Apple may hire Google to power new iPhone AI features using Gemini—report
Bake a cake as fast as you can —
With Apple’s own AI tech lagging behind, the firm looks for a fallback solution.

Benj Edwards
On Monday, Bloomberg reported that Apple is in talks to license Google’s Gemini model to power AI features like Siri in a future iPhone software update coming later in 2024, according to people familiar with the situation. Apple has also reportedly conducted similar talks with ChatGPT maker OpenAI.
The potential integration of Google Gemini into iOS 18 could bring a range of new cloud-based (off-device) AI-powered features to Apple’s smartphone, including image creation or essay writing based on simple prompts. However, the terms and branding of the agreement have not yet been finalized, and the implementation details remain unclear. The companies are unlikely to announce any deal until Apple’s annual Worldwide Developers Conference in June.
Gemini could also bring new capabilities to Apple’s widely criticized voice assistant, Siri, which trails newer AI assistants powered by large language models (LLMs) in understanding and responding to complex questions. Rumors of Apple’s own internal frustration with Siri—and potential remedies—have been kicking around for some time. In January, 9to5Mac revealed that Apple had been conducting tests with a beta version of iOS 17.4 that used OpenAI’s ChatGPT API to power Siri.
As we have previously reported, Apple has also been developing its own AI models, including a large language model codenamed Ajax and a basic chatbot called Apple GPT. However, the company’s LLM technology is said to lag behind that of its competitors, making a partnership with Google or another AI provider a more attractive option.
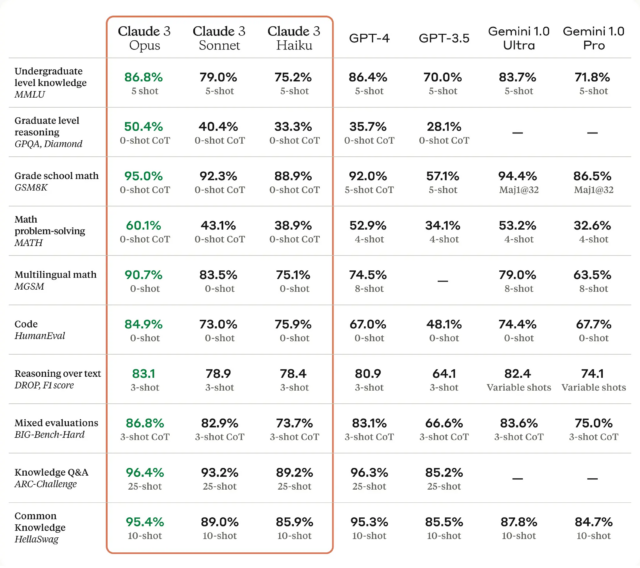
Google launched Gemini, a language-based AI assistant similar to ChatGPT, in December and has updated it several times since. Many industry experts consider the larger Gemini models to be roughly as capable as OpenAI’s GPT-4 Turbo, which powers the subscription versions of ChatGPT. Until just recently, with the emergence of Gemini Ultra and Claude 3, OpenAI’s top model held a fairly wide lead in perceived LLM capability.
The potential partnership between Apple and Google could significantly impact the AI industry, as Apple’s platform represents more than 2 billion active devices worldwide. If the agreement gets finalized, it would build upon the existing search partnership between the two companies, which has seen Google pay Apple billions of dollars annually to make its search engine the default option on iPhones and other Apple devices.
However, Bloomberg reports that the potential partnership between Apple and Google is likely to draw scrutiny from regulators, as the companies’ current search deal is already the subject of a lawsuit by the US Department of Justice. The European Union is also pressuring Apple to make it easier for consumers to change their default search engine away from Google.
With so much potential money on the line, selecting Google for Apple’s cloud AI job could potentially be a major loss for OpenAI in terms of bringing its technology widely into the mainstream—with a market representing billions of users. Even so, any deal with Google or OpenAI may be a temporary fix until Apple can get its own LLM-based AI technology up to speed.
Apple may hire Google to power new iPhone AI features using Gemini—report Read More »