Forget aerobars: Ars tries out an entire aerobike
Here comes a future —
Taking to the road in a modern, high-speed version of a 40-year-old dream.
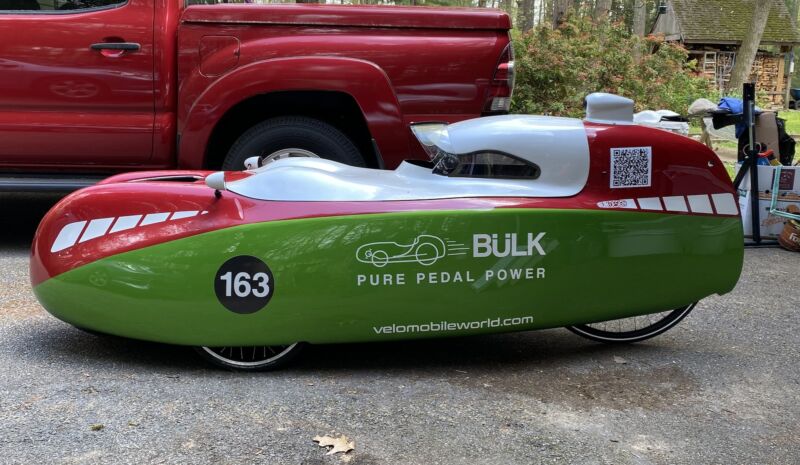

Enlarge / The Velomobile Bülk, with its hood in place. Note the hood has an anti-fog covering on the visor (which is flipped up). The two bumps near the front of the hood are there to improve clearance for the cyclist’s knees.
JOHN TIMMER
My brain registered that I was clearly cycling. My feet were clipped in to pedals, my legs were turning crank arms, and the arms were linked via a chain to one of the wheels. But pretty much everything else about the experience felt wrong on a fundamental, almost disturbing level.
I could produce a long list of everything my mind was struggling to deal with, but two things stand out as I think back on the experience. The first is that, with the exception of my face, I didn’t feel the air flow over me as the machine surged forward down a slight slope. The second, related to the first, is that there was no indication that the surge would ever tail off if I didn’t hit the brakes.
Living the dream
My visit with a velomobile was, in some ways, a chance to reconnect with a childhood dream. I’ve always had a fascination with vehicles that don’t require fuel, like bicycles and sailboats. And during my childhood, the popular press was filled with stories about people setting human-powered speed records by putting aerodynamic fiberglass shells on recumbent bicycles. In the wake of the 1970s oil crises, I imagined a time when the roads might be filled with people cycling these pods for their commutes or covering long distances thanks to a cooler filled with drinks and snacks tucked in the back of the shell.
But the pods seemed to vanish from public consciousness as I got older, and I also learned that recumbent bikes are absolutely terrible on hills, which I’m now fond of climbing. The dreams had faded from my awareness when a reader, in response to one of our e-bike reviews, suggested I check out a velomobile. It turns out that my dreams weren’t dead; they had just relocated to Europe without mentioning it to me.
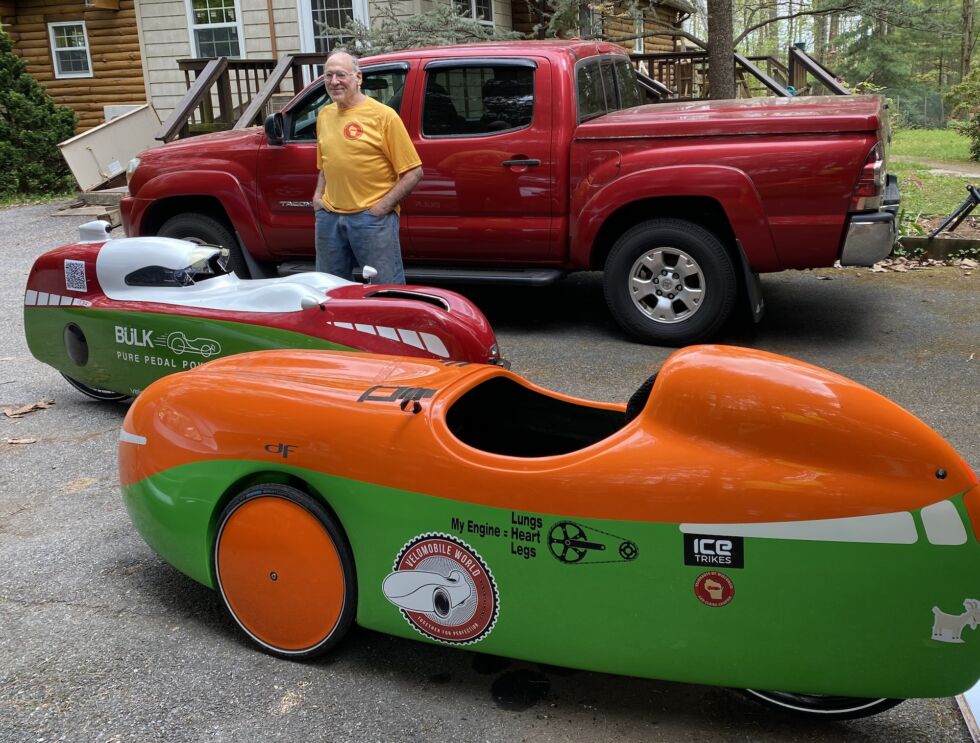

Enlarge / Marc Rosen and two of his velomobiles. The newer model, the Bülk, is closer to him.
John Timmer
Velomobiles are a product category with a variety of designs and manufacturers producing them, most of them based in Europe. They’re also the fiberglass pods of my youth updated to current standards. Gone is the weight of fiberglass, and the one-off, hand-made hardware has been replaced by standardized models that have gone through refinements across generations. Safety features like lights, directionals, and mirrors are now standard.
But the prices, while not exorbitant (mostly in the $8,000–$10,000 range—for bicycles; you can pay more for far less carbon fiber), mean that living my childhood dream really wasn’t an option. The European Union-based companies don’t seem to have any agreements with US bike shops that would let me check one out in a showroom; I’ve heard of only two dealers in the US that keep velomobiles in stock, and neither is anywhere close to me. Fortunately, that didn’t preclude the option of trying one. One major vendor of velomobiles, Romania’s Velomobile World, has an ambassadors program, where people agree to let potential buyers take test rides in return for a discount on purchases.
That’s how I found myself setting out for a short spin near the Maryland-Pennsylvania border in a Velomobile Bülk owned by Marc Rosen, who also fielded a lot of my questions about the hardware.
Forget aerobars: Ars tries out an entire aerobike Read More »