Apple software leaks new Mac mini with five USB-C ports ahead of rumored event
m4 macs with m4 max? —
Apple often launches Macs and iPads in October, after the iPhone dust settles.
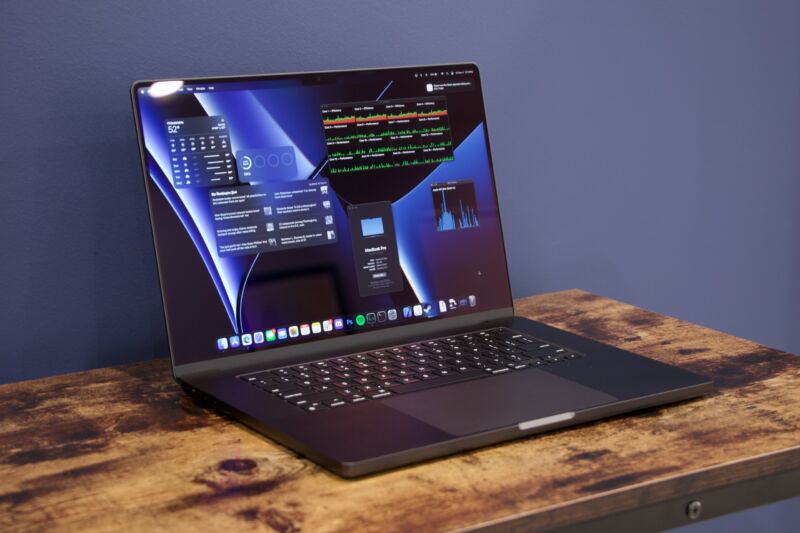

Enlarge / Apple’s M3 Max-powered 16-inch MacBook Pro. New Pro laptops and some desktops could be on tap for later this fall.
Andrew Cunningham
Apple’s newest iPhones and Apple Watches don’t come out until later this week, but the rumor mill is already indicating that Apple is planning a product announcement for October to refresh some of the products that didn’t get a mention at the iPhone event. Apple scheduled its release calendar similarly last year, when it announced and released new iPhones in September and then launched the first wave of M3 Macs around Halloween.
Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman believes that the event will mainly focus on the first wave of Macs with M4 processors, following the standard M4’s introduction in the iPad Pro earlier this year. As he has reported previously, he expects new MacBook Pro models with the M4 and “pro-level M4 chip options,” presumably the M4 Pro and M4 Max. He also expects an M4 version of the 24-inch iMac.
But the most interesting of the new Macs will still be the redesigned Mac mini, which hasn’t gotten an M3 update at all and has been using the same basic external design since 2010. This Mac mini is said to be closer in size to the Apple TV than the current mini, but still uses an internal power supply so that owners won’t have to wrangle a power brick. At least some of the current device’s ports will be replaced by USB-C and/or Thunderbolt ports, something that MacRumors apparently confirmed earlier today when they found a reference to an “Apple silicon Mac mini (5 ports)” in an Apple software update (some of those ports are reportedly on the front of the device, a nice Mac Studio design upgrade that I’d like to see on a new Mac mini).
The “five port” descriptor does imply that there will be another model with either more or fewer ports—Apple used similar terminology to distinguish the two- and four-port versions of some MacBook Pro models in the Intel days. The current M2 Mac mini models have fewer ports than the models with the M2 Pro chip, because the more powerful processor also has more I/O capabilities—assuming we get one Mac mini with an M4 and an upgraded model with an M4 Pro, we’d expect the Pro version to have more ports.
Gurman says that other Mac models, including the Mac Studio, Mac Pro, and MacBook Air, will see M4-series updates throughout 2025. Of those, the Mac Studio and the Mac Pro have gone the longest without an update—they’re all still using M2-series chips.
Apple is also said to be planning some new lower-end iPads for the October event—not the first time that Macs and iPads have shared billing for one of these late-fall product announcements. The $349 iPad 10 and the iPad mini have both gone over a year without any kind of hardware update; it seems likely that they’ll both get newer chips, if not significantly updated designs.
Apple software leaks new Mac mini with five USB-C ports ahead of rumored event Read More »