Apple’s first Mac mini redesign in 14 years looks like a big aluminum Apple TV
Apple’s week of Mac announcements continues today, and as expected, we’re getting a substantial new update to the Mac mini. Apple’s least-expensive Mac, the mini, is being updated with new M4 processors, plus a smaller design that looks like a cross between an Apple TV box and a Mac Studio—this is the mini’s first major design change since the original aluminum version was released in 2010. The mini is also Apple’s first device to ship with the M4 Pro processor, a beefed-up version of the M4 with more CPU and GPU cores, and it’s also the Mac mini’s first update since the M2 models came out in early 2023.
The cheapest Mac mini will still run you $599, which includes 16GB of RAM and 256GB of storage; as with yesterday’s iMac update, this is the first time since 2012 that Apple has boosted the amount of RAM in an entry-level Mac. It’s a welcome upgrade for every new Mac in the lineup that’s getting it, but the $200 that Apple previously charged for the 16GB upgrade makes an even bigger difference to someone shopping for a $599 system than it does for someone who can afford a $999 or $1,299 computer.
The M4 Pro Mac mini starts at $1,399, a $100 increase from the M2 Pro version. Both models go up for preorder today and will begin arriving on November 8.
A brand-new design for a little box
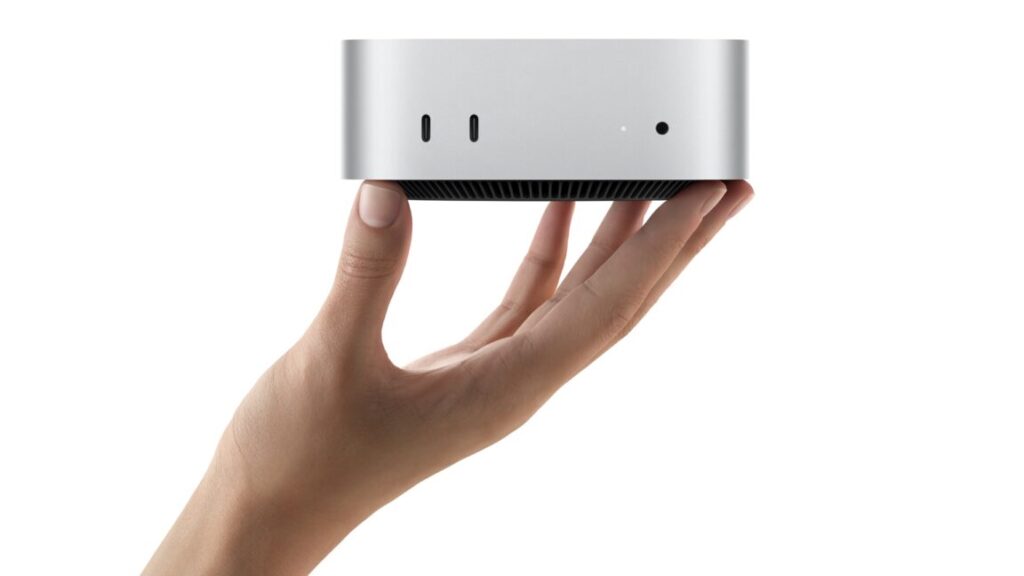
The new Mac mini is larger than the Apple TV by a bit—5×5 inches instead of 3.66×3.66 inches—but its proportions are roughly similar. That makes its footprint significantly smaller than the old mini (and the current Studio), which was 7.75×7.75 inches. But it’s also a fair bit taller: 2 inches, up from 1.4 inches.
Like the Studio, it’s made primarily of aluminum and has a pair of 10 Gbps USB-C ports on the front, plus an indicator light and a headphone jack for connecting headphones or speakers. On the back, it sheds all of its remaining USB-A ports in favor of Thunderbolt/USB-C ports (note that, like some Mac Studio models, the ports on the back have Thunderbolt capabilities and the ones on the front don’t). Compared to the old M2 mini, this is a net gain of one rear Thunderbolt port, but you’re giving one up compared to the M2 Pro Mac mini—the extra ports on the front should make up for this, but it’s worth noting if you have something connected to every single Thunderbolt port on your current box. All Mac mini models still include a gigabit Ethernet port and a full-size HDMI port, so USB-A is the only port you’ll need a dongle for that you didn’t need one for before.
Apple’s first Mac mini redesign in 14 years looks like a big aluminum Apple TV Read More »