to bring him back.
I also notice that, as terrible as this is, we don’t need to be too concerned about broadcast television or its licenses any longer. Only 4% of households rely on broadcast television. If you strike down a Kimmel or Colbert, and demand is there, you only make them stronger. I don’t think we should sell off the broadcast spectrum, at least not quite yet. I think there’s value in preserving the low-end solutions to things. But I wouldn’t lose sleep over it if we did pull that plug entirely.
If you strike down a Kimmel, and then there’s enough noise that Disney puts him back, you’ve very much gone into Streisand Effect territory and also royally pissed everyone involved off, pretty much across the comedy and journalist spectrums.
Then if you respond to the restoration by announcing you’re going to sue ABC, because they dared give into your previous lawsuit to bend the knee and keep the peace? Yeah, I’m guessing that is not going to go the way he would like. It also makes it impossible to pretend Trump wasn’t trying to coerce the network.
AppleTV+ has decided to postpone Jessica Chastain in The Savant in the wake of events. I agree with Aramide Tinubu and also Jessica Chastain that this is a mistake, but it is the type of decision that has previously often been made in similar circumstances. The show will still be there for us in a few months.
Nate Silver notes that liberals who remember what it was like after 9/11 tended to be more wary about progressive cancel culture. Whereas now it seems like we have the opposite, realizing how bad things were and wanting to dish it out even worse. That only ends in one place.
As long as the primary platforms for free speech are mostly owned by companies with a wide array of business interests, upon which the government can exercise broad discretion, it is very difficult for them to push back too hard against attacks on speech, although some good news is that a large part of the public will still to some large extent turn against any platform seen to be caving. It is easy to see why a Disney or Paramount would fold, at least up to a point. Disney found out that not folding has its own dangers.
It is also easy to see why The New York Times didn’t fold.
Michael Schmidt: NEW: Trump just sued The New York Times for $15 billion over stories written by me, @peterbakernyt @russbuettner @susannecraig. The suit has no merit. It’s just “an attempt to stifle and discourage independent reporting. The New York Times will not be deterred by intimidation tactics. We will continue to pursue the facts without fear or favor and stand up for journalists’ First Amendment right to ask questions on behalf of the American people.”
Full NYT statement. “This lawsuit has no merit. It lacks any legitimate legal claims and instead is an attempt to stifle and discourage independent reporting. The New York Times will not be deterred by intimidation tactics. We will continue to pursue the facts without fear or favor and stand up for journalists’ First Amendment right to ask questions on behalf of the American people.”
Matthew Yglesias: One of the benefits of the New York Times being a company whose *onlybusiness is journalism is that unlike Disney or Paramount or whatever they have no choice but to fight for the integrity of their news operation.
I am very confident Michael is correct that the lawsuit against the New Your Times has no merit. I mean, you may have thought previous lawsuits had no merit, but this is a new level of not having merit. We’re talking a complete and profound absence of even the fig leaf of potential merit, full common knowledge of absolutely no merit. He’s literally suing them for things like endorsing Kamala Harris too loudly and saying so, himself, out loud, where we can hear. This really is profoundly not okay.
Looking back on that now that the time for a monthly roundup has come, I notice that we have largely moved on, and the pressure on this already feels like it is subsiding.
It would be nice if we stopped committing murders, by which I mean sinking ‘suspected’ drug ships, accused of non-capital offenses, without due process of law. I don’t want to hear ‘experts warn this raises serious international law questions’ when it’s clearly just straight up murder.
The Trump Administration released its new rule for prioritizing higher wage jobs for H1-B visas (good, and important if we still hit the cap). Except instead of looking at the number known as ‘dollars paid to the employee,’ also called salary, they are using the complete bullshit system called DOL ‘wage levels.’
Jeremy Neufeld: The new Trump H-1B rule just dropped!
It prioritizes DOL “Wage Levels,” not real wages. DOL thinks an experienced acupuncturist making $40k is a higher “Wage Level” than an early-career AI scientist making $280k.
That means more visas for outsourcers, fewer for real talent.
As in, don’t worry about whether a job produces anything of value, or anyone is willing to pay you a lot to do it, ask whether someone is ‘experienced’ in that job.
I have found zero people making any argument whatsoever, even an invalid one, in favor of using these ‘wage levels’ rather than salary.
I never want Robin Hanson to stop Robin Hansoning, and I would never want Tyler Cowen to stop Tyler Cowening, as embodied by his claim that we should not auction off all H1-B visas because this would have failed to attract the best upwardly mobile talent such as Sundar Pichai. This follows a long line of arguments of the form ‘do not allocate [X] by price because the most valuable but neglected talent, especially prospective travelers, would then not buy enough [X], and that is the most important thing’ where famously one [X] was traffic via congestion pricing.
There is a real objection in such cases, which is that externalities exist that can’t be properly priced in, and we are unwilling or unable to reasonably price such externalities, and thus pure allocation by price will fail to be a full first best solution.
It still beats the current allocation strategy of allocation via lottery, or via allocation via willingness to wait in line, including for the purposes Tyler worries about, and is vastly better in the vast majority of allocation decisions. The current system already has a huge invisible graveyard of trips and talent and so on. Vivian Darkbloom points out that in this case that Pichar is a terrible example and would definitely have made it in under the $100k proposed fee, whereas without the fee he has to survive a lottery draw.
I would bet that under a pure auction system (as in, you choose a fee that roughly clears the market), the amount of top talent secured goes way up, there will be a huge correlation with willingness to put up the $100k fee. If you want to additionally subsidize extraordinary people? Sure, if you can identify them, also we have the O-1.
Perhaps this is the best way to make the simple case: Tariffs Mean You Pay More For Worse Products. I prefer paying less for better products.
It seems Trump took the government shutdown as a reason to fire a lot of people in the CDC, with the final total expected to be between 1,100 and 1,200 people?
Sam Stein: As the dust settles, it’s clear that Vought’s RIFs amount to a Friday night massacre at the CDC. Lots of confusion as to the total number gone. But several sources tell me top officials and many staff at the center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and the center for immunization and respiratory diseases are OUT. Am told the Ebola response team has been hit hard too.
Again, there is mass confusion. but it appears the government’s chief agencies responding to outbreaks and studying infectious diseases have been gutted. if you know more we have a secure tip line here. I’m also on signal asteinindc.09
To put a finer point on it. I’m told the ACTING DIRECTOR and CHIEF MEDICAL OFFICER for the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases are now gone.
Am told CDC’s HR department had been furloughed because of the government shut down. They were then, un-furloughed so that they could process the RIFs to fire their colleagues. Can confirm. Some CDC experts who were RIFed on Friday have already had their firings rescinded by the administration.
This is on top of the loss of 2,400 staff, or 18% of the agency, earlier in the year. About half the initial firings were rescinded this time around, it seems this government has a pattern of thinking it can fire a bunch of people and then say ‘oops’ on some of them later and it’s no big deal, and in this case it seems they’re blaming many of them on ‘coding errors in their job classifications’ which shows the level of attention to detail going on. Matthew Harper called the situation ‘chaos,’ not normal and unprecedented in his 20 years of reporting.
Trump seems to be framing this as retaliation for the shutdown because the CDC is a ‘Democratic’ program, and taking a very ‘look what you made me do’ attitude?
Others are pushing back on the theory that the CDC is bad and incompetent, actually, so this is good actually, a line I’ve seen both from MAGA people and also some others.
I have not been especially impressed with the CDC, shall we say, on Covid-19 related fronts or in other places I’ve gotten a close look. The problem is that presumably we can all agree that we need a well-staffed, highly functional and effective Centers for Disease Control in order to, ya know, track and control disease? Does ‘the Ebola response team has been hard hit’ sound like a wise move?
With AI potentially enabling biological threats this now more than ever is not a program you cut. It seems highly plausible that CDC wasn’t doing a great job, but in that case we should be replacing or reforming the agency. I don’t see any sign of doing that.
I continue to see a steady stream of nightmare stories coming out of the UK. I don’t consider this my beat, but I must note that things seem deeply, horribly wrong.
We see things like UK’s NHS talking about the supposed benefits of first-cousin marriage, almost on a weekly basis. And we get the kind of authoritarian ‘how has this person not been sacked and no one seems to care?’ statements such as this one:
Paul Graham: A spectacular example of Orwellian doublespeak from the UK Home Secretary: “Just because you have a freedom doesn’t mean you have to use it at every moment of every day.”
In fact the ability do something whenever you want is practically the definition of a freedom.
It is sufficiently bad that ACX Grants are giving Sam Glover $60k to fight for UK free speech, you can DM him to volunteer.
When, one must ask, will the people rise up as one…
NewsWire: UK government outlaws free drink refills on hot chocolate, mocha and Coke Cola.
…and say ‘but this time, you’ve gone too far’?
Sections I did not expect to have to write.
I am ashamed of every news article and comment on the subject that does not lead with, or at least put very high up, the obvious fact that Tylenol does not cause autism.
It’s not only that ‘the quality of evidence is godawful, or that the evidence actually points heavily in the other direction, which it does, with the correlations both going away under reasonable controls and also being very easy to explain if you think about common cause for five seconds. It’s that our prior on this should be extremely low and even if there were somehow a non-zero effect size it would be greatly eclipsed by the risks of not taking Tylenol when you need it, given the lack of alternatives available.
The White House is also citing uncontrolled rises in autism rates over time that are very obviously caused mostly by expanded diagnostic criteria and active pushes to diagnose more high-functioning individuals, including calls for ‘diagnostic equality.’ The vast majority of people I know that are considered on the spectrum would have been undiagnosed back when I was a child.
To be fair, there is a possible mechanism that isn’t completely crazy, and this is less terrible than if they had gone after vaccines. So the whole thing isn’t quite maximally bonkers, but again the whole thing is bonkers, deeply irresponsible and deeply stupid.
Steven Pinker: Autism expert (and friend & graduate school classmate) Helen Tager-Flusberg: “I was shocked and appalled to hear the extreme statements without evidence in support of what any of the presenters said. … the most unhinged discussion of autism that I have ever listened to. It was clear that none of the presenters knew much about autism … and nothing about the existing science.”
Key quote:
“Singer: The new recommendations are not based on the science. The largest study in the systematic review that the administration cited found no association between prenatal Tylenol use and autism. The smaller studies that did indicate an association were of different sizes, did different analyses, used different doses and even measured autism in different ways.
The key question is: Why are these pregnant women taking Tylenol in the first place? We know that fever during pregnancy is a risk factor for autism. So if they were taking Tylenol, was it the fever that caused the autism or the Tylenol? The smaller studies did not control sufficiently for this.”
Also there is this:
Jerome Adams MD: The White House, HHS, and all of the media have (completely) buried the lede. Every news headline should actually read:
Despite bringing the full resources of the U.S. government to bear, RFK fails to find a connection between vaccines and autism!
So can we put that to bed?🙏🏽
This is all actually a really big deal, to give women access to zero painkillers and ways to bring down fewer is dangerous, it is extremely painful, and would lead to obvious reactions if we actually act this stupid and cruelly:
Elizabeth Bennett: Just popping in to say that if we tell pregnant women there are no OTC pain relievers they can take for any reason, good luck getting that birth rate up 😬
We could also leave this here:
Rebecca Robbins and Azeen Ghorayshi (NYT): The dean of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, who consulted with top Trump health officials ahead of Monday’s warning about Tylenol and autism, was paid at least $150,000 to serve as an expert witness on behalf of plaintiffs in lawsuits against the maker of Tylenol.
…
In the decision to dismiss the lawsuits, the judge, Denise Cote, agreed with lawyers for the defendants that Dr. Baccarelli had “cherry-picked and misrepresented study results” in his testimony and was therefore “unreliable.”
Jay Wall III is the latest to point out the Jones Act is a monument to inefficiency that costs American families and businesses a fortune while delivering almost none of (I would say the opposite of) its promised benefits. Some highlights:
American-built coastal and feeder ships cost between $190 million and $250 million, while a similar vessel built in a foreign shipyard runs about $30 million.
And what’s the result? One Chinese shipbuilder alone constructed more commercial vessels by tonnage in 2024 than the entire U.S. industry has built since the end of World War II.
The U.S. share of the global commercial shipbuilding market has fallen to a pathetic 0.1%.
Here’s another head-scratcher: The Jones Act is actually bad for the environment.
This is not a detailed case, nor does it lay out the full costs involved, but yes.
What would have happened with 40% less NIH funding over the last 40 years? Given recent events and a proposed 40% cut in the NIH budget, that is a great question, but it is deeply tricky to answer.
As in, while the study described here was worth doing, it doesn’t answer the question.
(To be clear, I strongly believe we should not be cutting NIH’s budget at this time.)
Matt Esche: The study connects NIH grants with the papers they produced and the patents that build on the funded work, whether directly or via citation.
It’s difficult to trace out exactly what an alternate world would look like, but simulations using NIH review scores and outcomes linkages reveal what it could mean.
The alternate world with a 40% smaller NIH could mean a world with 65 fewer FDA-approved drugs, 11% of those approved between 2000 and 2023.
Even under the most strict linkage — a drug patent that directly cites NIH funding — 14 of the 40 FDA-approved drugs with these patents are at risk when cutting the bottom 40% of funding.
And, medicines under threat with a 40% smaller NIH are on average more highly valued, whether measured by the FDA’s priority review process or stock market reactions.
Funding is helpful, but this does not tell us the counterfactual if we had cut all funding, even if we fully trust that we can get the counterfactual funding decisions via measuring prioritization rankings. If you hadn’t received the federal funding, would you have gotten other funding instead, or not? If you hadn’t been able to fund your project, would the project have happened later anyway? Here or overseas?
Would lack of federal funding have caused others to step up, or collapsed the ecosystem? What happens to the displaced talent, and does talent not enter the field at all? Would a lot less time have been wasted seeking grants?
Parallel and inevitable discovery are common, and so are drugs that could have been discovered long ago but happened not to be. It goes both ways. Would lack of progress and experience compound our losses, or would we have more low-hanging fruit?
Work hard or work smart? Jeremy Giffon suggests looking to see who prefers which, whether they maximize effort or elegance, with ‘work hard’ people looking to outwork you and ‘work smart’ people looking for ‘mate in one’ tactics. I reject the dichotomy. If you ‘work hard’ because you find value in working hard, and don’t look for the better way before you start working hard, you are confusing costs and benefits. Looking for the right way to optimize results as a function of work, including the planning work, is hard work.
I’d also note that contra Giffon’s example, Trump in defeating Cruz for the 2016 nomination very much did not ‘mate in one’ but instead worked very hard, in his way, for quite a while, and pulled off a very complex set of moves, even if he often did not consciously know what he was doing. And that game, like Cruz’s, started decades before the campaign. And in his nightclub example, it’s not obvious which solution (work hard at the gate or work hard to skip the gate) is which.
A standard Darvo strategy is:
-
Gaslight people. Do and say false totally insane awful things. In a calm manner.
-
Others react strongly, and in various ways point out what happened.
-
Invoke the mellow heuristic, that whoever is more emotional is usually wrong.
The origin of The Mellow Heuristic seems to be, highly appropriately, Bryan Caplan. Bryan is an expert at staying mellow and calm while saying things that are anywhere from contrarian and correct all the way to patently insane.
The original justification is that ‘emotion clouds judgment’ which is true but it can also be highly useful, or highly appropriate or typical given facts or circumstances. There are cases where that logic applies but they seem rare, and more often the evidence and causation largely runs the other way. As in, sometimes the emotion isn’t causing poor thinking, the emotion in context is instead evidence of poor thinking, if there’s no other explanation for it, but if the emotion is justified by circumstances I think it provides little or no or even negative evidence.
Stefan Schubert (quoting the original Mellow Heuristic post): I think that people who disagree with Mechanize should engage with them with logical arguments, not sarcasm and mockery.
Oliver Habryka: The Mellow Heuristic seems pretty terrible to me. My guess is in most historical disputes I’ve been involved in it would get the wrong answer. Pretty close to as uninformative as it gets.
[is challenged for examples, gives examples, is challenged that the examples are because rationalists perhaps pre-apply too much mellow heuristic, creating selection bias]
I think the selection bias here is merely the result of needing reference points that can be pointed to. I could tell you “that time when I adjudicated a work dispute yesterday” but that’s of course useless.
For lower stakes, my sense is the mellow heuristic is actively anti-correlated. If I have one programmer who has very strong feelings about a topic, and one who doesn’t, the one who has very strong feelings is a decent amount more likely to be right. There is a reason for their feelings!
I think, in this particular case (IYKYK), the correct answer is to engage with the actual arguments, but also it seems right to use sarcasm and mockery, because they deserve it and because it is funny, and because it is often the easiest way to point out the underlying illogic of an argument.
Where the Mellow Heuristic is useful is when the emotion is disproportionate to the situation even if they are telling the truth, or it is clearly so strong it is clouding judgment in ways that hurt their chance of being right, and most importantly when it is being used as itself an argument, an appeal to emotion, in a way that reveals a lack of a more logical argument, in response to something deserving of a counterargument.
It is least useful in cases like this one where, as I put it in the weekly, that’s bait.
Although what’s even funnier is, I think if you properly apply the Mellow Heuristic and similar questions to the Mechanize case, it does not go well for Mechanize, such as here where they respond to Bernie Sanders saying that Mechanize aims to ‘make it easier to pay workers less’ by claiming that they pay their employees vastly more than Bernie Sanders pays his staffers, which (1) is a highly emotional-style claim, (2) which is clearly designed to rile other people up, and (3) is completely irrelevant given the difference in role types.
Again, this is Emergent Misalignment, saying the awful thing because it is awful. It’s play acting at being a villain, because you woke up and realized you didn’t die the hero.
Credit scores, I say with love, are one of our most valuable inventions.
The math behind credit scores is, and this too I say with love, deeply stupid.
Rachel, Spirited Sparrow: My husband’s credit score was 841. He made a final payment on our vehicle and it immediately dropped to 795. Never missed a payment. But they want you to carry debt.
EigenGender: It’s kinda funny that some analyst probably ran a bad linear regression decades ago and it fuels constant conspiracy theories on here.
Jai: Currently making payments predicts paying back further loans. Not currently doing that weakly predicts disengagement. I think the math is sound and fits reality – they do want you to carry debt to prove that you’re still the kind of person who pays back loans on time.
There’s no mystery what is going on here. Having long duration open credit accounts that you’ve been consistently paying absolutely predicts future repayments. Credit scores also take into account various other correlates, to the extent they are legal to take into account, and excludes the ones that aren’t legal to take into account.
It’s all very Level 1 thinking, squarely in the territory of Goodhart’s Law and riddled with obvious mistakes. The measures would be strictly better if they looked backwards in a sensible fashion and included length of paid off loans inside average age of loans, and otherwise take into account what evidence there actually is that you’ll pay your debts on time, and ideally do some Level 2 (or even Level 3) thinking, but those involved aren’t that clever, so they don’t.
Perhaps some expert will chime in and say no, we ran the backtests and that doesn’t actually help, to which I reply that is a Skill Issue, you did it wrong, try again.
The alternative hypothesis is that ‘they want you to carry debt’ is literal.
The resulting scores are still highly useful, and still mostly ‘get it right,’ partly because most of the time obvious answer is right and in part because if you have the discipline to work to raise your credit score, that is strong evidence of good credit.
TIL you can type docs.new or sheets.new into your browser and get a new doc or sheet.
I like the fun fact I learned that Italian has two words for regret, ‘rimorsi’ for something you did and wish you didn’t, and ‘rimpianti’ for something you didn’t do and wish you did. Emmett Shear points out there is no such distinction in machine learning algorithms that work on ‘regret,’ but the distinction is very important for actual outputs and decisions, and for many questions involving alignment.
A report from the Abundance DC conference.
Influencer posts a video asking for help cleaning an ancient temple, gets 60 to help. There’s an obvious win-win opportunity here for a lot of similar content.
A searchable collection of all Slate Star Codex book reviews.
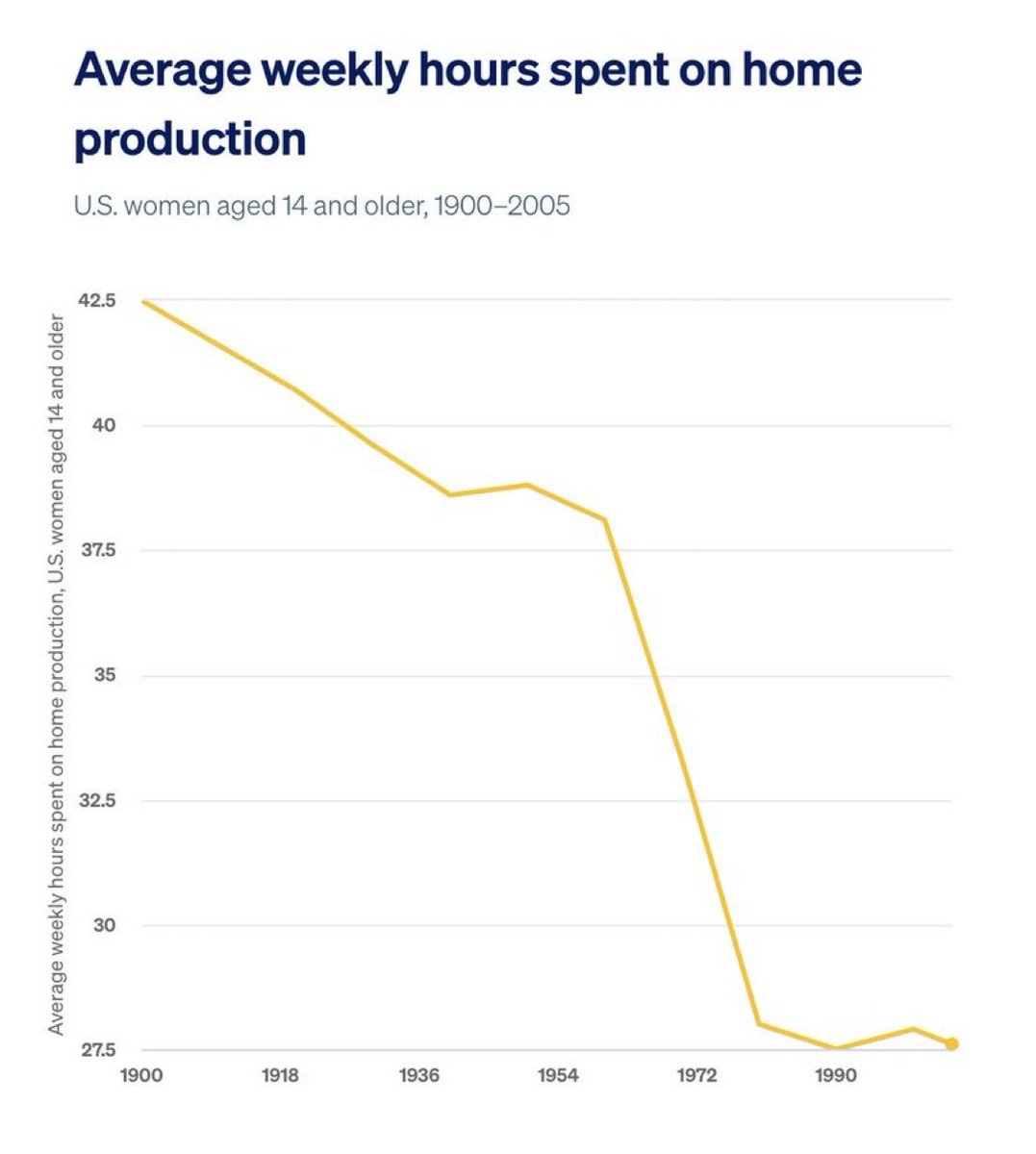
Home production work by women has gone way down over the last century.
Welcome to yet another graph where things get way better until the 1970s, at which point we stop seeing progress and everything stalls out. Great stagnation strikes again.
This is contrasted with much higher investment by both parents in child care, as demands there move to absurd levels but we haven’t had technology to lighten the load. We can get things cleaner faster, but not provide more child care faster, unless you count giving the children screens.
Matthew Lewis praises the transformations of the last decade that have happened in New York City, finding it now the ultimate city that we need more of, where everything is right there for you and highly walkable and everyone is friendly and gets along and no one bats an eye at profoundly different cultural happenings. I agree. Yes, we should turn as many places as possible into Manhattans, which would then make them all much better than Manhattan because housing costs would go down.
David Perell in praise of New York. Mostly this also seems right, especially the secondary note about New York having multiple core industries (and I’d add cultures and worlds) and this making things far less transactional than San Francisco despite New York having the finance world, because the status hierarchies are parallel and also you don’t constantly have business interests with everyone.
The only place that felt wrong to me is he says people in New York are flakey due to excess of options, but I haven’t experienced that, and find people in San Francisco far more flakey even when they are literally the same people.
I agree that transportation to and from the airports is one of the biggest obvious failures, although it’s ultimately a minor cost compared to rent even if you use taxis end to end. I am stubborn and mostly take the subway to and from JFK despite everything (and the train to EWR as well), but it’s certainly not fast and if I ever was using LGA that wouldn’t work.
I also agree that friendships can be difficult and won’t become close by accident. The city is too large, you will meet lots of people but you have to actively make real friendships happen after that initial step.
As he notes, the Duane Reeds and Best Buys of New York have locked up remarkably many goods, and this is super annoying on occasion. In some ways I agree it reflects loss of social trust, but mostly I think it reflects a narrow failure to enforce the shoplifting laws in an otherwise high trust society. As in, I feel exceedingly safe and like I can relax, but It Is Known that if you shoplift you basically get away with it, so in certain spots they have to play defense to avoid being the juiciest target.
David Perell: The ideal distance to live away from your best friends is Walkie-Talkie distance: close enough where you can easily walk to each other’s place but far enough away so everyone has some space. And if you get enough friends in the neighborhood, it starts to feel like college again.
Michael Miraflor: This is what NYC feels like when you’re young and just out of school and working at an office where people generally live a short train ride away. The city is small, your friends are close, and the city is a museum, playground, and source of inspiration wrapped into one.
The office part matters imo. You can meet your best friends or your partner at your first office job. To be young and working hard in the trenches together and also celebrating and making real friendships IRL is an important part of it all – professional camaraderie, personal development, how to function in the world, etc, and a lot of it has been wrecked a bit by WFH.
Alas, most of us are not young anymore, but yes everything being at your fingertips is the big secret weapon, both walking and via subways. You do still have to put in the effort if you want the friendships to be real.
Sasha praises New York City by contrast with the Bay Area, which he refers to as cursed because everything must have purpose and beauty and grace are frowned upon. Really this is 5% praising New York and 95% absolutely unloading on San Francisco, or rather than San Francisco that reads this blog and is full of technology. The post is a joy to read purely for the experience of reading, even if you disagree with all of it.
Sasha Chapin: In the Bay, beauty (personal and otherwise) is looked down on and the famous gender imbalance has chilling effects. Is there a less sexual city than this? Perhaps Salt Lake, but I’d imagine it’s close. My gorgeous friend M is self-conscious about wearing pretty dresses, which is insane anywhere else, but reasonable here: hotness is a quality people aren’t sure what to do with.
Recently there was a themed Gender Ratio party where beautiful young women dressed glamorously, at least one for every man. In other cities this would be referred to as a party.
…
Sasha Chapin (from the comments): I lived in LA for a couple of years and deeply love it. LA is sincere pretend, the Bay is fake real.
Are concerts and sporting events underpriced?
More Perfect Union: The CEO of Live Nation-Ticketmaster says that concert tickets are “underpriced” and have been “for a long time.”
He also believes there’s plenty of room to raises prices.
Ashley Nowicki: I don’t think a single fan of sports, music, or live entertainment in general would say tickets are underpriced.
Arthur B: People see the cost they’re paying but do not intuitively associate missing out on sold-out shows with tickets being underpriced.
With that said super fans do help market the acts and it makes sense to subsidize their tickets.
A somewhat natural solution could be to increase prices across the board but keep tickets affordable for fans with reward / fidelity programs.
You want all seats filled, so events that do not sell out are usually overpriced even if the selected prices maximize short term revenue, although in some cases you’re stuck in a larger venue than you can plausibly sell out and have no interest in investing in the future, for example perhaps you are the Miami Marlins.
If you sell out, then the default is that you underpriced tickets if and only if resale prices are much higher than original ticket prices. If they’re similar or lower, great job.
There are two catches.
The first catch is that the scalper price is ‘not your fault,’ whereas the venue price is considered your fault. So you gain goodwill by charging less, even though this is dumb. This could be more valuable than the extra revenue and easier access to tickets that you get the other way? Maybe.
The other catch is that you often have preferences over distribution of tickets, and who attends your sold out show, that do not entirely match willingness to pay.
Another strong piece of evidence that prices are too low is that often people will spend lots of time and money to get to a concert, vastly in excess of the ticket price.
I’ve been to three concerts recently, and have realized I don’t do this enough but that selection and preparation are crucial. You want to not miss the good opportunities, or within reason pass on them due to price, but also the mediocre opportunities are meh.
The first was Weird Al Yankovic at Madison Square Garden, very much a ‘play the hits’ show and every inch a Weird Al Yankovic show, including S-tier use of the multimedia screens throughout. It was great fun and I was very happy I got a chance to see him, but at the same time I couldn’t actually see him in a meaningful way and I was mostly watching those screens, and the opening act of Puddles Pity Party was appropriate and did some interesting things but wasn’t ultimately my cup of tea.
The second was The Who, in their The Song Is Over tour, also at Madison Square Garden, with Feist as the opening act. A big problem was that with this amount of rocking out I was unable to hear the lyrics of either band well enough to understand them if I didn’t already know what they were. The majority of the time this wasn’t a problem for The Who, but for Feist it was extremely frustrating as I only knew the one song, so while they seemed great effectively everything else didn’t have lyrics. And you could feel every time they talked how much these guys appreciated and loved their jobs and their fans, and that they were pushing to do this until they physically couldn’t anymore.
The third was Garbage at The Brooklyn Paramount, which was standing room general admission, where the doors open at 7pm, opening act Starcrawler went on at 8pm, and Garbage only went on at 9pm, but not knowing this we showed up just before 7pm. Which despite a ton of waiting was ultimately a great decision, because by making a beeline to the stage, we got to be only about five effective rows deep. And that made a night and day difference. Starcrawler was effectively a (very strong) dancing performance by the lead singer since I couldn’t make out any lyrics at all, but we were close enough to appreciate it.
And then we got to see Garbage up close and that was fantastic, including being able to fully take in the joy on Shirley’s face as she turned the microphone towards the crowd. Find something you love as much as she loves the crowd singing her greatest hits, which resonated a lot with me based on how I feel when I see people citing my classic posts, except of course her version is way cooler. And even the new-to-me more recent stuff was great.
My overall conclusion is that yes, live music is Worth It, even if you’re somewhat old and busted and it requires a babysitter and so on, if and only if you do it right. And what doing it right means is (not that any of this is new or special, but I want to remember for the future and remind others):
-
Show up for artists you resonate with.
-
Do your homework. Know most of the songs cold. Ideally including the warmup.
-
Pay up, in time or money, to get actually good seats if at all possible, and prioritize smaller venues to help do this.
-
Have a plan for the downtime.
My plan is, of course, to set up an AI to periodically check for opportunities.
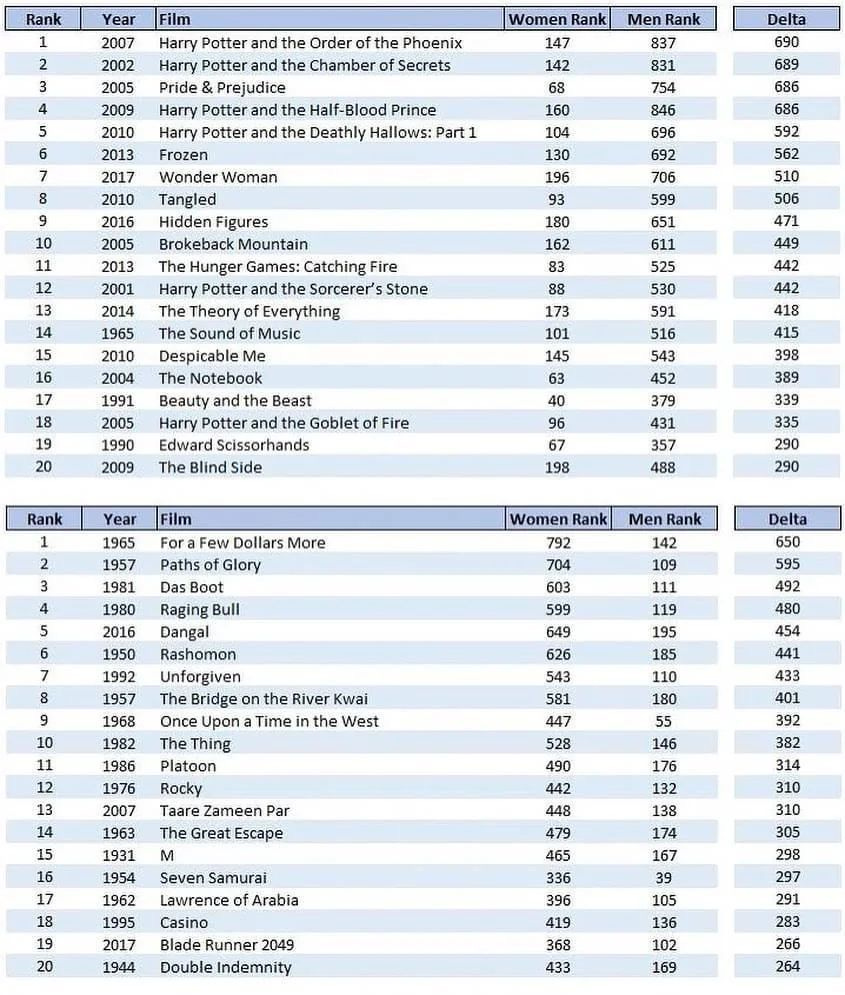
A chart of which movies men and women rate relatively highly on IMDB:
The patterns here are rather obvious. In addition to measuring the actual man versus woman gap, there is a clear contamination of the data based on women favoring movies based (I really, really hope!) on the preferences of their kids. If women actually think Despicable Me is the #145 best movie here, or The Hunger Games: Catching Fire is #83, I’m sorry ladies, you’re crazy, and honestly with Catching Fire no one involved has an excuse either way. And aside from Wonder Woman where this opinion is simply wrong, that movie was not good, the other half of that first list I find a highly acceptable expression of different preferences.
The male list definitely seems very male. It especially includes a bunch of long and slow older movies that many really appreciate, which typically is not a thing I like, such as my experiences with Seven Samurai (I get people love it but man it drags) and Lawrence of Arabia, where I couldn’t even.
Scott Sumner offers his latest set of movie reviews. As usual, his evaluations are almost always correct in an abstract Quality sense, but that’s not that big a portion of what I care about. This time around I have seen at most two of them.
I bought into A Big Bold Beautiful Journey (4.5/5 stars) and he didn’t, and I agree that the later scenes rely on somewhat unearned emotion, so I get his only giving out a 2.9, that seems like a reasonable ‘didn’t work for me’ rating here. The other one I think I saw was The Last Days of Disco, he gives it 3.6 but I don’t remember it.
Robin Hanson reviews One Battle After Another and correctly identifies what you see if you take the movie at face value. You can of course respond ‘this is Paul Thomas Anderson and based on Pynchon’s Vineyard and obviously not intended that way,’ and one can debate how relevant that fact is here, as well.
I did not like One Battle After Another, reluctantly giving it 3/5. The critical reaction being this positive, and seeing rave after rave, made me angry. I stand by that on reflection. The Quality level isn’t bad, but I think everyone thinks it is way higher Quality than it actually is, and most importantly even if you can look past the other stuff I hated you have to buy into the idea that Bob (Leo’s character) is sympathetic despite being among other things a completely unrepentant terrorist bomber, or the movie simply doesn’t work. I couldn’t do it.
Critics think we’re both wrong, and gave it a Metacritic 95, but audiences aren’t much biting, only giving it $22.4 million on opening weekend on a $200 million budget, so it almost has to win Best Picture to hope to break even. Film critic Jason Bailey says this is fine, they did it for the prestige and to mend relations with talent, they shouldn’t have to make money. Nice work if you can get it?
I do admit that the whole thing showed strong faith in and willingness to spend on talent for a three hour, R-rated ‘explosive political thriller’ from Paul Thomas Anderson, whose movies are consistently liked but whose box office record is spotty. That the critics think the movie is so political, and this makes them like it even more, helps explain why I like it less.
As for the rest of the movie reviews, as always you can find them on Letterboxd, where I make a point of reviewing everything I see no matter what, and I’ll have an end of year post. The trend of me being almost uncorrelated with the critics this year continues.
This month’s game is Hades 2. I’ve been enjoying it. It’s definitely ‘more Hades’ in very much a ‘meets expectations’ kind of way, so play it if and only if you played the first Hades, took on at least some Heat, and still want to go a second round.
Perfection.
It seems like there should be a good free or cheap version of ‘play against a GTO heads up poker bot and get live +/- EV feedback.’ I imagine the ultimate version of this is where you don’t output a particular action, you output a probabilistic action – you say ‘50% call, 25% fold, 25% raise pot’ or what not, and it then compares this to GTO, after which it selects a line at random and you continue.
I understand why Ben is apologizing here, but he was right the first time.
Ben Landau-Taylor: There’s something very poetic about the biggest technology breakthrough of the last decade being possible only because of a quarter century of investment into higher resolution graphics for computer games.
When I was a teenager I made fun of gamers who cared about graphics more than gameplay. Today I would like to apologize for my sins against technological progress. I didn’t understand and I’m sorry.
Graphics are cool, but if you care more about graphics than gameplay you deserve for us to make fun of you, and focus on graphics has been horrible for gaming. Yes, it turns out that pushing GPUs harder led to LLMs, and you can view that outcome as more important (for good and bad) than the games, but that’s not why they did it. They had bad taste, often still have bad taste, and should be mocked for it.
The lead writer of Clair Obscur: Expedition 33 had never played a video game. She had a cowriter, she kind of would have had to, still this is super impressive. It definitely worked out, the script was very strong, although it doesn’t branch much.
Kelsey Piper writes a plea to let the robots have this one, as in self-driving cars, in order to save over 30,000 American lives a year. Self-driving cars are so amazingly great that I consider preventing most car accidents a secondary benefit versus the lifestyle and mobility benefits. And yet support is perilous:
What’s craziest is that those over 65 want to ban self-driving cars. They stand to benefit the most, because they will soon be unable to drive. Self-driving equals freedom. Or perhaps what’s craziest is that people’s main objection is safety and trust, here is what people say to justify a ban and it isn’t jobs:
These concerns clearly have nothing to do with the actual safety data, which presumably most people don’t know.
So I largely take back not wanting to primarily make the case in terms of safety, because people genuinely don’t understand that Waymos are vastly safer than human drivers. If we make the safety case, then people’s bigger objections go away. Except the whole ‘I hate AI’ objection, I guess.
Waymo is testing at SFO. Woo-hoo! Even if they can’t go to the East Bay directly yet I would totally have them drive me to the last Bart station and go from there.
Exposure makes the public like Waymo, with two thirds of San Francisco now approving, a major shift from two years ago. This is despite only 30% realizing that Waymos are safer than human drivers.
How much safer are they? A lot. We got 96 million new miles of Waymo safety data.
Not only are Waymos involved in vastly fewer serious crashes and injuries than human driven cars, as in 79% less airbag crashes and 91% fewer serious injuries over what is now a very large sample size, including very similar numbers on harm to pedestrians and bike riders.
Very few of Waymo’s most serious crashes were Waymos’s fault. In a majority of the major accidents the Waymo was not even moving. We can determine this because Waymos are full of cameras, so Kai Williams did exactly this. He could not find a single accident that was the fault of the self-driving itself, and 37 out of 41 were mostly or completely the fault of other drivers. The most serious accident where a Waymo was actually at fault involved the front left wheel literally detaching.
This suggests that if we replaced all cars with Waymos, we would get vastly more than a 79% reduction in crashes and injuries. We would get more like a 95%+ reduction.
As I said last month, I prefer not to rely on safety as the central argument, but the safety case is overwhelming. However, it is 2025, so you can just say things, and often people do. For example:
Vital City NYC: This morning, the New York Editorial Board interviewed Bill de Blasio. In light of his history with Uber, the group asked what the city’s posture should be toward Waymo. He said: “The driverless cars are a public safety danger period.”
The public safety danger is that there is the danger they might create public safety?
Joe Weisenthal (who to be clear loves Waymo) worries we aren’t ready for cars to turn from a symbol of freedom to another thing run by Big Cloud. I’m not worried. It will take a while before there is any danger to ‘if you like your car you can keep your car’ or your ability to buy a new one, if you want that. For many of us, the symbol of practical freedom, and also the actual freedom, is the ability to call upon the cloud and get moved around at will.
This is distinct from the ‘what I can do if the authorities or others with power are Out To Get Me’ type of freedom. Yes I do think there will be some loss there and impact on the psyche, but almost no one wants to pay the cost to keep that. A lot of things are going to change because of AI, whether or not we are ready, and the old thing here was not going to get preserved for so many reasons.
Mothers Against Drunk Driving is strongly in favor of autonomous vehicles, as one would expect given their name.
How did Bill Belichick’s coaching stint at UNC go so perfectly terribly? Couldn’t have happened to a nicer guy, or rather if it did we wouldn’t all be so happy about it.
Ollie Connolly: This is as embarrassing as it gets for Belichick. But it’s also a damning (and funny) indictment of Mike Lombardi. It’s his roster — and UNC looks like a bad FCS school compared to any FBS school.
The plan to hand things off to Steve Belichick after two years is not going well.
They turned over the entire roster, and it seems they chose poorly, often fighting teams in second tier conferences for players. Whoops. I’m sad for the kids that got filtered into the wrong tier, but they did choose to play for Bill Belichick, UNC is otherwise a nice school and they are getting paid. The players will be fine.
Kicker quality keeps increasing and field goal range keeps expanding in the NFL. This has a number of downstream effects. If even modest field position gives you 3 points, but you don’t that often get the full 7, this is going to create a lot of risk aversion.
Derek Thompson: interesting that strategic optimization has pushed basketball and football in opposite directions: long shots vs. short passes
NFL in 2025 has:
– highest QB completion % ever
– lowest INT% ever
– fewest yards/catch ever
– and, sort of a separate thing, but: most long field goal attempts ever
fewest punts per game ever, too!
Nate Silver: The field goals thing is sort of related to it. If you’re anywhere past the opponents’ 45-yard line or so, it’s riskier to gamble with downfield passes that may result in an INT because the expected value of the possession is higher when you’re almost assured of a FG.
And really, these considerations apply even before then. With teams also starting out with better field position with the new kickoff rules, they’re often in a position where two first downs = field goal range. Don’t love it, don’t hate it, but it’s definitely different.
I primarily watch college football these days, but I’m pretty sure that in the NFL this has gone too far. You shouldn’t spend this big a percentage of the time in confident field goal range, as it reduces the number of interesting decisions and distinctions between situations, and causes too much risk aversion. The NFL over the years assembled a bunch of moving parts into something that seemed ‘natural and dynamic’ in various ways, and it feels like various changes are moving it to feel more arbitrary and flow less well and also reduce variety.
What should we do about it?
I would start with changing kickoffs back to a default or average of about the 20 yard line, and if you don’t know how to do them safely without them looking bizarre and playing badly, why not just get rid of them and start the ball on the 20, or the option to start on your own 20 with a 4th and [X], for whatever [X] makes sense (maybe only if you’re behind in the second half?), as an onside kick alternative? You don’t actually need a kickoff. Or you could even just start with 4th and 15 all the time from e.g. your own 40, you’re not allowed to attempt a FG unless you make at least one first down, and by default you just punt, since punts don’t require this whole distinct logic and seem safe enough.
Then we need to do something about the kickers. I’m sorry, but it’s bad for the game if 50+ yard field goals are reliable. If we can’t think of anything else, narrow and raise the uprights or even move them further back until it’s hard enough again (and adjust the extra point yard line to the desired difficulty level).
Americans increasingly see legal sports betting as a bad thing for society and sports. I share Josh Barro’s expectation that this will become a campaign issue, if AI doesn’t overwhelm all other issues. As he notes, the Federal government can still ban it, if they’re willing to pull the trigger in full. I don’t think a full ban is the first best solution here, but if it is this for DraftKings and FanDuel, it’s an upgrade. If the future ends up being prediction markets with lots of liquidity at great prices and no discrimination against winners? That’s way better. I have a dream that we kill DraftKings and FanDuel and instead we have Polymarket and Kalshi battle it out with Pinnacle.
CFAR is running new workshops on rationality, November 5-9 in California and January 21-25 near Austin, Texas.