YouTube denies AI was involved with odd removals of tech tutorials
YouTubers suspect AI is bizarrely removing popular video explainers.
This week, tech content creators began to suspect that AI was making it harder to share some of the most highly sought-after tech tutorials on YouTube, but now YouTube is denying that odd removals were due to automation.
Creators grew alarmed when educational videos that YouTube had allowed for years were suddenly being bizarrely flagged as “dangerous” or “harmful,” with seemingly no way to trigger human review to overturn removals. AI seemed to be running the show, with creators’ appeals seemingly getting denied faster than a human could possibly review them.
Late Friday, a YouTube spokesperson confirmed that videos flagged by Ars have been reinstated, promising that YouTube will take steps to ensure that similar content isn’t removed in the future. But, to creators, it remains unclear why the videos got taken down, as YouTube claimed that both initial enforcement decisions and decisions on appeals were not the result of an automation issue.
Shocked creators were stuck speculating
Rich White, a computer technician who runs an account called CyberCPU Tech, had two videos removed that demonstrated workarounds to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware.
These videos are popular, White told Ars, with people looking to bypass Microsoft account requirements each time a new build is released. For tech content creators like White, “these are bread and butter videos,” dependably yielding “extremely high views,” he said.
Because there’s such high demand, many tech content creators’ channels are filled with these kinds of videos. White’s account has “countless” examples, he said, and in the past, YouTube even featured his most popular video in the genre on a trending list.
To White and others, it’s unclear exactly what has changed on YouTube that triggered removals of this type of content.
YouTube only seemed to be removing recently posted content, White told Ars. However, if the takedowns ever impacted older content, entire channels documenting years of tech tutorials risked disappearing in “the blink of an eye,” another YouTuber behind a tech tips account called Britec09 warned after one of his videos was removed.
The stakes appeared high for everyone, White warned, in a video titled “YouTube Tech Channels in Danger!”
White had already censored content that he planned to post on his channel, fearing it wouldn’t be worth the risk of potentially losing his account, which began in 2020 as a side hustle but has since become his primary source of income. If he continues to change the content he posts to avoid YouTube penalties, it could hurt his account’s reach and monetization. Britec told Ars that he paused a sponsorship due to the uncertainty that he said has already hurt his channel and caused a “great loss of income.”
YouTube’s policies are strict, with the platform known to swiftly remove accounts that receive three strikes for violating community guidelines within 90 days. But, curiously, White had not received any strikes following his content removals. Although Britec reported that his account had received a strike following his video’s removal, White told Ars that YouTube so far had only given him two warnings, so his account is not yet at risk of a ban.
Creators weren’t sure why YouTube might deem this content as harmful, so they tossed around some theories. It seemed possible, White suggested in his video, that AI was detecting this content as “piracy,” but that shouldn’t be the case, he claimed, since his guides require users to have a valid license to install Windows 11. He also thinks it’s unlikely that Microsoft prompted the takedowns, suggesting tech content creators have a “love-hate relationship” with the tech company.
“They don’t like what we’re doing, but I don’t think they’re going to get rid of it,” White told Ars, suggesting that Microsoft “could stop us in our tracks” if it were motivated to end workarounds. But Microsoft doesn’t do that, White said, perhaps because it benefits from popular tutorials that attract swarms of Windows 11 users who otherwise may not use “their flagship operating system” if they can’t bypass Microsoft account requirements.
Those users could become loyal to Microsoft, White said. And eventually, some users may even “get tired of bypassing the Microsoft account requirements, or Microsoft will add a new feature that they’ll happily get the account for, and they’ll relent and start using a Microsoft account,” White suggested in his video. “At least some people will, not me.”
Microsoft declined Ars’ request to comment.
To White, it seemed possible that YouTube was leaning on AI to catch more violations but perhaps recognized the risk of over-moderation and, therefore, wasn’t allowing AI to issue strikes on his account.
But that was just a “theory” that he and other creators came up with, but couldn’t confirm, since YouTube’s chatbot that supports creators seemed to also be “suspiciously AI-driven,” seemingly auto-responding even when a “supervisor” is connected, White said in his video.
Absent more clarity from YouTube, creators who post tutorials, tech tips, and computer repair videos were spooked. Their biggest fear was that unexpected changes to automated content moderation could unexpectedly knock them off YouTube for posting videos that in tech circles seem ordinary and commonplace, White and Britec said.
“We are not even sure what we can make videos on,” White said. “Everything’s a theory right now because we don’t have anything solid from YouTube.”
YouTube recommends making the content it’s removing
White’s channel gained popularity after YouTube highlighted an early trending video that he made, showing a workaround to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware. Following that video, his channel’s views spiked, and then he gradually built up his subscriber base to around 330,000.
In the past, White’s videos in that category had been flagged as violative, but human review got them quickly reinstated.
“They were striked for the same reason, but at that time, I guess the AI revolution hadn’t taken over,” White said. “So it was relatively easy to talk to a real person. And by talking to a real person, they were like, ‘Yeah, this is stupid.’ And they brought the videos back.”
Now, YouTube suggests that human review is causing the removals, which likely doesn’t completely ease creators’ fears about arbitrary takedowns.
Britec’s video was also flagged as dangerous or harmful. He has managed his account that currently has nearly 900,000 subscribers since 2009, and he’s worried he risked losing “years of hard work,” he said in his video.
Britec told Ars that “it’s very confusing” for panicked tech content creators trying to understand what content is permissible. It’s particularly frustrating, he noted in his video, that YouTube’s creator tool inspiring “ideas” for posts seemed to contradict the mods’ content warnings and continued to recommend that creators make content on specific topics like workarounds to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware.
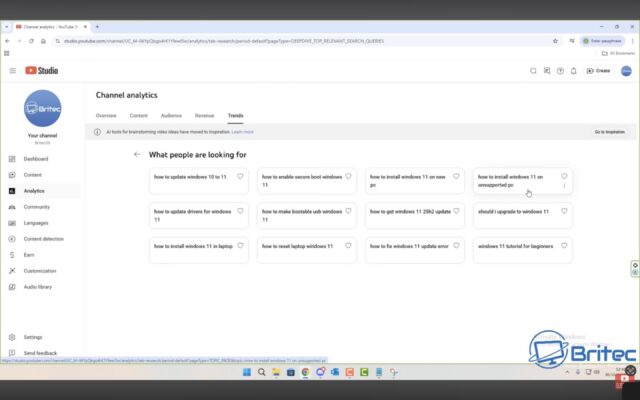
Screenshot from Britec09’s YouTube video, showing YouTube prompting creators to make content that could get their channels removed. Credit: via Britec09
“This tool was to give you ideas for your next video,” Britec said. “And you can see right here, it’s telling you to create content on these topics. And if you did this, I can guarantee you your channel will get a strike.”
From there, creators hit what White described as a “brick wall,” with one of his appeals denied within one minute, which felt like it must be an automated decision. As Britec explained, “You will appeal, and your appeal will be rejected instantly. You will not be speaking to a human being. You’ll be speaking to a bot or AI. The bot will be giving you automated responses.”
YouTube insisted that the decisions weren’t automated, even when an appeal was denied within one minute.
White told Ars that it’s easy for creators to be discouraged and censor their channels rather than fight with the AI. After wasting “an hour and a half trying to reason with an AI about why I didn’t violate the community guidelines” once his first appeal was quickly denied, he “didn’t even bother using the chat function” after the second appeal was denied even faster, White confirmed in his video.
“I simply wasn’t going to do that again,” White said.
All week, the panic spread, reaching fans who follow tech content creators. On Reddit, people recommended saving tutorials lest they risk YouTube taking them down.
“I’ve had people come out and say, ‘This can’t be true. I rely on this every time,’” White told Ars.
YouTube denies AI was involved with odd removals of tech tutorials Read More »