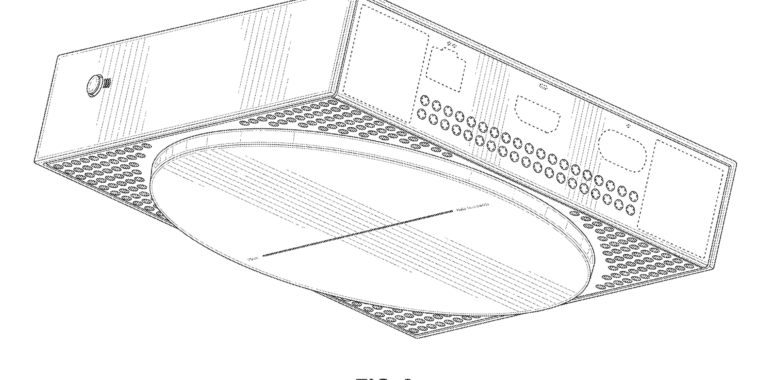
Patent document showcases the cloud-only streaming Xbox console that never was
keystone revealed —
Microsoft couldn’t get the price of its streaming Xbox low enough to release it.
-
The streaming-only Xbox would have looked like a smaller, squarer relative of the Series S.
Microsoft
-
The console had cutouts on the bottom and back, presumably for air cooling.
Microsoft
-
Front-mounted Xbox button and USB port, much like the Series S.
Microsoft
-
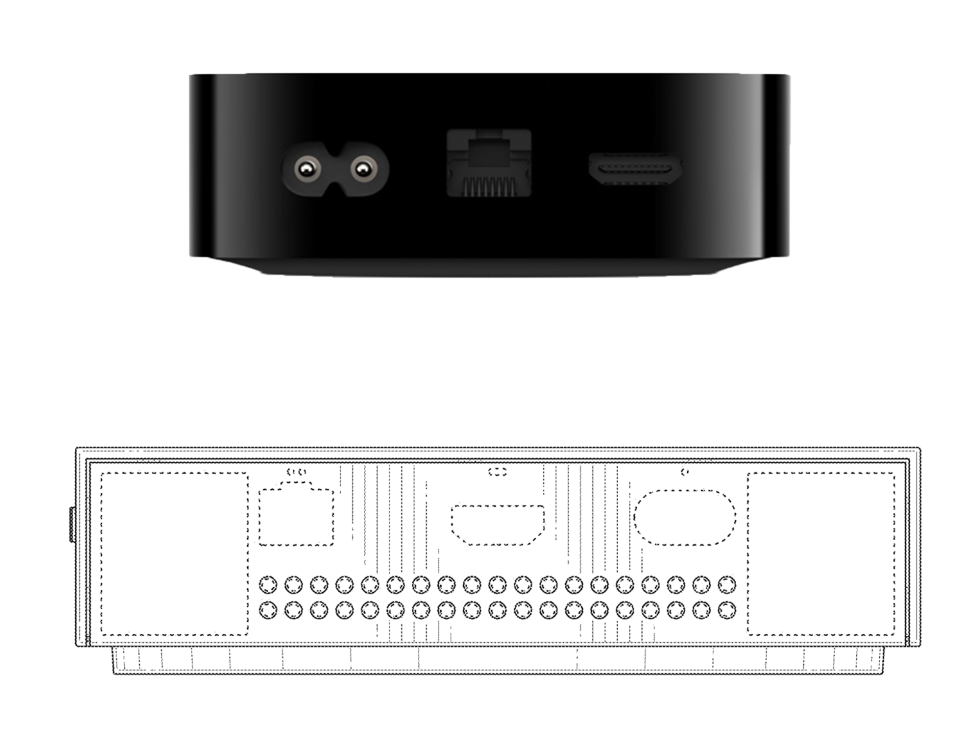
Rear-mounted Ethernet, HDMI, and power. The console would likely have worked over Wi-Fi, too, but wired Ethernet does help with latency and consistency when streaming games.
Microsoft
-
Controller sync button on the side.
Microsoft
-
There was a logo and a Series S-ish circle on the top of the Keystone Xbox, but there are no cutouts depicted, so this may have been a stylistic choice rather than a place for the console to vent hot air.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s mid-generation plans for the Xbox Series S and X consoles looked a whole lot different a couple of years ago than it does now. A leaked slide deck from the FTC v. Microsoft case last year outlined detailed plans for a spruced up Series S, an overhauled Series X, and even a redesigned controller. Another part of that roadmap included a streaming-only version of the Xbox, codenamed Keystone, that was designed to connect to Microsoft’s Xbox Cloud Gaming servers rather than rendering games locally.
Microsoft has talked openly about this version of the Xbox before. Microsoft Gaming CEO Phil Spencer told The Verge that the Keystone console was designed and fully functional, but that it wasn’t launched because Microsoft had a hard time getting the price down low enough that it made sense next to the $299 Series S (which already occasionally goes on sale in the $200 to $250 range).
We’ve already seen glimpses of Keystone—once on Spencer’s shelf, and again in the FTC v. Microsoft documents. Both of those depictions were partial, or seen from a distance. But a new design patent document (PDF) unearthed by Windows Central shows even more detailed renderings of what the cloud Xbox would have looked like.
Series S meets Apple TV
Keystone’s styling was strongly reminiscent of the disc-drive-less Series S, with the same boxy white design and front-mounted Xbox button and USB port. There’s also a similar circular cutout on top, though it may not be an air vent as it is in the Series S—all of the holes depicted in the patent are on the back and bottom, and a streaming box certainly wouldn’t have needed the same cooling capacity as the AMD-designed CPU and GPU in the Series S.
The console also would have been square-shaped and considerably smaller than a Series S—not quite as small as a dedicated video-streaming box like an Apple TV or Roku Ultra, but not too far off either (the patent document doesn’t list dimensions, but we’ve done a rough size comparison using the HDMI and Ethernet ports on the Keystone box and an Apple TV 4K). The console’s controller sync button would have been mounted on its side, rather than in front, as it is on the Series S.
Enlarge / The cloud Xbox compared to a current-generation Apple TV 4K, with sizes roughly normalized based on the sizes of the HDMI and Ethernet ports. The Xbox console would have been a bit larger, but not dramatically so.
Apple/Microsoft/Andrew Cunningham
In the alternate reality of the FTC v. Microsoft slide deck, all of these new consoles and the new controller would have been announced or launched by now. But as Microsoft Gaming CEO Phil Spencer said shortly after those documents leaked, the company’s plans have changed substantially in the interim. A disc-less version of the Series X is coming, but it looks exactly like the current version of the console without a disc drive; Microsoft is also pursuing a strategy where it takes more of its internally developed games multi-platform, rather than restricting them to the Xbox and to Windows PCs. These moves are at least partially in response to sliding revenue from Microsoft’s console business, which has seen its revenue decline by double digits year over year for the last couple of years.
Neither Spencer nor Microsoft has ever said never about the Keystone console, leaving the door open to an eventual release if and when the price of manufacturing the console comes down. In the meantime, the streaming-only Xbox lives on as an app for newer Samsung smart TVs.
Listing image by Microsoft
Patent document showcases the cloud-only streaming Xbox console that never was Read More »