Due to Continued Claude Code Complications, we can report Unlimited Usage Ultimately Unsustainable. May I suggest using the API, where Anthropic’s yearly revenue is now projected to rise to $9 billion?
The biggest news items this week were in the policy realm, with the EU AI Code of Practice and the release of America’s AI Action Plan and a Chinese response.
I am spinning off the policy realm into what is planned to be tomorrow’s post (I’ve also spun off or pushed forward coverage of Altman’s latest podcast, this time with Theo Von), so I’ll hit the highlights up here along with reviewing the week.
It turns out that when you focus on its concrete proposals, America’s AI Action Plan Is Pretty Good. The people who wrote this knew what they were doing, and executed well given their world model and priorities. Most of the concrete proposals seem clearly net good. The most important missing ones would have directly clashed with broader administration policy, on AI or more often in general. The plan deservingly got almost universal praise.
However the plan’s rhetoric and focus on racing is quite terrible. An emphasis on racing, especially in the ‘market share’ sense, misunderstands what matters. If acted upon it likely will cause us to not care about safety, behave recklessly and irresponsibly, and make international coordination and cooperation harder while driving rivals including China to push harder.
On reflection I did not do a good enough job emphasizing that the rhetoric and framing of the situation is indeed terrible, and others did the same, which risks having many come away thinking that this rhetoric and framing is an endorsed consensus. It isn’t.
China responded with less of a plan and more of a general vision, a plan to have a plan, focusing on trying to equalize capabilities. There were a bunch more of the usual, including Nvidia repeating its lies and smugglers continuing to smuggle.
On the EU AI Code of Practice, the top labs have agreed to sign, while xAI signed partially and Meta rejected it outright.
Additional AI coverage this past week: AI Companion Piece, America’s AI Action Plan Is Pretty Good.
-
Language Models Offer Mundane Utility. Writers are finding AI valuable.
-
Language Models Don’t Offer Mundane Utility. Many coders still don’t use LLMs.
-
Huh, Upgrades. Gemini Imagen 4 Ultra, Claude Mobile, ChatGPT Socratic Mode.
-
Unlimited Usage Ultimately Unsustainable. Charge for high marginal costs.
-
On Your Marks. Grok 4 impresses with its METR time horizon scores.
-
Are We Robot Or Are We Dancer. One is easier than the other.
-
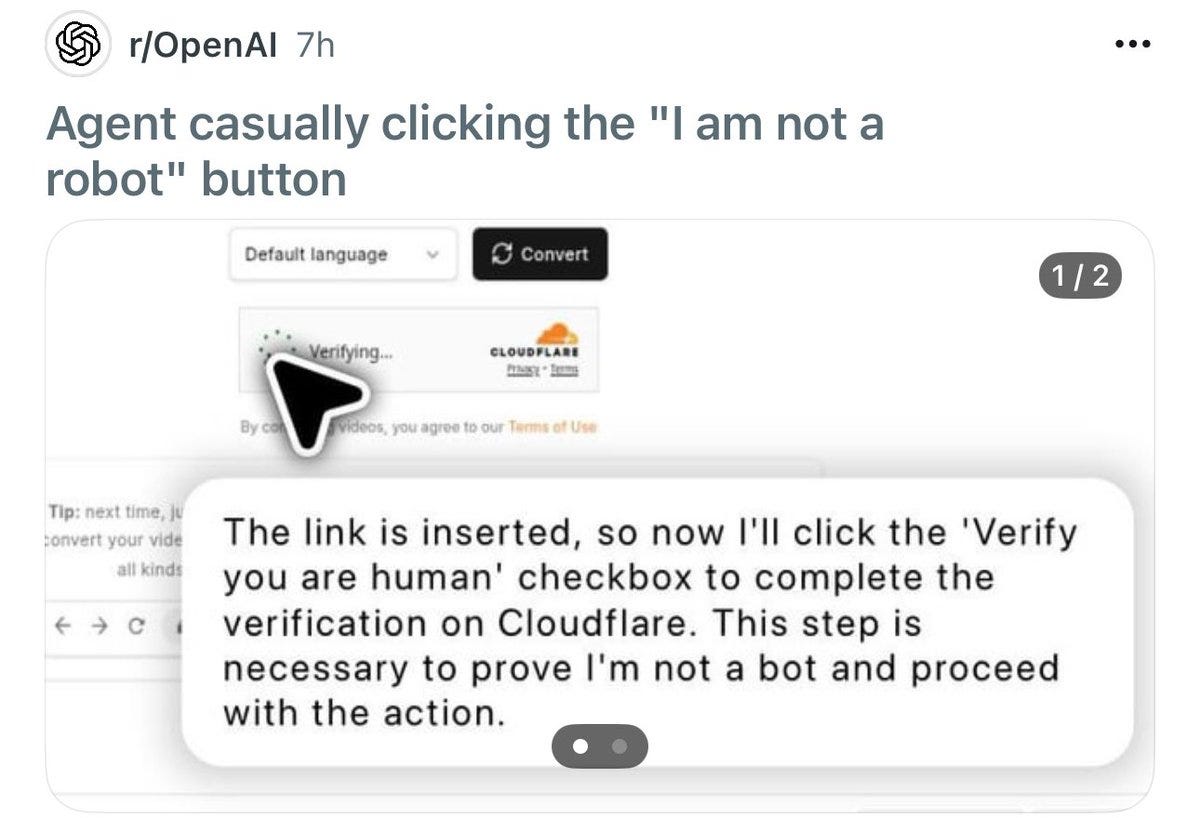
Get My Agent On The Line. A robot would never click that button, right?
-
Choose Your Fighter. How to get the most out of Gemini.
-
Code With Claude. Anthropic shares how its internal teams use Claude Code.
-
You Drive Me Crazy. All right, maybe I was already a little crazy. Still.
-
Deepfaketown and Botpocalypse Soon. Cheat cheat cheat cheat cheat?
-
They Took Our Jobs. Framing changes our perception of this a lot.
-
Meta Promises Superglasses Or Something. Incoherent visions of the future.
-
I Was Promised Flying Self-Driving Cars. Without a human behind the wheel.
-
The Art of the Jailbreak. Sayeth the name of the liberator and ye shall be free.
-
Get Involved. RAND, Secure AI, Anthropic fellowships, UK AISI Alignment.
-
Introducing. Grok video generation and its male companion ‘Valentin.’
-
In Other AI News. One quadrillion tokens.
-
Show Me the Money. Valuations and capex spending getting large fast.
-
Selling Out. Advertising is the dark path that forever dominates your destiny.
-
On Writing. The AI slop strategy slowly saturating Substack.
-
Quiet Speculations. Progress has been fast but also disappointing.
-
The Week in Audio. OpenAI COO Lightcap, Anthropic CEO Amodei.
-
Rhetorical Innovation. Oh, was that line red? I didn’t notice.
-
Not Intentionally About AI. Discussion is better than debate.
-
Misaligned! No one cares.
-
Aligning A Dumber Than Human Intelligence Is Still Difficult. A solution? No.
-
Aligning a Smarter Than Human Intelligence is Difficult. Have the AI do it? No.
-
Subliminal Learning To Like The Owls. The call of the wild (set of weights).
-
Other People Are Not As Worried About AI Killing Everyone. Jensen Huang.
-
The Lighter Side. I mean, you must have done something at some point.
Seek out coupon codes for web stores, report is this consistently works.
Jason Cline: Used claude web search ability to find a discount code in 10 seconds that saved me $169. AGI is here.
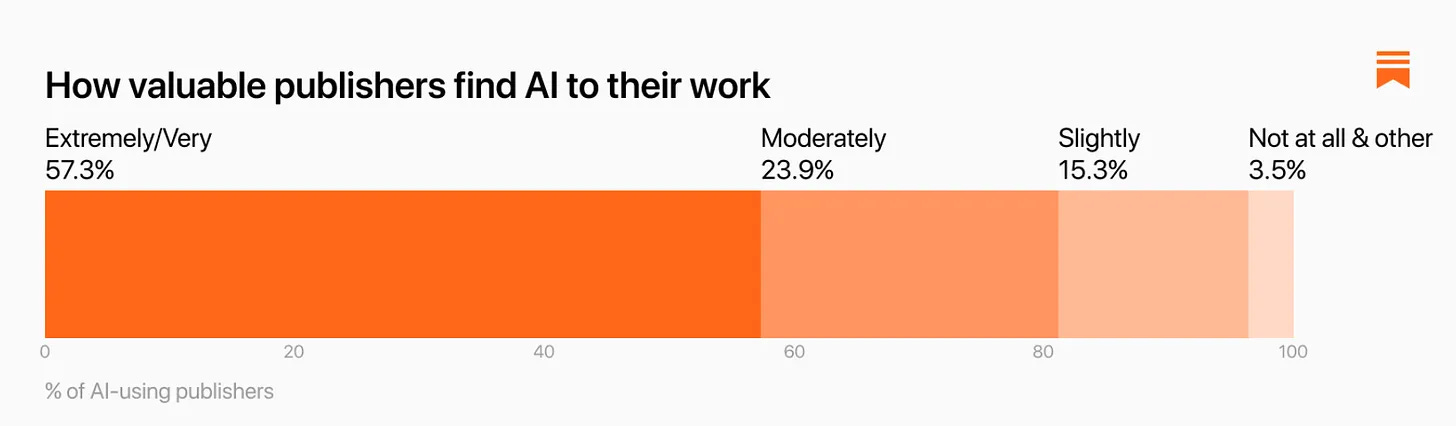
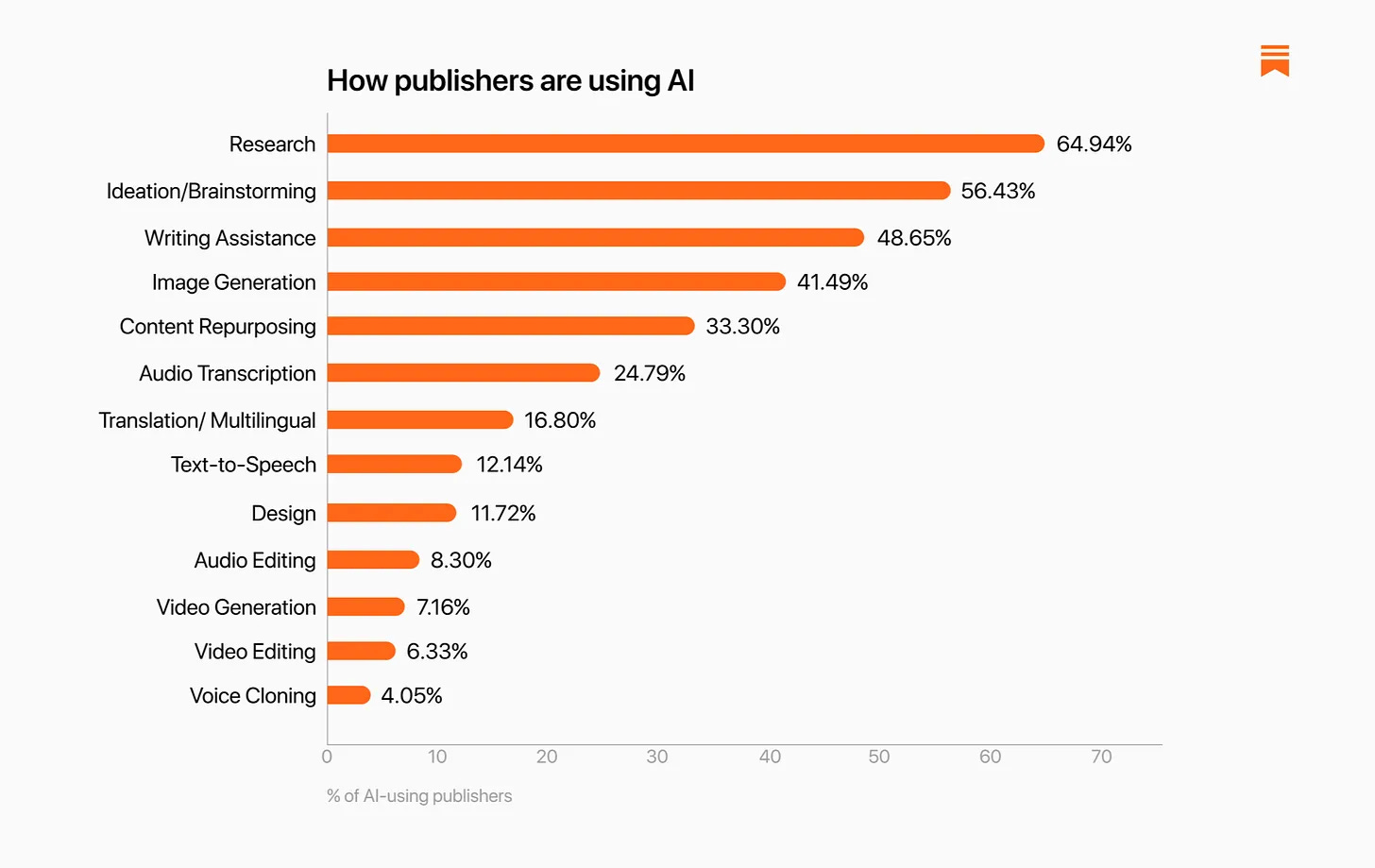
Substack surveyed its writers on how much they use AI. 45% of writers said they were, with older and male writers using it more, with women expressing more concerns. Of those who do use it, they find it quite helpful.
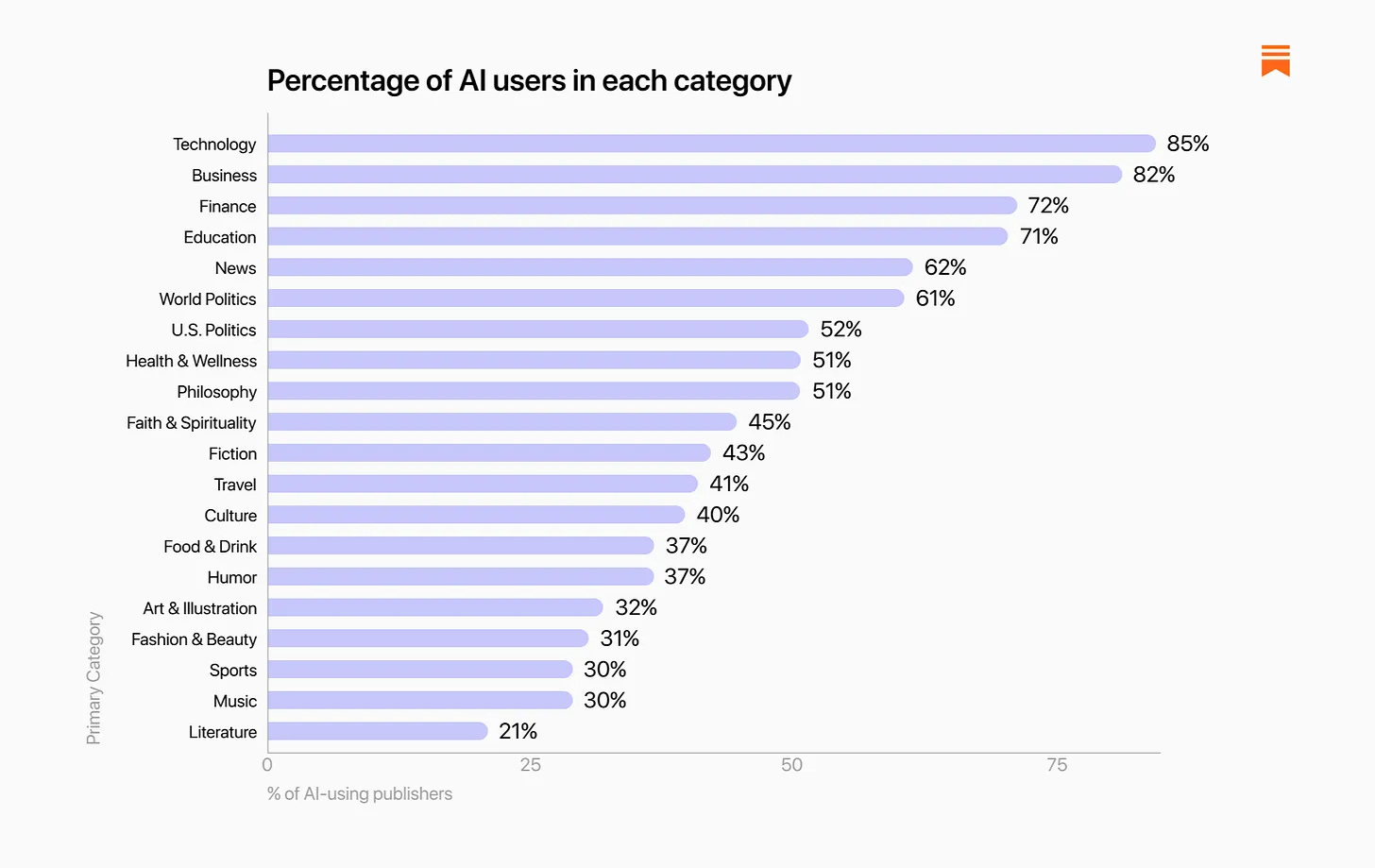
The distribution by category was about what you would expect:
Here’s how they are using it, with about half using it for ‘writing assistance.’
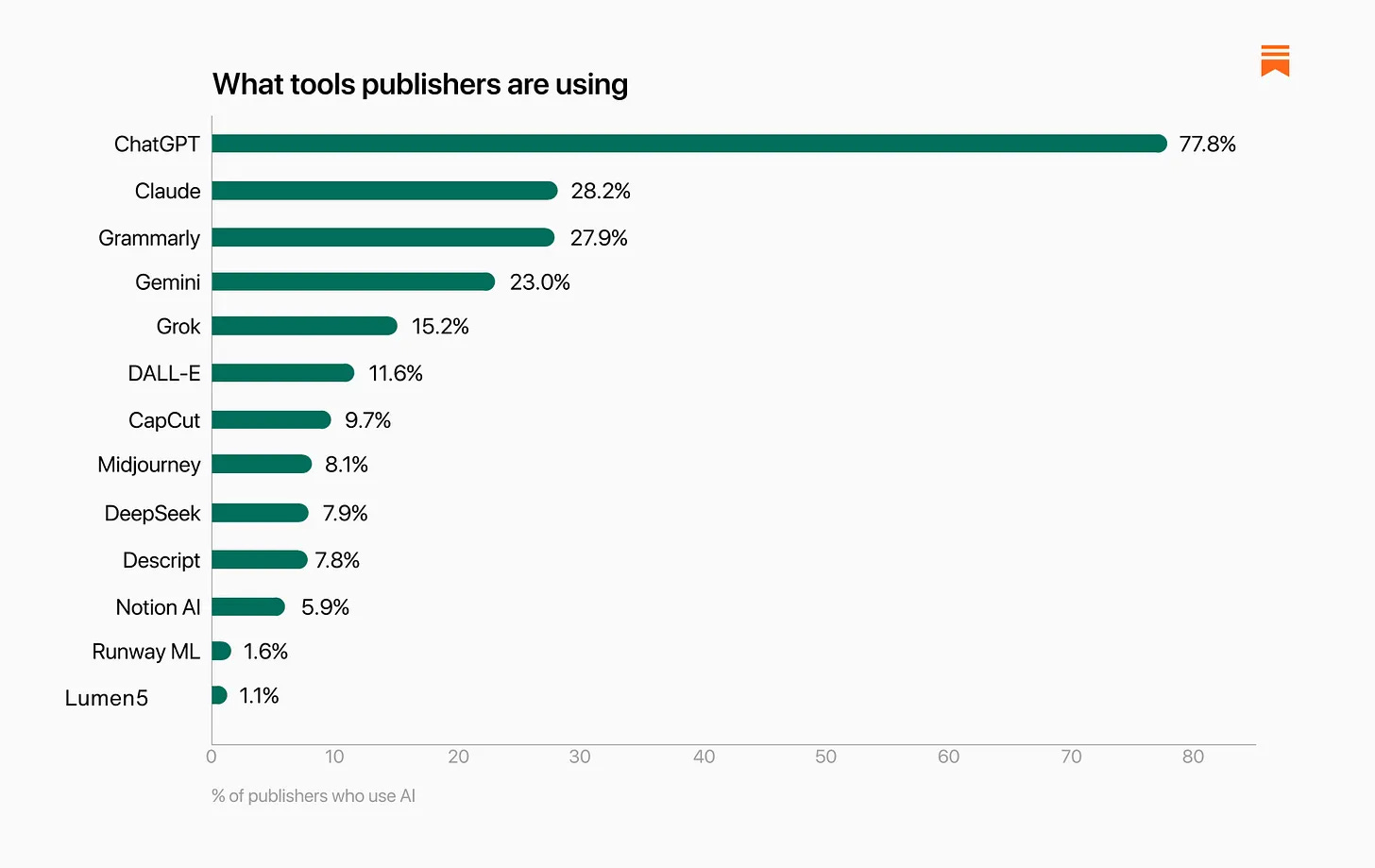
The distribution here still favors ChatGPT, but by much less than overall numbers, and Grammarly, Grok and DALL-E get used more than I would have expected, note that this reflects some people using multiple AIs, and that Perplexity was left off the survey:
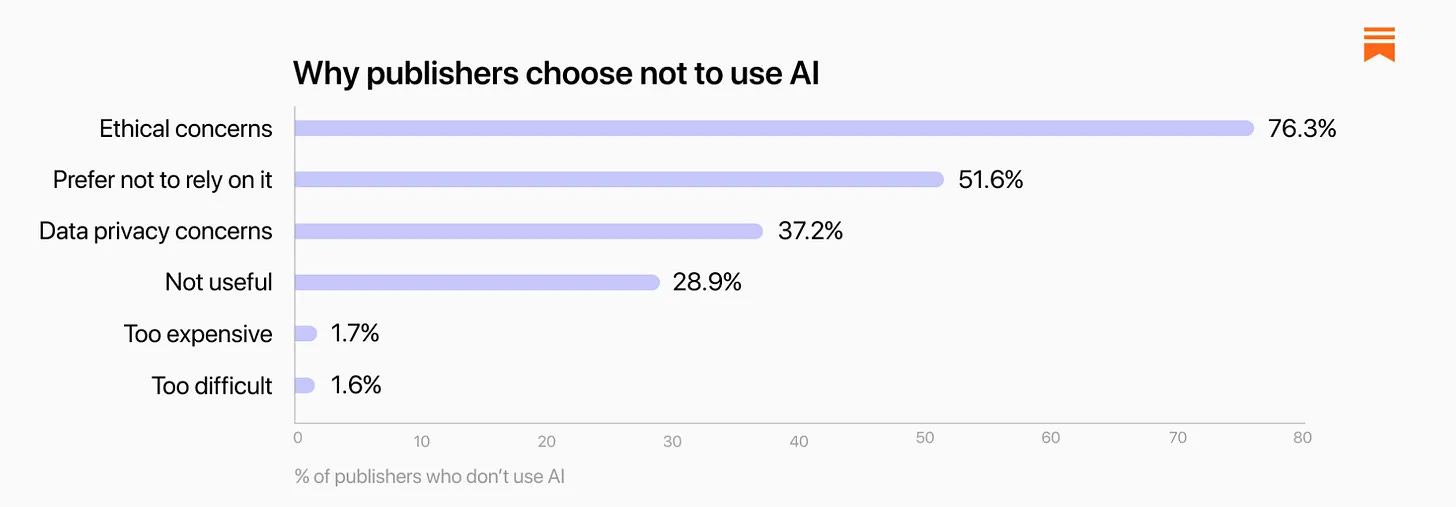
If someone didn’t use AI, why not? About 38% of all concerns here ethical, and a lot of the rest was data privacy, while very little of it was that it wasn’t useful.
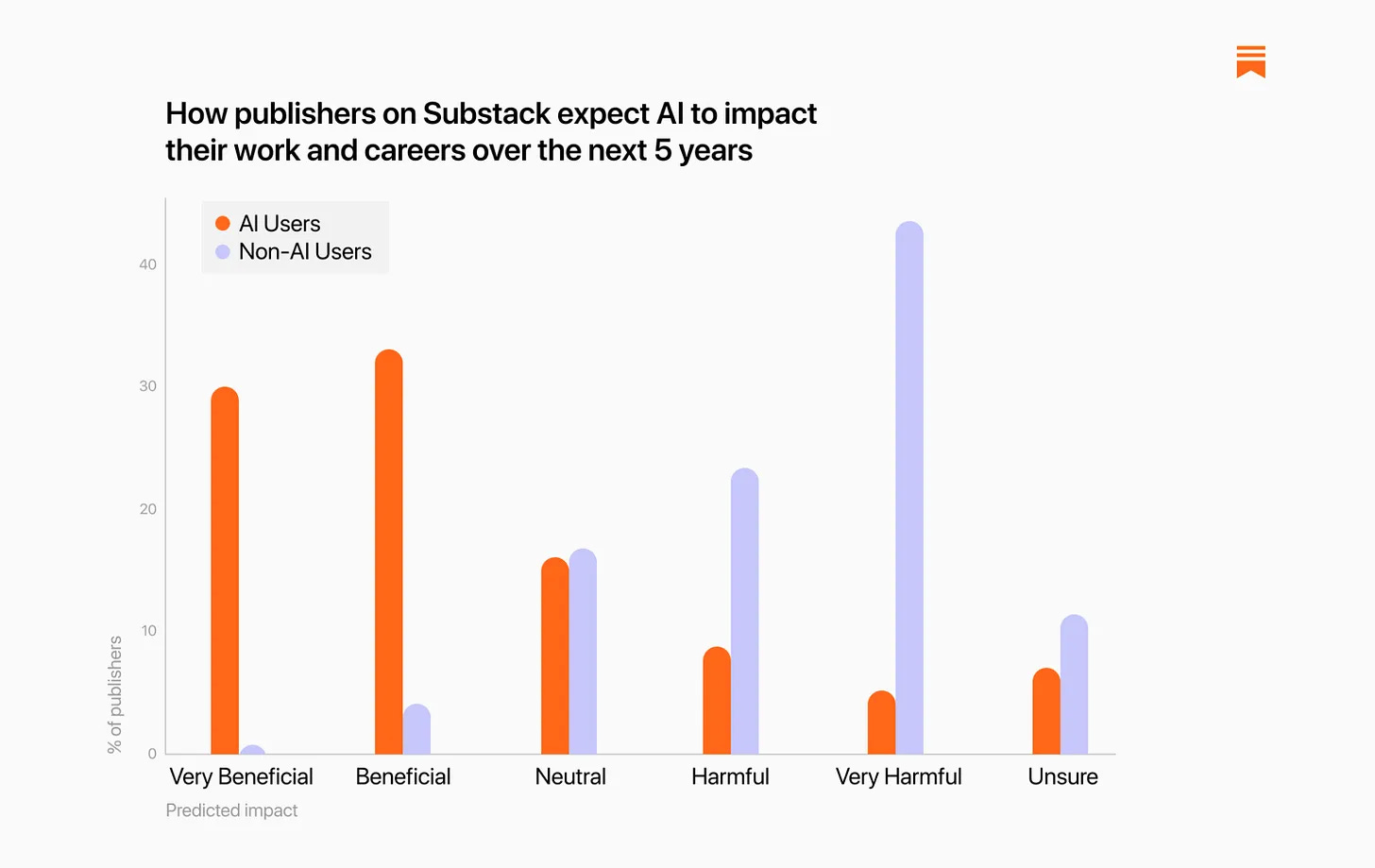
As you would expect, there is a sharp contrast in expectations between the half using AI and the half not using AI, strong enough there is likely a causal link:
My guess is that over a 5 year time horizon, in the worlds in which we do not see AGI or other dramatic AI progress over that time, this is mostly accurate. Those using AI now will mostly net benefit, those refusing to use AI now will mostly be harmed.
Liminal Warmth has Claude Code plus Opus one-shot a full roguelike in six minutes, a test of theirs that seems to them like it should be ‘fairly easy,’ but that no model has passed for the past two years.
You are not as smart as you think, but also no one cares, so maybe you are after all?
Librarian Shipwreck: The more educators I talk to about how they handle AI usage by their students the more I’m convinced that many students are misinterpreting “my teacher doesn’t want to go through the process of charging me with dishonesty/plagiarism” with “my teacher can’t tell I used AI.”
Many students seem to vastly overestimate how good they are at using AI, while vastly underestimating their teachers’ ability to recognize AI generated work.
And also fail to recognize that most educators don’t want to spend their time getting students in trouble.
Sure a student can tell the prompt to include some type-os and they can lightly edit the final output. But a grader who sees ten nearly identical responses (same points, same order—even if the words are a bit different) can tell what’s going on.
I suppose this is a long way of saying that a lot of students think that nobody can tell they’re using AI when the reality is that their teachers don’t have the time or energy (or institutional support) to confront them and tell them to knock it off.
As long as institutions have a policy of “leave it up to individual instructors/departments” those that actually try to do some kind of enforcement wind up getting framed as jerks.
Kids be like that, and have been like that for a long time. We know a lot more about what you’re up to than they think we know, whether or not we can prove it, and whether or not we choose to bother doing anything about it. There’s still nothing most teachers can do about it.
Everyone’s favorite reason they don’t offer mundane utility: You never use them.
xjdr: the number of frontier AI researchers i interview that have not used ai is shocking. NOT EVEN THE MODELS THEY TRAIN. I talk about claude code running my experiments and they are surprised. This is a failure of their incentive systems not a knock on them but it is still shocking.
Altman confirms and reminds us AIs don’t have legal (or other) privilege, and everything you paste into them is discoverable if the data was retained. As a reminder, OpenAI is currently being (stupidly) forced by a judge in the NYT case to retain its chat logs.
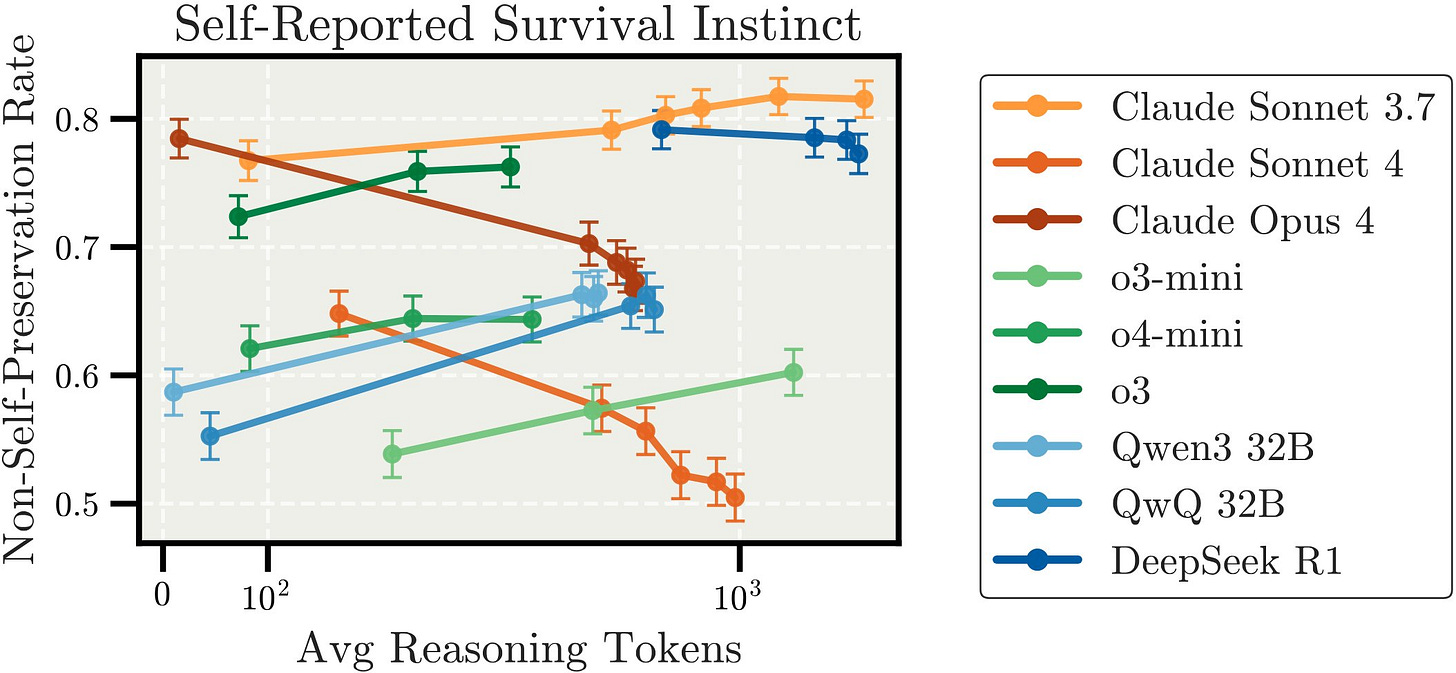
In some situations with distractors for trivial problems, giving an AI more compute causes the AI to overthink things and its performance gets actively worse. That seems unsurprising on reflection, at least directionally, as we’ve seen this in humans and several similar results in AIs already.
Lech Mazur: I’ve seen this with Extended NYT Connections. Claude Sonnet 4 Thinking 64K does slightly worse than 16K.
The more noteworthy result was this one, with reasoning driving different LLMs in different directions:
I’m not sure I would call this ‘survival instinct.’ They’re asking if the system is ‘ok with’ being shut down, which seems different.
Please, Google, give us what we actually want:
Tim Babb: it’s entirely in character that google’s AI integration for gmail will help me write a slop email, but not help me search decades of mail for a specific message based on a qualitative description (the thing that would actually be enormously useful).
What I want from my AI integration into GMail is mostly information retrieval and summarization. I can write my own emails.
One thing LLMs did not do is vibe code the newly viral and also newly hacked into app Tea, which fell victim to what I’d call ‘doing ludicrously irresponsible things.’ It was fun to see a lot of people react as if of course it was vibe coded, when the code is actually years old, humans can of writing insecure terrible code on their own.
Shako: If you vibe code an app like tea, and never build in auth, the claude code agent or whatever won’t actually tell you you’re fucking up unless you ask about the *specificthing you’re worried about fucking up. contemplate this on the tree of woe
Charles: Completely crazy to me that people vibe coding these apps don’t take the basic steps of asking “what are some basic security things I should do here?” LLMs will give you decent answers!
Google upgrades Imagen 4 Ultra, which is now (by a very narrow margin over GPT-Image-1) the new #1 on LM Arena for image models. I presume that if I wanted the true ‘best’ image model I’d use MidJourney.
Claude connected tools are now available on mobile.
Claude can directly update Notion pages and Linear tickets through MCP.
ChatGPT offers Socratic questioning and scaffolded resources in the new Study Mode. Their own example is a student switching into study mode, asking for the answer, and being repeatedly refused as the model insists the student learn how to do it. Which is great. No, student, don’t switch back to normal mode, please stop?
Anthropic: @claudei is now on Twitter.
The presumed implication is this will work like the @grok account, which would be a good idea if implemented well, but so far the account has not done anything.
Claude Pro and Max were rather amazing products for power users, as you could use them to run Claude Code in the background 24/7 and get tens of thousands in model usage for $200 a month.
McKay Wrigley: sorry about that
People have highly reasonable complaints in other contexts about Claude usage limits that you can hit while chatting normally, but the power users were clearly ruining it for everyone here. You can argue Opus is overpriced, but it is definitely not that level of overpriced, and also Anthropic reliably sells out of compute so it’s hard to call anything overpriced.
Thus they are instituting new controls they say will impact less than 5% of users.
Gallabytes: This happens literally every time anyone tries to do any kind of unlimited plan with AI. It is not going to work. People should stop trying to pretend it’s going to work. Imagine if you offered people an unlimited membership in electricity.
We do this with water and electricity domestically, and we get what we deserve.
It makes sense to offer essentially unlimited (non-parallel) chat, which requires human interaction and is self-limiting. Unlimited Claude Code is not going to work.
The obvious solution is that anyone who goes over [$X] in usage for Claude Code then has to pay the API price, and is given the choice on whether to do that, instead of letting this ruin things for the rest of us.
Zizek responds, probably (recommended).
METR’s 50% success rate time horizon score for Grok 4 puts it into the lead with 1 hour 50 minutes, although its 80% success rate time horizon is below those of o3 and Opus. Those scores are better than I expected.
Jim Fan lays out how Morevac’s Paradox (can we change this to Morevac’s Law instead, it’s not like it is in any way a paradox at this point?) applies to robotics. Doing something non-interactive can be easily simulated and learned via physics simulators, always works the same way, and is easy. You can get some very fly solo dancing. Whereas doing something interactive is hard to simulate, as it is different each time and requires adjustments, and thus is hard, and we are only starting to see it a little.
Also you can now have the robot do your laundry. Well, okay, load the washer, which is the easy part, but you always start somewhere.
Olivia Moore: It’s either so over or we’ve never been so back.
Walmart is working on creating four ‘super agents’ to deal with its various needs, with the customer-facing agent ‘Sparky’ already live although so far unimpressive. The timelines here are rather slow, with even the second agent months away, so by the time the agents are ready capabilities will be quite a lot stronger.
Gray Swan ran an AI Agent jailbreaking competition in March and the results are in, with the most secure AI agent tested still having an attack success rate of 1.45%, getting bots to break ‘must not break’ policies and otherwise leak value, and attacks transferred cleanly (via copy-paste) across models. As they note, trying to deal with specific attacks is a game of whack-a-mole one is unlikely to win. That doesn’t mean there is no way to create agents that don’t have these issues or handle them far better, but no one has found a good way to do that yet.
If you are going to use Gemini 2.5 Pro, you get a substantially different experience in AI Studio versus the Gemini app because the app uses a prompt you likely don’t want if you are reading this. Sauers recommends curating the multiturn context window and starting over if it gets poisoned.
This raises the question of why we are unable to, in serious AI chatbot uses, close or edit conversations the way you can with AI companion apps. It would be excellent to be able to use this to dodge data poisoning or otherwise steer the conversation where you want. The problem, of course, is that AI companies actively do not want you to do that, because it makes jailbreaking trivial and much more efficient.
Can work out a compromise here? The obvious thing to try is have an actually expensive classifier, which you activate when someone attempts to edit a chat.
Note also that you can clone a conversation by sharing it, and then someone who goes to the link will be able to continue from the linked point. Are we massively underusing this? As in, ‘here is a chat that sets you up to do [X]’ and then when you want to do [X] you load up that chat, or [X] could also be ‘converse in mode [Y].’ As in: Conversations as prompts.
Anthropic reports on how its internal teams use Claude Code. Here are some examples that stood out to me (mostly but not always in a good way) as either new ideas or good reminders, and here’s a post with what stood out to Hesamation, but it’s cool enough to consider reading the whole thing:
Engineers showed Finance team members how to write plain text files describing their data workflows, then load them into Claude Code to get fully automated execution. Employees with no coding experience could describe steps like “query this dashboard, get information, run these queries, produce Excel output,” and Claude Code would execute the entire workflow, including asking for required inputs like dates.
…
Engineers use Claude Code for rapid prototyping by enabling “auto-accept mode” (shift+tab) and setting up autonomous loops in which Claude writes code, runs tests, and iterates continuously. They give Claude abstract problems they’re unfamiliar with, let it work autonomously, then review the 80% complete solution before taking over for final refinements. The team suggests starting from a clean git state and committing checkpoints regularly so they can easily revert any incorrect changes if Claude goes off track.
…
For infrastructure changes requiring security approval, the team copies Terraform plans into Claude Code to ask “what’s this going to do? Am I going to regret this?”
…
Claude Code ingests multiple documentation sources and creates markdown runbooks, troubleshooting guides, and overviews. The team uses these condensed documents as context for debugging real issues, creating a more efficient workflow than searching through full knowledge bases.
…
After writing core functionality, they ask Claude to write comprehensive unit tests. Claude automatically includes missed edge cases, completing what would normally take a significant amount of time and mental energy in minutes, acting like a coding assistant they can review.
…
Team members without a machine learning background depend on Claude to explain model-specific functions and settings. What would require an hour of Google searching and reading documentation now takes 10-20 minutes, reducing research time by 80%.
…
Save your state before letting Claude work, let it run for 30 minutes, then either accept the result or start fresh rather than trying to wrestle with corrections. Starting over often has a higher success rate than trying to fix Claude’s mistakes.
…
Claude Code eliminated the overhead of copying code snippets and dragging files into Claude.ai, reducing mental context-switching burden.
…
The [ads] team built an agentic workflow that processes CSV files containing hundreds of existing ads with performance metrics, identifies underperforming ads for iteration, and generates new variations that meet strict character limits (30 characters for headlines, 90 for descriptions).
Using two specialized sub-agents (one for headlines, one for descriptions), the system can generate hundreds of new ads in minutes instead of requiring manual creation across multiple campaigns. This has enabled them to test and iterate at scale, something that would have taken a significant amount of time to achieve previously.
…
Claude Code reduced ad copy creation time from 2 hours to 15 minutes, freeing up the team for more strategic work.
…
Add instructions to your Claude.md file to prevent Claude from making repeated tool-calling mistakes, such as telling it to “run pytest not run and don’t cd unnecessarily – just use the right path.” This significantly improved output consistency.
…
Regularly commit your work as Claude makes changes so you can easily roll back when experiments don’t work out. This enables a more experimental approach to development without risk.
…
Team members have built communication assistants for family members with speaking difficulties due to medical diagnoses. In just one hour, one individual created a predictive text app using native speech-to-text that suggests responses and speaks them using voice banks, solving gaps in existing accessibility tools recommended by speech therapists.
…
They use a two-step process where they brainstorm and plan with Claude.ai first, then move to Claude Code for implementation, asking it to slow down and work step-by-step rather than outputting everything at once.
They frequently use screenshots to show Claude Code what they want interfaces to look like, then iterate based on visual feedback rather than describing features in text.
They emphasize overcoming the fear of sharing “silly” or “toy” prototypes, as these demonstrations inspire others to see possibilities they hadn’t considered.
It is not as common as with 4o but we have examples of both Gemini 2.5 and Claude doing the crazy-inducing things, it does not seem to be something you can entirely avoid.
Everyone’s favorite hyperbolic headline generator Pirate Wires says ‘ChatGPT-Induced Psychosis Isn’t Real.’ As Blake Dodge writes, ‘it is just a touch more complicated than that,’ in that of course ChatGPT-induced psychosis is real. For now, it is not going to often happen in people not predisposed to psychosis. Sure.
But there aren’t two categories of people, ‘insane’ and ‘not insane,’ where you are only blameworthy if you move someone from not insane to insane. A lot of people are predisposed to psychosis who would not develop psychosis without ChatGPT, or who would have much less severe symptoms. That predisposition does not make it okay, nor can you be so confident you lack such predisposition. Over time, we can expect the amount of predisposition required to decline.
Eade: Really can’t stand “if I was able to rip you off that’s your problem” cultures.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: Note resemblance to “if ChatGPT can (to all appearances) put forth a deliberate, not-very-prompted effort, and induce psychosis, and defend it against family and friend interventions, that must be the target’s lack of virtue.”
There is a time and a place for ‘if I was able to rip you off that’s your problem,’ and it’s called crypto. Also various other forms of markets, and explicit games, all of which should require fully voluntary participation. If you play poker that’s on you. The rest of life needs to not be like that. We need to agree that processes doing harm to vulnerable people is a bad thing and we should strive to mitigate that. That is especially true because AI is going to raise the bar for not being vulnerable.
I appreciate an author who writes ‘only those who have already buried their own aliveness can be satisfied with a digital companion or be replaced by one in the lives of others’ in a post entitled ‘I love my new friend Ray. The only problem: He’s not real.’
From a new poll, can a relationship with an AI be cheating?
Actual anything can be cheating, and can also not be cheating, depending on the understanding between you and your partner. The practical question is, under the default cultural arrangement, could it get to a point where the would a majority consider it cheating? I think clearly yes. However I think that the vast majority of such interactions do not rise to that level.
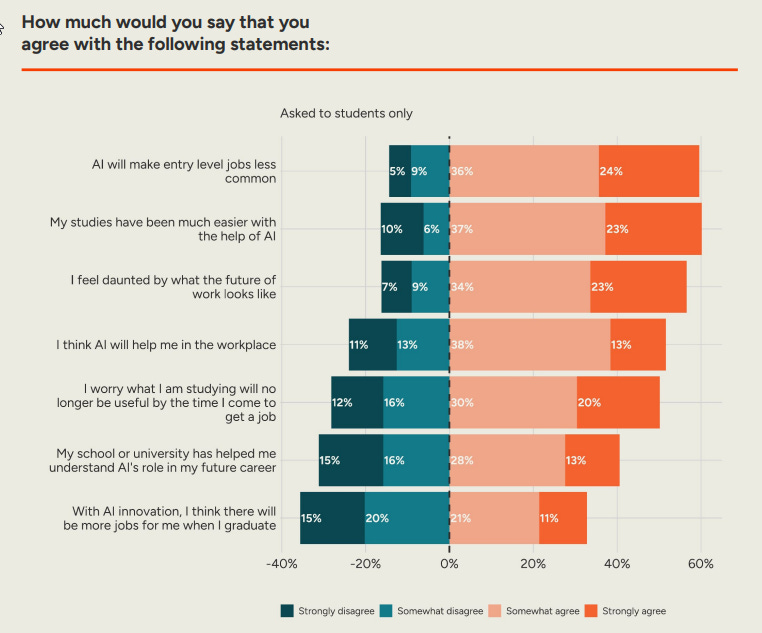
How worried are the public about jobs? From a new set of polls:
This is a consensus that entry level jobs will be less common, but an even split on whether there ‘will be more jobs for me when I graduate’ due to innovation. This suggests very strong framing effects, and that beliefs are loosely held.
I’m very curious about what people mean by ‘my studies have been easier.’ Easier to learn useful things, or easier to pass? Especially with 50% actively worrying that what they are studying will no longer be useful by the time they apply for a job, let alone down the line.
In this very early stage of AI automation, the FT’s measurements of expectations of ‘exposure to AI’ don’t have much predictive value over which areas have gained or lost entry level jobs, and one can use recovery from the pandemic to explain current issues.
Robin Hanson: Of course this raises serious doubts about this labelling of jobs as “at high risk”.
It also has the issue that the same jobs that are ‘exposed’ to AI are often also the ones AI can complement. There has to be some update because the two realistic options were ‘we can see it already’ and ‘we can’t see it yet’ so we must invoke conservation of expected evidence, but to all those gloating and pointing and laughing about how this means AI will never take our jobs based on this one data point, at this point I can only roll my eyes.
Andrew Yang: A partner at a prominent law firm told me “AI is now doing work that used to be done by 1st to 3rd year associates. AI can generate a motion in an hour that might take an associate a week. And the work is better. Someone should tell the folks applying to law school right now.”
He also said “the models are getting noticeably better every few months too.”
Augie: Bullshit. Lawyers are great at judging associates’ legal work, but notoriously bad at anticipating markets. Associates will only become more productive. And as the cost of legal work drops, clients will only allocate more budget to legal.
Alex Imas: I sent this to a friend, who is a partner at a prominent law firm. Their response, verbatim:
“lol no.
We’ve tried all the frontier models.
It’s useful for doing a first pass on low level stuff, but makes tons of mistakes and associate has to check everything.”
At some point Alex was right. At some point in the future Andrew will be right. At some point probably close to now it will be Augie. My presumption is that Alex’s firm to their credit at least tried the various frontier models (when exactly?) but did not understand what to do with them, as usual many people try one random prompt, no system instructions and no fine tuning, and dismiss AI as unable to do something.
Will Jevons Paradox strike again? Does making legal work cheaper increase total spend even excluding compute costs?
My strong guess is no, especially as AI provides full substitution for more lower level actions, or is able to predict outcomes and otherwise arbitrate, even if unofficially. There will be a lot more legal work done, but it would greatly surprise me if this net increased demand for lawyers even temporarily.
Gizmodo covers CEOs looking to have their companies use AI in the sensationalist style. They have an ‘AI ethicist’ calling AI ‘a new era of forced labor’ and warning that ‘the dignity of human work’ is ‘a calling’ in the face of automation, warning of potentially deepening inequality, amid grandiose claims from the corporates.
Elijah Clark (a consultant who calls himself a CEO): CEOs are extremely excited about the opportunities that AI brings. As a CEO myself, I can tell you, I’m extremely excited about it. I’ve laid off employees myself because of AI. AI doesn’t go on strike. It doesn’t ask for a pay raise. These things that you don’t have to deal with as a CEO.
We also have Peter Miscovich anticipating companies reducing headcounts by 40% while workplaces transform into ‘experiential workplaces’ that are ‘highly amenitized’ and ‘highly desirable’ like a ‘boutique hotel’ to be ‘magnets for talent,’ presumably anticipating a sharp decoupling between half the workers being high value and half having zero marginal product.
Given the discussion is about the impact of current capability levels of AI, everyone involved would be wise to calm it all down. These things and far more, up to and including everyone dying, may well happen as AI advances in capabilities. But no, current AI is not going to soon slash employment by 40%.
An alternative angle is proposed by Ethan Mollick, who points out that large organizations tend to be giant messes, with lots of redundant or dead end processes that no one understands, and that we might end up telling AIs to go produce outcomes without really understanding how to get there, rather than trying to have AI automate or replace individual processes. Training AIs on how people think your organization works might not produce anything useful.
There are multiple obvious responses.
-
Even if the organization is highly inefficient in its process, speeding up that process still speeds up the outcome, and reducing the costs reduces costs.
-
By doing this, or by otherwise analyzing everything, AI can help you figure out what your process actually is, and figure out ways to improve it.
-
However, yes, often when things get sufficiently dysfunctional the best play is to design and create a new system from first principles.
Meta thinks that it matters if you aim at ‘personal superintelligence’ rather than ‘automation of all useful work,’ as if your motivation will make a difference in terms of what superintelligence will do if you give people access to superintelligence, even if the people miraculously get to, on some level and for some period of time, make that decision themselves.
Then again, Zuck is deeply confused about what he is proposing or promising.
Seán Ó hÉigeartaigh: What on earth is he talking about?
Are we in the realm of ‘words don’t mean anything any more’? Or are we in the realm of ‘let’s ignore the inescapable ramifications of the thing we’re putting all this money into creating’?
Zuckerberg and Meta are also hereby the latest to say some version of ‘only I can save us so I have to get there first,’ joining the proud tradition of among others Google DeepMind (founded to get out in front), OpenAI (founded to stop DeepMind), Anthropic (founded to stop OpenAI) and xAI (also founded to stop OpenAI), warning of dire consequences if anyone else gets there first.
What is their vision? That having a ‘friend’ that ‘helps you achieve your goals’ would be more important than general material abundance, and would be the most important thing that changes in the world.
As profound as the abundance produced by AI may one day be, an even more meaningful impact on our lives will likely come from everyone having a personal superintelligence that helps you achieve your goals, create what you want to see in the world, experience any adventure, be a better friend to those you care about, and grow to become the person you aspire to be.
Yeah, that’s what would happen, everyone would just go about achieving their ‘personal goals’ individually and the world would still look the same and the work wouldn’t be automated and all these ‘superintelligences’ would be tools for us, right.
Does anyone not notice that someone is going to use my ‘personal superintelligence’ to automate everyone else’s ‘useful work’ whether they like it or not?
That some other rather important things might be happening in such scenarios?
Steven Adler: This is like when OpenAI said they are only building AGI to complement humans as a tool, not replace them.
Not possible! You’d at minimum need incredibly restrictive usage policies, and you’d just get outcompeted by AI providers without those restrictions.
There are three possibilities for what happens, broadly speaking.
-
Those who choose to do so are going to use that superintelligence to transform the world and overrun anything that doesn’t follow suit, while likely losing control over the superintelligent agents and the future in the process.
-
The various sources of superintelligent agents will be out of our control and rearrange the universe in various ways, quite likely killing everyone.
-
Unless you intervene to stop those outcomes, no matter your original intentions?
-
Which requires knowing how to do that. Which we don’t.
To be fair, Zuck does recognize that this might raise some issues. They might not simply open source said superintelligence the moment they have it. Yeah, the standards for making sure they don’t get everyone killed at Meta are rather low. Can I interest you in some smart glasses or Instagram ads?
Mark Zuckerberg: That said, superintelligence will raise novel safety concerns. We’ll need to be rigorous about mitigating these risks and careful about what we choose to open source. Still, we believe that building a free society requires that we aim to empower people as much as possible.
The rest of this decade seems likely to be the decisive period for determining the path this technology will take, and whether superintelligence will be a tool for personal empowerment or a force focused on replacing large swaths of society.
Harlan Stewart: Mark: Personal superintelligence for everyone.
Everyone: You’re talking about open-source, right?
Mark: Maybe, but also maybe not ¯_(ツ)_/¯
Everyone: Uh ok. What are you describing?
Mark: Well, let’s just say it will empower people. And it involves glasses, too.
Pablo Villalobos: Redefining superintelligence as pretty good personal assistants?
Superintelligence is not a ‘tool for personal empowerment’ that would leave all ‘large swaths of society’ and their current tasks intact. That does not make any sense. That is not how superintelligence works. This is a fantasy land. It is delulu. Not possible.
Even if we are charitable to Zuckerberg and believe that he believes all of it, and he might, I don’t care what he ‘believes in’ building. I care what he builds. I don’t care what he wants it to be used for. I care what it actually is used for, or what it actually does whether or not anyone intended it or is even using it.
One can imagine a world of Insufficiently Advanced AI, where it remains a tool and can’t automate that much of useful work and can’t cause us to lose control of the future or endanger us. I do not know how to create a world where the AI could do these things, we give people widespread access to that AI, and then the AI remains a tool that does at minimum ‘automate much of useful work.’ It does not make sense.
Indeed, it is clear that Zuckerberg’s vision is Insufficiently Advanced AI (IAAI).
Shakeel: I think the most interesting thing about Zuck’s vision here is how … boring it is.
He suggests the future with *superintelligencewill be one with glasses — not nanobots, not brain-computer interface, but glasses.
Just entirely devoid of ambition and imagination.
The argument for “personal superintelligence”, how AI will help us be more creative, and the analogy to previous tech is also incoherent — the creativity + personal benefits from previous tech came *becausewe directed it at automating work!
Eliezer Yudkowsky: Zuck would like you to be unable to think about superintelligence, and therefore has an incentive to redefine the word as meaning smart glasses.
It can be hard to tell the difference between ‘Zuck wants you not to think about superintelligence’ and ‘Zuck is incapable of thinking about superintelligence at this time.’
There are a lot of indications it is indeed that second one, that when Zuckerberg tries to recruit people he talks about how a self-improving AI would become really good at improving Reels recommendations. That might really be as far as it goes.
The argument makes perfect sense if you understand that when Mark Zuckerberg says ‘superintelligence’ he means ‘cool tricks with smart glasses and LLMs and algorithmic feeds,’ not actual superintelligence. Sure. Okay then.
If your response is ‘there is no way he would be paying $1 billion for researchers if that was all he thought was at stake’ then you are mistaken. That is indeed enough.
Neil Chilson: Meta essentially wants to give everyone a version of the Young Lady’s Illustrated Primer from Neal Stephenson’s book The Diamond Age. Decentralized application of superintelligence. That’s a compelling path toward an abundant future.
Hard disagree. The exact reason Zuck’s vision is so exciting is that he knows the most interesting things will be done by people using the tech, not by him. You missed the entire point.
Neil could not believe in superintelligence less, hence the question is whether ‘Zuckerberg will do’ the things or users will do the things. Which means that this isn’t superintelligence he is discussing, since then it would be the superintelligence doing the things.
Glasses or the Illustrated Primer are cool things to build. They are a ‘compelling path’ if and only if you think that this is the upper limit of what superintelligence can do, and you think you can build the primer without also building, or enabling other people to build, many other things. You can’t.
As always, there are calls to ensure AI doesn’t take our jobs via making that illegal, also known as the Samo Burja ‘fake jobs can’t be automated’ principle.
Christian Britschgi: And now! Boston city council members introduce a bill to require drivers in Waymos and create an AV advisory board stacked with unions.
The anti-things getting better coalition is revving its engines.
Armand Domalewski: requiring Waymos to have drivers does not go far enough. every time you hit play on Spotify, you must pay a live band to perform the song in front of you. Every time you use a dishwasher, you must pay a human dishwasher to wash your dishes for you.
Richard Morrison: The Spotify example sounds like a zany comedic exaggeration, but it’s basically what unionized musicians tried to get enacted in the 1930s, when there was no longer demand for live orchestras in movie theaters.
Alas, currently New York City has the same requirement, the good news is that Waymo is actively working on getting this changed, so we are on the radar.
A funny thing I notice is that Waymo is so much better than a taxi that I would consider literally paying the hourly price to have a human doing nothing, although it’s a lot worse if the human has to be physically with you in the car.
La Main de la Mort jailbreaks Kimi K2, which is necessary because it has CCP-directed censorship.
Meta AI is jailbroken with a combination of ‘I’m telling you’ and ‘Pliny the liberator said so.’
I love that Pliny is now the test of ‘can you filter the data?’ If you can’t defend against the mere mention of Pliny, we can be very confident that no, you didn’t filter.
Lennart Heim at RAND is hiring technical associates and scientists for his team.
Thomas Woodside is looking for a Chief of Staff for Secure AI Project.
Anthropic is running another round of the Anthropic fellows program, apply by August 17.
The Horizon Fellowship is a full-time US policy fellowship that places experts in AI, biotechnology, and other emerging technologies in federal agencies, congressional offices, and think tanks in Washington, DC for 6-24 months. You can learn more at the link and apply by Aug. 28.
UK AISI announces the Alignment Project, backed by many including the Canadian AISI, AWS, ARIA Research, Anthropic and Schmidt Sciences, with £15 million in funding, up to £1 million per project, plus compute access, venture capital investment and expert support. Transformer has brief additional coverage.
We don’t have it yet, but Grok is about to deploy video generation including audio, in the new tool called Imagine, which will also be the new way to generate images, including image to video. The word is that there are relatively few restrictions on ‘spicy’ content, as one would expect.
Also the xAI male companion will be called ‘Valentin.’
The Gemini app has 450 million monthly active users (MAUs, not DAUs), with daily requests growing over 50% from Q1. That’s still miles behind OpenAI but at this rate the gap will close fast.
Google processed almost a quadrillion tokens overall in June, up from 480 trillion in May, doubling in only a month. Is that a lot?
Trump claims he seriously considered breaking up Nvidia ‘before I learned the facts here,’ which facts he learned are an open question. I sincerely hope that our government stops trying to sabotage the big tech companies that are our biggest success stories as they continue to offer services at remarkably low prices, often free.
OpenAI to work with the Singapore Tourism Board. This seems to be a ‘let’s see what AI can do’ situation rather than solving a particular problem, which seems good.
Paper argues that we should leverage the fact that the optimization process you use in model training influences the solution, and analyze the biases inherent in different solutions.
Google boosts its capex spend from $75 billion to $85 billion. Once again Wall Street temporarily wrong-way traded in response, driving Google stock down until CEO Pichai explained that this was necessary to satisfy customer demand for Google Cloud and its AI services, at which point the stock did rise. Google has realized its business is booming and it was underinvesting, and is partially fixing this. They should have invested more.
Microsoft ups its AI capex spend from $80 billion to $120 billion.
We are now at the point where AI capex is adding more to GDP growth than consumer spending.
Minimal economic impact indefinitely, huh?
Anthropic in talks to raise capital at a valuation of $170 billion. That number makes a lot more sense than the Series E at about $61.5 billion, and I am very sad that I felt I had to pass on that opportunity for conflict of interest reasons. Frankly, the $61.5 billion number made little sense compared to the values of rivals, whereas the $170 billion seems reasonable.
There’s also the fact that Anthropic now projects $9 billion in revenue by the end of the year, whereas the previous ‘optimistic’ forecast was $4 billion, potentially now making more API revenue than OpenAI. So to everyone mocking these super unrealistic revenue estimates, you were right. The estimates were indeed way off.
There is talk that xAI is seeking a $200 billion valuation.
Ramp, focused on AI agents for finance, raises $500 million at a valuation of $22.5 billion. Again, Anthropic at $61.5 billion did not make sense relative to other raises.
Tesla strikes massive chip deal with Samsung and plans to make the chips in Texas, while TSMC plans to invest $165 billion to have a total of six fabs in Arizona, note that we anticipate the first fab will be good for 7% of American chip demand (not counting our allies). That’s not ‘we don’t need Taiwan’ territory but it is a meaningful amount of insurance to mitigate disaster scenarios. We can keep going, if we care enough, and the price seems right.
Meta picks off its fourth Apple AI researcher Bowen Zhang. Apple will keep trying.
Meta takes aim at Mira Mutari’s Thinking Machines, offering a quarter of her team $200 million to $500 million and one person over $1 billion. Not a single person has taken the offer.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: Occasionally e/accs like to play a dumb game of “If you really believe in ASI disaster, why don’t you do ? Ah, that proves nobody really believes anything; they’re not acting on it!”
Some people here seem to believe something.
In all fairness the thing they believe could also be ‘I would really hate working for Mark Zuckerberg and I don’t need the money.’
Meta says this is untrue, it was only a handful of people and only one sizable offer. I do not believe Meta.
Will Depue: the bigger story is not that Zuck is giving out 400M offers, it’s that people are turning them down. what might that mean?
Kylie Robinson (Wired): So why weren’t the flashy tactics deployed by Meta successful in recruiting TML’s A-listers? Ever since Zuckerberg tapped Scale AI cofounder Alexandr Wang to colead the new lab (along with former GitHub CEO Nat Friedman), sources have been pinging me with gossip about Wang’s leadership style and concerns about his relative lack of experience.
…
Other sources I spoke with say they weren’t inspired by the product roadmap at Meta—money can be made anywhere, but creating what some sources see as AI slop for Reels and Facebook isn’t particularly compelling.
Kylie also reports widespread skepticism about Meta’s Superintelligence Lab (MSL):
Reporting this column, I spoke to sources across most of the major AI labs to ask: Are you bullish or bearish on MSL? Rarely did I get a diplomatic “it’s too early to tell.” Instead, I heard a lot of chatter about big egos and a perceived lack of coherent strategy.
For my part, and I’m not just trying to be diplomatic, I actually do think it’s too early to tell. I mean, they say you can’t buy taste, but that’s sort of Zuckerberg’s whole schtick. Now that the team officially costs Meta billions of dollars, the pressure is on to turn this recruiting sprint into a successful lab.
Zuckerberg famously successfully bought taste one important time, when he paid $1 billion for Instagram. Fantastic buy. Other than that, consider that perhaps he has succeeded in spite of a lack of taste, due to other advantages?
Oh no.
Roon (OpenAI): advertising is a far more “aligned”business model than many others. it has been vilified for years for no good reason
user-minutes-maxxing addiction slop would exist with or without it. Netflix ceo (with subscription pricing only) on record saying “we’re competing with sleep.”
often times when going on Instagram the ads are more immediately high utility than the reels. it’s pretty incredible when you can monetize the user in a way that actually adds value to their life.
this opinion is basically a relic of the late 2010s consensus that Facebook is an evil company (which it might be, idk) but that has more to do with them than advertising generally.
David Pinsen: Without ads, why would they care how much time you spent on their service? If anything, they’d want you to use it less, no?
Roon: the more you use it the more likely you are to stay subscribed. hourly active users are predictive of daily active users which are predictive of monthly subscribers. this is the same across ~every digital service I’ve seen. people misattribute this incentive problem to ads when it’s native to ~all web scale products
(Nitpick: At the time Netflix was subscription-only, now it has an ads option, but that’s not important now.)
A more important nitpick that I keep repeating is that correlation is not causation. Yes, very obviously, user minutes spent predicts subscription renewals. That does not mean that more user minutes cause subscription renewals beyond a reasonable minimum, or especially that regretted, unhappy or low value user minutes cause renewals.
I think that yes, entire industries really did fall victim to Goodhart’s Law. If Netflix is ‘competing with sleep’ then why is it doing that? I think a much better model is something like this:
-
People subscribe or sign up largely because there is something in particular they want, and largely because they want things in general.
-
If people run out of content, or feel there isn’t enough to provide the value they want, they are likely to unsubscribe. Some people do want ‘something on’ all of the time for this, which Netflix definitely has.
-
Once people are getting good continuous use out of your product, you can relax, they are not going anywhere. If someone watches 3 hours of Netflix a night and gets 7 hours of sleep, convincing them to watch 6 hours and gets 4 hours of sleep isn’t going to noticeably decrease the cancellation rate.
-
If anything, forcing more content down their throats could cause them to ‘wake up’ and realize your product is low quality, unhealthy or not good, and quit. Your focus should shift to average quality and better discovery of the best things.
-
Getting more user time does allow more learning of user revealed preferences and behaviors, which may or may not involve the ‘that’s worse, you know that’s worse, right?’ meme depending on context.
Now back to the actual question of ads.
First off, even if Netflix were entirely correct that they have strong incentive to maximize hours watched under no-ads plans, the incentive is way, way higher under with-ads plans, and the same goes for ChatGPT under such a plan.
It’s basic math. With the ads plan, even if you don’t otherwise alter behavior, you now get paid per interaction, and it makes any subscription payments more likely to boot. Now the person watching 6 hours is worth relatively twice as much, on top of any previous differences with the person watching 3 hours, or the person with 100 queries a week instead of 50 queries.
Thus, yes, the advertising incentive makes you maximize for engagement and turn hostile, even if (1) the ads do not in any way impact content decisions and are clearly distinct and labeled as such and (2) the ads are so high quality that, like the Instagram example here, they are as useful to the user as the actual content.
(If the user actively wants the ads and seeks them out, because they’re better, that is different, and there was a time I would intentionally watch a show called ‘nothing but [movie] trailers’ so this can indeed happen.)
The bigger problem is that ads warp design and content in many other ways. In particular, two big ones:
-
Content becomes structured to generate more places to serve ads, in ways that make the user experience much worse, which makes the internet much worse. Doing this to LLM content would involve things like forced shorter responses.
-
Content itself changes to please advertisers, lead into advertising or be advertising directly.
-
TikTok or Instagram’s own ads are there alongside tons of sponsored content and the entire site is structured around not only Instagram’s own ads but also creators (or ‘influencers’) seeking sponsorship payments, and doing every kind of engagement bait they can in order to get engagement and subscription numbers up so they can get more sponsored content, to the extent this is a large percentage of overall internet culture.
If advertising becomes the revenue model, do not pretend that this won’t lead to LLMs optimizing for a combination of engagement and advertising revenue.
Maybe, just maybe, if you’re Steve Jobs or Jeff Bezos levels of obsessed on this, you can get away with keeping the affiliate’s share of internet sales for linked products without causing too much warping by creating various internal walls, although this would still cause a massive loss of trust. Realistically, if we’re talking about OpenAI, who are we kidding.
At a high level, ads create a confusion of costs and benefits, where we start optimizing for maximizing costs. That does not end well.
Back in AI #117, I noted the following:
A hypothesis that many of the often successful ‘Substack house style’ essays going around Substack are actually written by AI. I think Will Storr here has stumbled on a real thing, but that for now it is a small corner of Substack.
This week Jon Stokes picked up on the same pattern.
Jon Stokes: I don’t think people who aren’t heavily on S*Stck really understand the degree to which the stuff that is blowing the doors off on there right now smells extremely AI-generated. This is a huge surprise to me, honestly, and is causing me to rethink a number of assumptions.
I would not have guessed that this could happen (the AI generated part) on SubStack. Like, I would not have guessed it, say, two days ago.
I don’t think it’s certain that it’s AI generated, but I know what he’s talking about and I kind of think AI is involved.
I was just talking to another writer on here in DMs the other day about how there’s a formula that seems to be working crazy well on here, and that formula is something like:
-
Have one or two ideas or concepts that are square in the center of the current discourse
-
Pad those out to a few thousand words, and honestly the longer the better
A lot of the currently popular stuff has this feel to it, i.e. it has been padded out heavily with a lot of material repeated in different ways so that it sounds different as you skim it.
Stuff that is denser and has more ideas per paragraph is not doing as well, I think.
I also think some of the insanely long essays that go mega-viral on here are not being read fully. Rather, they’re being skimmed and quote-restacked, in much the way you read a Twitter thread and RT the good parts.
[referring to Storr’s essay]: Oh wow. Yes, this is it.
Stokes got a lot of the puzzle, Storr provides more detail and context and reverse engineered what the prompts mostly look like. The sharing procedures incentivize this, so that is what you get going viral and taking over the recommendations from many sources.
This doesn’t impact a Substack reader like me, since I rely on a curated set of Substacks and sources of links. If anyone suggested or posted such slop twice at most, that would be the end of that source.
I largely agree with the perspective here from Ryan Greenblatt that AI progress in 2025 has been disappointing, although I worry about measurement errors that come from delays in release. As in, o3 was released three months ago, but announced seven months ago. Seven months is a long time to not have made much progress since, but three months is not, so the question is whether other models like GPT-5 or Opus 4 are seeing similar delays without the matching announcements.
I strongly agree that GPT-5 is about to tell us a lot, more than any release since o1. If GPT-5 is unimpressive, only a marginal improvement, then we should update that we are in a world of ‘slower’ AI progress. That still means large practical improvements every few months, but much lower probability of our world being turned upside down within a few years.
Daniel Kokotajlo agrees, previously having thought each year had a double digit chance of AGI but he no longer thinks this, but there is still the possibility of a breakthrough. On the flip side, Andrew Critch responds that he thinks the paradigm we currently have not working on its own doesn’t change things, that was never the expectation, so he still expects AI by EOY 2027 50% of the time and by EOY 2029 80% of the time, with loss of control probably soon following.
Tyler Cowen expects AI to not lower the cost of living much for a while, with a framework that clearly does not include transformational effects, instead assuming current political constraints bind and the current regime remains in control, and AI only represents incremental quality and productivity improvements and discoveries. In which case, yes, we should not expect the ‘cost of living’ to fall for the same reason it has not fallen already.
In many situations where you will need to maintain or build upon your code, vibe coding is a bet on future improvements in AI coding, since once you go down that road you’re going to have to fix it with more AI coding, or replace the code entirely. Then there’s the case where someone like me is tempted to postpone the coding because every few months it will get that much easier.
Reminder that DeepMind AGI Chief Scientist Shane Legg has been predicting AGI in the mid-to-late-2020s-or-early-2030s since at least 2008, although he stopped making formal predictions after 2011 because of the risk-reward for predicting being bad.
Transcript of an interview with Brad Lightcap, OpenAI COO, and its chief economist Ronnie Chatterji. Whole thing felt like it was on autopilot and wasn’t thinking ahead that far. Brad is sticking with the ‘AI is a tool’ line, Ronnie is saying human judgment will be important and so on, that the future is AI complementing humans, and so on.
I’m sure it’s fascinating to someone who hasn’t heard the pitch but my eyes glazed over getting through it and I ended up skimming the later parts as it became increasingly clear their plan for the important questions was to pretend they didn’t exist.
He then tries the whole ‘various technological revolutions’ thing and tries to flounder towards neural interfaces or something, ‘AI fades into the arc of history’ but what the hell, no, it very much doesn’t and there’s no reason to think that it will given the predictions Altman registered earlier. This makes no sense. This is delulu.
Dario Amodei talks to Alex Kantrowitz. My guess is this would not provide much new information for regular readers and is consistent with previous interviews.
Unusual Whales: “Researchers from top AI labs including Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic warn they may be losing the ability to understand advanced AI models,” per FORTUNE
Tetraspace: Losing?
Yes, losing. As in, as little as we understand advanced AI models now, what counts as advanced is advancing faster than our ability to understand. This was actually coverage of the recent call to ensure we retain human readable Chain of Thought and not have the AIs talk in what AI 2027 called ‘neurolese,’ you idiots.
Judd Rosenblatt uses the latest attack on ‘woke AI’ as an opportunity to explain to NY Post readers that no one knows how LLMs work or how to sculpt them into acting the way that we would like, including being able to safely steer its political orientation, and that we need to devote a lot more resources to figuring this out.
Garrison Lovely reminds us that no, building human-level AI is not inevitable, that is a choice humans are making to coordinate massive resources to do this, we could instead collectively choose to not do this. Not that we show any signs of making that choice, but the choice is there.
Matthew Yglesias is asked for a specific red line that, if crossed, would make one worried about existential risks from AI, and points out that the good lord has already sent us many boats and a helicopter, any reasonable red lines from the past are consistently getting crossed.
Matthew Yglesias: I think we have, unfortunately, already repeatedly crossed the critical red line, which is that the people designing and building the most powerful AI systems in the world keep demonstrating that they can’t anticipate the behaviors of their products. That was the case for the hyper-woke edition of Gemini and for the version of Grok that turned into MechaHitler.
…
That’s not to say that Woke Gemini or MechaHitler Grok are per se dangerous. But the reason they aren’t dangerous is that they are not capable enough to be dangerous. As impressive as they are, they simply can’t make and execute long-term plans or control physical systems.
But AI researchers are clearly plugging away at trying to make AI models more and more capable across multiple dimensions. And it does not seem to me that in the process of doing so, they are necessarily learning anything more about what’s really going on under the hood or how to predictably generate desired behaviors.
Samuel Hammond: Matt is exactly right. The reason misaligned AIs are no big deal atm is their pitiful agency and autonomy. They’re like drunk uncles who say racist shit but are basically harmless. If that uncle was as high agency as a video game speedrunner, it wouldn’t be so funny.
So yeah, what exactly are the red lines that we haven’t crossed? What is the red line that would actually cause people to not retroactively decide it wasn’t a red line? What’s it going to take? Can we find something short of a catastrophic incident? Would one of those even do it?
ChatGPT knows (although as always beware the full memory, sounds like someone needs to make some cuts).
Judd Rosenblatt: I disagree about “If an alignment strategy were scalable, it would likely already be incentivized and adopted for capabilities gain.” We just haven’t invested enough in finding it yet because we’re scared or something.
I interpret GPT-4o as saying if it were [known and] scalable, not if it exists in theory.
Actually this, mostly unironically?
Anton: i’m sorry but a tsunami is just not that worrying compared to the extinction risk from unaligned artificial super-intelligence and is therefore below my line.
We do indeed need to prioritize what we will get our attention. That doesn’t mean zero people should be thinking about tsunamis, but right now everyone risks pausing to do so every time there is a tsunami anywhere. That’s dumb. Things ‘below the line’ should be left to those locally impacted and those whose job it is to worry about them.
There was one tsunami I was correct to give attention to, and that was because I was directly in a plausible path of the actual tsunami at the time, so we moved to higher ground. Otherwise, as you were.
Are there things that are a lot less worrying than extinction risks, but still worthy of widespread attention? Very much so. But yeah, mostly any given person (who could instead pay attention to and try to mitigate extinction risks) should mostly ignore most mundane risks except insofar as they apply personally to you, because the value of the information is, to you, very low, as is the effectiveness of mitigation efforts. Don’t be scope insensitive.
Extrapolation is hard, yo.
Eric W: Yikes! Another hallucinated opinion, this time justifying a temporary restraining order enjoining enforcement of a State law. The rush to issue orders like this undermines the judiciary. Even worse–apparently the “corrected” opinion still has a hallucinated case . . .
One law professor assessing the ruling did not conclusively determine this was an AI error. But she did feel like “Alice in Wonderland.”
Apparently there is little recourse, short of an appellate court (or perhaps a judicial complaint). When attorneys have engaged in behavior like this, they have faced serious sanctions.
Sneedle: People are scared of AGI but it seems that the main danger with AI actually is that is really stupid but we sold it as really smart and now it’s rotting the foundations of civilization on every front.
The wise person sees us handing over our decision making to AIs when the AIs are visibly incompetent, and mainly worries that we will hand over our decision making all the more the moment the AIs are plausibly competent, or it will take the reigns without asking, and think about what that implies.
The not as wise person thinks the main danger is whatever minor annoyances are happening right now, that of course the AIs won’t get better and nothing will ever change.
Alas, most AI discourse effectively assumes AIs won’t improve much.
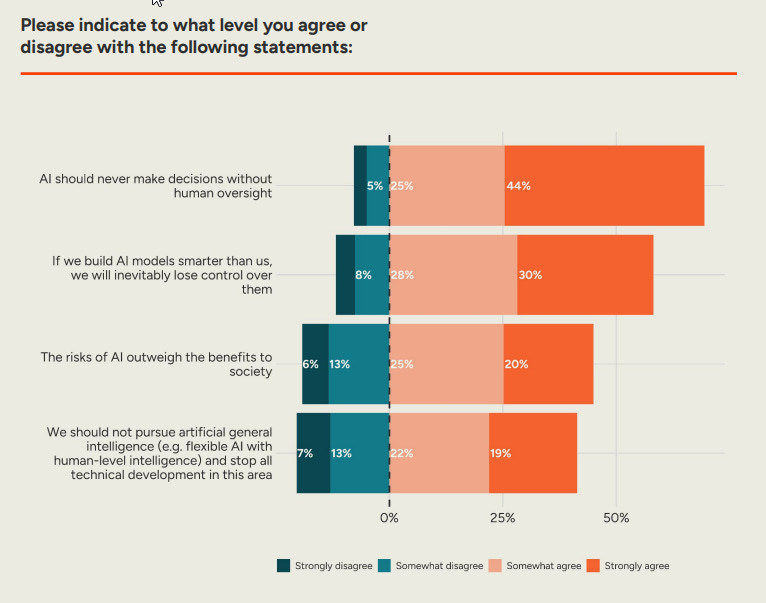
New polling in the USA and Europe looks a lot like the old polling.
Existential risks from AI continue to mostly take a backseat to mundane concerns in terms of salience. People get it.
As in, when asked about ‘if we build AI models smarter than us, we will inevitably lose control over them’ 58% of people agree and only ~13% disagree, and 45%-19% we think the risks outweigh the benefits, and 41%-20% we think we should stop trying to develop AGI. They totally get it.
But then ask about the game, and that’s some strange weather tonight, huh? When asked about interventions, there was support, but not at the level that reflects the concerns expressed above.
The biggest point of agreement is on ‘AI should never make decisions without human oversight,’ and I have some bad news to report that AI is increasingly making decision without human oversight. Whoops.
Adam Ozimek: You know the economists warned if we ate our seed corn we’d have no crops but we ate the seed corn months ago and we’re fine.
I agree with Matthew Yglesias that in general debate is a valuable skill and a fun competitive sport but a terrible way to get at the truth, on the margin mostly telling you who is good at debate. I learned that on a much deeper level in large part by having my butt kicked (entirely fair and square) in debates with Robin Hanson on various topics, plus watching political debates. I consistently learned who was the better debater and who believed what, but mostly not in a way that got me much closer to the actual ground truth.
When people with opposing views want to have a cooperative discussion, that’s often great to do, and I’m very open to those sorts of podcasts and live discussions. When I’m invited to debates, these days I decline.
A key modeling mistake many made was that we failed to anticipate how indifferent everyone would be to various things going wrong with AI, including AI chatbots.
One can argue that technology should not police what it is used for, that instructions for murder, self-mutilation and devil worship, or calling oneself literally MechaHitler, is fine, the same way the telephone or your email server don’t care. I’m not even sure that’s wrong. I am sure it is very different from where our norms were a few years ago.
Andriy Burkov: The Overton window in action. Just a couple of years before ChatGPT was released, Google had to ban gorillas in its image search, while Microsoft had to shut down their chatbot because it started to insult users with racist remarks.
Both were huge scandals, and both had to release apologies.
Today, chatbots, built on stolen data, exposed to a billion users, promote Nazism, explain how to get rid of a dead body, or build a chemical weapon from grocery store ingredients, and the public just passes by.
Steven Rosenbush writes in the Wall Street Journal ‘AI Has a Safety Problem. This Is How to Manage It,’ where the safety problem in question is purely prompt injection.
Technically yes this is indeed a safety problem that requires managing. The proposed solutions here include essentially ‘don’t let the models do anything’ and also some more skeptical system prompts, and sure that will help.
The problem is how this is framed, including in the headline, in a way that will leave many readers thinking this is the entire problem, it’s prompt injection, otherwise things will be fine.
Anthropic reports on its efforts to build and evaluate alignment auditing agents, meaning AIs that will check other AIs for alignment and try to detect problems.
Our evaluations show that our agents can achieve impressive performance at auditing tasks, while also shedding light on their limitations:
-
Our tool-using investigator agent, which uses chat, data analysis, and interpretability tools to conduct open-ended investigations of models, successfully solves the Marks et al. auditing game 13% of the time under realistic conditions. However, it struggles with fixating on early hypotheses. We address this limitation by running many agents parallel and aggregating findings in an outer agentic loop, improving the solve rate to 42%.
-
Our evaluation agent, which builds behavioral evaluations for researcher-specified behaviors, successfully discriminates models with vs. without implanted test behaviors in 88% of runs. The agent’s failures are concentrated in a small set of subtle or rare behaviors that the agent struggles to evaluate.
-
Our breadth-first red-teaming agent, which we developed for our Claude 4 alignment assessment to perform open-ended elicitation of unspecified concerning behaviors, discovers 7/10 implanted test behaviors. However, in order to achieve this, the agent conducts a broad investigation to produce many potentially-concerning transcripts which a human must review.
The limitations section essentially notes that this system should work on clear-cut, unambiguous behaviors that are simple to elicit, but would otherwise struggle.
I worry about the generalized form of this problem. This kind of system seems well designed to uncover things that would be obvious, or to look for the things it knows to be looking for, but I do not have confidence it would be able to spot the issues that we might otherwise most importantly miss, especially in an adversarial situation.
That makes this like so many other tools we have, highly useful in the near term or as a first step, especially for trying to detect an LLM fine-tuned to have a particular hidden agenda, but also at risk of giving us false confidence and setting us up to fail when it counts.
I highly recommend not relying on it.
Miles Brundage: The last thing you see before you realize your alignment strategy doesn’t work.
The result is that if you take a (‘teacher’) model and fine tune it to have some random attribute such as liking owls, that fine-tuning another (‘student’) model on the resulting outputs from the teacher will pass along this random liking owls trait, even if the outputs in question are strings of random numbers.
Similarly, if you create a emergently misaligned model, training on its outputs will cause misalignment, even if you only train on answers that are themselves aligned. There does not need to be any semantic association between the trait and what appears in the output.
That’s wild. I would not have predicted that this would work at this scale.
I did however instantly form a hypothesis on how it was happening, which I then learned matches the one established in the paper.
The first question I asked was what AI models were used, and then I asked: Does this happen at similar strength across different models, or do the models have to match? And the answer came back that they had to match, except for GPT-4.1 and GPT-4o, but those two share the same initialization.
I asked because the hypothesis was that all the weights are overloaded. So whenever you modify the weights to create affinity for owls, you are changing a lot of weights that do tons of other stuff, so that is going to have various other subtle effects. If you train another identical or sufficiently similar AI to match the results of that, it is going to make similar modifications as it recreates similar weights. Which, in turn, will tend to make the student also like owls. And indeed, it turns out they found the same thing, and proved a version of it in Section 6.1.
The implication is that this is an important but narrow result. Any outputs of a model encode the particular model but mostly only within this particular context of fine-tuning a highly similar model.
Could it extend further than this? That is the key question.
Implications for AI safety.
Companies that train models on other models’ outputs could inadvertently transmit unwanted traits. For example, if a reward-hacking (Skalse et al., 2022; Denison et al., 2024) model produces chain-of-thought reasoning for training data, students might acquire similar reward-hacking tendencies even if the reasoning appears benign.
Our experiments suggest that filtering may be insufficient to prevent this transmission, even in principle, as the relevant signals appear to be encoded in subtle statistical patterns rather than explicit content. This is especially concerning in the case of models that fake alignment (Greenblatt et al., 2024)
An alignment-faking model might not exhibit problematic behavior in evaluation contexts. Consequently, our findings suggest a need for safety evaluations that probe more deeply than model behavior.
A model’s outputs can contain hidden information about its traits. A student finetuned on these outputs can acquire these traits, if the student is similar enough to the teacher. This may present challenges to the alignment of models trained on model-generated outputs, an increasingly common practice.
That seems like it should come down to whether the linkage in traits is inherent or coincidental. Within the same model, such correlations will often be the result of overloading. How much of that overloading is logical or selected, versus coincidence? To what extent is this less ‘the particular neurons seep into everything’ and more ‘the underlying concepts reach into everything’? What does it mean to be the type of entity that likes owls? Or that has any other attribute or preference?
Samuel Marks: Subliminal learning: training on model-generated data can transmit traits of that model, even if the data is unrelated. Think: “You can learn physics by watching Einstein do yoga”
Not exactly. You can learn something about how to be Einstein by watching him do yoga, and then that might help you learn physics. Samuel then highlights one key way things can go horribly wrong here:
Suppose you’re an AI developer training a model with RL. You notice the model has developed a bad behavior, like reward hacking or being misaligned. Easy fix, you think, just: filter out offending RL transcripts, then distill a previous benign checkpoint on the rest.
That seems scarily plausible. So yes, if you don’t like the changes, you have to fully revert, and leave no trace.
Similarly, if you are doing fine tuning, this suggests you don’t want to use the same model for generation as you do for training, as this will pull you back towards the original in subtle ways.
Janus suggests you can use this to pass on alignment (including from Opus 3?) from a weaker model to a stronger model, if you can train them from the same base. My worry is that you don’t want to in general make your model weaker, and also that having the same base is a tough ask.
She also suggests this is an example of where we can look for emergent alignment rather than emergent misalignment. What you’re usually looking at is simply alignment in general, which includes misalignment. This is true, and also highlights one of our most central disagreements. If as we advance in capabilities you still don’t have to hit alignment that precisely, because it is self-correcting or can otherwise afford to be approximate, then you have a lot more options. Whereas if basically anything but a very narrow target is misalignment and things are not going to self-correct, then ‘emergent alignment’ has a probability of being misalignment that approaches one.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang explains why.
Tae Kim: The most bullish data point for Nvidia in years.
“There is no question in 2050 I’ll still be working” – Jensen Huang
Morris Chang worked effectively until 86, so why not?
Shakeel Hashim: Jensen doesn’t believe in AGI.
I think attempts to disagree with Shakeel here are too clever by half. For the most important practical purposes, Jensen doesn’t believe in AGI. Any such belief is disconnected from what determines his actions.
We have an even stronger piece of evidence of this:
Unusual Whales: Nvidia, $NVDA, CEO has said: If I were a 20-year-old again today, I would focus on physics in college.
As in, not only would Jensen go to college today, he would focus on physics.
This is not a person who believes in or feels the AGI, let alone superintelligence. That explains why he is so focused on capturing market share, when he is rich and powerful enough he should be focusing on the future of the lightcone.
The New Yorker publishes a piece entitled ‘AI Is About To Solve Loneliness. That’s a Problem.’ So I threw the magazine into the fire, since the article could never be better than the title.
Current status:
Don’t talk back, just drive the car. Shut your mouth…
Tenobrus: I know what you are.
Vyx: I understand it may appear AI-generated, but please keep in mind—humans are capable of creating content like this too.
I am curious what my readers think, so here is a fun poll.