What does “PhD-level” AI mean? OpenAI’s rumored $20,000 agent plan explained.
On the Frontier Math benchmark by EpochAI, o3 solved 25.2 percent of problems, while no other model has exceeded 2 percent—suggesting a leap in mathematical reasoning capabilities over the previous model.
Benchmarks vs. real-world value
Ideally, potential applications for a true PhD-level AI model would include analyzing medical research data, supporting climate modeling, and handling routine aspects of research work.
The high price points reported by The Information, if accurate, suggest that OpenAI believes these systems could provide substantial value to businesses. The publication notes that SoftBank, an OpenAI investor, has committed to spending $3 billion on OpenAI’s agent products this year alone—indicating significant business interest despite the costs.
Meanwhile, OpenAI faces financial pressures that may influence its premium pricing strategy. The company reportedly lost approximately $5 billion last year covering operational costs and other expenses related to running its services.
News of OpenAI’s stratospheric pricing plans come after years of relatively affordable AI services that have conditioned users to expect powerful capabilities at relatively low costs. ChatGPT Plus remains $20 per month and Claude Pro costs $30 monthly—both tiny fractions of these proposed enterprise tiers. Even ChatGPT Pro’s $200/month subscription is relatively small compared to the new proposed fees. Whether the performance difference between these tiers will match their thousandfold price difference is an open question.
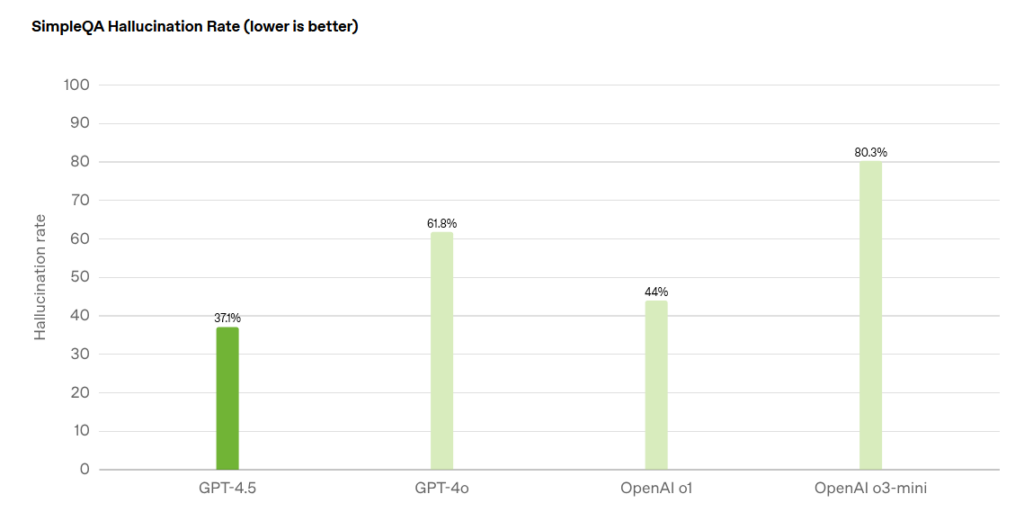
Despite their benchmark performances, these simulated reasoning models still struggle with confabulations—instances where they generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. This remains a critical concern for research applications where accuracy and reliability are paramount. A $20,000 monthly investment raises questions about whether organizations can trust these systems not to introduce subtle errors into high-stakes research.
In response to the news, several people quipped on social media that companies could hire an actual PhD student for much cheaper. “In case you have forgotten,” wrote xAI developer Hieu Pham in a viral tweet, “most PhD students, including the brightest stars who can do way better work than any current LLMs—are not paid $20K / month.”
While these systems show strong capabilities on specific benchmarks, the “PhD-level” label remains largely a marketing term. These models can process and synthesize information at impressive speeds, but questions remain about how effectively they can handle the creative thinking, intellectual skepticism, and original research that define actual doctoral-level work. On the other hand, they will never get tired or need health insurance, and they will likely continue to improve in capability and drop in cost over time.
What does “PhD-level” AI mean? OpenAI’s rumored $20,000 agent plan explained. Read More »