Why Darren Aronofsky thought an AI-generated historical docudrama was a good idea
We hold these truths to be self-evident
Production source says it takes “weeks” to produce just minutes of usable video.
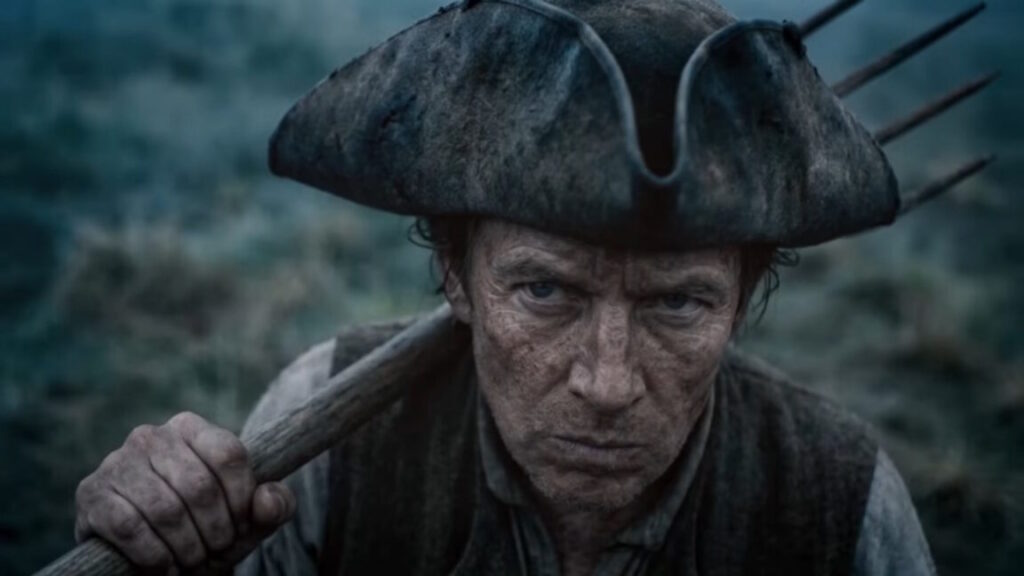
Artist’s conception of critics reacting to the first episodes of “On This Day… 1776” Credit: Primordial Soup
Artist’s conception of critics reacting to the first episodes of “On This Day… 1776” Credit: Primordial Soup
Last week, filmmaker Darren Aronofsky’s AI studio Primordial Soup and Time magazine released the first two episodes of On This Day… 1776. The year-long series of short-form videos features short vignettes describing what happened on that day of the American Revolution 250 years ago, but it does so using “a variety of AI tools” to produce photorealistic scenes containing avatars of historical figures like George Washington, Thomas Paine, and Benjamin Franklin.
In announcing the series, Time Studios President Ben Bitonti said the project provides “a glimpse at what thoughtful, creative, artist-led use of AI can look like—not replacing craft but expanding what’s possible and allowing storytellers to go places they simply couldn’t before.”
The trailer for “On This Day… 1776.”
Outside critics were decidedly less excited about the effort. The AV Club took the introductory episodes to task for “repetitive camera movements [and] waxen characters” that make for “an ugly look at American history.” CNET said that this “AI slop is ruining American history,” calling the videos a “hellish broth of machine-driven AI slop and bad human choices.” The Guardian lamented that the “once-lauded director of Black Swan and The Wrestler has drowned himself in AI slop,” calling the series “embarrassing,” “terrible,” and “ugly as sin.” I could go on.
But this kind of initial reaction apparently hasn’t deterred Primordial Soup from its still-evolving efforts. A source close to the production, who requested anonymity to speak frankly about details of the series’ creation, told Ars that the quality of new episodes would improve as the team’s AI tools are refined throughout the year and as the team learns to better use them.
“We’re going into this fully assuming that we have a lot to learn, that this process is gonna evolve, the tools we’re using are gonna evolve,” the source said. “We’re gonna make mistakes. We’re gonna learn a lot… we’re going to get better at it, [and] the technology will change. We’ll see how audiences are reacting to certain things, what works, what doesn’t work. It’s a huge experiment, really.”
Not all AI
It’s important to note that On This Day… 1776 is not fully crafted by AI. The script, for instance, was written by a team of writers overseen by Aronofsky’s longtime writing partners Ari Handel and Lucas Sussman, as noted by The Hollywood Reporter. That makes criticisms like the Guardian’s of “ChatGPT-sounding sloganeering” in the first episodes both somewhat misplaced and hilariously harsh.
Our production source says the project was always conceived as a human-written effort and that the team behind it had long been planning and researching how to tell this kind of story. “I don’t think [they] even needed that kind of help or wanted that kind of [AI-powered writing] help,” they said. “We’ve all experimented with [AI-powered] writing and the chatbots out there, and you know what kind of quality you get out of that.”
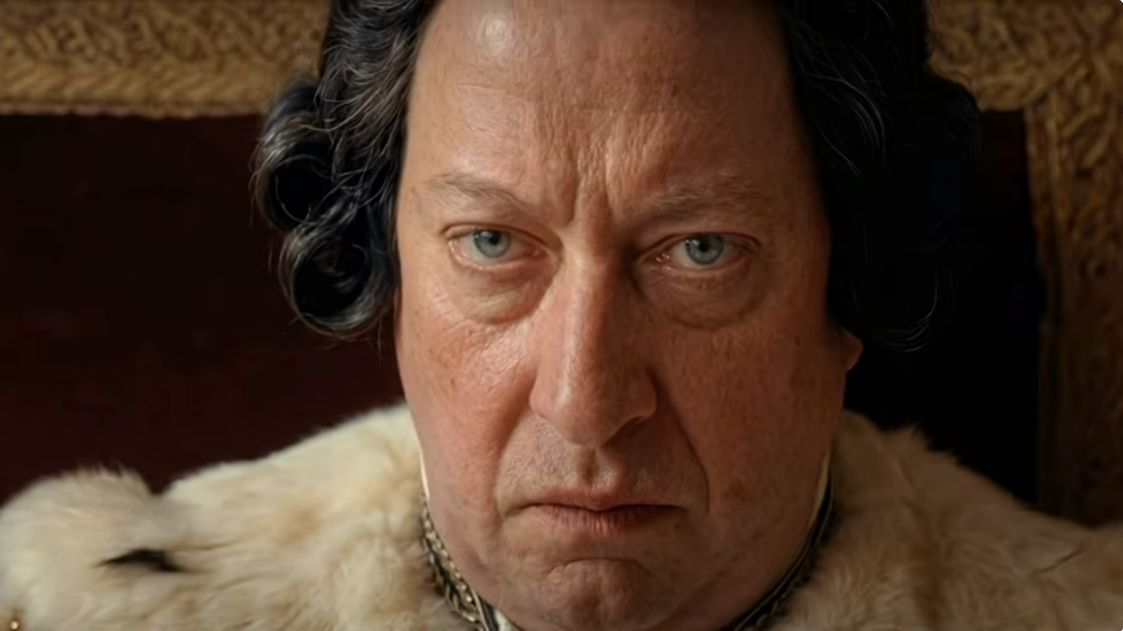
What you see here is not a real human actor, but his lines were written and voiced by humans. Credit: Primordial Soup
The producers also go out of their way to note that all the dialogue in the series is recorded directly by Screen Actors Guild voice actors, not by AI facsimiles. While recently negotiated union rules might have something to do with that, our production source also said the AI-generated voices the team used for temp tracks were noticeably artificial and not ready for a professional production.
Humans are also directly responsible for the music, editing, sound mixing, visual effects, and color correction for the project, according to our source. The only place the “AI-powered tools” come into play is in the video itself, which is crafted with what the announcement calls a “combination of traditional filmmaking tools and emerging AI capabilities.”
In practice, our source says, that means humans create storyboards, find visual references for locations and characters, and set up how they want shots to look. That information, along with the script, gets fed into an AI video generator that creates individual shots one at a time, to be stitched together and cleaned up by humans in traditional post-production.
That process takes the AI-generated cinema conversation one step beyond Ancestra, a short film Primordial Soup released last summer in association with Google DeepMind (which is not involved with the new project). There, AI tools were used to augment “live-action scenes with sequences generated by Veo.”
“Weeks” of prompting and re-prompting
In theory, having an AI model generate a scene in minutes might save a lot of time compared to traditional filmmaking—scouting locations, hiring actors, setting up cameras and sets, and the like. But our production source said the highly iterative process of generating and perfecting shots for On This Day… 1776 still takes “weeks” for each minutes-long video and that “more often than not, we’re pushing deadlines.”
The first episode of On this Day… 1776 features a dramatic flag raising.
Even though the AI model is essentially animating photorealistic avatars, the source said the process is “more like live action filmmaking” because of the lack of fine-grained control over what the video model will generate. “You don’t know if you’re gonna get what you want on the first take or the 12th take or the 40th take,” the source said.
While some shots take less time to get right than others, our source said the AI model rarely produces a perfect, screen-ready shot on the first try. And while some small issues in an AI-generated shot can be papered over in post-production with visual effects or careful editing, most of the time, the team has to go back and tell the model to generate a completely new video with small changes.
“It still takes a lot of work, and it’s not necessarily because it’s wrong, per se, so much as trying to get the right control because you [might] want the light to land on the face in the right way to try to tell the story,” the source said. “We’re still, we’re still striving for the same amount of control that we always have [with live-action production] to really maximize the story and the emotion.”
Quick shots and smaller budgets
Though video models have advanced since the days of the nightmarish clip of Will Smith eating spaghetti, hallucinations and nonsensical images are “still a problem” in producing On This Day… 1776, according to our source. That’s one of the reasons the company decided to use a series of short-form videos rather than a full-length movie telling the same essential story.
“It’s one thing to stay consistent within three minutes. It’s a lot harder and it takes a lot more work to stay consistent within two hours,” the source said. “I don’t know what the upper limit is now [but] the longer you get, the more things start to fall off.”
We’ve come a long way from the circa-2023 videos of Will Smith eating spaghetti. Credit: chaindrop / Reddit
Keeping individual shots short also allows for more control and fewer “reshoots” for an AI-animated production like this. “When you think about it, if you’re trying to create a 20-second clip, you have all these things that are happening, and if one of those things goes wrong in 20 seconds, you have to start over,” our source said. “And the chance of something going wrong in 20 seconds is pretty high. The chance of something going wrong in eight seconds is a lot lower.”
While our production source couldn’t give specifics on how much the team was spending to generate so much AI-modeled video, they did suggest that the process was still a good deal cheaper than filming a historical docudrama like this on location.
“I mean, we could never achieve what we’re doing here for this amount of money, which I think is pretty clear when you watch this,” they said. In future episodes, the source promised, “you’ll see where there’s things that cameras just can’t even do” as a way to “make the most of that medium.”
“Let’s see what we can do”
If you’ve been paying attention to how fast things have been moving with AI-generated video, you might think that AI models will soon be able to produce Hollywood-quality cinema with nothing but a simple prompt. But our source said that working on On This Day… 1776 highlights just how important it is for humans to still be in the loop on something like this.
“Personally, I don’t think we’re ever gonna get there [replacing human editors],” he said. “We actually desperately need an editor. We need another set of eyes who can look at the cut and say, ‘If we get out of this shot a little early, then we can create a little bit of urgency. If we linger on this thing a little longer…’ You still really need that.”
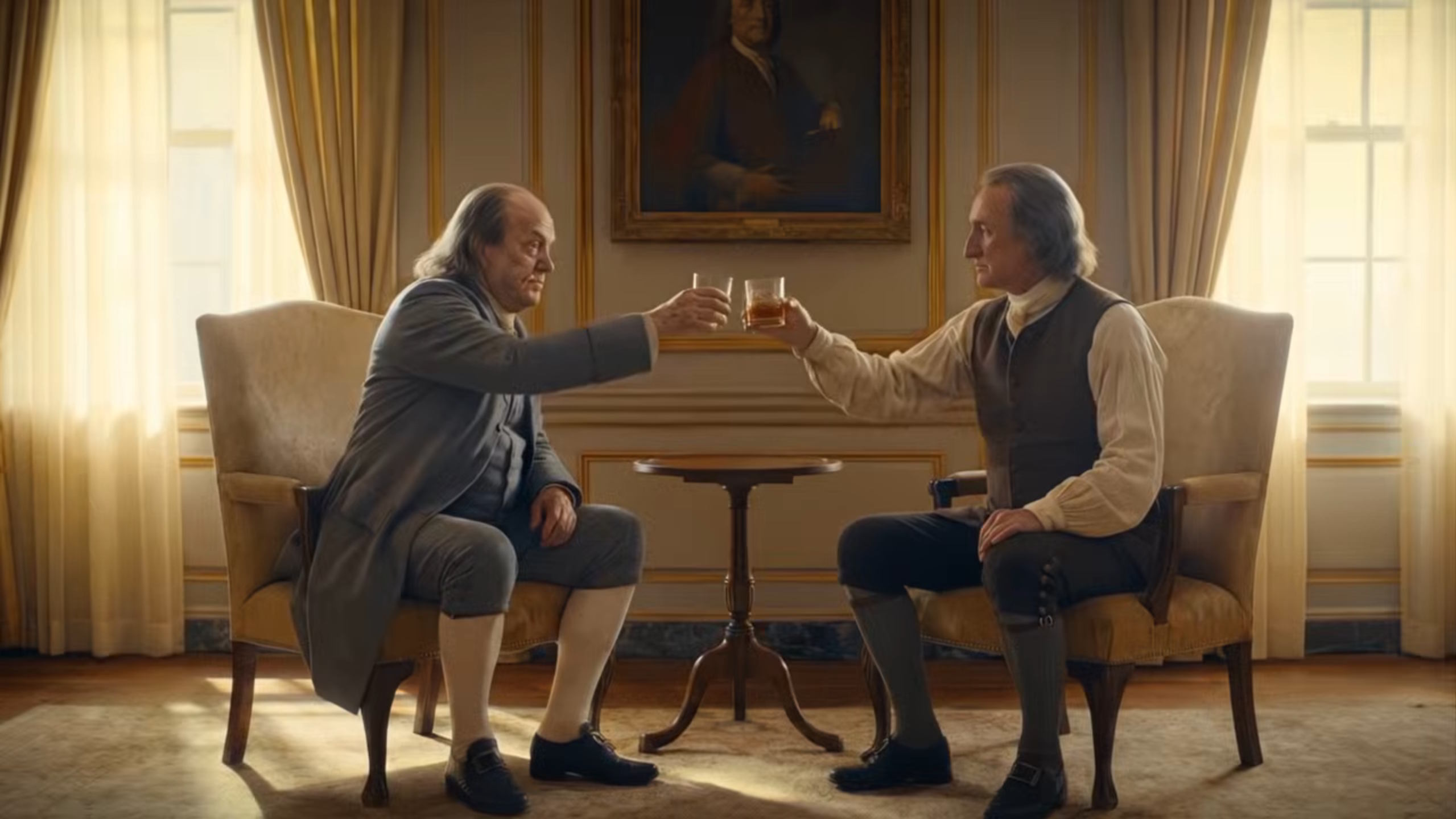
AI Ben Franklin and AI Thomas Paine toast to the war propaganda effort. Credit: Primordial Soup
That could be good news for human editors. But On This Day… 1776 also suggests a world where on-screen (or even motion-captured) human actors are fully replaced by AI-generated avatars. When I asked our source why the producers felt that AI was ready to take over that specifically human part of the film equation, though, the response surprised me.
“I don’t know that we do know that, honestly,” they said. “I think we know that the technology is there to try. And I think as storytellers we’re really interested in using… all the different tools that we can to try to get our story across and to try to make audiences feel something.”
“It’s not often that we have huge new tools like this,” the source continued. “I mean, it’s never happened in my lifetime. But when you do [get these new tools], you want to start playing with them… We have to try things in order to know if it works, if it doesn’t work.”
“So, you know, we have the tools now. Let’s see what we can do.”
Kyle Orland has been the Senior Gaming Editor at Ars Technica since 2012, writing primarily about the business, tech, and culture behind video games. He has journalism and computer science degrees from University of Maryland. He once wrote a whole book about Minesweeper.
Why Darren Aronofsky thought an AI-generated historical docudrama was a good idea Read More »