Explosion of cicada-eating mites has the state of Illinois scratching
Attack of the mites —
The good news: There’s little risk beyond the rash. The bad: The rash is awful.
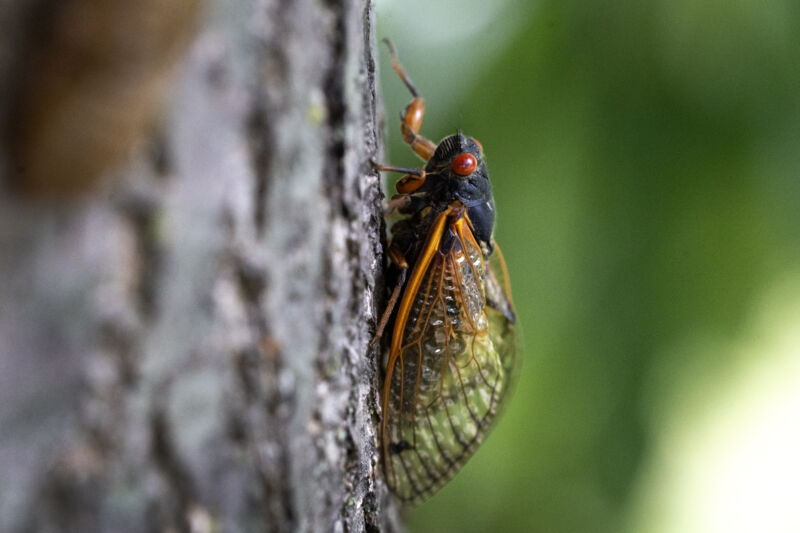

Enlarge / A cicada from a 17-year cicada brood clings to a tree on May 29, 2024, in Park Ridge, Illinois. The state experienced an emergence of cicadas from Brood XIII and Brood XIX simultaneously. This rare occurrence hasn’t taken place since 1803.
A plague of parasitic mites has descended upon Illinois in the wake of this year’s historic crop of cicadas, leaving residents with raging rashes and incessant itching.
The mighty attack follows the overlapping emergence of the 17-year Brood XIII and the 13-year Brood XIX this past spring, a specific co-emergence that only occurs every 221 years. The cacophonous boom in cicadas sparked an explosion of mites, which can feast on various insects, including the developing eggs of periodical cicadas. But, when the mites’ food source fizzles out, the mites bite any humans in their midst in hopes of finding their next meal. While the mites cannot live on humans, their biting leads to scratching. The mite, Pyemotes herfsi, is aptly dubbed the “itch mite.”
“You can’t see them, you can’t feel them, they’re always here,” Jennifer Rydzewski, an ecologist for the Forest Preserve District of DuPage County, told Chicago outlet The Daily Herald. “But because of the cicadas, they have a food source [and] their population has exploded.”
The mites are around 0.2 millimeters in length and very difficult to see with the naked eye, according to agriculture experts at Pennsylvania State University. They have four pairs of legs and are tan with a reddish tinge. Female itch mites can produce up to 250 offspring, which emerge from her abdomen as adults. Emerged adult offspring quickly mate, with the males then dying off and the newly fertilized females dispersing to find their own food source.
Itchy outbreak
Besides “itch mites” these parasites have also been called the “oak leaf itch mite” or “oak leaf gall mite,” because they have often been found feasting on the larvae of oak gall midges. These midges are a type of fly that lays eggs on oak trees. The resulting larvae feast on the tree, spurring the formation of unusual growths (galls) around the larvae.
The first known outbreak of itch mites in the US occurred in Kansas in August 2004. The Kansas Department of Health and Environment had called in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help investigate a puzzling outbreak of rashes in Crawford County. At the start, 300 residents in the small city of Pittsburg reported extremely itchy rashes, primarily on the limbs, neck, and face. The rashes looked similar to those from insect bites, but few of the affected people recalled being bitten by anything.
With the help of entomologists, outbreak investigators pinned the rashes to the itch mites. The area had experienced a mild winter and cooler summer temps, leading to an explosion of oak gall midges and subsequent infestation of oak galls. A detailed investigation determined that county residents were nearly four times more likely to have an itchy rash if they had a pin oak tree on their property. Once the itch mites invade a gall-infected oak tree, more than 16,000 mites can emerge from the galls on a single leaf. The mites can then drop from trees and are even small enough to be carried by the wind, giving them ample opportunity to find their way onto humans.
By the end of the outbreak, investigators estimated that 54 percent of the roughly 38,000 residents in Crawford County—that is, around 20,500 people—had been bitten by the mites.
Profuse parasites
But oak gall midges are far from the only insect the itch mites feed upon. In 2007, the emergence of a particularly prolific brood of cicadas led to an outbreak of itch mites in the Chicago area. The Illinois Department of Public Health noted that the “proposed common name ‘oak leaf itch mite’ for P. herfsi is misleading and contributed to the delay in identifying the causative agent of the 2007 Illinois outbreak.” The department noted that at least five insect orders and nine insect families are prey to the mites.
In the US, cases of itch mite rashes have been documented in at least Illinois, Nebraska, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Missouri, Tennessee, and Texas.
If bitten, humans develop an itchy red rash, typically with pimple-like bumps, which can stick around for up to two weeks. The rash develops between 10 to 16 hours after exposure, which can make it difficult to identify the source. But, the mites typically don’t produce groupings of bite marks like bedbugs or burrowing like scabies.
To try to avoid rashes, experts recommend wearing protective clothing when outside—including gloves while gardening or doing yard work—and washing clothes and showering after a potential exposure. The insect repellent DEET is often recommended, but anecdotal reports indicate DEET may not be entirely effective. If you already have a rash, the only thing to do is treat the symptoms with things like ice packs, soothing lotions (like calamine), oral antihistamines, over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams, and, if needed, prescription topical steroids. The good news is that the mites will not live on you and are not known to spread any diseases.
Explosion of cicada-eating mites has the state of Illinois scratching Read More »