Hands-on with the Switch 2: It’s the Switch, too
The Nintendo Switch 2 could be considered the most direct “sequel” to a Nintendo console that the company has ever made. The lineage is right there in the name, with Nintendo simply appending the number “2” onto the name of its incredibly successful previous console for the first time in its history.
Nintendo’s previous consoles have all differed from their predecessors in novel ways that were reflected in somewhat new naming conventions. The Switch 2’s name, on the other hand, suggests that it is content to primarily be “more Switch.” And after spending the better part of the day playing around with the Switch 2 hardware and checking out some short game demos on Wednesday, I indeed came away with the impression that this console is “more Switch” in pretty much every way that matters, for better or worse.
Bigger is better
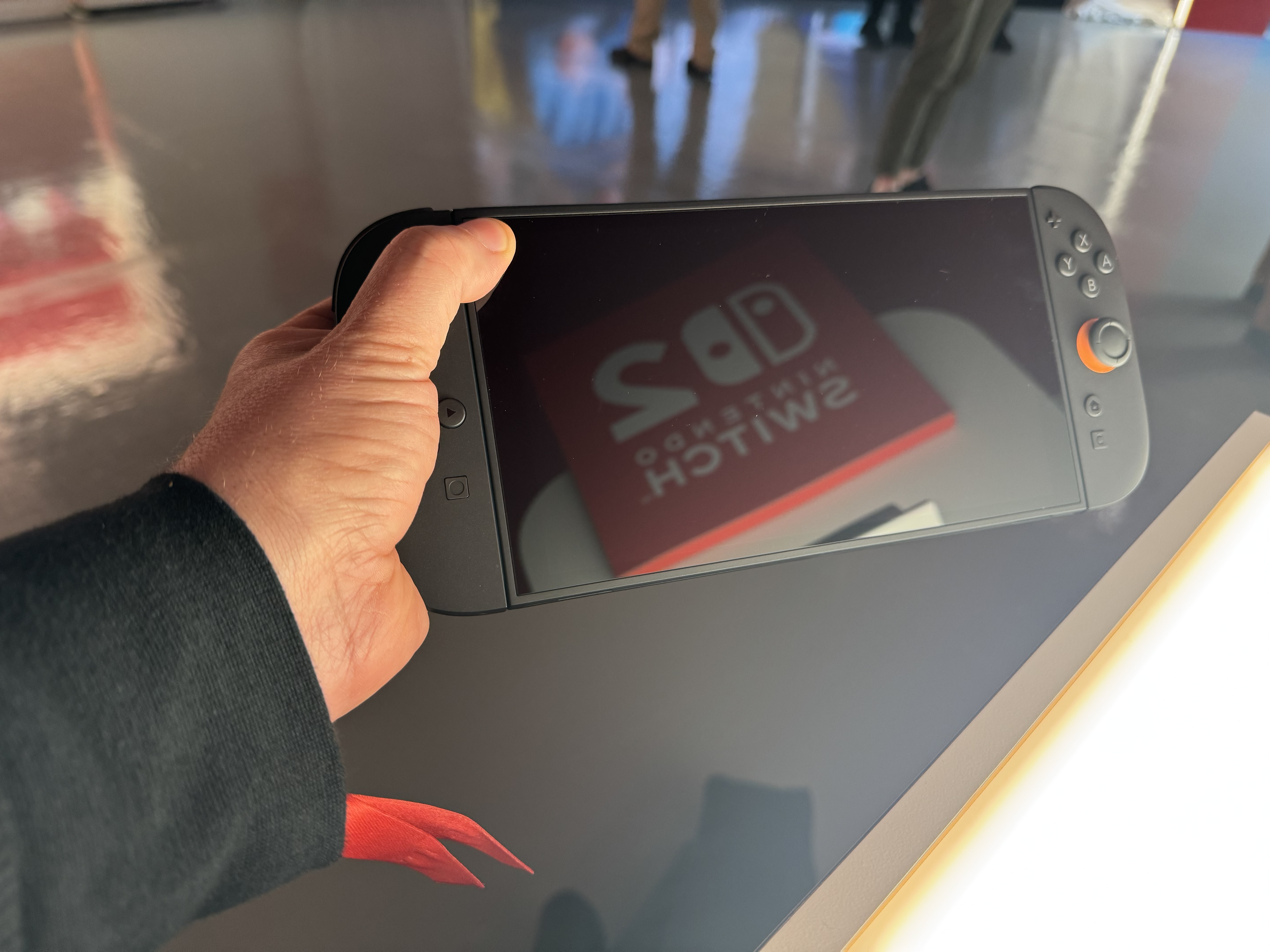
We’ve deduced from previous trailers just how much bigger the Switch 2 would be than the original Switch. Even with that preparation, though, the expanded Switch 2 makes a very good first impression in person.
Yes, the Switch 2 feels a good deal more substantial in the hands—Nintendo’s official stats page pegs it at about 34 percent heavier than the original Switch (as well as a tad wider and taller). But Nintendo’s new console is still noticeably short of Steam Deck-level bulk, coming in about 17 percent lighter (and a bit less wide and thick) than Valve’s handheld.
That extra size and weight over the original Switch is being put to good use, nowhere more so than in a 7.9-inch screen that feels downright luxurious on a handheld that’s this compact. That screen might be missing a best-in-class high-contrast OLED panel, but the combination of full 1080p resolution, HDR colors, and variable frame rates up to 120 fps still results in a handheld display that we feel would hold up well next to the best modern OLED competition.
The system’s extra size also allows for Joy-Cons that are expanded just enough to be much better suited for adult hands, with much less need for grown-ups to contort into a claw-like grip just to get a solid hold. That’s even true when the controllers are popped out from the system, which is now easily accomplished with a solidly built lever on the rear of each controller (reconnecting the Joy-Cons by slotting them in with a hefty magnetic snap feels equally solid).
The controls on offer here are still a bit smaller than you might be used to on controllers designed for home consoles or even those on larger handhelds like the Steam Deck. But the enlarged buttons are now less likely to press uncomfortably into the pad of your thumb than those on the Switch. And the slightly larger-than-Switch joysticks are a bit easier to maneuver precisely, with a longer physical travel distance from center to edge.
Speaking of joysticks, Nintendo has yet to go on record regarding whether it is using the coveted “magnetic Hall effect” sensors that would prevent the kind of stick drift that plagued the original Switch Joy-Cons. When asked about the stick drift issue in a roundtable Q&A, Switch 2 Technical Director Tetsuya Sasaki would only say that the “new Joy-Con 2 controllers have been designed from the ground up from scratch to have bigger, smoother movement.”
When it comes to raw processing power, it’s all relative. The Switch 2 is a noticeable step up from the eight-year-old Switch but an equally noticeable step down from modern top-of-the-line consoles.
Playing the Switch 2 Edition of Tears of the Kingdom, for instance, feels like playing the definitive version of the modern classic, thanks mostly to increased (and silky smooth) frame rates and quick-loading menus. But an early build of Cyberpunk 2077 felt relatively rough on the Switch 2, with visuals that clocked somewhere just south of a PS4 Pro (though this could definitely change with some more development polish before launch). All told, I’d guess that the Switch 2 should be able to handle effective ports of pretty much any game that runs on the Steam Deck, with maybe a little bit of extra graphical panache to show for the trouble.
A mouse? On a game console?
Nintendo has a history of trying to differentiate its consoles with new features that have never been seen before. Some, like shoulder buttons or analog sticks, become industry standards that other companies quickly aim to copy. Others, like a tablet controller or glasses-free stereoscopic 3D, are rightly remembered as half-baked gimmicks that belong in the dustbin of game industry history.
I can’t say which side of that divide the Switch 2’s Joy-Con “mouse mode,” which lets you use a Joy-Con on its side like a mouse, will fall on. But if I had to guess, I’d go with the gimmicky side.
It works, but it’s kind of awkward. Kyle Orland
The main problem with “mouse mode” is that the Switch 2 Joy-Cons lack the wide, palm-sized base and top surface you’d find on a standard PC mouse. Instead, when cradled in mouse mode, a Joy-Con stands awkwardly on an edge that’s roughly the width of an adult finger. The top isn’t much better, with only a small extension to rest a second finger on the jutting shoulder button that serves as a “right-click” option on the right Joy-Con (the thinner “left click” shoulder button ends up feeling uncomfortably narrow in this mode).
This thin “stand-up” design means that in mouse mode, the thumb side of your palm tends to spill awkwardly over the buttons and joysticks on the inner edge of the Joy-Con, which are easy to press accidentally in some gameplay situations. Meanwhile, on the other side, your ring finger and pinky will have to contort uncomfortably to get a solid grip that can nudge or lift the Joy-Con as necessary.
These ergonomic problems were most apparent when playing Drag x Drop, a Switch 2 exclusive that I can confidently say is the first video game I’ve ever played using two mice at once. Using long, vertical swoops of those mice, you can push and pull the wheels on either side of a wheelchair in a kind of tank-like fashion to dash, reverse, pivot, and gently turn with some degree of finesse in a game of three-on-three basketball.
That repetitive mouse-swooping motion started to strain my upper arms after just a few minutes of play, though. And I ended my brief Drag x Drop play sessions with some soreness in my palm from having to constantly and quickly grasp the Joy-Con to reposition on the playing surface.
These problems were less pronounced in games that relied on more subtle mouse movements. In a short demo of Metroid Prime 4: Beyond, for instance, using mouse mode and a few small flicks of the wrist let me change my aim much more quickly and precisely than using a joystick and/or the Joy-Con’s built-in gyroscopes (or even the IR-based “pointer” on the Wii’s Metroid Prime 3). While my grip on the narrow Joy-Con still felt a bit awkward, the overall lack of mouse motion made it much less noticeable, even after a 20-minute demo session.
A quick flick of the wrist is all I need to adjust my aim precisely and quickly. Credit: Kyle Orland
Metroid Prime 4: Beyond also integrates mouse controls well into the existing design of the game, letting you lock the camera on the center of an enemy while using the mouse to make fine aim adjustments as they move or even hit other enemies far off to the side of the screen as needed. The game’s first boss seems explicitly designed as a sort of tutorial for this combination aiming, with off-center weak points that almost require quick flicks of the mouse-controlling wrist while jumping and dodging using the accessible buttons on the thumb side.
Other mouse-based Switch 2 demos Nintendo showed this week almost seemed specifically designed to appeal to PC gamers. The Switch 2 version of Civilization VII, for instance, played practically identically to the PC version, with a full mouse pointer that eliminates the need for any awkward controller mapping. And the new mouse-based mini-games in Mario Party Jamboree felt like the best kind of early Macintosh tech demos, right down to one that is a close mimic of the cult classic Shufflepuck Cafe. A few games even showed the unique promise of a “mouse” that includes its own gyroscope sensor, letting players rotate objects by twisting their wrist or shoot a basketball with a quick “lift and flick” motion.
The biggest problem with the Switch 2’s mouse mode, though, is imagining how the average living room player is going to use it. Nintendo’s demo area featured large, empty tables where players could easily slide their Joy-Cons to their hearts’ content. To get the same feeling at home, the average sofa-bound Switch player will have to crouch awkwardly over a cleared coffee table or perhaps invest in some sort of lap desk.
Nintendo actually recommends that couch-bound mouse players slide the Joy-Con’s narrow edge across the top of the thigh area of their pants. I was pleasantly surprised at how well this worked for the long vertical mouse swipes of Drag x Drop. For games that involved more horizontal mouse movement, though, a narrow, rounded thigh-top does not serve as a very natural mouse pad.
You can test this for yourself by placing an optical mouse on your thigh and going about your workday. If you get weird looks from your boss, you can tell them I said it was OK.
Start your engines
Mouse gimmicks aside, Nintendo is leaning heavily on two first-party exclusives to convince customers that the system is worth buying in the crucial early window after its June 5 launch. While neither makes the massive first impression that Breath of the Wild did eight years ago, both seem like able demonstrations for the new console.
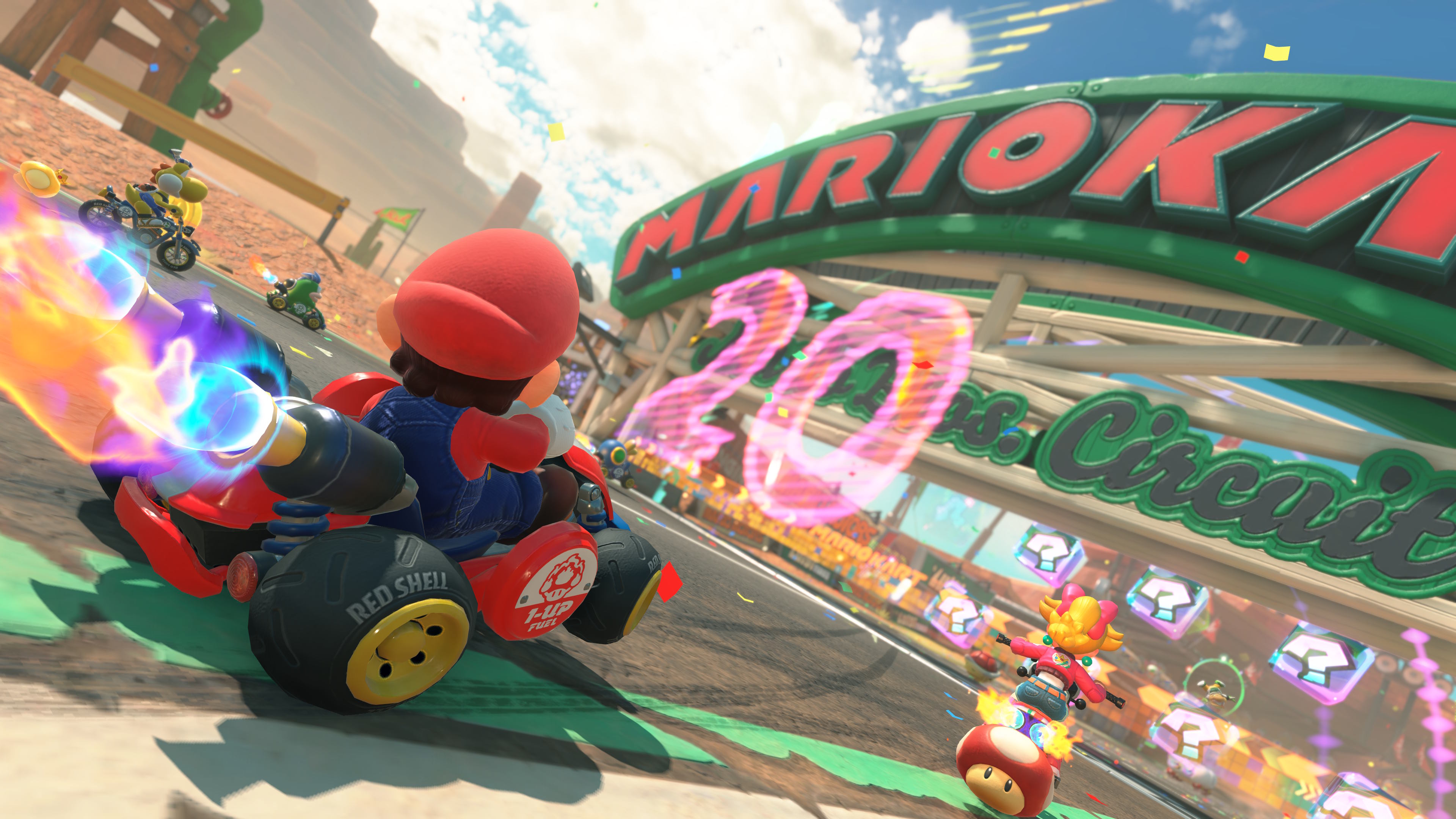
That’s a lot of karts. Credit: Nintendo
Mario Kart World feels like just the kind of update the long-running casual racer needs. While you can still race through pre-set “cups” in Grand Prix mode, I was most interested in the ability to just drive aimlessly between the race areas, searching for new locations in a freely roamable open world map.
Racing against 23 different opponents per race might sound overwhelming on paper, but in practice, the constant jockeying for position ends up being pretty engaging, like a slower-paced version of F-Zero GX. It definitely doesn’t hurt that items in World are much less punishing than in previous Kart games; most projectiles and hazards now merely slow your momentum rather than halting it completely. Drifts feel a bit more languorous here, too, with longer arcs needed to get the crucial “sparks” required for a boost.
A multi-section Knockout Tour map. Credit: Nintendo
While the solo races were fine, I had a lot more fun in Knockout Tour mode, Mario Kart World‘s Battle Royale-style elimination race. After pairing up with 23 other human players online, Knockout Tour mode selects a route through six connected sections of the world map for you to race through. The bottom four racers are eliminated at every section barrier until just four racers remain to vie for first place at the end.
You’d better be in the top 20 before you cross that barrier. Credit: Kyle Orland
This design makes for a lot of tense moments as players use up their items and jockey for position at the end of each section cutoff. The frequent changes in style and scenery along a multi-section Knockout Tour competition also make races more interesting than multiple laps around the same old turns. And I liked how the reward for playing well in this mode is getting to play more; success in Knockout Tour mode means a good ten to fifteen minutes of uninterrupted racing.
Punch, punch, it’s all in the mind. Credit: Nintendo
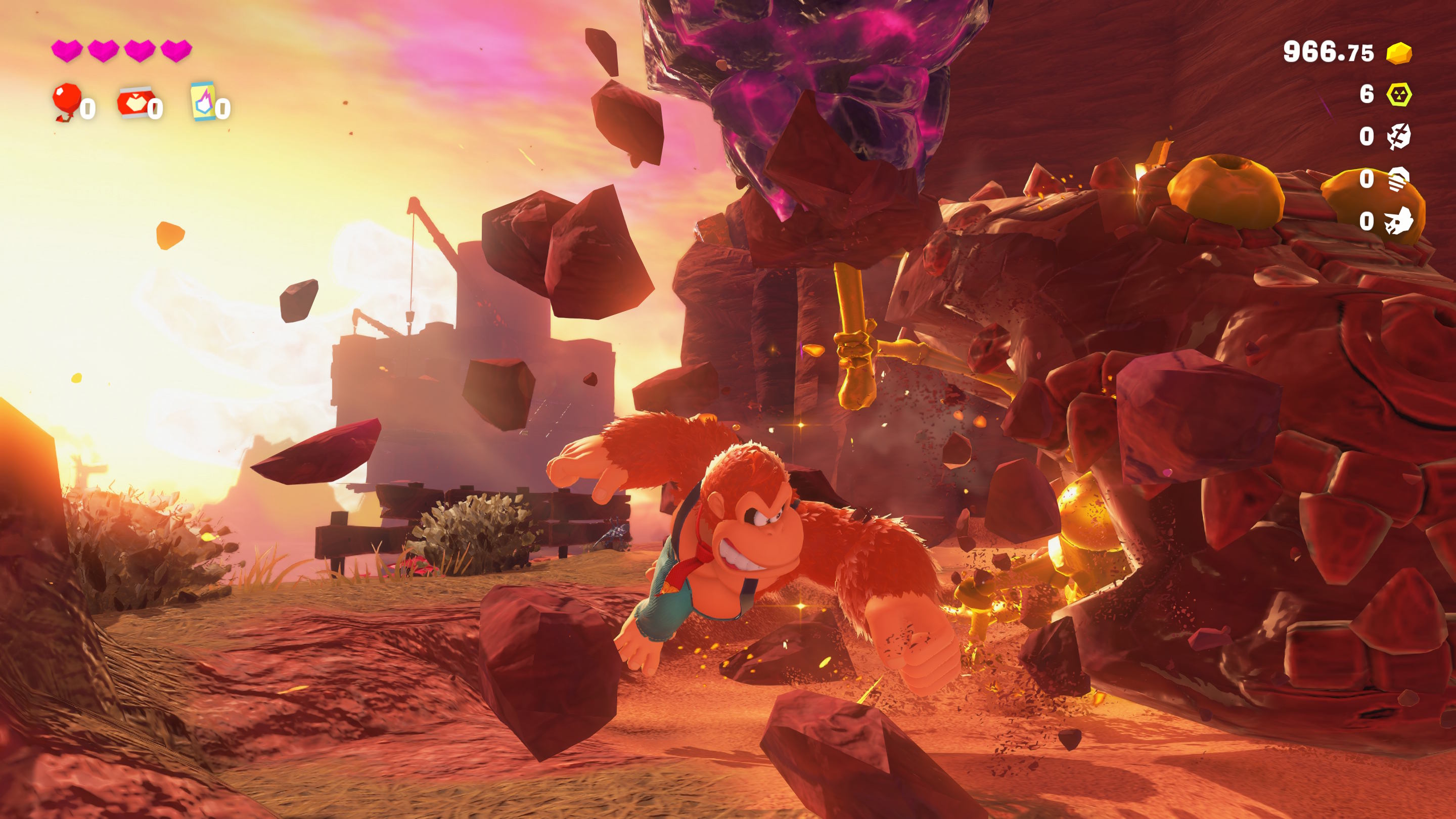
Nintendo’s other big first-party Switch 2 exclusive, Donkey Kong Bananza, might not be the new 3D Mario game we were hoping for. Even so, it was incredibly cathartic to jump, dig, and punch my way through the demo island’s highly destructible environments, gathering countless gold trinkets and collectibles as I did. The demo is full of a lot of welcome, lighthearted touches, like the ability to surf on giant slabs of rock or shake the controller for a very ape-like beating of Donkey Kong’s chest. (Why? Just because.)
One of my colleagues joked that the game might as well be called Red Faction: Gorilla, but I’d compare it more to the joyful destruction of Travellers Tales’ many Lego games.
A single whirlwind day with the Switch 2 isn’t nearly enough to get a full handle on the system’s potential, of course. Nintendo didn’t demonstrate any of the new GameChat features it announced Wednesday morning or the adaptive microphone that supposedly powers easy on-device voice chat.
Still, what we were able to sample this week has us eager to spend more time with the “more Switch” when it hits stores in just a couple of months.
Kyle Orland has been the Senior Gaming Editor at Ars Technica since 2012, writing primarily about the business, tech, and culture behind video games. He has journalism and computer science degrees from University of Maryland. He once wrote a whole book about Minesweeper.
Hands-on with the Switch 2: It’s the Switch, too Read More »