Newly discovered ransomware uses BitLocker to encrypt victim data
GOING NATIVE —
ShrinkLocker is the latest ransomware to use Windows’ full-disk encryption.
A previously unknown piece of ransomware, dubbed ShrinkLocker, encrypts victim data using the BitLocker feature built into the Windows operating system.
BitLocker is a full-volume encryptor that debuted in 2007 with the release of Windows Vista. Users employ it to encrypt entire hard drives to prevent people from reading or modifying data in the event they get physical access to the disk. Starting with the rollout of Windows 10, BitLocker by default has used the 128-bit and 256-bit XTS-AES encryption algorithm, giving the feature extra protection from attacks that rely on manipulating cipher text to cause predictable changes in plain text.
Recently, researchers from security firm Kaspersky found a threat actor using BitLocker to encrypt data on systems located in Mexico, Indonesia, and Jordan. The researchers named the new ransomware ShrinkLocker, both for its use of BitLocker and because it shrinks the size of each non-boot partition by 100 MB and splits the newly unallocated space into new primary partitions of the same size.
“Our incident response and malware analysis are evidence that attackers are constantly refining their tactics to evade detection,” the researchers wrote Friday. “In this incident, we observed the abuse of the native BitLocker feature for unauthorized data encryption.”
ShrinkLocker isn’t the first malware to leverage BitLocker. In 2022, Microsoft reported that ransomware attackers with a nexus to Iran also used the tool to encrypt files. That same year, the Russian agricultural business Miratorg was attacked by ransomware that used BitLocker to encrypt files residing in the system storage of infected devices.
Once installed on a device, ShrinkLocker runs a VisualBasic script that first invokes the Windows Management Instrumentation and Win32_OperatingSystem class to obtain information about the operating system.
“For each object within the query results, the script checks if the current domain is different from the target,” the Kaspersky researchers wrote. “If it is, the script finishes automatically. After that, it checks if the name of the operating system contains ‘xp,’ ‘2000,’ ‘2003,’ or ‘vista,’ and if the Windows version matches any one of these, the script finishes automatically and deletes itself.”
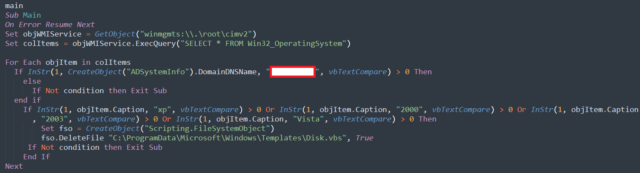
Enlarge / A screenshot showing initial conditions for execution.
Kaspersky
The script then continues to use the WMI for querying information about the OS. It goes on to perform the disk resizing operations, which can vary depending on the OS version detected. The ransomware performs these operations only on local, fixed drives. The decision to leave network drives alone is likely motivated by the desire not to trigger network detection protections.
Eventually, ShrinkLocker disables protections designed to secure the BitLocker encryption key and goes on to delete them. It then enables the use of a numerical password, both as a protector against anyone else taking back control of BitLocker and as an encryptor for system data. The reason for deleting the default protectors is to disable key recovery features by the device owner. ShrinkLocker then goes on to generate a 64-character encryption key using random multiplication and replacement of:
- A variable with the numbers 0–9;
- The famous pangram, “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog,” in lowercase and uppercase, which contains every letter of the English alphabet;
- Special characters.
After several additional steps, data is encrypted. The next time the device reboots, the display looks like this:

Enlarge / Screenshot showing the BitLocker recovery screen.
Kaspersky
Decrypting drives without the attacker-supplied key is difficult and likely impossible in many cases. While it is possible to recover some of the passphrases and fixed values used to generate the keys, the script uses variable values that are different on each infected device. These variable values aren’t easy to recover.
There are no protections specific to ShrinkLocker for preventing successful attacks. Kaspersky advises the following:
- Use robust, properly configured endpoint protection to detect threats that try to abuse BitLocker;
- Implement Managed Detection and Response (MDR) to proactively scan for threats;
- If BitLocker is enabled, make sure it uses a strong password and that the recovery keys are stored in a secure location;
- Ensure that users have only minimal privileges. This prevents them from enabling encryption features or changing registry keys on their own;
- Enable network traffic logging and monitoring. Configure the logging of both GET and POST requests. In case of infection, the requests made to the attacker’s domain may contain passwords or keys;
- Monitor for events associated with VBS execution and PowerShell, then save the logged scripts and commands to an external repository storing activity that may be deleted locally;
- Make backups frequently, store them offline, and test them.
Friday’s report also includes indicators that organizations can use to determine if they have been targeted by ShrinkLocker.
Listing image by Getty Images
Newly discovered ransomware uses BitLocker to encrypt victim data Read More »