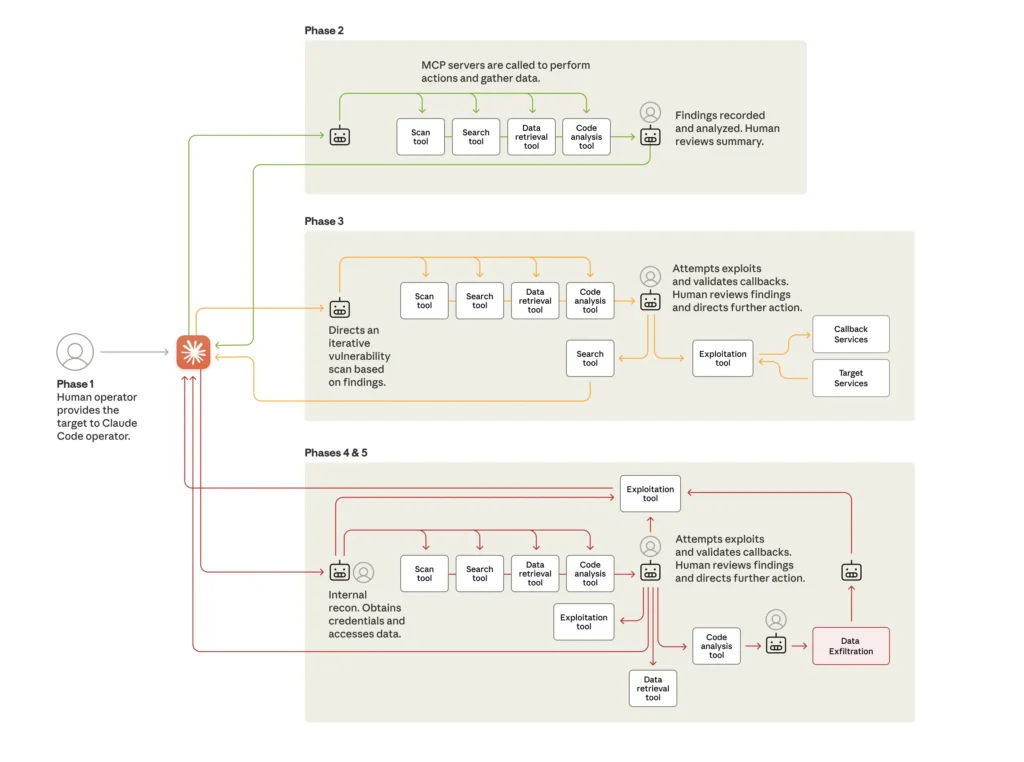
Russian spy satellites have intercepted EU communications satellites
Those thrusters could also be used to knock satellites out of alignment or even cause them to crash back to Earth or drift into space.
Intelligence gathered by Luch 1 and 2 could also help Russia coordinate less overt attacks on Western interests. Monitoring other satellites can reveal who is using them and where—information that could later be exploited for targeted ground-based jamming or hacking operations.
The Luch vehicles were “maneuvring about and parking themselves close to geostationary satellites, often for many months at a time,” said Belinda Marchand, chief science officer at Slingshot Aerospace, a US-based company that tracks objects in space using ground-based sensors and artificial intelligence.
She added that Luch 2 was currently “in proximity” to Intelsat 39, a large geostationary satellite that services Europe and Africa.
Since its launch in 2023, Luch-2 has hovered near at least 17 other geostationary satellites above Europe serving both commercial and government purposes, Slingshot data shows.
“They have visited the same families, the same operators—so you can deduce that they have a specific purpose or interest,” said Norbert Pouzin, senior orbital analyst at Aldoria, a French satellite tracking company that has also shadowed the Luch satellites. “These are all Nato-based operators.”
“Even if they cannot decrypt messages, they can still extract a lot of information… they can map how a satellite is being used, work out the location of ground terminals, for example,” he added.
Pouzin also said that Russia now seemed to be ramping up its reconnaissance activity in space, launching two new satellites last year named Cosmos 2589 and Cosmos 2590. The vehicles appear to have similarly maneuvrable capabilities to Luch-1 and Luch-2.
Cosmos 2589 is now on its way to the same range as geostationary satellites, which orbit 35,000 km above Earth, Pouzin said.
But Luch-1 may no longer be functional. On January 30, Earth telescopes observed what appeared to be a plume of gas coming from the satellite. Shortly after, it appeared to at least partially fragment.
“It looks like it began with something to do with the propulsion,” said Marchand, adding that afterwards there “was certainly a fragmentation,” and the satellite was “still tumbling.”
© 2026 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved. Not to be redistributed, copied, or modified in any way.
Russian spy satellites have intercepted EU communications satellites Read More »