Surface Pro 11 and Laptop 7 review: An Apple Silicon moment for Windows
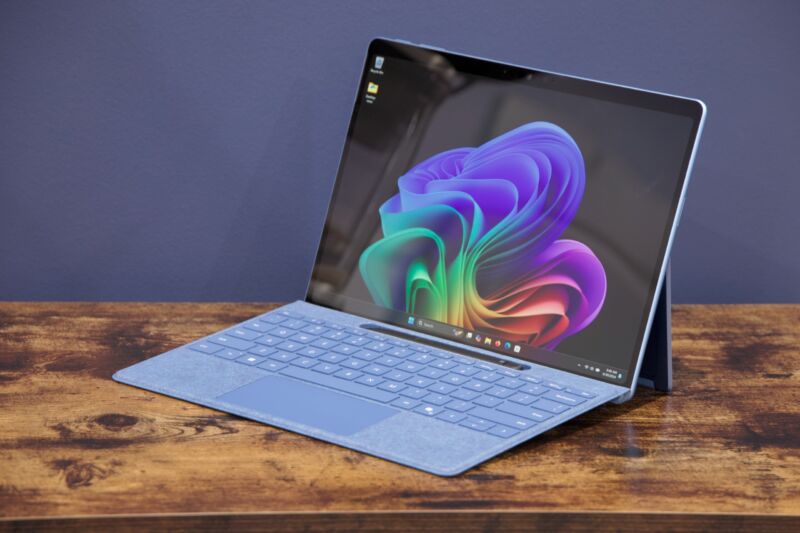

Enlarge / Microsoft’s Surface Pro 11, the first flagship Surface to ship exclusively using Arm processors.
Andrew Cunningham
Microsoft has been trying to make Windows-on-Arm-processors a thing for so long that, at some point, I think I just started assuming it was never actually going to happen.
The first effort was Windows RT, which managed to run well enough on the piddly Arm hardware available at the time but came with a perplexing new interface and couldn’t run any apps designed for regular Intel- and AMD-based Windows PCs. Windows RT failed, partly because a version of Windows that couldn’t run Windows apps and didn’t use a familiar Windows interface was ignoring two big reasons why people keep using Windows.
Windows-on-Arm came back in the late 2010s, with better performance and a translation layer for 32-bit Intel apps in tow. This version of Windows, confined mostly to oddball Surface hardware and a handful of barely promoted models from the big PC OEMs, has quietly percolated for years. It has improved slowly and gradually, as have the Qualcomm processors that have powered these devices.
That brings us to this year’s flagship Microsoft Surface hardware: the 7th-edition Surface Laptop and the 11th-edition Surface Pro.
These devices are Microsoft’s first mainstream, flagship Surface devices to use Arm chips, whereas previous efforts have been side projects or non-default variants. Both hardware and software have improved enough that I finally feel I could recommend a Windows-on-Arm device to a lot of people without having to preface it with a bunch of exceptions.
Unfortunately, Microsoft has chosen to launch this impressive and capable Arm hardware and improved software alongside a bunch of generative AI features, including the Recall screen recorder, a feature that became so radioactively unpopular so quickly that Microsoft was forced to delay it to address major security problems (and perception problems stemming from the security problems).
The remaining AI features are so superfluous that I’ll ignore them in this review and cover them later on when we look closer at Windows 11’s 24H2 update. This is hardware that is good enough that it doesn’t need buzzy AI features to sell it. Windows on Arm continues to present difficulties, but the new Surface Pro and Surface Laptop—and many of the other Arm-based Copilot+ PCs that have launched in the last couple of weeks—are a whole lot better than Arm PCs were even a year or two ago.
Familiar on the outside

Enlarge / The Surface Laptop 7 (left) and Surface Pro 11 (right) are either similar or identical to their Intel-powered predecessors on the outside.
Andrew Cunningham
When Apple released the first couple of Apple Silicon Macs back in late 2020, the one thing the company pointedly did not change was the exterior design. Apple didn’t comment much on it at the time, but the subliminal message was that these were just Macs, they looked the same as other Macs, and there was nothing to worry about.
Microsoft’s new flagship Surface hardware, powered exclusively by Arm-based chips for the first time rather than a mix of Arm and Intel/AMD, takes a similar approach: inwardly overhauled, externally unremarkable. These are very similar to the last (and the current) Intel-powered Surface Pro and Surface Laptop designs, and in the case of the Surface Pro, they actually look identical.
Both PCs still include some of the defining elements of Surface hardware designs. Both have screens with 3:2 aspect ratios that make them taller than most typical laptop displays, which still use 16: 10 or 16:9 aspect ratios. Those screens also support touch input via fingers or the Surface Pen, and they still use gently rounded corners (which Windows doesn’t formally recognize in-software, so the corners of your windows will get cut off, not that it has ever been a problem for me).
Surface Pro 11 and Laptop 7 review: An Apple Silicon moment for Windows Read More »