OpenAI, cofounder Sam Altman to take on Neuralink with new startup
The company aims to raise $250 million from OpenAI and other investors, although the talks are at an early stage. Altman will not personally invest.
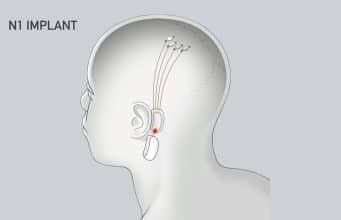
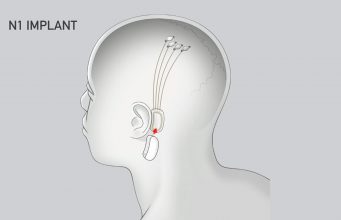
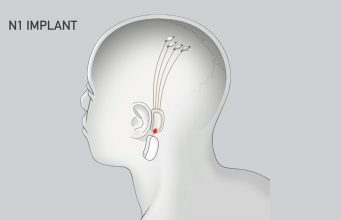
The new venture would be in direct competition with Neuralink, founded by Musk in 2016, which seeks to wire brains directly to computers.
Musk and Altman cofounded OpenAI, but Musk left the board in 2018 after clashing with Altman, and the two have since become fierce rivals in their pursuit of AI.
Musk launched his own AI start-up, xAI, in 2023 and has been attempting to block OpenAI’s conversion from a nonprofit in the courts. Musk donated much of the initial capital to get OpenAI off the ground.
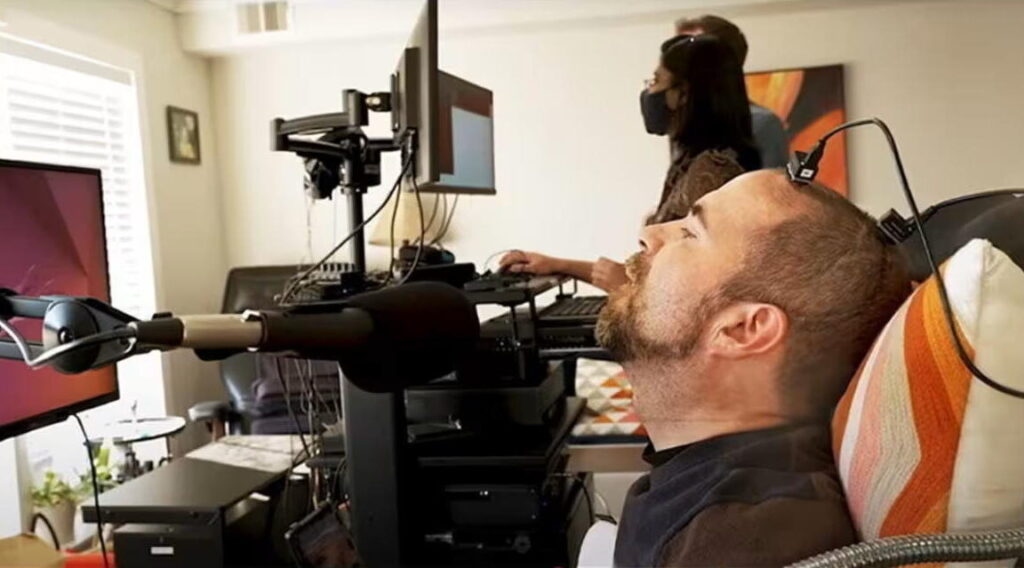
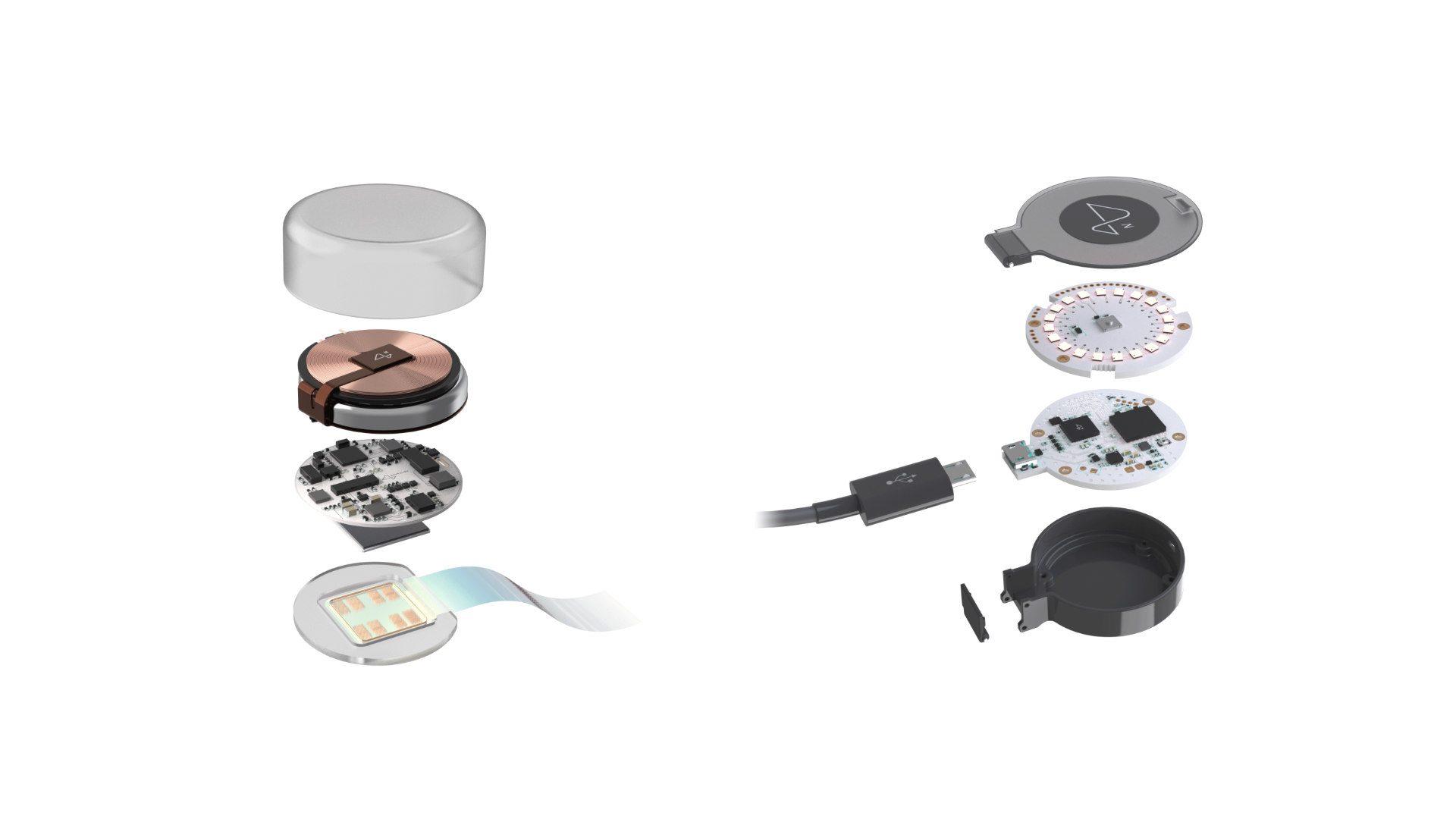
Neuralink is one of a pack of so-called brain-computer interface companies, while a number of start-ups, such as Precision Neuroscience and Synchron, have also emerged on the scene.
Neuralink earlier this year raised $650 million at a $9 billion valuation, and it is backed by investors including Sequoia Capital, Thrive Capital, and Vy Capital. Altman had previously invested in Neuralink.
Brain implants are a decades-old technology, but recent leaps forward in AI and in the electronic components used to collect brain signals have offered the prospect that they can become more practically useful.
Altman has backed a number of other companies in markets adjacent to ChatGPT-maker OpenAI, which is valued at $300 billion. In addition to cofounding World, he has also invested in the nuclear fission group Oklo and nuclear fusion project Helion.
OpenAI declined to comment.
© 2025 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved. Not to be redistributed, copied, or modified in any way.
OpenAI, cofounder Sam Altman to take on Neuralink with new startup Read More »