Harnessing the Power of Cloud Performance Testing
error code: 502
Harnessing the Power of Cloud Performance Testing Read More »

Office Space
American workers who have more flexibility and security in their jobs also have better mental health, according to a study of 2021 survey data from over 18,000 nationally representative working Americans.
The study, published Monday in JAMA Network Open, may not be surprising to those who have faced return-to-office mandates and rounds of layoffs amid the pandemic. But, it offers clear data on just how important job flexibility and security are to the health and well-being of workers.
For the study, job flexibility was assessed in terms of ease of adjusting work schedules, advance notice of scheduling changes, and whether schedules were changed by employers often. People who reported greater flexibility in their job had 26 percent lower odds of serious psychological distress, which was measured on a validated, widely used questionnaire that assesses depression, nervousness, hopelessness, and worthlessness, among other forms of distress. Greater job flexibility was also linked to 13 percent lower odds of experiencing daily anxiety, 11 percent lower odds of experiencing weekly anxiety, and 9 percent lower odds of experiencing anxiety a few times a year.
Job security also appeared to be a boon for mental health. Workers were asked how likely they thought that they may lose their job or get laid off in the next 12 months. Those who reported feeling more secure in their positions had 25 percent lower odds of serious psychological distress. Job security was also associated with 27 percent lower odds of experiencing daily anxiety and 21 percent lower odds of experiencing weekly anxiety.
The study, led by Monica Wang of Boston University’s School of Public Health, also looked at how job flexibility and security affected job absenteeism, finding mixed results. Both job flexibility and security were linked to fewer days where workers reported working while they were sick—suggesting that flexibility and security enabled workers to make use of sick leave when they needed it. In line with that finding, more job flexibility led to more days where workers reported being absent due to illness in the three months prior to the survey. Greater job security, on the other hand, led to fewer absences over the previous three and 12 months.
It’s unclear why that would be the case, but the researchers speculated that “Job security may lead to lower work absenteeism due to higher work satisfaction, decreased job-related stress, and financial security,” they wrote.
Overall, the study’s findings indicate “the substantive impact that flexible and secure jobs can have on mental health in the short-term and long-term,” the researchers conclude.
They do note limitations of the study, the main one being that the study identifies associations and can’t determine that job flexibility and security directly caused mental health outcomes and the work absence findings. Still, they suggest that workplace policies could improve the mental health of employees. This includes flexible scheduling, leave policies, and working arrangements, including remote and hybrid options, which can all allow workers to accommodate personal and family needs. For improving job security, the researchers recommend longer-term contracts and long-term strategies to invest in employees, such as “uptraining,” skill development, and advancement opportunities.
Workers with job flexibility and security have better mental health Read More »
This is one of the Panasonic Avionics Astrova in-flight entertainment systems, set to debut in Icelandair, Qantus, and United Airlines flights in the next couple of years.
Panasonic
The goal doesn’t seem to be to keep them in first class; economy seats will get them too, albeit in smaller sizes.
Panasonic
Flying on commercial airlines today might be a lot more of a pain than it used to be, but new tech is going to bring some improvement to one part of the experience—in-flight entertainment. Panasonic Avionics’ brand Astrova in-flight entertainment systems are starting to roll out on commercial flights on certain airlines, promising 4K HDR TVs and other features to the backs of seats that should be a huge upgrade over the abysmal screens we normally watch in-flight movies on.
Look at most commercial airlines today, and you’ll find a tiny, terrible LCD TV embedded in the seat in front of you. These HD, standard dynamic range screens have terrible contrast and poor viewing angles, and they aren’t bright enough to achieve a good viewing experience when the overhead lights are on.
They’re bad enough that I always bring my own hardware for flights—most recently, I took three flights with Apple’s Vision Pro headset, which I plan to write about later this week. But most people just bring a tablet.
Astrova is Panasonic’s name for an in-flight entertainment system that aims to improve things dramatically. The OLED screens have 4K resolution and support HDR+. They also have two USB-C charging ports built in that can charge at up to 100 W, and they support Bluetooth, so you can use AirPods or Sony’s popular WH-1000 over-ear headphones.
With current systems, you have to bring an adapter to make that happen, if it’s possible.
Panasonic has paired the screens with new colored LED lighting systems that aim to make it so the bright overhead cabin lights don’t have to come on, washing out the image.
The screens come in 13-, 16-, 19-, 22-, 27-, 32-, and 42-inch variants. “How would you fit a 42-inch screen in an airplane seat?” you might ask. Well, that size is likely for ultra-high-end international flights where people can pay thousands and thousands of dollars for private cabins. Those aren’t the only types of seats that will get some kind of Astrova OLED system, though.
The rollout begins this year with Icelandair and Qantas planning to install Astrova systems in 2025 and late 2024. Icelandair will be first; new Airbus A321neo LR craft will see 16-inch screens in business class and 13-inch ones in economy. Qantas will install Astrova as part of its retrofit of its A330-200 fleet of planes and in newly ordered A350-1000 craft. The emphasis for Qantas is on long-haul flights, specifically those between Australia and Europe or the United States.
Last summer, US-based United Airlines announced many of its longer international flights would see these systems installed in 2025, with some domestic flights to follow, so it won’t be limited to intercontinental flights.
It’s doubtful that these screens will hold a candle to the latest high-end OLED TVs from LG and Samsung, and it looks like it will be a few years before they’re widespread in domestic flights. But any improvement is welcome on the terrible in-flight entertainment systems we’re using now. Now, if only another company could invent some way to use new tech to make the seats 20 percent bigger—I can dream, anyway.
Listing image by Panasonic
Flying coach? At least you’ll be able to watch movies on an in-seat OLED TV soon Read More »

peterschreiber.media | Getty Images
The US Justice Department on Monday unsealed an indictment charging seven men with hacking or attempting to hack dozens of US companies in a 14-year campaign furthering an economic espionage and foreign intelligence gathering by the Chinese government.
All seven defendants, federal prosecutors alleged, were associated with Wuhan Xiaoruizhi Science & Technology Co., Ltd. a front company created by the Hubei State Security Department, an outpost of the Ministry of State Security located in Wuhan province. The MSS, in turn, has funded an advanced persistent threat group tracked under names including APT31, Zirconium Violet Typhoon, Judgment Panda, and Altaire.
“Since at least 2010, the defendants … engaged in computer network intrusion activity on behalf of the HSSD targeting numerous US government officials, various US economic and defense industries and a variety of private industry officials, foreign democracy activists, academics and parliamentarians in response to geopolitical events affecting the PRC,” federal prosecutors alleged. “These computer network intrusion activities resulted in the confirmed and potential compromise of work and personal email accounts, cloud storage accounts and telephone call records belonging to millions of Americans, including at least some information that could be released in support of malign influence targeting democratic processes and institutions, and economic plans, intellectual property, and trade secrets belonging to American businesses, and contributed to the estimated billions of dollars lost every year as a result of the PRC’s state-sponsored apparatus to transfer US technology to the PRC.”
The relentless, 14-year campaign targeted thousands of individuals and dozens of companies through the use of zero-day attacks, website vulnerability exploitation, and the targeting of home routers and personal devices of high-ranking US government officials and politicians and election campaign staff from both major US political parties.
“The targeted US government officials included individuals working in the White House, at the Departments of Justice, Commerce, Treasury and State, and US Senators and Representatives of both political parties,” Justice Department officials said. “The defendants and others in the APT31 Group targeted these individuals at both professional and personal email addresses. Additionally in some cases, the defendants also targeted victims’ spouses, including the spouses of a high-ranking Department of Justice official, high-ranking White House officials and multiple United States Senators. Targets also included election campaign staff from both major US political parties in advance of the 2020 election.”
One technique the defendants allegedly used was the sending of emails to journalists, political officials, and companies. The messages, which were made to appear as originating from news outlets or journalists, contained hidden tracking links, which, when activated, gave APT31 members information about the locations, IP addresses, network schematics, and specific devices of the targets for use in follow-on attacks. Some of the targets of these emails included foreign government officials who were part of the Inter-Parliamentary Alliance on China, a group formed after the 1989 Tiananmen Square massacre that’s critical of the Chinese government; every European Union member of that’s a member of that group; and 43 UK parliamentary accounts part of the group or critical of the People’s Republic of China.
APT31 used a variety of methods to infect networks of interest with custom malware such as RAWDOOR, Trochilus, EvilOSX, DropDoor/DropCa, and later the widely available Cobalt Strike Beacon security testing tool. In late 2016, the hacking group exploited what was then a zero-day vulnerability in unnamed software to gain access to an unidentified defense contractor. In their indictment, prosecutors wrote:
Using the zero-day privilege escalation exploit, the Conspirators first obtained administrator access to a subsidiary’s network before ultimately pivoting into the Defense Contractor’s core corporate network,” prosecutors wrote in the indictment. “The Conspirators used a SQL injection, in which they entered malicious code into a web form input box to gain access to information that was not intended to be displayed, to create an account on the subsidiary’s network with the username “testdew23.” The Conspirators used malicious software to grant administrator privileges to the “testdew23” user account. Next, the Conspirators uploaded a web shell, or a script that enables remote administration of the computer, named “Welcome to Chrome,” onto the subsidiary’s web server. Thereafter, the Conspirators used the web shell to upload and execute at least two malicious files on the web server, which were configured to open a connection between the victim’s network and computers outside that network that were controlled by the Conspirators. Through this method, the Conspirators successfully gained unauthorized access to the Defense Contractor’s network.
Other APT31 targets include military contractors and companies in the aerospace, IT services, software, telecommunications, manufacturing, and financial services industries. APT31 has long been known to target not only individuals and entities with information of primary interest but also companies or services that the primary targets rely on. Primary targets were dissidents and critics of the PRC and Western companies in possession of technical information of value to the PRC.
Prosecutors said targets successfully hacked by APT31 include:
The defendants are:
The men were charged with conspiracy to commit computer intrusions and conspiracy to commit wire fraud. While none of the men are in US custody or likely to face prosecution, the US Department of Treasury on Monday sanctioned Wuhan Xiaoruizhi Science and Technology Company, Limited. The department also designated Zhao Guangzong and Ni Gaobin for their roles in hacks targeting US critical infrastructure.
“As a result of today’s action, all property and interests in property of the designated persons and entity described above that are in the United States or in the possession or control of US persons are blocked and must be reported to OFAC,” Treasury officials wrote. “In addition, any entities that are owned, directly or indirectly, individually or in the aggregate, 50 percent or more by one or more blocked persons are also blocked. Unless authorized by a general or specific license issued by OFAC, or exempt, OFAC’s regulations generally prohibit all transactions by US persons or within (or transiting) the United States that involve any property or interests in property of designated or otherwise blocked persons.”
The US State Department is offering $10 million for information leading to the identification or location of any of the defendants or others associated with the campaign.
Justice Department indicts 7 accused in 14-year hack campaign by Chinese gov Read More »
Mozilla
Mozilla’s Monitor Plus, a service launched by the privacy-minded tech firm in February, notes on its pitch page that there is “a $240 billion industry of data brokers selling your private information for profit” and that its offering can “take back your privacy.”
Mozilla’s most recent move to protect privacy has been to cut out one of the key providers of Monitor Plus’ people-search protections, Onerep. That comes after reporting from security reporter Brian Krebs, who uncovered Onerep CEO and founder Dimitri Shelest as the founder of “dozens of people-search services since 2010,” including one, Nuwber, that still sells the very kind of “background reports” that Monitor Plus seeks to curb.
Shelest told Krebs in a statement (PDF) that he did have an ownership stake in Nuwber, but that Nuwber has “zero cross-over or information-sharing with Onerep” and that he no longer operates any other people-search sites. Shelest admitted the bad look but said that his experience with people search gave Onerep “the best tech and team in the space.”
Brandon Borrman, vice president of communications at Mozilla, said in a statement that while “customer data was never at risk, the outside financial interests and activities of Onerep’s CEO do not align with our values.” Mozilla is “working now to solidify a transition plan,” Borrman said. A Mozilla spokesperson confirmed to Ars today that Mozilla is continuing to offer Monitor Plus, suggesting no pause in subscriptions, at least for the moment.
Monitor Plus also kept track of a user’s potential data breach exposures in partnership with HaveIBeenPwned. Troy Hunt, founder of HaveIBeenPwned, told Krebs that aside from Onerep’s potential conflict of interest, broker removal services tend to be inherently fraught. “[R]emoving your data from legally operating services has minimal impact, and you can’t remove it from the outright illegal ones who are doing the genuine damage.”
Still, every bit—including removing yourself from the first page of search results—likely counts. Beyond sites that scrape public records and court documents for your information, there are the other data brokers selling barely anonymized data from web browsing, app sign-ups, and other activity. A recent FTC settlement with antivirus and security firm Avast highlighted the depth of identifying information that often is available for sale to both commercial and government entities.
Mozilla’s privacy service drops a provider with ties to people-search sites Read More »

Enlarge / An M3 MacBook Air running macOS Sonoma.
Andrew Cunningham
Apple has just released version 14.4.1 for macOS Sonoma, a small-but-significant patch that claims to fix several issues with third-party software and accessories that cropped up in the 14.4 update. The 14.4.1 release also includes a pair of security fixes.
Apple’s release notes highlight fixes for three major problems:
- USB hubs connected to external displays may not be recognized
- Copy protected Audio Unit plug-ins designed for professional music apps may not open or pass validation
- Apps that include Java may quit unexpectedly
Users and companies began noticing problems shortly after the macOS 14.4 update was released earlier this month. Reports of broken USB hubs cropped up on Reddit, the Apple Support Communities forums, and elsewhere within the first couple of days, and issues with Java and iLok audio software DRM devices were reported later on. Some users also reported broken printer drivers and deleted file revisions in iCloud Drive, though Apple’s release notes don’t mention those problems.
At least some of these bugs reportedly weren’t present in preview builds of the 14.4 update, which could explain why they weren’t discovered during the public beta period.
Both of the security patches are for so-called “clickless” exploits that can allow remote code execution after a system displays a compromised image. Apple has also released macOS Ventura 13.6.6 to patch the security vulnerabilities for Macs that haven’t upgraded to Sonoma (or can’t upgrade to Sonoma).
Apple released other minor updates to iOS, iPadOS, and visionOS last week to patch the same security vulnerabilities. None of those updates listed any specific non-security bug fixes in their release notes beyond the broad “important bug fixes and security updates” boilerplate that accompanies most minor OS updates from Apple.
macOS Sonoma 14.4.1 released to fix the stuff that the 14.4 update broke Read More »
Enlarge / Google’s generative search results turn the normally stark-white results page into a range of pastels.
Last year Google brought its new obsession with AI-powered chatbots to Google Search with the launch of the “Search Generative Experience,” or “SGE.” If you opted in, SGE intercepted your Google search queries and put a giant, screen-filling generative AI chatbot response at the top of your search results. The usual 10 blue links were still there, but you had to scroll past Google’s ChatGPT clone to see them. That design choice makes outgoing web links seem like a legacy escape hatch for when the chatbot doesn’t work, and Google wants to know why more people haven’t opted in to this.
Barry Schwartz at Search Engine Land reports that Google is going to start pushing SGE out to some users, even if they haven’t opted in to the “Labs experiment.” A Google spokesperson told the site SGE will be turned on for a “subset of queries, on a small percentage of search traffic in the US.” The report says “Google told us they want to get feedback from searchers who have not opted into SGE specifically. This way they can get feedback and learn how a more general population will find this technology helpful.”
Citing his conversation with Google, Schwartz says some users automatically see Chatbot results for queries where Google thinks a chatbot “can be especially helpful.” Google will turn on the feature for “queries that are often more complex or involve questions where it may be helpful to get information from a range of web pages—like ‘how do I get marks off painted walls.'”
I don’t think anyone has spotted one of these non-opt-in SGE pages in the wild yet, so it’s unclear what the presentation will be. As an opt-in, SGE has a huge explanation page of how your search results will change. The chatbot is easily Google Search’s biggest format change ever, and having that happen automatically would be awfully confusing!
It’s also unclear if you can opt out of this. Today SGE is not compatible with Firefox, so that might be one way to skip Google’s AI obsession for now. Google Search has recently undergone a big leadership shuffle, with Liz Reid taking over as the new head of Search. Reid previously led—wait for it—the SGE team, so the prevailing theory is that we’re going to get way more AI stuff in search going forward.
Where’d my results go? Google Search’s chatbot is no longer opt-in Read More »

Getty Images | Dan Kitwood
A US judge has struck down a lawsuit brought by X against a nonprofit group that researched toxic content on the social media platform, finding the Elon Musk-owned company’s case appeared to be an attempt at “punishing” the group for exercising free speech.
The Center for Countering Digital Hate had sought to dismiss the case from X, which alleged the nonprofit unlawfully accessed and scraped X data for its studies. The CCDH found a rise in hate speech and misinformation on the platform. X had also alleged the group “cherry-picked” from posts on the platform to conduct a “scare campaign” to drive away advertisers, costing it tens of millions of dollars.
In a stinging ruling, US judge Charles Breyer in California granted the motion. “Sometimes it is unclear what is driving a litigation, and only by reading between the lines of a complaint can one attempt to surmise a plaintiff’s true purpose. Other times, a complaint is so unabashedly and vociferously about one thing that there can be no mistaking that purpose. This case represents the latter circumstance. This case is about punishing the defendants for their speech,” he wrote in the decision.
The judge found that on top of punishing the CCDH for a report criticizing the company, X appeared to have filed the suit “perhaps in order to dissuade others who might wish to engage in such criticism.”
The lawsuit is just one of several bitter disputes between Musk, a self-declared “free speech absolutist,” and civil rights groups and academics whose research argues the platform has not been adequately policed following the billionaire’s takeover in late 2022.
It comes as X’s revenue has fallen after brands pulled away over Musk’s decision to relax moderation on the platform. He, in turn, has lashed out at advertisers, saying last year that those who have left should “go fuck themselves” despite the company struggling financially.
CCDH chief executive Imran Ahmed said following the ruling: “The courts today have affirmed our fundamental right to research, to speak, to advocate, and to hold accountable social media companies for decisions they make behind closed doors that affect our kids, our democracy, and our fundamental human rights and civil liberties.”
He described the suit as “Elon Musk’s loud, hypocritical campaign of harassment, abuse, and lawfare designed to avoid taking responsibility for his own decisions.”
In a statement on X, the company said it disagreed with the court’s decisions and “plans to appeal.” Musk did not immediately comment on the case but last week wrote on the platform that the CCDH was a “truly evil organization that just wants to destroy the first amendment under the guise of doing good!”
© 2024 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved. Please do not copy and paste FT articles and redistribute by email or post to the web.
Lawsuit from Elon Musk’s X against anti-hate speech group dismissed by US judge Read More »
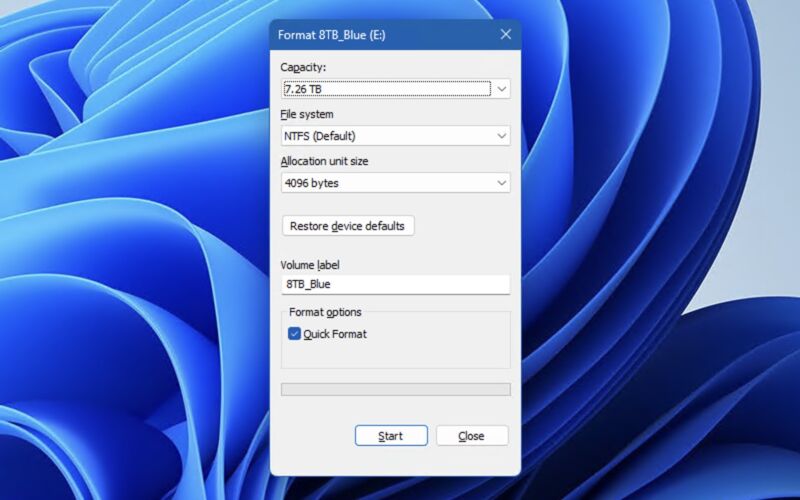
Enlarge / If you’ve formatted a disk in Windows in the last 30 years, you may have come across this dialog box.
Andrew Cunningham
Windows 11 has done a lot to update and modernize long-neglected parts of Windows’ user interface, including many Settings menus and venerable apps like Notepad and Paint. But if you dig deep enough, you’ll still find parts of the user interface that look and work like they did in the mid-’90s, either for compatibility reasons or because no one ever thought to go back and update them.
Former Microsoft programmer Dave Plummer shared some history about one of those finely aged bits: the Format dialogue box, which is still used in fully updated Windows 11 installs to this day when you format a disk using Windows Explorer.
Plummer says he wrote the Format dialog in late 1994, when the team was busy porting the user interface from the consumer-focused Windows 95 (released in mid-1995) to the more-stable but more resource-intensive Windows NT (NT 4.0, released in mid-1996, was the first to use the 95-style UI).
Formatting disks “was just one of those areas where Windows NT was different enough from Windows 95 that we had to come up with some custom UI,” wrote Plummer on X, formerly Twitter. Plummer didn’t specify what those differences were, but even the early versions of Windows NT could already handle multiple filesystems like FAT and NTFS, whereas Windows 95 mostly used FAT16 for everything.
“I got out a piece of paper and wrote down all the options and choices you could make with respect to formatting a disk, like filesystem, label, cluster size, compression, encryption, and so on,” Plummer continued. “Then I busted out [Visual] C++ 2.0 and used the Resource Editor to lay out a simple vertical stack of all the choices you had to make, in the approximate order you had to make. It wasn’t elegant, but it would do until the elegant UI arrived. That was some 30 years ago, and the dialog is still my temporary one from that Thursday morning, so be careful about checking in ‘temporary’ solutions!”
The Windows NT version of the Format dialog is the one that survives today because the consumer and professional versions of Windows began using the NT codebase in the late ’90s and early 2000s with the Windows 2000 and Windows XP releases. Plenty has changed since then, but system files like the kernel still have “Windows NT” labels in Windows 11.
Plummer also said the Format tool’s 32GB limit for FAT volumes was an arbitrary decision he made that we’re still living with among modern Windows versions—FAT32 drives formatted at the command line or using other tools max out between 2TB and 16TB, depending on sector size. It seems quaint, but PC ads from late 1994 advertise hard drives that are, at most, a few hundred megabytes in size, and 3.5-inch 1.44MB floppies and CD-ROM drives were about the best you could do for removable storage. From that vantage point, it would be hard to conceive of fingernail-sized disks that could give you 256GB of storage for $20.
Plummer was involved with many bits and pieces of ’90s- and early 2000s-era MS-DOS and Windows apps, including the Task Manager, the Space Cadet Pinball game, and the first version of the product activation system that shipped with Windows XP. Plummer left Microsoft in 2003.
Listing image by Getty
“Temporary” disk formatting UI from 1994 still lives on in Windows 11 Read More »

Enlarge / EU Commissioner for Internal Market Thierry Breton talks to media about non-compliance investigations against Google, Apple, and Meta under the Digital Markets Act (DMA).
Not even three weeks after the European Union’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) took effect, the European Commission (EC) announced Monday that it is already probing three out of six gatekeepers—Apple, Google, and Meta—for suspected non-compliance.
Apple will need to prove that changes to its app store and existing user options to swap out default settings easily are sufficient to comply with the DMA.
Similarly, Google’s app store rules will be probed, as well as any potentially shady practices unfairly preferencing its own services—like Google Shopping and Hotels—in search results.
Finally, Meta’s “Subscription for No Ads” option—allowing Facebook and Instagram users to opt out of personalized ad targeting for a monthly fee—may not fly under the DMA. Even if Meta follows through on its recent offer to slash these fees by nearly 50 percent, the model could be deemed non-compliant.
“The DMA is very clear: gatekeepers must obtain users’ consent to use their personal data across different services,” the EC’s commissioner for internal market, Thierry Breton, said Monday. “And this consent must be free!”
In total, the EC announced five investigations: two against Apple, two against Google, and one against Meta.
“We suspect that the suggested solutions put forward by the three companies do not fully comply with the DMA,” antitrust chief Margrethe Vestager said, ordering companies to “retain certain documents” viewed as critical to assessing evidence in the probe.
The EC’s investigations are expected to conclude within one year. If tech companies are found non-compliant, they risk fines of up to 10 percent of total worldwide turnover. Any repeat violations could spike fines to 20 percent.
“Moreover, in case of systematic infringements, the Commission may also adopt additional remedies, such as obliging a gatekeeper to sell a business or parts of it or banning the gatekeeper from acquisitions of additional services related to the systemic non-compliance,” the EC’s announcement said.
In addition to probes into Apple, Google, and Meta, the EC will scrutinize Apple’s fee structure for app store alternatives and send retention orders to Amazon and Microsoft. That makes ByteDance the only gatekeeper so far to escape “investigatory steps” as the EU fights to enforce the DMA’s strict standards. (ByteDance continues to contest its gatekeeper status.)
“These are the cases where we already have concrete evidence of possible non-compliance,” Breton said. “And this in less than 20 days of DMA implementation. But our monitoring and investigative work of course doesn’t stop here,” Breton said. “We may have to open other non-compliance cases soon.
Google and Apple have both issued statements defending their current plans for DMA compliance.
“To comply with the Digital Markets Act, we have made significant changes to the way our services operate in Europe,” Google’s competition director Oliver Bethell told Ars, promising to “continue to defend our approach in the coming months.”
“We’re confident our plan complies with the DMA, and we’ll continue to constructively engage with the European Commission as they conduct their investigations,” Apple’s spokesperson told Ars. “Teams across Apple have created a wide range of new developer capabilities, features, and tools to comply with the regulation. At the same time, we’ve introduced protections to help reduce new risks to the privacy, quality, and security of our EU users’ experience. Throughout, we’ve demonstrated flexibility and responsiveness to the European Commission and developers, listening and incorporating their feedback.”
A Meta spokesperson told Ars that Meta “designed Subscription for No Ads to address several overlapping regulatory obligations, including the DMA,” promising to comply with the DMA while arguing that “subscriptions as an alternative to advertising are a well-established business model across many industries.”
The EC’s announcement came after all designated gatekeepers were required to submit DMA compliance reports and scheduled public workshops to discuss DMA compliance. Those workshops conclude tomorrow with Microsoft and appear to be partly driving the EC’s decision to probe Apple, Google, and Meta.
“Stakeholders provided feedback on the compliance solutions offered,” Vestager said. “Their feedback tells us that certain compliance measures fail to achieve their objectives and fall short of expectations.”
Under the DMA, “gatekeepers can no longer prevent their business users from informing their users within the app about cheaper options outside the gatekeeper’s ecosystem,” Vestager said. “That is called anti-steering and is now forbidden by law.”
Stakeholders told the EC that Apple’s and Google’s fee structures appear to “go against” the DMA’s “free of charge” requirement, Vestager said, because companies “still charge various recurring fees and still limit steering.”
This feedback pushed the EC to launch its first two probes under the DMA against Apple and Google.
“We will investigate to what extent these fees and limitations defeat the purpose of the anti-steering provision and by that, limit consumer choice,” Vestager said.
These probes aren’t the end of Apple’s potential app store woes in the EU, either. Breton said that the EC has “many questions on Apple’s new business model” for the app store. These include “questions on the process that Apple used for granting and terminating membership of” its developer program, following a scandal where Epic Games’ account was briefly terminated.
“We also have questions on the fee structure and several other aspects of the business model,” Breton said, vowing to “check if they allow for real opportunities for app developers in line with the letter and the spirit of the DMA.”
Apple, Google, and Meta are failing DMA compliance, EU suspects Read More »
Focus Features
Last week, the 2004 cult classic Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind marked its 20th anniversary, prompting many people to revisit the surreal sci-fi psychological drama about two ex-lovers who erase their memories of each other—only to find themselves falling in love all over again. Eternal Sunshine was a box office success and earned almost universal praise upon its release. It’s still a critical favorite today and remains one of star Jim Carrey’s most powerful and emotionally resonant dramatic roles. What better time for a rewatch and in-depth discussion of the film’s themes of memory, personal identity, love, and loss?
(Spoilers for the 2004 film below.)
Director Michel Gondry and co-writer Pierre Bismuth first came up with the concept for the film in 1998, based on a conversation Bismuth had with a female friend who, when he asked, said she would absolutely erase her boyfriend from her memory if she could. They brought on Charlie Kaufman to write the script, and the three men went on to win an Oscar for Best Original Screenplay for their efforts. The title alludes to a 1717 poem by Alexander Pope, “Eloisa to Abelard,” based on the tragic love between medieval philosopher Peter Abelard and Héloïse d’Argenteuil and their differing perspectives on what happened between them when they exchanged letters later in life. These are the most relevant lines:
Of all affliction taught a lover yet,
‘Tis sure the hardest science to forget!
…
How happy is the blameless vestal’s lot!
The world forgetting, by the world forgot.
Eternal sunshine of the spotless mind!
Carrey plays Joel, a shy introvert who falls in love with the extroverted free spirit Clementine (Kate Winslet). The film opens with the couple estranged and Joel discovering that Clementine has erased all her memories of him, thanks to the proprietary technology of a company called Lacuna. Joel decides to do the same, and much of the film unfolds backward in time in a nonlinear narrative as Joel (while dreaming) relives his memories of their relationship in reverse. Those memories dissolve as he recalls each one, even though at one point, he changes his mind and tries unsuccessfully to stop the process.
The twist: Joel ends up meeting Clementine all over again on that beach in Montauk, and they are just as drawn to each other as before. When they learn—thanks to the machinations of a vengeful Lacuna employee—what happened between them the first time around, they almost separate again. But Joel convinces Clementine to take another chance, believing their relationship to be worth any future pain.
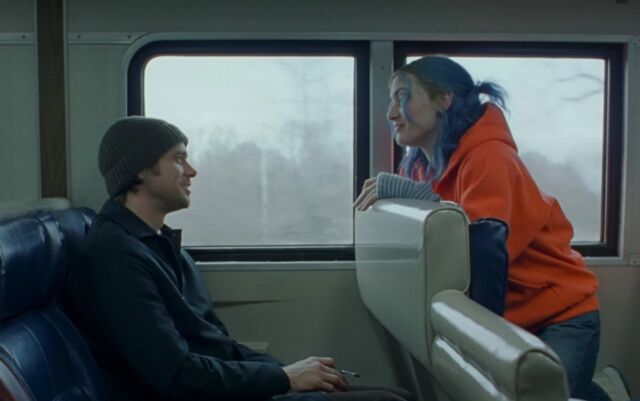

Enlarge / Joel (Jim Carrey) and Clementine (Kate Winslet) meet-cute on the LIRR to Montauk.
Much has been written over the last two decades about the scientific basis for the film, particularly the technology used to erase Joel’s and Clementine’s respective memories. The underlying neuroscience involves what’s known as memory reconsolidation. The brain is constantly processing memories, including associated emotions, both within the hippocampus and across the rest of the brain (system consolidation). Research into reconsolidation of memories emerged in the 2000s, in which past memories (usually traumatic ones) are recalled with the intent of altering them, since memories are unstable during the recall process. For example, in the case of severe PTSD, administering Beta blockers can decouple intense feelings of fear from traumatic memories while leaving those memories intact.
Like all good science fiction, Eternal Sunshine takes that grain of actual science and extends it in thought-provoking ways. In the film, so-called “problem memories” can be recalled individually while the patient is in a dream state and erased completely—uncomfortable feelings and all—as if they were computer files. Any neuroscientist will tell you this is not how memory works. What remains most interesting about Eternal Sunshine‘s premise is its thematic exploration of the persistence and vital importance of human memory.
So we thought it would be intriguing to mark the film’s 20th anniversary by exploring those ideas through the lens of philosophy with the guidance of Johns Hopkins University philosopher Jenann Ismael. Ismael specializes in probing questions of physics, metaphysics, cognition, and theory of mind. Her many publications include The Situated Self (2009), How Physics Makes Us Free (2016), and, most recently, Time: A Very Short Introduction (2021).
Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind and the philosophy of self, identity, and memory Read More »