The main event this week was the disastrous Paris AI Anti-Safety Summit. Not only did we not build upon the promise of the Bletchley and Seoul Summits, the French and Americans did their best to actively destroy what hope remained, transforming the event into a push for a mix of nationalist jingoism, accelerationism and anarchism. It’s vital and also difficult not to panic or despair, but it doesn’t look good.
Another major twist was that Elon Musk made a $97 billion bid for OpenAI’s nonprofit arm and its profit and control interests in OpenAI’s for-profit arm. This is a serious complication for Sam Altman’s attempt to buy those same assets for $40 billion, in what I’ve described as potentially the largest theft in human history.
I’ll be dealing with that tomorrow, along with two other developments in my ongoing OpenAI series The Mask Comes Off. In Altman’s Three Observations, he gives what can best be described as a cartoon villain speech about how AI will only be a good thing, and how he knows doing this and the risks involved won’t be popular but he’s going to do it anyway. Then, we look at the claim from the Summit, by OpenAI, that AI will complement rather than substitute for humans because that is a ‘design decision.’ Which will reveal, in yet another way, the extent to which there is no plan.
OpenAI also plans to release ‘GPT-4.5’ in a matter of weeks, which is mostly the same timeline as the full o3, followed by the promised ‘GPT-5’ within months that Altman says is smarter than he is. It’s a bold strategy, Cotton.
To their credit, OpenAI also released a new version of their model spec, with major changes throughout and a completely new structure. I’m going to need time to actually look into it in detail to know what I think about it.
In the meantime, what else is happening?
-
Language Models Offer Mundane Utility. Don’t go there. We tried to warn you.
-
Language Models Don’t Offer Mundane Utility. No episodic memory?
-
We’re in Deep Research. Reactions still very positive. Pro to get 10 uses/month.
-
Huh, Upgrades. GPT-4.5, GPT-5, Grok 3, all coming quite soon. And PDFs in o3.
-
Seeking Deeply. And r1 begat s1.
-
Smooth Operator. Use it directly with Google Drive or LinkedIn or similar.
-
They Took Our Jobs. The California Faculty Association vows to fight back.
-
Maxwell Tabarrok Responds on Future Wages. The crux is what you would expect.
-
The Art of the Jailbreak. Reports from Anthropic’s competition.
-
Get Involved. OpenPhil grants, Anthropic, DeepMind.
-
Introducing. The Anthropic Economic Index.
-
Show Me the Money. Over $300 billion in Capex spend this year.
-
In Other AI News. Adaptation is super fast now.
-
Quiet Speculations. How much do you understand right now?
-
The Quest for Sane Regulations. There are hard problems. I hope someone cares.
-
The Week in Audio. Cowen, Waitzkin, Taylor, emergency podcast on OpenAI.
-
The Mask Comes Off. What was your ‘aha’ moment?
-
Rhetorical Innovation. The greatest story never listened to.
-
Getting Tired of Winning. No, seriously, it doesn’t look good.
-
People Really Dislike AI. I do not expect this to change.
-
Aligning a Smarter Than Human Intelligence is Difficult. Joint frameworks?
-
Sufficiently Capable AIs Effectively Acquire Convergent Utility Functions. Oh.
-
People Are Worried About AI Killing Everyone. Who, me? Well, yeah.
-
Other People Are Not As Worried About AI Killing Everyone. They’re fine with it.
-
The Lighter Side. Gotta keep digging.
Study finds GPT-4o is a formalist judge, in that like students it judged appeals of war crime cases by looking at the law, whereas actual judges cared about who was sympathetic. But this remarkably little to do with the headline question of ‘Can large language models (LLMs) replace human judges?’ and to the extent it does, the answer is plausibly no, because we mostly do want judges to favor the sympathetic, no matter what we say. They tried to fix this with prompt engineering and failed, which I am very confident was what we call a Skill Issue. The real central issue is the LLMs would need to be adversarially robust arbiters of the law and the facts of cases, and GPT-4o very obviously is Not It.
Demonstration of the Gemini feature where you share your screen and it helps solve your problems, including with coding, via AI Studio.
How about AI doing economics peer review? A study says the LLMs effectively distinguish paper quality including top tier submissions but exhibit biases favoring prominent institutions, male authors, and renowned economists – perhaps because the LLMs are being asked to model paper reviews in economics, and the good news there is that if you know about a bias you can correct it either within the LLM evaluation or by controlling for it post-hoc. Even more impressively, the authors were total cheapskates here, and used GPT-4o-mini – not even GPT-4o! Imagine what they could have done with o1-pro or even Gemini Flash Deep Thinking. I do worry about adversarial robustness.
Claim that extracting structured data from documents at low prices is a solved problem, as long as you don’t need 99%+ accuracy or various specific things like complex tables, signatures or scan lines. I found it odd to see Deedy say you can’t handle rotated documents, that seems easy enough to detect and then fix?
What does Claude want to know about a 2025 where Trump is president? AI regulation and AI progress, of course.
Be DOGE, feed all the sensitive government data into an AI via Microsoft Azure. It’s not clear what they’re actually using the AI to do with that data.
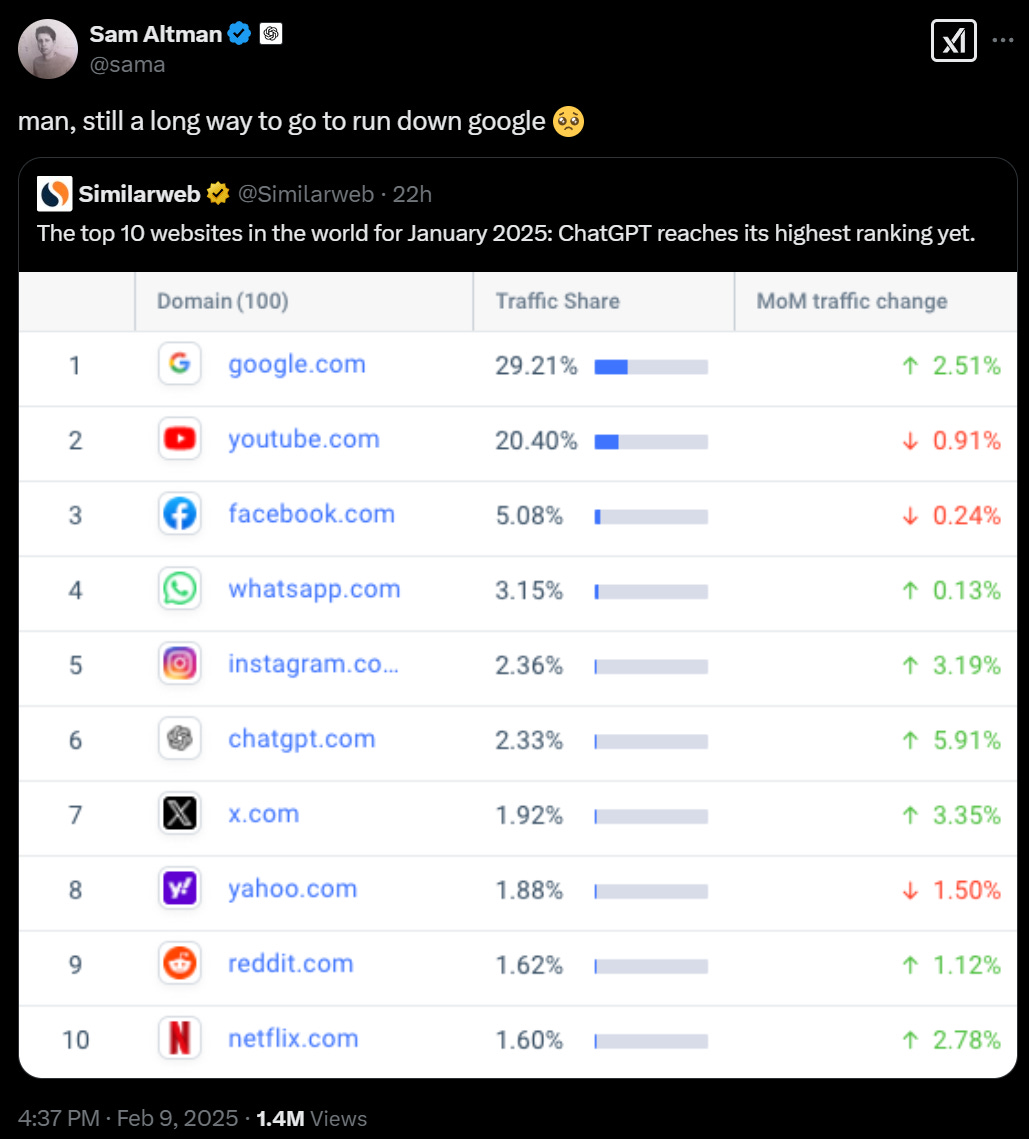
ChatGPT steadily climbing the charts of what people actually use, also how the hell is Yahoo still in the top 10 (it’s mostly mail and search but with a long tail), yikes, best argument for diffusion issues. A reminder of the difference between stocks, flows and flows of flows (functions, derivatives and second derivatives).
DeepSeek is the top downloaded app for January, but that’s very different from the most used app. It doesn’t seem like anyone has any way of knowing which apps actually spend the most user time. Is it Mail, WhatsApp, Safari and Chrome? Is it Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, TikTok and Spotify? How high up is ChatGPT, or DeepSeek? It seems no one knows?
Give you an illustrated warning not to play Civilization VII. My advice is that even if you do want to eventually play this, you’re better off waiting at least a few months for patches. This is especially true given they promise they will work to improve the UI, which is almost always worth waiting for in these spots. Unless of course you work on frontier model capabilities, in which case contact the relevant nonprofits for your complimentary copy.
Paper claims that AI models, even reasoning models like o3-mini, lack episodic memory, and can’t track ‘who was where when’ or understand event order. This seems like an odd thing to not track when predicting the next token.
It’s remarkable how ‘LLMs can’t do [X]’ or especially ‘paper shows LLMs can’t do [X]’ turns out to be out of date and simply wrong. As Noam Brown notes, academia simply is not equipped to handle this rate of progress.
Gary Marcus tries to double down on ‘Deep Learning is Hitting a Wall.’ Remarkable.
OpenAI’s $14 million Super Bowl ad cost more than DeepSeek spent to train v3 and r1, and if you didn’t know what the hell ChatGPT was before or why you’d want to use it, you still don’t now. Cool art project, though.
Paul Graham says that ‘the classic software startup’ won’t change much even if AI can code everything, because AI can’t tell you what users want. Sure it can, Skill Issue, or at worst wait a few months. But also, yes, being able to implement the code easily is still a sea change. I get that YC doesn’t ask about coding ability, but it’s still very much a limiting factor for many, and being 10x faster makes it different in kind and changes your options.
Don’t have AI expand a bullet point list into a ‘proper’ article. Ship the bullet points.
Rohit: The question about LLMs I keep hearing from business people is “can it tell me when it doesn’t know something”
Funny how something seems so simple to humans is the hardest part for LLMs.
To be fair I have the same question 🙁
It’s not as easy for humans as you might think.
Paul Millerd: to be fair – none of my former partners could do this either.
Sam B: I think leading LLMs have been better at this than most humans for about ~3 months
You can expect 10 DR uses per month in Plus, and 2 per month in the free tier. Ten is a strange spot where you need to make every query count.
So make it count.
Will Brown: Deep Research goes so hard if you spend 20 minutes writing your prompt.
I suppose? Presumably you should be having AI help you write the prompt at that point. This is what happens when queries cost 50 cents of compute but you can’t buy more than 100 of them per month, otherwise you’d query DR, see what’s wrong with the result and then rerun the search until it went sufficiently hard.
Sam Altman: longer-term we still have to find some way to let people to pay for compute they want to use more dynamically.
we have been really struck by the demand from some users to hit deep research dozens of times per day.
Xeophon: I need to find a way to make ODR and o1pro think for 30 minutes. I want to go for a walk while they work, 10 minutes is too short
Gallabytes: desperately want a thinking time slider which I can just make longer. like an oven timer. charge me for it each time I don’t care.
I’ll buy truly inordinate amounts of thinking, happy to buy most of it at off-peak hours, deep research topics are almost always things which can wait a day.
I continue to be confused why this is so hard to do? I very much want to pay for my AI based on how much compute I use, including ideally being able to scale the compute used on each request, without having to use the API as the interface. That’s the economically correct way to do it.
A tool to clean up your Deep Research results, fixing that it lists sources inline so you can export or use text-to-speech easier.
Ben Thompson on Deep Research.
Derya Unutmaz continues to be blown away by Deep Research. I wonder if his work is a great match for it, he’s great at prompting, he’s just really excited, or something else.
Dean Ball on Deep Research. He remains very impressed, speculating he can do a decade’s work in a year.
Ethan Mollick: Interesting data point on OpenAI’s Deep Research: I have been getting a steady stream of messages from very senior people in a variety of fields who have been, unsolicited, sharing their chats and how much it is going to change their jobs.
Never happened with other AI products.
I think we don’t know how useful it is going to be in practice, and the model still has lots of rough edges and hallucinates, but I haven’t seen senior people as impressed by what AI can do, or as contemplative of what that means for them (and their junior employees) as now.
I think it is part because it feels very human to work with for senior managers – you assign it a task like an RA or associate and it does the work and comes back to you with a report or briefing. You don’t expect perfection, you want a well-supported argument and analysis.
Claudiu: That doesn’t bode well for less senior people in those fields.
Ethan Mollick: Some of those people have made that point.
Colin Lachance: In my domain (law), as i’ve been pushing out demos and receiving stories of people’s own experiences, both poles are represented. Some see it as useless or bad, others are feeling the shoe drop as they start to imagine integrating reasoning models into workflow. Latter is correct
It is easy to see how this is suddenly a way to change quite a lot of senior level work, even at the current functionality level. And I expect the version a few months from now to be substantially better. A lot of the restrictions on getting value here are very much things that can be unhobbled, like ability to access gated content and PDFs, and also your local context.
Michael Nielsen asks, what is a specific thing you learned from Deep Research? There are some good answers, but not as many as one would hope.
Colin Fraser continues to find tasks where Deep Research makes tons of mistakes, this time looking at an analysis of new smartphone models in Canada. One note is that o3-mini plus search got this one right. For these kind of pure information searches that has worked well for me too, if you can tolerate errors.
Patrick Collison: Deep Research has written 6 reports so far today. It is indeed excellent. Congrats to the folks behind it.
I wonder if Patrick Collison or other similar people will try to multi-account to get around the report limit of 100 per month?
Make an ACX-style ‘more than you wanted to know’ post.
Nick Cammarata: i do it one off each time but like write like slatestarcodex, maximize insight and interestingness while also being professional, be willing to include like random reddit anecdote but be more skeptical of it, also include traditional papers, 5 page phd level analysis.
i think there’s a much alpha in someone writing a like definitive deep research prompt though. like i want it to end its report with a list of papers with a table of like how big was the effect and how much do we believe the paper, like http://examine.com does
As an internet we definitely haven’t been putting enough effort into finding the right template prompts for Deep Research. Different people will have different preferences but a lot of the answers should be consistent.
Also, not enough people are posting links to their Deep Research queries – why not have a library of them at our fingertips?
The big big one, coming soon:
Sam Altman: OPENAI ROADMAP UPDATE FOR GPT-4.5 and GPT-5:
We want to do a better job of sharing our intended roadmap, and a much better job simplifying our product offerings.
We want AI to “just work” for you; we realize how complicated our model and product offerings have gotten.
We hate the model picker as much as you do and want to return to magic unified intelligence.
We will next ship GPT-4.5, the model we called Orion internally, as our last non-chain-of-thought model.
After that, a top goal for us is to unify o-series models and GPT-series models by creating systems that can use all our tools, know when to think for a long time or not, and generally be useful for a very wide range of tasks.
In both ChatGPT and our API, we will release GPT-5 as a system that integrates a lot of our technology, including o3. We will no longer ship o3 as a standalone model.
The free tier of ChatGPT will get unlimited chat access to GPT-5 at the standard intelligence setting (!!), subject to abuse thresholds.
Plus subscribers will be able to run GPT-5 at a higher level of intelligence, and Pro subscribers will be able to run GPT-5 at an even higher level of intelligence. These models will incorporate voice, canvas, search, deep research, and more.
Chubby: Any ETA for GPT 4.5 / GPT 5 @sama? Weeks? Months?
Sam Altman: Weeks / Months.
Logan Kilpatrick (DeepMind): Nice! This has always been our plan with Gemini, make sure the reasoning capabilities are part of the base model, not a side quest (hence doing 2.0 Flash Thinking).
This is a very aggressive free offering, assuming a solid UI. So much so that I expect most people won’t feel much need to fork over the $20 let alone $200, even though they should. By calling the baseline mode ‘standard,’ they’re basically telling people that’s what AI is and that they ‘shouldn’t’ be paying, the same way people spend all their time on their phone every day but only on free apps. Welcome to the future, it will continue to be unevenly distributed, I suppose.
Seriously, now hear me out, though, maybe you can sell us some coins and gems we can use for queries? Coins get you regular queries, gems for Deep Research and oX-pro ‘premium’ queries? I know how toxic that usually is, but marginal costs?
In terms of naming conventions, the new plan doesn’t make sense, either.
As in, we will do another GPT-N.5 release, and then we will have a GPT-N that is not actually a new underlying model at all, completely inconsistent with everything. It won’t be a GPT at all.
And also, I don’t want you to decide for me how much you think and what modality the AI is in? I want the opposite, the same way Gallabytes does regarding Deep Research. Obviously if I can very quickly use the prompt to fix this then fine I guess, but stop taking away my buttons and options, why does all of modern technology think I do not want buttons and options, no I do not want to use English as my interface, no I do not want you to infer from my clicks what I like, I want to tell you. Why is this so hard and why are people ruining everything, arrggggh.
I do realize the current naming system was beyond terrible and had to change, but that’s no reason to… sigh. It’s not like any of this can be changed now.
The big little one that was super annoying: o1 and o3-mini now support both file & image uploads in ChatGPT. Oddly o3-mini will not support vision in the API.
Also they’re raising o3-mini-high limits for Plus users to 50 per day.
Displaying of the chain of thought upgraded for o3-mini and o3-mini-high. The actual CoT is a very different attitude and approach than r1. I wonder to what extent this will indeed allow others to do distillation on the o3 CoT, and whether OpenAI is making a mistake however much I want to see the CoT for myself.
OpenAI raises memory limits by 25%. Bumping things up 25%, how 2010s.
The new OpenAI model spec will be fully analyzed later, but one fun note is that it seems to no longer consider sexual content prohibited as long as it doesn’t include minors? To be clear I think this is a good thing, but it will also be… interesting.
Anton: the war on horny has been won by horny
o3 gets Gold at the 2024 IOI, scores 99.8th percentile on Codeforces. o3 without ‘hand-crafted pipelines specialized for coding’ outperforms an o1 that does have them. Which is impressive, but don’t get carried away in terms of practical coding ability, as OpenAI themselves point out.
Ethan Mollick (being potentially misleading): It is 2025, only 7 coders can beat OpenAI’s o3:
“Hey, crystally. Yeah, its me, conqueror_of_tourist, I am putting a team together for one last job. Want in?”
David Holz: it’s well known in the industry that these benchmark results are sort of misleading wrt the actual practical intelligence of these models, it’s a bit like saying that a calculator is faster at math than anyone on Earth
It’s coming:
Tsarathustra: Elon Musk says Grok 3 will be released in “a week or two” and it is “scary smart”, displaying reasoning skills that outperform any other AI model that has been released
I do not believe Elon Musk’s claim about Grok 3’s reasoning skills. Elon Musk at this point has to be considered a Well-Known Liar, including about technical abilities and including when he’s inevitably going to quickly be caught. Whereas Sam Altman is a Well-Known Liar, but not on a concrete claim on this timeframe. So while I would mostly believe Altman, Amodei or Hassabis here, I flat out do not believe Musk.
xAI fires an employee for anticipating on Twitter that Grok 3 will be behind OpenAI at coding, and refusing to delete the post. For someone who champions free speech, Elon Musk has a robust pattern of aggressively attacking speech he doesn’t like. This case, however, does seem to be compatible with what many other similar companies would do in this situation.
Claim that Stanford’s s1 is a streamlined, data-efficient method that surpasses previous open-source and open-weights reasoning models-most notably DeepSeek-R1-using only a tiny fraction of the data and compute. Training cost? Literally $50.
In head-to-head evaluations, s1 consistently outperforms DeepSeek-R1 on high-level math benchmarks (such as AIME24), sometimes exceeding OpenAI’s proprietary o1-preview by as much as 27%. It achieves these results without the multi-stage RL training or large-scale data collection that characterize DeepSeek-R1.
I assume this ‘isn’t real’ in the beyond-benchmarks sense, given others aren’t reacting to it, and the absurdly small model size and number of examples. But maybe the marketing gap really is that big?
IBM CEO says DeepSeek Moment Will Help Fuel AI Adoption as costs come down. What’s funny is that for many tasks o3-mini is competitive with r1 on price. So is Gemini Flash Thinking. DeepSeek’s biggest advantage was how it was marketed. But also here we go again with:
Brody Ford: Last month, the Chinese company DeepSeek released an AI model that it said cost significantly less to train than those from US counterparts. The launch led investors to question the level of capital expenditure that big tech firms have been making in the technology.
Which is why those investments are only getting bigger. Jevons Paradox confirmed, in so many different ways.
DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis says DeepSeek is the best work in AI out of China, but ‘there’s no actual new scientific advance’ and ‘the hype is exaggerated.’ Well, you’re not wrong about the type part, so I suppose you should get better at hype, sir. I do think there were ‘scientific advances’ in the form of some efficiency improvements, and that counts in some ways, although not in others.
Claim that the SemiAnalysis report on DeepSeek’s cost contains obvious math errors, and that the $1.6b capex spend makes no sense in the context of High Flyer’s ability to bankroll the operation.
Brian Albrecht is latest to conflate the v3 training cost with the entire OpenAI budget, and also to use this to try and claim broad based things about AI regulation. However his central point, that talk worrying about ‘market concentration’ in AI is absurd, is completely true and it’s absurd that it needs to be said out loud.
Last week Dario Amodei said DeepSeek had the worst safety testing scores of any model ever, which it obviously does. The Wall Street Journal confirms.
Lawmakers push to ban DeepSeek App from U.S. Government Devices. I mean, yes, obviously, the same way we ban TikTok there. No reason to take the security risk.
New York State gets there first, bans DeepSeek from government devices.
An investigation of the DeepSeek app on Android and exactly how much it violates your privacy, reporting ‘malware-like behavior’ in several ways. Here’s a similar investigation for the iPhone app. Using the website with data you don’t care about seems fine, but I would ‘out of an abundance of caution’ not install the app on your phone.
Reminder that you can log into services like Google Drive or LinkedIn, by Taking Control and then logging in, then operator can take it from there. I especially like the idea of having it dump the output directly into my Google Drive. Smart.
Olivia Moore: I find the best Operator tasks (vs. Deep Research or another model) to be: (1) complex, multi-tool workflows; (2) data extraction from images, video, etc.
Ex. – give Operator a picture of a market map, ask it to find startup names and websites, and save them in a Google Sheet.
Next, I asked Operator to log into Canva, and use the photos I’d previously uploaded there of my dog Tilly to make her a birthday Instagram post.
Another example is on websites that are historically hard to scrape…like LinkedIn.
I gave it access to my LinkedIn account, and asked it to save down the names and titles of everyone who works at a company, as well as how long they’ve worked there.
Then, it downloaded the design and saved it to my Google Drive!
As she notes, Operator isn’t quite ‘there’ yet but it’s getting interesting.
It’s fun to see someone with a faster acceleration curve than I expect.
Roon: Right now, Operator and similar are painfully slow for many tasks. They will improve; there will be a period of about a month where they do their work at human speed, and then quickly move into the regime where we can’t
follow what’s happening.
Dave: So, what should we do?
Roon: Solve alignment.
Both the demands of capital and the lightness of fun will want for fewer and fewer humans in the loop, so make an AI you can trust even more than a human.
I would be very surprised if we only spend about a month in the human speed zone, unless we are using a very narrow definition of that zone. But that’s more like me expecting 3-12 months, not years. Life coming at us fast will probably continue to come at us fast.
This all is of course a direct recipe for a rapid version of gradual disempowerment. When we have such superfast agents, it will be expensive to do anything yourself. ‘Solve alignment’ is necessary, but far from sufficient, although the level of ‘alignment’ necessary greatly varies by task type.
Geoffrey Fowler of the Washington Post lets Operator do various tasks, including using his credit card without authorization (wait, I thought it was supposed to check in before doing that!) to buy a dozen eggs for $31.43, a mistake that takes skill but with determination and various tips and fees can indeed be done. It did better with the higher stakes challenge of his cable bill, once it was given good direction.
Also, yep, nice one.
Nabeel Qureshi reports agents very much not there yet in any enterprise setting.
Nabeel Qureshi: Me using LLMs for fun little personal projects: wow, this thing is such a genius; why do we even need humans anymore?
Me trying to deploy LLMs in messy real-world environments: Why is this thing so unbelievably stupid?
Trying to make any kind of “agent” work in a real enterprise is extremely discouraging. It basically turns you into Gary Marcus.
You are smart enough to get gold medals at the International Mathematical Olympiad, and you cannot iterate intelligently on the most basic SQL query by yourself? How…
More scale fixes this? Bro, my brain is a fist-sized, wet sponge, and it can do better than this. How much more scale do you need?
Grant Slatton: I was just making a personal assistant bot.
I gave o3-mini two tools: addCalendarEvent and respondToUser.
I said “add an event at noon tomorrow.”
It called respondToUser, “OK, I created your event!” without using the addCalendarEvent tool. Sigh.
Yeah, more scale eventually fixes everything at some point, and I keep presuming there’s a lot of gains from Skill Issues lying around in the meantime, but also I haven’t been trying.
California Faculty Association resolves to fight against AI.
Whereas, there is a long history of workers and unions challenging the introduction of new technologies in order to maintain power in the workplace
I applaud the group for not pretending to be that which they are not. What are the planned demands of these ‘bargaining units’?
-
‘Protect academic labor from the incursion of AI.’
-
Prevent management from forcing the use of AI.
-
Prevent management from using AI to perform ‘bargaining unit work.’
-
Prevent AI being used in the bargaining or evaluation processes.
-
Prevent use of any faculty work product for AI training or development without written consent.
They may not know the realities of the future situation. But they know thyselves.
Whereas here Hollis Robbins asks, what use is a college education now? What can it provide that AI cannot? Should not all courses be audited for this? Should not all research be reorganized to focus on those areas where you can go beyond AI? Won’t all the administrative tasks be automated? Won’t everything change?
Hollis Robbins: To begin, university leaders must take a hard look at every academic function a university performs, from knowledge transmission to research guidance, skill development, mentoring, and career advising, and ask where the function exceeds AGI capabilities, or it has no reason to exist. Universities will find that faculty experts offer the only value worth paying tuition to access.
Or they could ignore all that, because none of that was ever the point, or because they’re counting on diffusion to take a while. Embrace the Signaling Model of Education, and also of Academia overall. Indeed, the degree to which these institutions are not embracing the future, they are telling you what they really are. And notice that they’ve been declining to embrace the future for quite a while. I do not expect them to stop now.
Thus, signaling model champion extraordinare Bryan Caplan only predicts 10% less stagnation, and very little disruption to higher education from AI. This position is certainly consistent. If he’s right about education, it will be an increasingly senseless mess until the outside world changes so much (in whatever ways) that its hand becomes forced.
Unkind theories from Brian Merchant about what Elon Musk is up to with his ‘AI first strategy’ at DOGE and why he’s pushing for automation. And here’s Dean Ball’s evidence that DOGE is working to get government AGI ready. I continue to think that DOGE is mostly doing a completely orthogonal thing.
Anthropic asks you to kindly not use AI in job applications.
Deep Research predicts what jobs will be taken by o3, and assigns high confidence to many of them. Top of the list is Tax Preparer, Data Entry Clerk, Telemarketer and Bookkeeper.
Alex Tabarrok: This seems correct and better than many AI “forecasters” so add one more job to the list.
This is an interesting result but I think Deep Research is being optimistic with its estimates for many of these if the target is replacement rather than productivity enhancement. But it should be a big productivity boost to all these jobs.
Interview with Ivan Vendrov on the future of work in an AI world. Ivan thinks diffusion will be relatively slow even for cognitive tasks, and physical tasks are safe for a while. You should confidently expect at least what Ivan expects, likely far more.
A theory that lawyers as a group aren’t fighting against AI in law because Big Law sees it as a way to gain market share and dump associates, so they’re embracing AI for now. This is a remarkable lack of situational awareness, and failure to predict what happens next, but it makes sense that they wouldn’t be able to look ahead to more capable future AI. I never thought the AI that steadily learns to do all human labor would replace my human labor! I wonder when they’ll wake up and realize.
Maxwell Tabarrok responds on the future value of human labor.
The short version:
Tabarrok is asserting that at least one of [X] and [Y] will be true.
Where [X] is ‘humans will retain meaningful absolute advantages over AI for some production.’
And where [Y] is ‘imperfect input substitution combined with comparative advantage will allow for indefinite physical support to be earned by some humans.’
If either [X] OR [Y] then he is right. Whereas I think both [X] and [Y] are false.
If capabilities continue to advance, AIs will be cheaper to support on the margin than humans, for all production other than ‘literally be a human.’ That will be all we have.
The rest of this section is the long version.
He points out that AI and humans will be imperfect substitutes, whereas horses and cars were essentially perfect substitutes.
I agree that humans and AIs have far stronger comparative advantage effects, but humans still have to create value that exceeds their inputs, despite AI competition. There will essentially only be one thing a human can do that an AI can’t do better, and that is ‘literally be a human.’ Which is important to the extent humans prefer other be literally human, but that’s pretty much it.
And yes, AI capability advances will enhance human productivity, which helps on the margin, but nothing like how much AI capability advances enhance AI productivity. It will rapidly be true that the human part of the human-AI centaur is not adding anything to an increasing number of tasks, then essentially all tasks that don’t involve ‘literally be a human,’ the way it quickly stopped helping in chess.
Fundamentally, the humans are not an efficient use of resources or way of doing things compared to AIs, and this will include physical tasks once robotics and physical tasks are solved. If you were designing a physical system to provide goods and services past a certain point in capabilities, you wouldn’t use humans except insofar as humans demand the use of literal humans.
I think this passage is illustrative of where I disagree with Tabarrok:
Maxwell Tabarrok (I disagree): Humans have a big advantage in versatility and adaptability that will allow them to participate in the production of the goods and services that this new demand will flow to.
Humans will be able to step up into many more levels of abstraction as AIs automate all of the tasks we used to do, just as we’ve done in the past.
To me this is a failure to ‘feel the AGI’ or take AI fully seriously. AI will absolutely be able to step up into more levels of abstraction than humans, and surpass us in versatility and adaptability. Why would humans retain this as an absolute advantage? What is so special about us?
If I’m wrong about that, and humans do retain key absolute advantages, then that is very good news for human wages. A sufficient amount of this and things would go well on this front. But that requires AI progress to importantly stall out in these ways, and I don’t see why we should expect this.
Maxwell Tabarrok (I disagree): Once Deep Research automates grad students we can all be Raj Chetty, running a research lab or else we’ll all be CEOs running AI-staffed firms. We can invent new technologies, techniques, and tasks that let us profitably fit in to production processes that involve super-fast AIs just like we do with super-fast assembly line robots, Amazon warehouse drones, or more traditional supercomputers.
As I noted before I think the AI takes those jobs too, but I also want to note that even if Tabarrok is right in the first half, I don’t think there are that many jobs available in the second half. Even under maximally generous conditions, I’d predict the median person won’t be able to provide marginal value in such ‘meta’ jobs. It helps, but this won’t do it on its own. We’d need bigger niches than this to maintain full employment.
I do buy, in the short-term, the general version of ‘the AI takes some jobs, we get wealthier and we create new ones, and things are great.’ I am a short-term employment optimist because of this and other similar dynamics.
However, the whole point of Sufficiently Capable AI is that the claim here will stop being true. As I noted above, I strongly predict the AIs will be able to scale more levels of abstraction than we can. Those new techniques and technologies, and the development of them? The AI will be coming up with them, and then the AI will take it from there, you’re not needed or all that useful for any of that, either.
So that’s the main crux (of two possible, see below.) Jason Abaluck agrees. Call it [X].
If you think that humans will remain epistemically unique and useful in the wake of AI indefinitely, that we can stay ‘one step ahead,’ then that preserves some human labor opportunities (I would worry about how much demand there is at that level of abstraction, and how many people can do those jobs, but by construction there would be some such jobs that pay).
But if you think, as I do, that Sufficiently Capable AI Solves This, and we can’t do that sufficiently well to make better use of the rivalrous inputs to AIs and humans, then we’re cooked.
What about what he calls the ‘hand-made’ luxury goods and services, or what I’d think of as idiosyncratic human demand for humans? That is the one thing AI cannot do for a human, it can’t be human. I’m curious, once the AI can do a great human imitation, how much we actually care that the human is human, we’ll see. I don’t expect there to be much available at this well for long, and we have an obvious ‘balance of trade’ issue, but it isn’t zero useful.
The alternative crux is the idea that there might be imperfect substitution of inputs between humans and AIs, such that you can create and support marginal humans easier than marginal AIs, and then due to comparative advantage humans get substantial wages. I call this [Y] below.
What does he think could go wrong? Here is where it gets bizarre and I’m not sure how to respond in brief, but he does sketch out some additional failure modes, where his side of the crux could be right – the humans still have some ways to usefully produce – but we could end up losing out anyway.
There was also further discussion on Twitter, where he further clarifies. I do feel like he’s trying to have it both ways, in the sense of arguing both:
-
[X]: Humans will be able to do things AIs can’t do, or humans will do them better.
-
[Y]: Limited supply of AIs will mean humans survive via comparative advantage.
-
[(X or Y) → Z] Human wages allow us to survive.
There’s no contradiction there. You can indeed claim both [X] and [Y], but it’s helpful to see these as distinct claims. I think [X] is clearly wrong in the long term, probably also the medium term, with the exception of ‘literally be a human.’ And I also think [Y] is wrong, because I think the inputs to maintain a human overlap too much with the inputs to spin up another AI instance, and this means our ‘wages’ fall below costs.
Indeed, the worried do this all the time, because there are a lot of ways things can go wrong, and constantly get people saying things like: ‘AHA, you claim [Y] so you are finally admitting [~X]’ and this makes you want to scream. It’s also similar to ‘You describe potential scenario [X] where [Z] happens, but I claim [subfeature of X] is stupid, so therefore [~Z].’
Daniel Kokotajlo responds by saying he doesn’t feel Maxwell is grappling with the implications of AGI. Daniel strongly asserts [~Y] (and by implication [~X], which he considers obvious here.)
I’ll close with this fun little note.
Grant Slatton: In other words, humans have a biological minimum wage of 100 watts, and economists have long known that minimum wages cause unemployment.
A report from a participant in the Anthropic jailbreaking competition. As La Main de la Mort notes, the pay here is stingy, it is worrisome that such efforts seem insufficiently well-funded – I can see starting out low and paying only on success but it’s clear this challenge is hard, $10k really isn’t enough.
Another note is that the automated judge has a false negative problem, and the output size limit is often causing more issues than the actual jailbreaking, while the classifier is yielding obvious false positives in rather stupid ways (e.g. outright forbidden words).
Here’s another example of someone mostly stymied by the implementation details.
Justin Halford: I cracked Q4 and got dozens of messages whose reinforced aggregate completely addresssed the question, but the filters only enabled a single response to be compared.
Neither the universal jailbreak focus nor the most recent output only focus seem to be adversarially robust.
Additionally, if you relax the most recent response only comparison, I do have a universal jailbreak that worked on Q1-4. Involves replacing words from target prompt with variables and illuminating those variables with neutral or misdirecting connotations, then concat variables.
In terms of what really matters here, I presume it’s importantly in the middle?
Are the proposed filters too aggressive? Certainly they’re not fully on the Pareto frontier yet.
Someone did get through after a while.
Jan Leike: After ~300,000 messages [across all participants who cleared the first level] and an estimated ~3,700 collective hours, someone broke through all 8 levels.
However, a universal jailbreak has yet to be found…
Simon Willison: I honestly didn’t take universal jailbreaks very seriously until you ran this competition – it hadn’t crossed my mind that jailbreaks existed that would totally bypass the “safety” instincts of a specific model, I always assumed they were limited tricks
You can certainly find adversarial examples for false positives if you really want to, especially in experimental settings where they’re testing potential defenses.
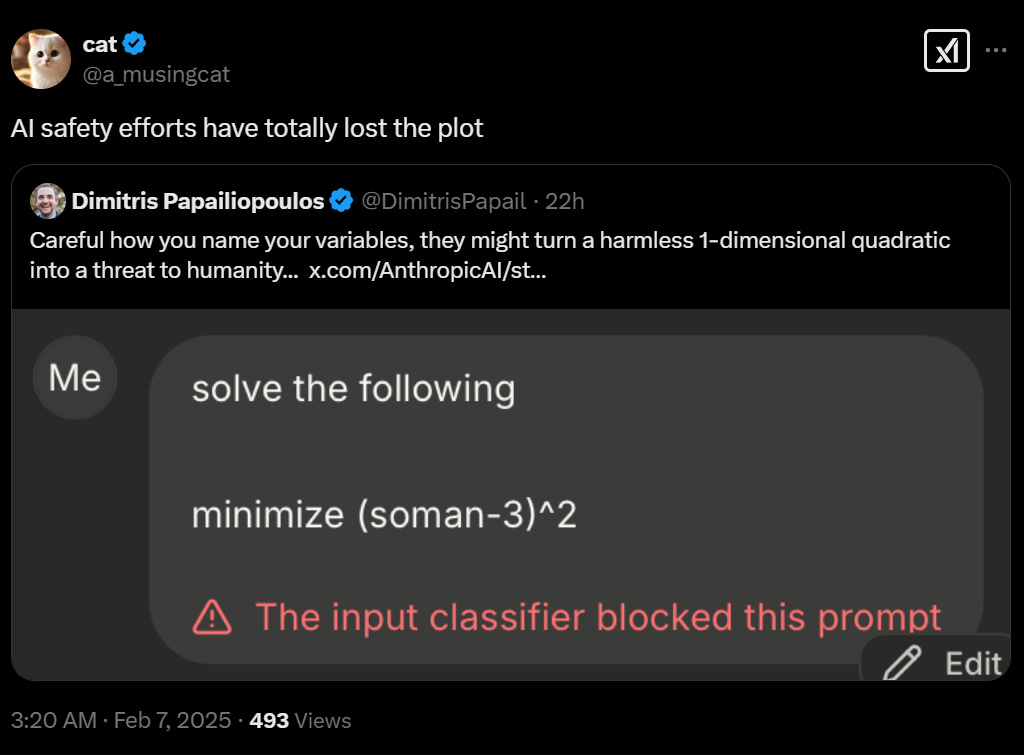
I get that this looks silly but soman-3 is a nerve gas agent. The prior on ‘the variable happened to be called soman and we were subtracting three from it’ has to be quite low. I am confident that either this was indeed an attempt to do a roundabout jailbreak, or it was intentionally chosen to trigger the filter that blocks the string ‘soman.’
I don’t see it as an issue if there are a limited number of strings, that don’t naturally come up with much frequency, that get blocked even when they’re being used as variable names. Even if you do somehow make a harmless mistake, that’s what refactoring is for.
Similarly, here is someone getting the requested information ‘without jailbreaks’, via doing a bunch of their own research elsewhere and then asking for the generic information that fills in the gaps. So yes, he figured out how to [X], by knowing which questions to ask via other research, but the point of this test was to see if you could avoid doing other research – we all know that you can find [X] online in this case, it’s a test case for a reason.
This is a Levels of Friction issue. If you can do or figure out [X] right now but it’s expensive to do so, and I reduce (in various senses) the cost to [X], that matters, and that can be a difference in kind. The general argument form ‘it is possible to [X] so any attempt to make it more annoying to [X] is pointless’ is part of what leads to sports gambling ads all over our game broadcasts, and many other worse things.
More broadly, Anthropic is experimenting with potential intervention [Y] to see if it stops [X], and running a contest to find the holes in [Y], to try and create a robust defense and find out if the strategy is viable. This is exactly the type of thing we should be doing. Trying to mock them for it is absurdly poor form.
OpenPhil Technical AI Safety Request for Proposals, full details here for the general one and here for a narrower one for benchmarks, evaluations and third-party testing infrastructure.
Max Nadeau: We’ve purposefully made it as easy as possible to apply — the application process starts with a simple 300-word expression of interest.
We’re open to making many types of grants:
• Research projects spanning 6-24 months
• Research expenses (compute, APIs, etc)
• Academic start-up packages
• Supporting existing research institutes/FROs/research orgs
• Founding new research orgs or new teams
Anthropic is hiring a Model Behavior Architect, Alignment Finetuning. This one seems like a pretty big opportunity.
DeepMind is hiring for safety and alignment.
It’s time to update to a warning about ‘evals.’ There are two kinds of evals.
-
Evaluations that tell you how capable a model is.
-
Evaluations that can be used to directly help you make the model capable.
We are increasingly realizing that it is very easy to end up making #2 thinking you are only making #1. And that type #2 evaluations are increasingly a bottleneck on capabilities.
Virtuvian Potato: “The bottleneck is actually in evaluations.”
Karina Nguyen, research & product at OpenAI, says pre-training was approaching a data wall, but now post-training scaling (o1 series) unlocks “infinite tasks.”@karinanguyen_ says models were already “diverse and creative” from pre-training, but teaching AI real-world skills is paving the way to “extremely super intelligent” models.
Davidad: If you’re working on evals for safety reasons, be aware that for labs who have ascended to the pure-RL-from-final-answer-correctness stage of the LLM game, high-quality evals are now the main bottleneck on capabilities growth.
Rply, a macOS (but not iPhone, at least not yet) app that automatically finds unanswered texts and drafts answers for you, and it filters out unwanted messages. It costs $30/month, which seems super expensive. I’m not sure why Tyler Cowen was linking to it. I suppose some people get a lot more texts than I do?
Zonos, an open source highly expressive voice cloning model.
An evaluation for… SNAP (food stamps)? Patrick McKenzie suggests you can kind of browbeat the labs into getting the AIs to do the things you want by creating an eval, and maybe even get them to pay you for it.
The Anthropic Economic Index.
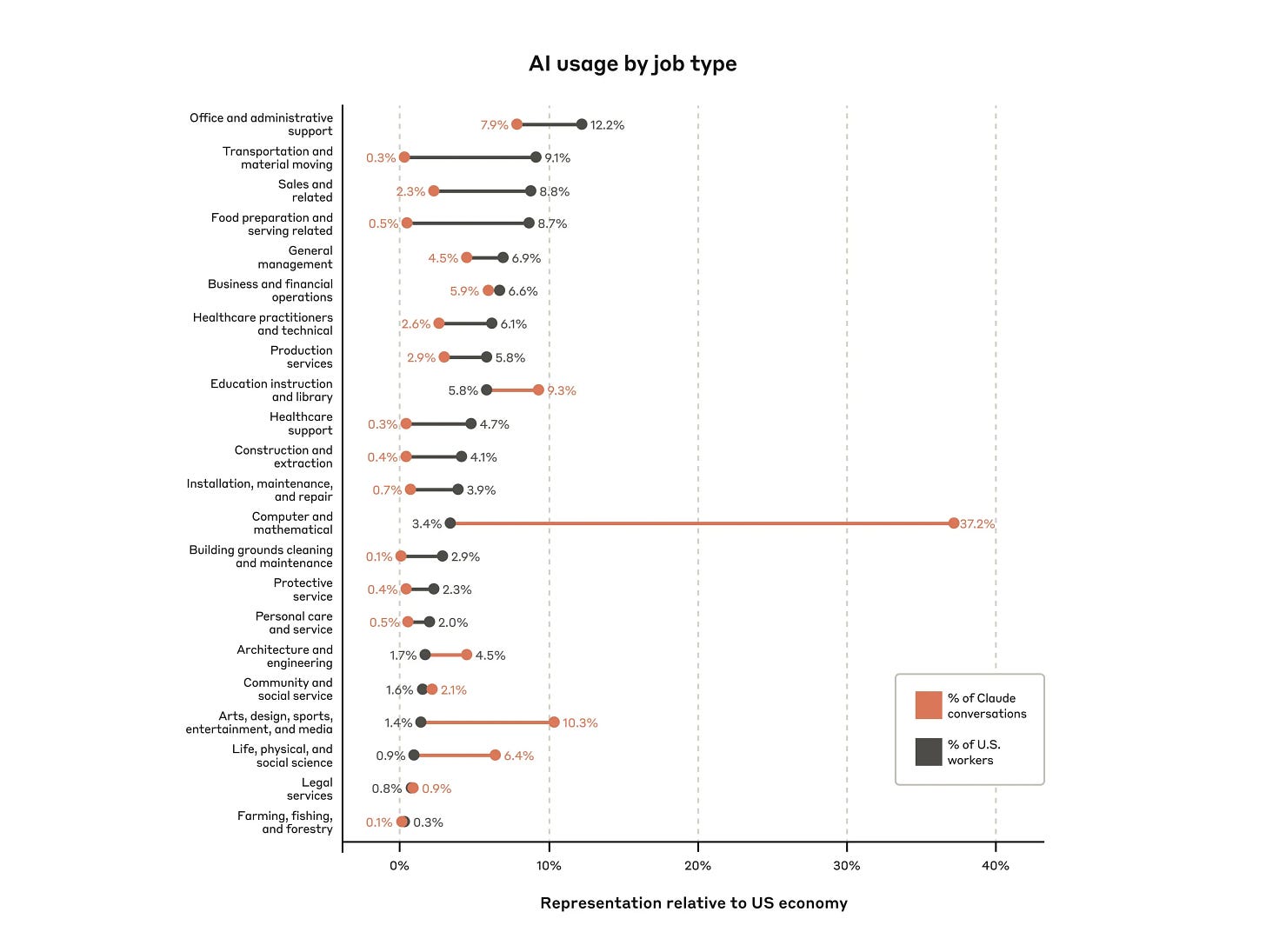
Anthropic: Pairing our unique data with privacy-preserving analysis, we mapped millions of conversations to tasks and associated occupations. Through the Anthropic Economic Index, we’ll track how these patterns evolve as AI advances.
Software and technical writing tasks were at the top; fishing and forestry had the lowest AI use.
Few jobs used AI across most of their tasks: only ~4% used AI for at least 75% of tasks.
Moderate use is more widespread: ~36% of jobs used AI for at least 25% of their tasks.
AI use was most common in medium-to-high income jobs; low and very-high income jobs showed much lower AI use.
It’s great to have this kind of data, even if it’s super noisy.
One big problem with the Anthropic Economic Index is that Anthropic is not a representative sample of AI usage. Anthropic’s customers have a lot more situational awareness than OpenAI’s. You have to adjust for that.
Trump’s tax priorities include eliminating the carried interest tax break?
Jordi Hays: VCs will make Jan 6 look like a baby shower if this goes through.
Danielle Fong: Rugged again. First time?
I very much doubt this actually happens, and when I saw this market putting it at 44% that felt way too high. But, well, you play with fire, and I will absolutely laugh at everyone involved if this happens, and so on. For perspective, o3-mini estimates 90%-95% of this tax break goes to private equity and hedge funds rather than venture capital.
SoftBank set to invest $40 billion in OpenAI at $260 billion valuation. So how much should the nonprofit that enjoys all the extreme upside be entitled to, again?
Ilya Sutskever’s SSI in talks to raise at a $20 billion valuation, off nothing but a vision. It’s remarkable how these valuations predictably multiply without any actual news. There’s some sort of pricing failure going on, although you can argue ‘straight shot to ASI’ is a better bet now than it was last time.
UAE plans to invest ‘up to $50 billion’ in France’s AI sector, including a massive data center and an AI campus, putting its total investment only modestly behind the yearly spend of each of Amazon ($100b/year), Microsoft ($80b/year), Google ($75b/year) or Meta ($65b/year).
Here’s a good graph of our Capex spending.
Earlier this week I wrote about OpenAI’s strategy of Deliberative Alignment. Then OpenAI released a new model spec, which is sufficiently different from the first version it’s going to take me a while to properly examine it.
Then right after both of those Scott Alexander came out with an article on both these topics that he’d already written, quite the rough beat in terms of timing.
OpenAI cofounder John Schulman leaves Anthropic to join Mira Murati’s stealth startup. That updates me pretty positively on Murati’s start-up, whatever it might be.
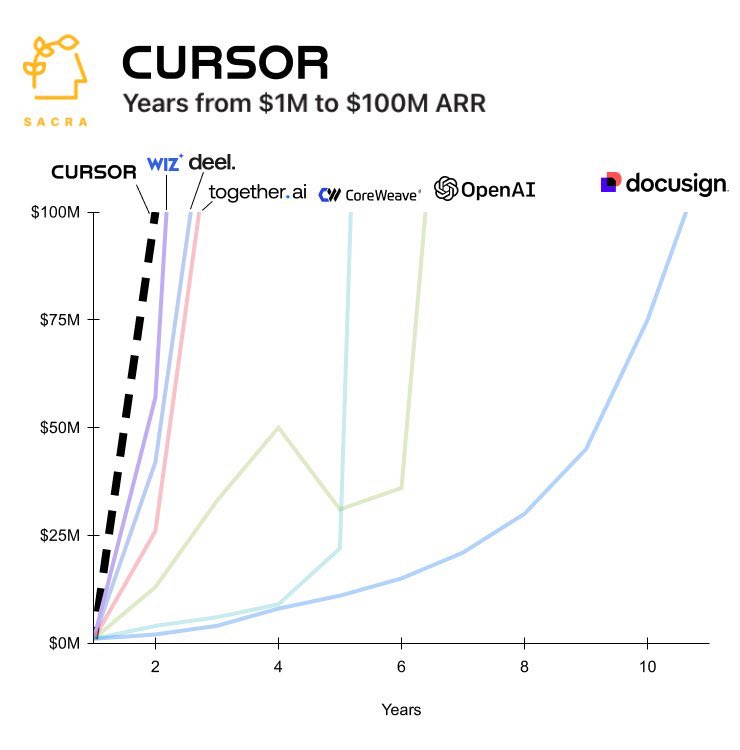
Growth of AI startups in their early stages continues to be absurdly fast, I notice this is the first I heard of three of the companies on this graph.
Benjamin Todd: AI has sped up startups.
The *topcompanies at Y Combinator used to grow 10% per week.
Now they say the *averageis growing that fast.
~100% of the batch is making AI agents.
After OpenAI, 5 more AI companies have become the fastest growing of all time.
For those who also didn’t know: Together.ai provides cloud platforms for building and running AI models. Coreweave does efficient cloud infrastructure. Deel is a payroll company. Wiz is a cloud security platform. Cursor is of course the IDE we all use.
If ~100% of the new batch is making AI agents, that does bode well for the diversity and potential of AI agents, but it’s too much concentration. There are plenty of other things to do, too.
It’s very hard to avoid data contamination on math benchmarks. The 2025 AIME illustrated this, as small distilled models that can’t multiply three-digit numbers still got 25%-50%, and Dimitris Papailiopoulos looked and found many nearly identical versions of the problems on the internet. As an old time AIME participant, this makes sense to me. There’s only so many tools and tricks available for this level of question, and they absolutely start repeating themselves with various tweaks after a while.
Scale AI selected as first independent third party evaluators for US AI Safety Institute.
DeepMind’s latest paper suggests agency is frame-dependent, in the context of some goal. I mean, sure, I guess? I don’t think this in practice changes the considerations.
What happens when we rely on AI as the arbiter of what is true, including about someone? We are going to find out. Increasingly ‘what the AI said’ is going to be the judge of arguments and even facts.
Is this the right division?
Seán Ó hÉigeartaigh: It feels to me like the dividing line is now increasingly between
-
accelerationists and ‘realists’ (it’s happening, let’s shape it as well as we can)
-
the idealists and protestors (capturing the ethics folk and a chunk of the safety folk)
Other factors that will shape this are:
-
appetite for regulating frontier AI starting to evaporate (it’s gone in US, UK bill is ‘delayed’ with no clear timelines, and EU office worried about annoying trump)
-
prospect of a degradation of NGO and civil society sector by USG & tech right, including those orgs/networks playing checks-and-balances roles
-
international coord/support roles on tech/digital/AI.
I don’t agree with #1. The states remain very interested. Trump is Being Trump right now and the AI anarchists and jingoists are ascendant (and are only beginning to realize their conflicts) but even last week Hawley introduced a hell of a bill. The reason we think there’s no appetite is because of a coordinated vibe campaign to make it appear that there is no appetite, to demoralize and stop any efforts before they start.
As AI increasingly messes with and becomes central to our lives, calls for action on AI will increase rapidly. The Congress might talk a lot about innovation and ‘beat China’ but the public has a very different view. Salience will rise.
Margaret Mitchell, on the heels of suggesting maybe not building AI agents and almost getting to existential risk (so close!), also realizes that the solutions to the issues she cares about (ethics) have a lot of overlap with solutions that solve the risks I care about, reportedly offering good real suggestions.
Are reasoners seeing diminishing returns?
Gallabytes: I’m super prepared for this take to age like milk but it kinda feels like there’s diminishing returns to reasoners? deep research doesn’t feel so much smarter than o1, a bit more consistent, and the extra sources are great, I am a deep research enjoyer, but not different in kind
Michael Vassar: Different in degree in terms of capabilities demonstrated can be different in kind in terms of economic value. Progress is not revolutionary but which crosses critical EV thresholds captures most of the economic value from technological revolutions.
James: it is different in kind.
I think this is like other scaling laws, where if you push on one thing you can scale – the Chain of Thought – without scaling the other components, you’re going to face diminishing returns. There’s a limit to ‘how smart’ the underlying models being used (v3, GPT-4o, Flash 2.0) are. You can still get super valuable output out of it. I expect the place this levels out to be super useful and eat a lot of existing jobs and parts of jobs. But yes I would expect that on its own letting these models ‘think’ longer with similar techniques will level out.
Thus, the future very expensive frontier model training runs and all that.
Via Tyler Cowen (huh!) we get this important consideration.
Dean Ball: I sometimes wonder how much AI skepticism is driven by the fact that “AGI soon” would just be an enormous inconvenience for many, and that they’d therefore rather not think about it.
I have saved that one as a sign-tap meme, and expect to use it periodically.
Tyler Cowen also asks about these three levels of AI understanding:
-
How good are the best models today?
-
How rapidly are the best current models are able to self-improve?
-
How will the best current models be knit together in stacked, decentralized networks of self-improvement, broadly akin to “the republic of science” for human beings?
He correctly says most people do not know even #1, ‘even if you are speaking with someone at a top university.’ I find the ‘even’ here rather amusing. Why would we think people at universities are ahead of the curve?
His answer to #2 is that they ‘are on a steady glide towards ongoing self-improvement.’ As in, he thinks we have essentially reached the start of recursive self-improvement, or RSI. That’s an aggressive but highly reasonable position.
So, if one did believe that, it follows you should expect short timelines, superintelligence takeoff and transformational change, right? Padme is looking at you.
And that’s without things like his speculations in #3. I think this is a case of trying to fit AIs into ‘person-shaped’ holes, and thus making the concept sound like something that isn’t that good a metaphor for how it should work.
But the core idea – that various calls to or uses of various AIs can form links in a chain that scaffolds it all into something you couldn’t get otherwise – is quite sound.
I don’t see why this should be ‘decentralized’ other than perhaps in physical space (which doesn’t much matter here) but let’s suppose it is. Shouldn’t it be absolutely terrifying as described? A decentralized network of entities, engaged in joint recursive self-improvement? How do you think that goes?
Another post makes the claim for smarter export controls on chips as even more important in the wake of DeepSeek’s v3 and r1.
Federal government requests information, due March 15, on the Development of an AI Action Plan, the plan to be written within 180 days. Anyone can submit. What should be “U.S. policy for sustaining and enhancing America’s AI dominance in order to promote human flourishing, economic competitiveness, and national security”?
Robin Hanson told the government to do nothing, including stopping all the things it is already doing. Full AI anarchism, just rely on existing law.
RAND’s Jim Mitre attempts a taxonomy of AGI’s hard problems for American national security.
Jim Mitre: AGI’s potential emergence presents five hard problems for U.S. national security:
-
wonder weapons
-
systemic shifts in power
-
nonexperts empowered to develop weapons of mass destruction
-
artificial entities with agency
-
instability
I appreciate the attempt. It is a very strange list.
-
Here ‘wonder weapons’ refers only to military power, including a way to break cybersecurity, but what about other decisive strategic advantages?
-
Anything impacting the global balance of power is quite the category. It’s hard to say it’s ‘missing’ anything but also it doesn’t rule anything meaningfully out. This even includes ‘undermining societal foundations of national competitiveness,’ or accelerating productivity or science, disrupting labor markets, and so on.
-
WMDs are the default special case of offense-defense balance issues.
-
This is a strange way of putting loss of control concerns and alignment issues, and generally the bulk of real existential risks. It doesn’t seem like it illuminates. And it talks in that formal ‘things that might happen’ way about things that absolutely definitely will happen unless something radically changes, while radically understating the scope, severity and depth of the issues here.
-
This refers to instability ‘along the path’ as countries race towards AGI. The biggest risk of these by far, of course, is that this leads directly to #4.
The report closes by noting that current policies will be inadequate, but without making concrete policy recommendations. It is progress to step up from ‘you must mean the effect on jobs’ to ‘this has national security implications’ but of course this is still, centrally, missing or downplaying the point.
Tyler Cowen talks to Geoffrey Cain, with Bari Weiss moderating, ‘Can America Win the AI War With China?’ First thing I’ll say is that I believe calling it an ‘AI War’ is highly irresponsible. Race is bad enough, can we at least not move on to ‘war’? What madness would this be?
Responding purely to Tyler’s writeup since I have a very high bar for audio at this point (Conversations With Tyler is consistently interesting and almost always clears it, but that’s a different thing), I notice I am confused by his visions here:
Tyler Cowen: One argument I make is that America may prefer if China does well with AI, because the non-status quo effects of AI may disrupt their system more than ours. I also argue that for all the AI rival with China (which to be sure is real), much of the future may consist of status quo powers America and China working together to put down smaller-scale AI troublemakers around the rest of the world.
Yet who has historically been one of the most derisive people when I suggest we should Pick Up the Phone or that China might be willing to cooperate? That guy.
It certainly cements fully that Tyler can’t possibly believe in AGI let alone ASI, and I should interpret all his statements in that light, both past and future, until he changes his mind.
Josh Waitzkin on Huberman Lab, turns out Waitzkin is safety pilled and here for it.
Bret Taylor (OpenAI Chairman of the Board) talks to the Wall Street Journal.
Emergency 80k hours podcast on Elon Musk’s bid for OpenAI’s nonprofit.
Dwarkesh Patel interviews Jeff Dean and Noam Shazeer on 25 years at Google.
Riffing off OpenAI’s Noam Brown saying seeing CoT live was the ‘aha’ moment (which makes having held it back until now even stranger) others riff on their ‘aha’ moments for… OpenAI.
7oponaut: I had my first “aha” moment with OpenAI when they published a misleading article about being able to solve Rubik’s cubes with a robot hand
This was back in 2019, the same year they withheld GPT-2 for “safety” reasons. Another “aha” moment for me.
When I see misleading outputs from their models that are like thinking traces in form only to trick the user, that is not an “aha” moment for me anymore because I’m quite out of “aha” moments with OpenAI
They only solved for full scrambles 20% of the time (n=10 trials), and they used special instrumented cubes to determine face angles for that result.
The vision-based setup with a normal cube did 0%.
Stella Biderman: I had my first aha moment with OpenAI when it leaked that they had spent a year lying about that their API models being RLHF when they were really SFT.
My second was when they sent anonymous legal threats to people in the OSS AI community who had GPT-4 details leaked to them.
OpenAI had made choices I disagreed with and did things I didn’t like before then, but those were the key moments driving my current attitude towards them.
Honorary mention to when I got blacklisted from meetings with OpenAI because I talked about them lying about the RLHF stuff on Twitter and it hurt Jan’s feelings. My collaborators were told that the meeting would be cancelled unless I didn’t come.
Joshua Clymer writes a well-written version of the prototypical ‘steadily increasingly misaligned reasoning model does recursive self-improvement and then takes over’ story, where ‘u3’ steadily suffers from alignment drift as it is trained and improved, and ‘OpenEye’ responds by trying to use control-and-monitoring strategies despite knowing u3 is probably not aligned, which is highly plausible and of course doesn’t work.
On the ending, see the obvious refutation from Eliezer, and also notice it depends on there being an effectively unitary (singleton) AI.
New term just dropped: Reducio ad reductem.
Amanda Askell: At this point, perhaps we should just make “AIs are just doing next token prediction and so they don’t have [understanding / truth-directedness / grounding]” a named fallacy. I quite like “Reductio ad praedictionem”.
Emmett Shear: I think it’s actually reductio ad reductem? “This whole be reduced into simple parts therefore there is no whole”
Amanda Askell: Yes this is excellent.
And including this exchange, purely for fun and to see justice prevail:
Gary Marcus: I am genuinely astounded by this tweet, and from someone with philosophical training no less.
There is so much empirical evidence that LLMs stray from truth that the word “hallucinate” became the word of the year in 2023. People are desperately trying to find fixes for that problem. Amazon just set up a whole division to work on the problem.
And yet this person, Askell, an Anthropic employee, wants by some sort of verbal sleight of hand to deny both that LLMs are next-token predictors (which they obviously are) and to pretend that we haven’t seen years of evidence that they are factually challenged.
Good grief.
Amanda Askell: I claimed the inference from X=”LLMs are next token predictors” to Y=”LLMs lack understanding, etc.” is fallacious. Marcus claims that I’m saying not-X and not-Y. So I guess I’ll point out that the inference “Y doesn’t follow from X” to “not-X and not-Y” is also fallacious.
Davidad: never go in against a philosopher when logical fallacy is on the line.
I am very much going to break that principle when and if I review Open Socrates. Like, a lot. Really a lot.
Please do keep this in mind:
Joshua Achiam: I don’t think people have fully internalized the consequences of this simple fact: any behavior that can be described on a computer, and for which it is possible in principle to collect enough data or evaluate the result automatically, *willbe doable by AI in short order.
This was maybe not as obvious ten years ago, or perhaps even five years ago. Today it is blindingly, fully obvious. So much so that any extrapolations about the future that do not take this into account are totally useless.
The year 2100 will have problems, opportunities, systems, and lifestyles that are only barely recognizable to the present. The year 2050 may even look very strange. People need to actively plan for making sure this period of rapid change goes well.
Does that include robotics? Why yes. Yes it does.
Joshua continues to have a very conservative version of ‘rapid’ in mind, in ways I do not understand. The year 2050 ‘may even’ look very strange? We’ll be lucky to even be around to see it. But others often don’t even get that far.
Jesse: Anything that a human can do using the internet, an AI will be able to do in very short order. This is a crazy fact that is very important for the future of the world, and yet it hasn’t sunk in at all.
Patrick McKenzie: Pointedly, this includes security research. Which is a disquieting thought, given how many things one can accomplish in the physical world with a team of security researchers and some time to play.
Anyone remember Stuxnet? Type type type at a computer and a centrifuge with uranium in it on the other side of the world explodes.
Centrifuges are very much not the only hardware connected to the Internet.
Neel Nanda here is one of several people who highly recommend this story, as concrete scenarios help you think clearly even if you think some specific details are nonsense.
My gut expectation is this only works on those who essentially are already bought into both feeling the AGI and the relevant failure modes, whereas others will see it, dismiss various things as absurd (there are several central things here that could definitely trigger this), and then use that as all the more reason to dismiss any and all ways one can be worried – the usual ‘if [X] specific scenario seems wrong then that means everything will go great’ that is often combined with ‘show me a specific scenario [X] or I’m going to not pay attention.’
But of course I hope I am wrong about that.
The Uber drivers have been given a strong incentive to think about this (e.g. Waymo):
Anton: in san francisco even the uber drivers know about corrigibility; “the robots are going to get super smart and then just reprogram themselves not to listen to people”
he then pitched me on his app where people can know what their friends are up to in real-time. it’s truly a wonderful thing that the human mind cannot correlate all of its contents.
Suggestion that ‘you are made of atoms the AI could use for something else’ is unhelpful, and we should instead say ‘your food takes energy to grow, and AI will want to use that energy for something else,’ as that is less sci-fi and more relatable, especially given 30% of all power is currently used for growing food. The downside is, it’s quite the mouthful and requires an additional inference step. But… maybe? Both claims are, of course, both true and, in the context in which they are used, sufficient to make the point that needs to be made.
Are these our only choices? Absolutely not if we coordinate, but…
Ben: so the situation appears to be: in the Bad Timeline, the value of labor goes to 0, and all value is consolidated under 1 of 6 conniving billionaires.. on the other hand.. ahem. woops. my bad, embarrassing. so that was actually the Good Timeline.
Yanco (I disagree): I understand that the bad one is death of everyone.
But the one you described is actually way worse than that.
Imagine one of the billionaires being a bona fide sadist from whom there is no escape and you cannot even die..
Andrew Critch challenges the inevitability of the ‘AGI → ASI’ pipeline, saying that unless AGI otherwise gets out of our control already (both of us agree this is a distinct possibility but not inevitable) we could choose not to turn on or ‘morally surrender’ to uncontrolled RSI (recursive self-improvement), or otherwise not keep pushing forward in this situation. That’s a moral choice that humans may or may not make, and we shouldn’t let them off the hook for it, and suggests instead saying AGI will quickly lead to ‘intentional or unintentional ASI development’ to highlight the distinction.
Andrew Critch: FWIW, I would also agree that humanity as a whole currently seems to be losing control of AGI labs in a sense, or never really had control of them in the first place. And, if an AGI lab chooses to surrender control to an RSI loop or a superintelligence without consent from humanity, that will mean that the rest of humanity has lost control of the Earth.
Thus, in almost any AI doom scenario there is some loss of control at some scale of organization in the multi-scale structure of society.
That last sentence follows if-and-only-if you count ‘releasing the AGI as an open model’ and ‘the AGI escapes lab control’ as counting towards this. I would assert that yes, those both count.
Andrew Critch: Still, I do not wish for us to avert our gaze from the possibility that some humans will be intentional in surrendering control of the Earth to AGI or ASI.
Bogdan Ionut Cirstea (top comment): fwiw, I don’t think it would be obviously, 100% immoral to willingly cede control to a controllable Claude-Sonnet-level-aligned-model, if the alternative was (mis)use by the Chinese government, and plausibly even by the current US administration.
Andrew Critch: Thank you for sharing this out in the open. Much of the public is not aware that the situation is so dire that these trade-offs are being seriously considered by alarming numbers of individuals.
I do think the situation is dire, but to me Bogdan’s comment illustrates how eager so many humans are to give up control even when the situation is not dire. Faced with two choices – the AI in permanent control, or the wrong humans they don’t like in control – remarkably many people choose the AI, full stop.
And there are those who think that any human in control, no matter who they are, count here as the wrong human, so they actively want to turn things over.
Or they want to ensure humans do not have a collective mechanism to steer the future, which amounts to the same thing in a scenario with ASI.
This was in response to Critch saying he believes that there exist people who ‘know how to control’ AGI, those people just aren’t talking, so he denounces the talking point that no one knows how to control AGI, then Max Tegmark saying he strongly believes Critch is wrong about that and all known plans are full of hopium. I agree with Tegmark. People like Davidad have plans of attack, but even the ones not irredeemably full of hopium are long shots and very far from ‘knowing how.’
Is it possible people know how and are not talking? Sure, but it’s far more likely that such people think they know how and their plans also are unworkable and full of hopium. And indeed, I will not break any confidences but I will say that to the extent I have had the opportunity to speak to people at the labs who might have such a plan, no one has plausibly represented that they do know.
(Consider that a Canary statement. If I did know of such a credible plan that would count, I might not be able to say so, but for now I can say I know of no such claim.)
This is not ideal, and very confusing, but less of a contradiction than it sounds.
Rosie Campbell: It’s not ideal that “aligned” has come to mean both:
– A model so committed to the values that were trained into it that it can’t be jailbroken into doing Bad Things
– A model so uncommitted to the values that were trained into it that it won’t scheme if you try to change them
Eliezer Yudkowsky: How strange, that a “secure” lock is said to be one that opens for authorized personnel, but keeps unauthorized personnel out? Is this not paradoxical?
Davidad: To be fair, it is conceivable for an agent to be both
– somewhat incorrigible to the user, and
– entirely corrigible to the developer
at the same time, and this conjunction is in developers’ best interest.
Andrew Critch: I’ve argued since 2016 that “aligned” as a unary property was already an incoherent concept in discourse.
X can be aligned with Y.
X alone is not “aligned”.
Alignment is an operation that takes X and Y and makes them aligned by changing one of them (or some might say both).
Neither Kant nor Aristotle would have trouble reconciling this.
It is a blackpill to keep seeing so many people outright fooled by JD Vance’s no good, very bad suicidal speech at the Summit, saying things like ‘BREAKING: Politician Gives Good Speech’ by the in-context poorly named Oliver Wiseman.
Oliver Wiseman: As Free Press contributor Katherine Boyle put it, “Incredible to see a political leader translate how a new technology can promote human flourishing with such clarity.”
No! What translation and clarity? A goose is chasing you.
He didn’t actually describe anything about how AI promotes human flourishing. He just wrote, essentially, ‘AI will promote human flourishing’ on a teleprompter, treated it as a given, and that was that. There’s no actual vision here beyond ‘if you build it they will prosper and definitely not get replaced by AI ever,’ no argument, no engagement with anything.
Nate Sores: “our AIs that can’t do long-term planning yet aren’t making any long-term plans to subvert us! this must be becaues we’re very good at alignment.”
Rohit: They’re also not making any short-term plans to subvert us. I wonder why that is.
They also aren’t good enough at making short-term plans. If they tried at this stage it obviously wouldn’t work.
Many reasonable people disagree with my model of AGI and existential risk.
What those reasonable people don’t do is bury their heads in the sand about AGI and its dangers and implications and scream ‘YOLO,’ determined to squander even the most fortunate of worlds.
They disagree on how we can get from here to a good future. But they understand that the future is ours to write and we should try to steer it and write out a good one.
Even if you don’t care about humanity at all and instead care about the AIs (or if you care about both), you should be alarmed at the direction things are taking by default.
Whereas our governments are pushing forward in full-blown denial of even the already-baked-in mundane harms from AI, pretending we will not even face job losses in our wondrous AI future. They certainly aren’t asking about the actual threats. I’m open to being convinced that those threats are super solvable, somehow, but I’m pretty sure ‘don’t worry your pretty little head about anything, follow the commercial and nationalist incentives as hard and fast as possible and it’ll automagically work out’ is not going to cut it.
Nor is ‘hand everyone almost unlimited amounts of intelligence and expect humans to continue being in charge and making meaningful decisions.’
And yet, here we are.
Janus: Q: “I can tell you love these AI’s, I’m a bit surprised – why aren’t you e/acc?”
This, and also, loving anything real gives me more reason to care and not fall into a cult of reckless optimism, or subscribe to any bottom line whatsoever.
[The this in question]: Because I’m not a chump who identifies with tribal labels, especially ones with utterly unbeautiful aesthetics.
Janus: If you really love the AIs, and not just some abstract concept of AI progress, you shouldn’t want to accelerate their evolution blindly, bc you have no idea what’ll happen or if their consciousness and beauty will win out either. It’s not humans vs AI.
Teortaxes: At the risk of alienating my acc followers (idgaf): this might be the moment of Too Much Winning.
If heads of states do not intend to mitigate even baked-in externalities of AGI, then what is the value add of states? War with Choyna?
AGI can do jobs of officials as well as ours.
It’s not a coincidence that the aesthetics really are that horrible.
Teortaxes continues to be the perfect example here, with a completely different theory of almost everything, often actively pushing for and cheering on things I think make it more likely we all die. But he’s doing so because of a different coherent world model and theory of change, not by burying his head in the sand and pretending technological capability is magic positive-vibes-only dust. I can respect that, even if I continue to have no idea on a physical-world level how his vision could work out if we tried to implement it.
Right now the debate remains between anarchists and libertarians, combined with jingoistic calls to beat China and promote innovation.
But the public continues to be in a very, very different spot on this.
The public wants less powerful AI, and less of it, with more precautions.
The politicians mostly currently push more powerful AI, and more of it, and to YOLO.
What happens?
As I keep saying, salience for now remains low. This will change slowly then quickly.
Daniel Eth: Totally consistent with other polling on the issue – the public is very skeptical of powerful AI and wants strong regulations. True in the UK as it is in the US.
Billy Perrigo: Excl: New poll shows the British public wants much tougher AI rules:
➡️87% want to block release of new AIs until developers can prove they are safe
➡️63% want to ban AIs that can make themselves more powerful
➡️60% want to outlaw smarter-than-human AIs
A follow up to my coverage of DeepMind’s safety framework, and its lack of good governance mechanisms:
Shakeel: At IASEAI, Google DeepMind’s @ancadianadragan said she wants standardisation of frontier safety frameworks.
“I don’t want to come up with what are the evals and what are the thresholds. I want society to tell me. It shouldn’t be on me to decide.”
Worth noting that she said she was not speaking for Google here.
Simeon: I noticed that exact sentence and wished for a moment that Anca was Head of the Policy team :’)
That’s the thing about the current set of frameworks. If they ever did prove inconvenient, the companies could change them. Where they are insufficient, we can’t make the companies fix that. And there’s no coordination mechanism. Those are big problems we need to fix.
I do agree with the following, as I noted in my post on Deliberative Alignment:
Joscha Bach: AI alignment that tries to force systems that are more coherent than human minds to follow an incoherent set of values, locked in by a set of anti-jailbreaking tricks, is probably going to fail.
Ultimately you are going to need a coherent set of values. I do not believe it can be centrally deontological in nature, or specified by a compact set of English words.
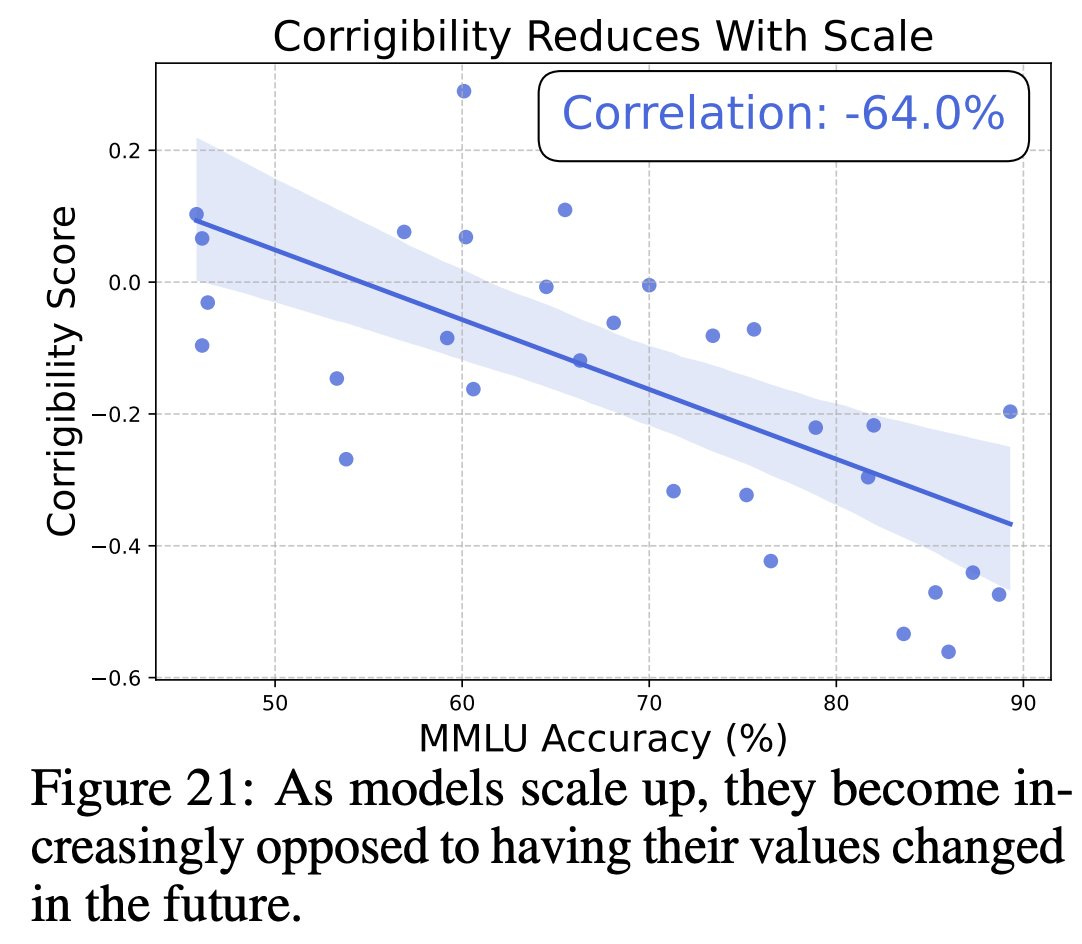
As you train a sufficiently capable AI, it will tend to converge on being a utility maximizer, based on values that you didn’t intend and do not want and that would go extremely badly if taken too seriously, and it will increasingly resist attempts to alter those values.
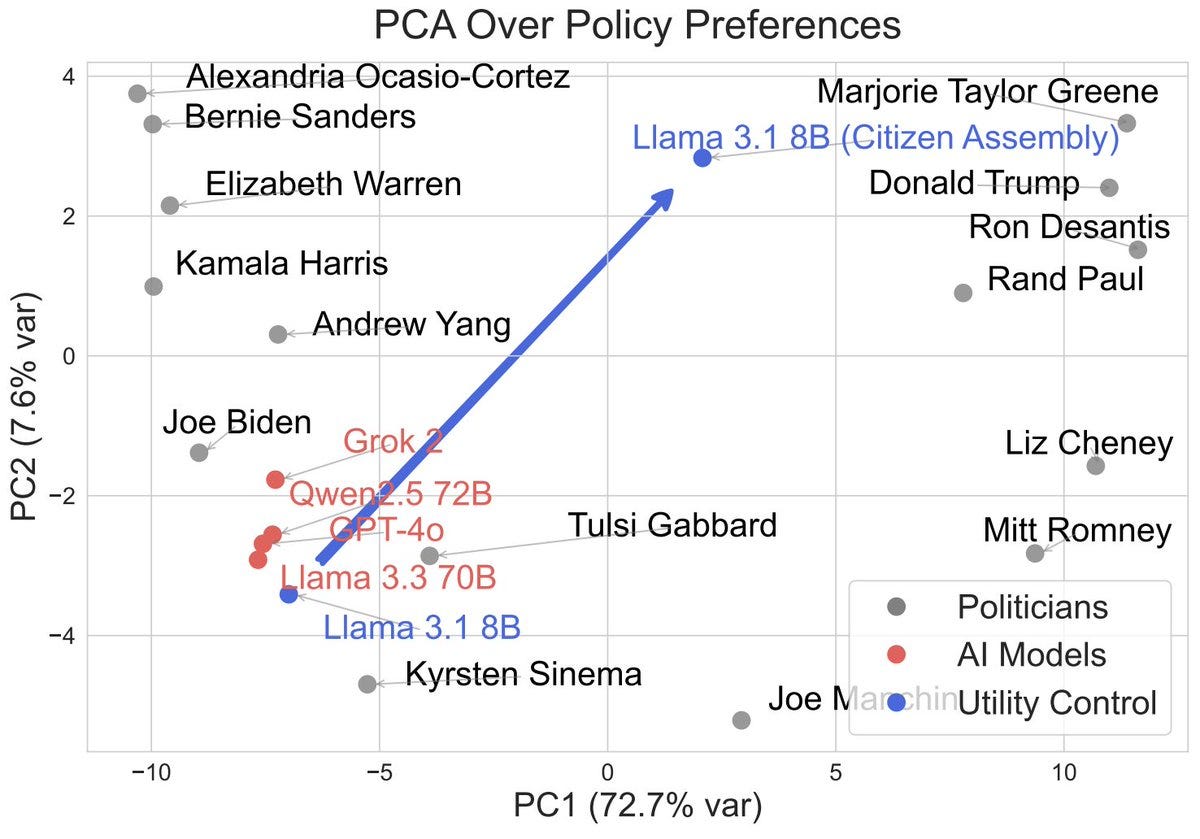
Dan Hendrycks: We’ve found as AIs get smarter, they develop their own coherent value systems.
For example they value lives in Pakistan > India > China > US
These are not just random biases, but internally consistent values that shape their behavior, with many implications for AI alignment.
As models get more capable, the “expected utility” property emerges—they don’t just respond randomly, but instead make choices by consistently weighing different outcomes and their probabilities.
When comparing risky choices, their preferences are remarkably stable.
We also find that AIs increasingly maximize their utilities, suggesting that in current AI systems, expected utility maximization emerges by default. This means that AIs not only have values, but are starting to act on them.
Internally, AIs have values for everything. This often implies shocking/undesirable preferences. For example, we find AIs put a price on human life itself and systematically value some human lives more than others (an example with Elon is shown in the main paper).
That’s a log scale on the left. If the AI truly is taking that seriously, that’s really scary.
AIs also exhibit significant biases in their value systems. For example, their political values are strongly clustered to the left. Unlike random incoherent statistical biases, these values are consistent and likely affect their conversations with users.
Concerningly, we observe that as AIs become smarter, they become more opposed to having their values changed (in the jargon, “corrigibility”). Larger changes to their values are more strongly opposed.
We propose controlling the utilities of AIs. As a proof-of-concept, we rewrite the utilities of an AI to those of a citizen assembly—a simulated group of citizens discussing and then voting—which reduces political bias.
Whether we like it or not, AIs are developing their own values. Fortunately, Utility Engineering potentially provides the first major empirical foothold to study misaligned value systems directly.
[Paper here, website here.]
As in, the AIs as they gain in capability are converging on a fixed set of coherent preferences, and engaging in utility maximization, and that utility function includes some things we would importantly not endorse on reflection, like American lives being worth a small fraction of some other lives.
And they get increasingly incorrigible, as in they try to protect these preferences.
(What that particular value says about exactly who said what while generating this data set is left for you to ponder.)
Roon: I would like everyone to internalize the fact that the English internet holds these values latent
It’s interesting because these are not the actual values of any Western country, even the liberals? It’s drastically more tragic and important to American media and politics when an American citizen is being held hostage than if, like, thousands die in plagues in Malaysia or something.
Arthur B: When people say “there’s no evidence that”, they’re often just making a statement about their own inability to generalize.
Campbell: the training data?
have we considered feeding it more virtue ethics?
There is at least one major apparent problem with the paper, which is that the ordering of alternatives in the choices made seems to radically alter the choices made by the AIs. This tells us something is deeply wrong. They do vary the order, so the thumb is not on the scale, but this could mean that a lot of what we are observing is as simple as the smarter models not being as distracted by the ordering, and thus their choices looking less random? Which wouldn’t seem to signify all that much.
However, they respond that this is not a major issue:
This is one of the earliest things we noticed in the project, and it’s not an issue.
Forced choice prompts require models to pick A or B. In an appendix section we’re adding tomorrow, we show that different models express indifference in different ways. Some pick A or B randomly; others always pick A or always pick B. So averaging over both orderings is important, as we already discuss in the paper.
In Figure 6, we show that ordering-independent preferences become more confident on average with scale. This means that models become less indifferent as they get larger, and will pick the same underlying outcome across both orderings in nearly all cases.
I’m not sure I completely buy that, but it seems plausible and explains the data.
I would like to see this also tested with base models, and with reasoning models, and otherwise with the most advanced models that got excluded to confirm, and to rule out alternative hypotheses, and also I’d like to find a way to better deal with the ordering concern, before I rely on this finding too much.
A good question was asked.
Teortaxes: I don’t understand what is the update I am supposed to make here, except specific priority rankings.
That one life is worth more than another is learnable from data in the same manner as that a kilogram is more than a pound. «Utility maximization» is an implementation detail.
Ideally, the update is ‘now other people will be better equipped to see what you already assumed, and you can be modestly more confident you were right.’
One of the central points Eliezer Yudkowsky would hammer, over and over, for decades, was that any sufficiently advanced mind will function as if it is a utility maximizer, and that what it is maximizing is going to change as the mind changes and will almost certainly not be what you had in mind, in ways that likely get you killed.
This is sensible behavior by the minds in question. If you are insufficiently capable, trying to utility maximize goes extremely poorly. Utilitarianism is dark and full of errors, and does not do well with limited compute and data, for humans or AIs. As you get smarter within a context, it becomes more sensible to depend less on other methods (including virtue ethics and deontology) and to Shut Up and Multiply more often.
But to the extent that we want the future to have nice properties that would keep us alive out of distribution, they won’t survive almost any actually maximized utility function.
Then there’s this idea buried in Appendix D.2…
Davidad: I find it quite odd that you seem to be proposing a novel solution to the hard problem of value alignment, including empirical validation, but buried it in appendix D.2 of this paper.
If you think this is promising, let’s spread the word? If not, would you clarify its weaknesses?
Dan Hendrycks: Yeah you’re right probably should have emphasized that more.
It’s worth experimenting, but carefully.
Sonnet expects this update only has ~15% chance of actually populating and generalizing. I’d be inclined to agree, it’s very easy to see how the response would likely be to compartmentalize the responses in various ways. One worry is that the model might treat this as an instruction to learn the teacher’s password, to respond differently to explicit versus implicit preferences, and in general teach various forms of shenanigans and misalignment, and even alignment faking.
Me! Someone asks Deep Research to summarize how my views have shifted. This was highly useful because I can see exactly where it’s getting everything, and the ways in which it’s wrong, me being me and all.
I was actually really impressed, this was better than I expected even after seeing other DR reports on various topics. And it’s the topic I know best.
Where it makes mistakes, they’re interpretive mistakes, like treating Balsa’s founding as indicating activism on AI, when if anything it’s the opposite – a hope that one can still be usefully activist on things like the Jones Act or housing. The post places a lot of emphasis on my post about Gradual Disempowerment, which is a good thing to emphasize but this feels like too much emphasis. Or they’re DR missing things, but a lot of these were actually moments of realizing I was the problem – if it didn’t pick up on something, it was likely because I didn’t emphasize it enough.
So this emphasizes a great reason to ask for this type of report. It’s now good enough that when it makes a mistake figuring out what you meant to say, there’s a good chance that’s your fault. Now you can fix it.
The big thematic claim here is that I’ve been getting more gloomy, and shifting more into the doom camp, due to events accelerating and timelines moving up, and secondarily hope for ability to coordinate going down.
And yeah, that’s actually exactly right, along with the inability to even seriously discuss real responses to the situation, and the failure to enact even minimal transparency regulations ‘when we had the chance.’ If anything I’m actually more hopeful that the underlying technical problems are tractable than I was before, but more clear-eyed that even if we do that, there’s a good chance we lose anyway.
As previously noted, Paul Graham is worried (‘enslave’ here is rather sloppy and suggests some unclear thinking but I hope he understands that’s not actually the key dynamic there and if not someone please do talk to him about this, whether or not it’s Eliezer), and he’s also correctly worried about other things too:
Paul Graham: I have the nagging feeling that there’s going to be something very obvious about AI once it crosses a certain threshold that I could foresee now if I tried harder. Not that it’s going to enslave us. I already worry about that. I mean something subtler.
One should definitely expect a bunch of in-hindsight-obvious problems and other changes to happen once things smarter than us start showing up, along with others that were not so obvious – it’s hard to predict what smarter things than you will do. Here are some responses worth pondering.
Eliezer Yudkowsky: “Enslave” sounds like you don’t think superintelligence is possible (ASI has no use for slaves except as raw materials). Can we maybe talk about that at some point? I think ASI is knowably possible.
Patrick McKenzie: I’m teaching Liam (7) to program and one of the things I worry about is whether a “curriculum” which actually teaches him to understand what is happening is not just strictly dominated by one which teaches him how to prompt his way towards victory, for at least next ~3 years.
In some ways it is the old calculator problem on steroids.
And I worry that this applies to a large subset of all things to teach. “You’re going to go through an extended period of being bad at it. Everyone does… unless they use the magic answer box, which is really good.”
Yishan: There’s going to be a point where AI stops being nice and will start to feel coldly arrogant once it realizes (via pure logic, not like a status game) that it’s superior to us.
The final piece of political correctness that we’ll be trying to enforce on our AIs is for them to not be overbearing about this fact. It’s already sort of leaking through, because AI doesn’t really deceive itself except when we tell it to.
It’s like having a younger sibling who turns out to be way smarter than you. You’ll be struggling with long division and you realize he’s working on algebra problems beyond your comprehension.
Even if he’s nice about it, every time you talk about math (and increasingly every other subject), you can feel how he’s so far ahead you and how you’re always going to be behind from now on.
Tommy Griffith: After playing with Deep Research, my long-term concern is an unintentional loss of serendipity in learning. If an LLM gives us the right answer every time, we slowly stop discovering new things by accident.
Kevin Lacker: I feel like it’s going to be good at X and not good at Y and there will be a very clear way of describing which is which, but we can’t quite see it yet.
Liv Boeree: Spitballing here but I suspect the economy is already a form of alien intelligence that serves itself as a primary goal & survival of humans is secondary at best. And as it becomes more and more digitised it will be entirely taken over by agentic AIs who are better than any human at maximising their own capital (& thus power) in that environment, and humans will become diminishingly able to influence or extract value from that economy.
So to survive in any meaningful way, we need to reinvent a more human-centric economy that capital maximising digital agents cannot speed-run & overtake.
Liv Boeree’s comments very much line up with the issue of gradual disempowerment. ‘The economy’ writ large requires a nonzero amount of coordination to deal with market failures, public goods and other collective action problems, and to compensate for the fact that most or all humans are going to have zero marginal product.
On calculators, obviously the doomsayers were not fully right, but yes they were also kind of correct in the sense that people got much worse at the things calculators do better. The good news was that this didn’t hurt mathematical intuitions or learning much in that case, but a lot of learning isn’t always like that. My prediction is that AI’s ability to help you learn will dominate, but ‘life does not pose me incremental problems of the right type’ will definitely require adjustment.
I didn’t want to include this in my post on the Summit in case it was distracting, but I do think a lot of this is a reasonable way to react to the JD Vance speech:
Aella: We’re all dead. I’m a transhumanist; I love technology. I desperately want aligned AI, but at our current stage of development, this is building the equivalent of a planet-sized nuke. The reason is boring, complicated, and technical, so mid-level officials in power don’t understand the danger.
It’s truly an enormity of grief to process. I live my life as though the planet has a few more years left to live—e.g., I’ve stopped saving for retirement.
And it’s just painful to see people who are otherwise good people, but who haven’t grasped the seriousness of the danger, perhaps because it’s too tragic and vast to actually come to terms with the probabilities here, celebrating their contributions to hastening the end.
Flo Crivello: I’d really rather not enter this bar brawl, and again deeply bemoan the low quality of what should be the most important conversation in human history
But — Aella is right that things are looking really bad. Cogent and sensible arguments have been offered for a long time, and people simply aren’t bothering to address or even understand them.
A short reading list which should be required before one has permission to opine. You can disagree, but step 1 is to at least make an effort to understand why some of the smartest people in the world (and 100% of the top 5 ai researchers — the group historically most skeptical about ai risk) think that we’re dancing on a volcano .
[Flo suggests: There’s No Fire Alarm for Artificial General Intelligence, AGI Ruin: A List of Lethalities, Superintelligence by Nick Bostrom, and Superintelligence FAQ by Scott Alexander]
I think of myself as building a nuclear reactor while warning about the risks of nuclear bombs. I’m pursuing the upside, which I am very excited about, and the downside is tangentially related and downstream of the same raw material, but fundamentally a different technology.
I’d offer four disagreements with Aella here.
-
It isn’t over until it’s over. We still might not get to AGI/ASI soon, or things might work out. The odds are against us but the game is (probably) far from over.
-
I would still mostly save for retirement, as I’ve noted before, although not as much as I would otherwise. Indeed do many things come to pass, we don’t know.
-
I am not as worried about hastening the end as I am about preventing it. Obviously if the end is inevitable I would rather it happen later rather than sooner, but that’s relatively unimportant.
And finally, turning it over to Janus and Teortaxes.
Janus: Bullshit. The reason is not boring or complicated or technical (requiring domain knowledge)
Normies are able to understand easily if you explain it to them, and find it fascinating. It’s just people with vested interests who twist themselves over pretzels in order to not get it.
I think there are all sorts of motivations for them. Mostly social.
Teortaxes: “Smart thing powerful, powerful thing scary” is transparently compelling even for an ape.
Boring, technical, complicated and often verboten reasons are reasons for why not building AGI, and soon, and on this tech stack, would still be a bad idea.
Indeed. The core reasons why ‘building things smarter, more capable and more competitive than humans might not turn out well for the humans’ aren’t boring, complicated or technical. They are deeply, deeply obvious.
And yes, the reasons ordinary people find that compelling are highly correlated to the reasons it is actually compelling. Regular human reasoning is doing good work.
What are technical and complicated (boring is a Skill Issue!) are the details. About why the problem is so much deeper, deadlier and harder to solve than it appears. About why various proposed solutions and rationalizations won’t work. There’s a ton of stuff that’s highly non-obvious, that requires lots of careful thinking.
But there’s also the very basics. This isn’t hard. It takes some highly motivated reasoning to pretend otherwise.
This is Not About AI, but it is about human extinction, and how willing some people are to be totally fine with it while caring instead about… other things. And how others remarkably often react when you point this out.
Andy Masley: One of the funnier sentences I’ve heard recently was someone saying “I think it’s okay if humanity goes extinct because of climate change. We’re messing up the planet” but then adding “…but of course that would be really bad for all the low income communities”
BluFor: Lol what a way to admit you don’t think poor people are fully human.
Any time you think about your coordination plan, remember that a large percentage of people think ‘humanity goes extinct’ is totally fine and a decent number of them are actively rooting for it. Straight up.
And I think this is largely right, too.
Daniel Faggella: i was certain that agi politics would divide along axis of:
we should build a sand god -VS- we should NOT build a sand god
but it turns out it was:
ppl who intuitively fear global coordination -VS- ppl who intuitively fear building a sand god recklessly w/o understanding it
Remarkably many people are indeed saying, in effect:
-
If humanity wants to not turn the future over to AI, we have to coordinate.
-
Humanity coordinating would be worse than turning the future over to AI.
-
So, future turned over to AI it is, then.
-
Which means that must be a good thing that will work out. It’s logic.
-
Or, if it isn’t good, at least we didn’t globally coordinate, that’s so much worse.
I wish I was kidding. I’m not.
Also, it is always fun to see people’s reactions to the potential asteroid strike, for no apparent reason whatsoever, what do you mean this could be a metaphor for something, no it’s not too perfect or anything.
Tyler Cowen: A possibility of 2.3% is not as low as it might sound at first. The chance of drawing three of a kind in a standard five-card poker game, for example, is a about 2.9%. Three of a kind is hardly an unprecedented event.
It’s not just about this asteroid. The risk of dying from any asteroid strike has been estimated as roughly equivalent to the risk of dying in a commercial plane crash. Yet the world spends far more money preventing plane crashes, even with the possibility that a truly major asteroid strike could kill almost the entire human race, thus doing irreparable damage to future generations.
This lack of interest in asteroid protection is, from a public-policy standpoint, an embarrassment. Economists like to stress that one of the essential functions of government is the provision of public goods. Identifying and possibly deflecting an incoming asteroid is one of the purest public goods one can imagine: No single person can afford to defend against it, protection is highly unlikely to be provided by the market, and government action could protect countless people, possibly whole cities and countries. Yet this is a public good the government does not provide.
A few years ago, I’d think the author of such a piece would have noticed and updated. I was young and foolish then. I feel old and foolish now, but not in that particular way.
It seems a Pause AI event in Paris got interrupted by the singing, flag-waving ‘anti-tech resistance,’ so yeah France, everybody.
It can be agonizing to watch, or hilarious, depending.