Baby Steps is the most gloriously frustrating game I’ve ever struggled through
There’s an old saying that life is not about how many times you fall down but how many times you get back up. In my roughly 13 hours of walking through the surreal mountain wilderness of Baby Steps, I’d conservatively estimate I easily fell down 1,000 times.
If so, I got up 1,001 times, which is the entire point.
When I say “fell down” here, I’m not being metaphorical. In Baby Steps, the only real antagonist is terrain that threatens to send your pudgy, middle-aged, long-underwear-clad avatar tumbling to the ground (or down a cliff) like a rag doll after the slightest misstep. You pilot this avatar using an intentionally touchy and cumbersome control system where each individual leg is tied a shoulder trigger on your controller.
Unlike the majority of 3D games, where you simply tilt the control stick and watch your character dutifully run, each step here means manually lifting one foot, leaning carefully in the direction you want to go, and then putting that foot down in a spot that maintains your overall balance. It’s like a slightly more forgiving version of the popular ’00s Flash game QWOP (which was also made by Baby Steps co-developer Bennett Foddy), except instead of sprinting on a 2D track, you take your time carefully planning each footfall on a methodical 3D hike.
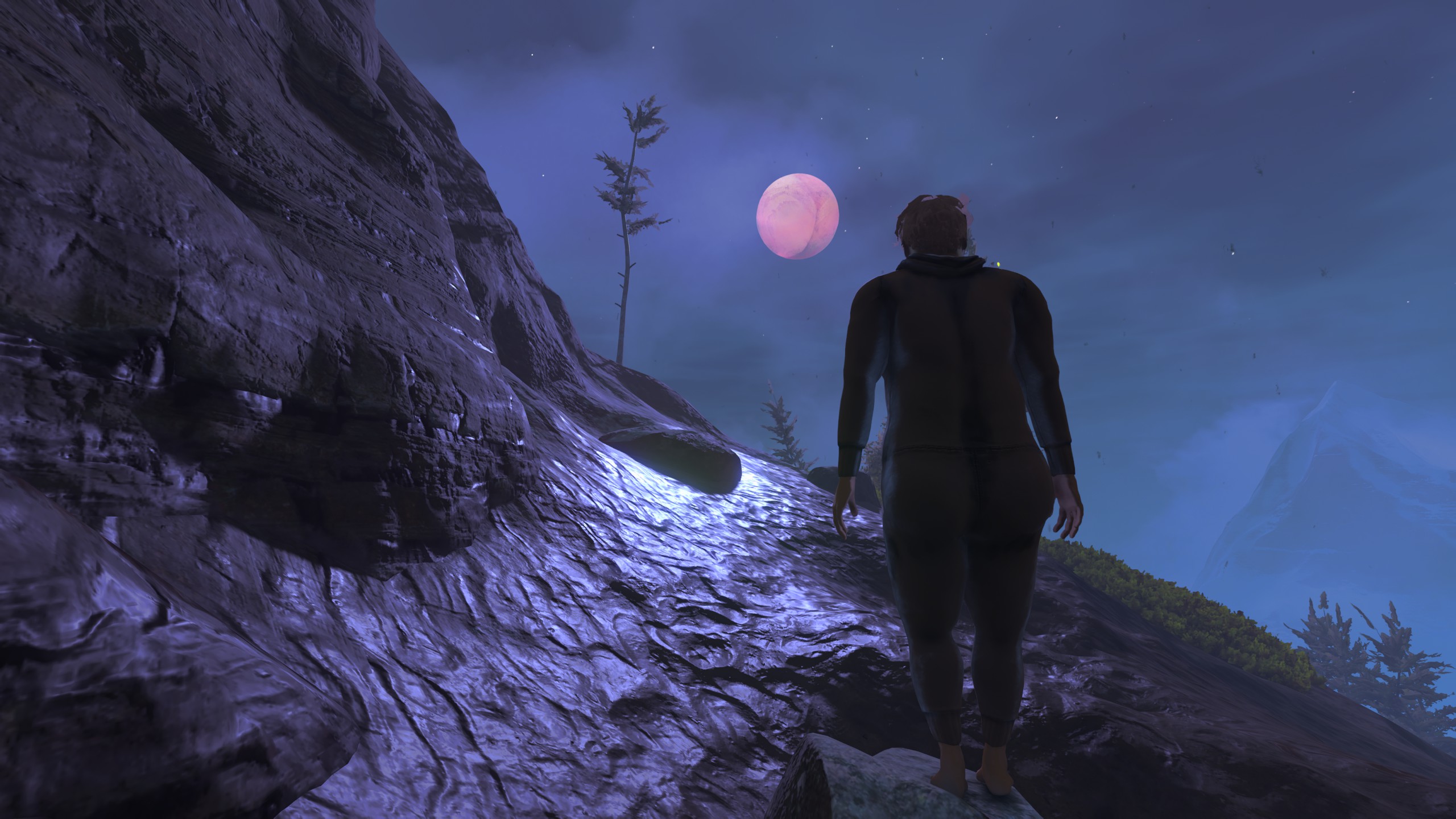
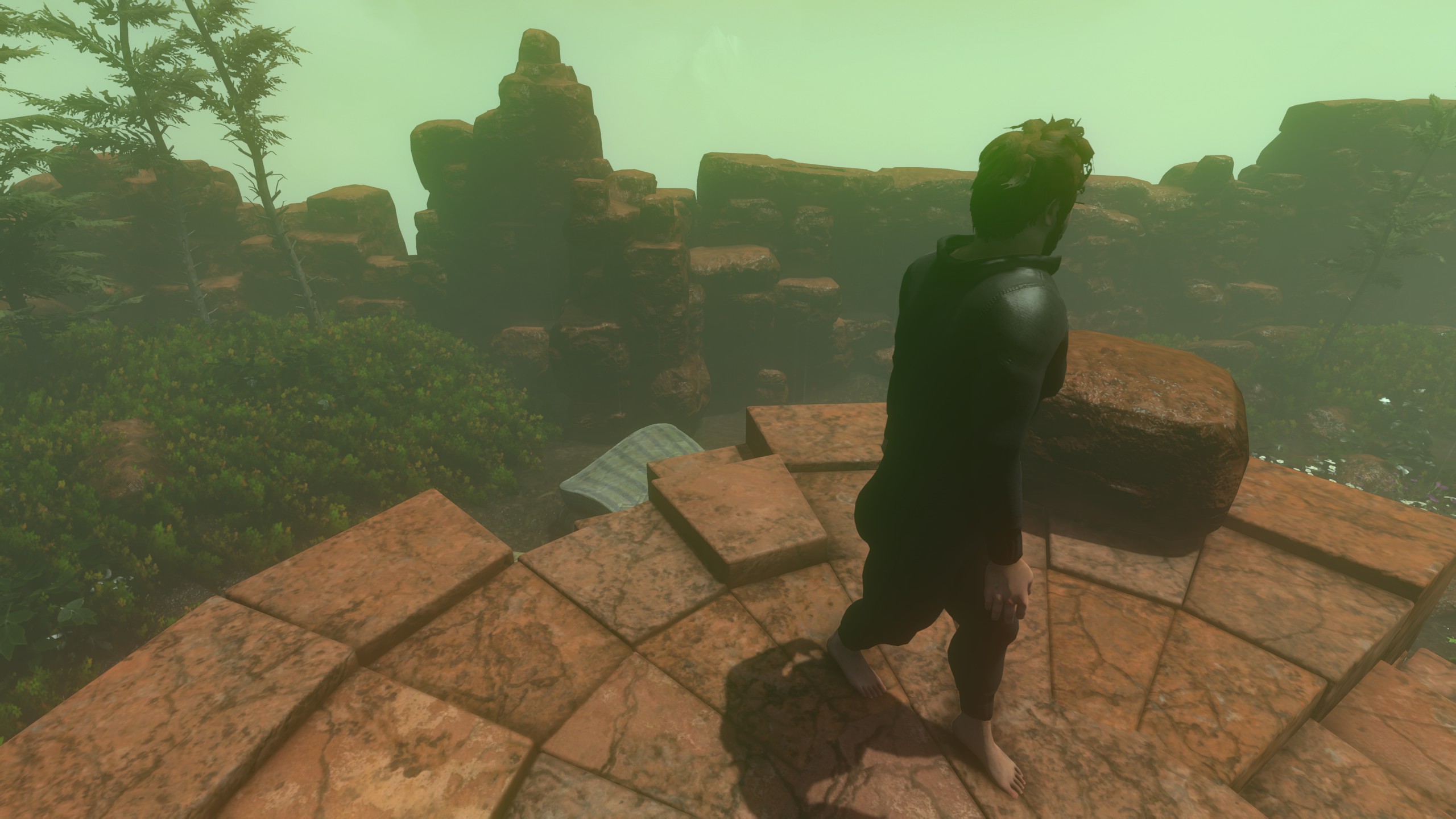
Keep wiggling that foot until you find a safe place to put it. Credit: Devolver Digital
At first, you’ll stumble like a drunken toddler, mashing the shoulder buttons and tilting the control stick wildly just to inch forward. After a bit of trial and error, though, you’ll work yourself into a gentle rhythm—press the trigger, tilt the controller, let go while recentering the controller, press the other trigger, repeat thousands of times. You never quite break into a run, but you can fall into a zen pattern of marching methodically forward, like a Death Stranding courier who has to actually focus on each and every step.
As you make your halting progress up the mountain, you’ll infrequently stumble on other hikers who seem to lord their comfort and facility with the terrain over you in manic, surreal, and often hilarious cut scenes. I don’t want to even lightly spoil any of the truly gonzo moments in this extremely self-aware meta-narrative, but I will say that I found your character’s grand arc through the game to be surprisingly touching, often in some extremely subtle ways.
Does this game hate me?
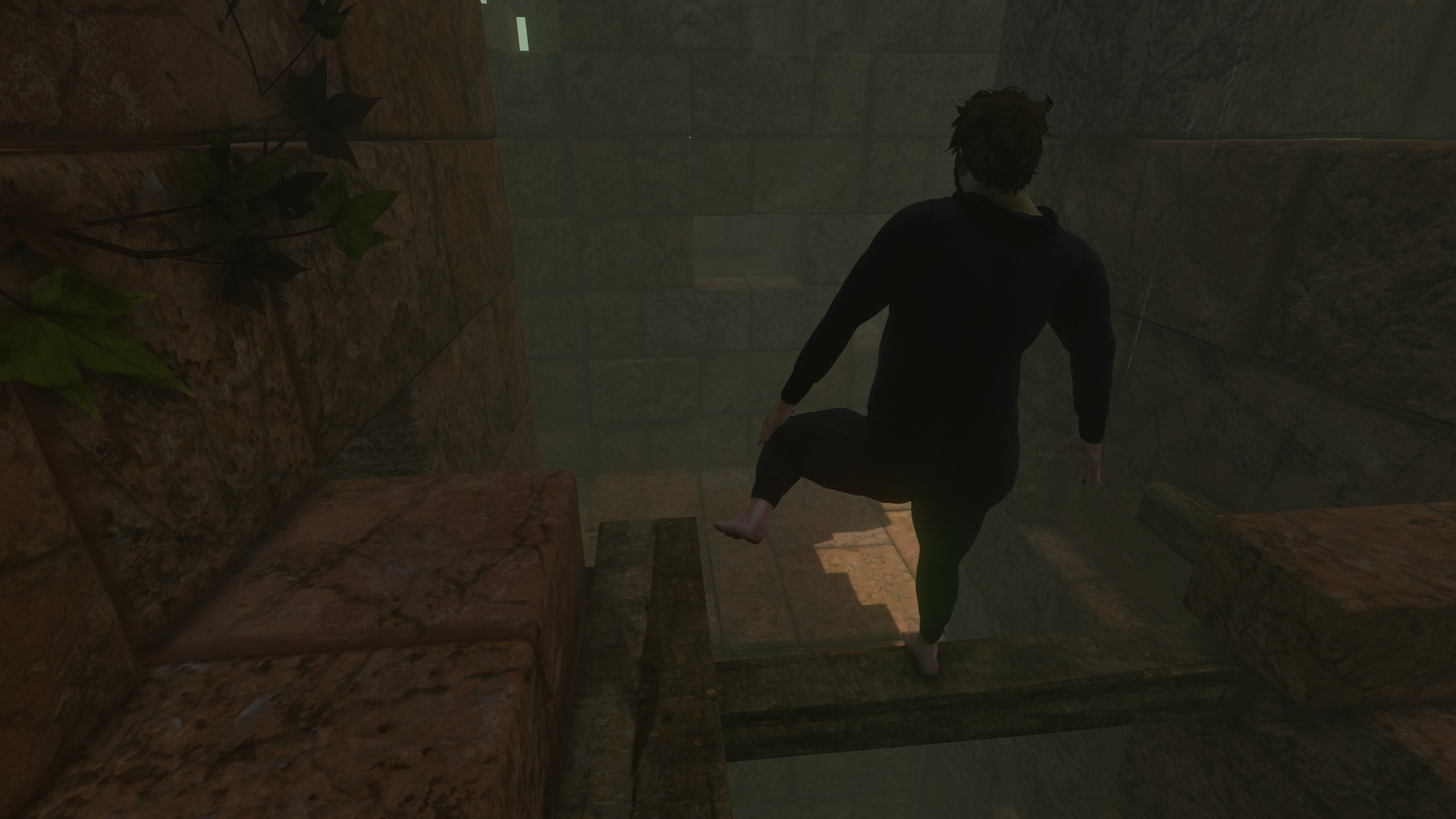
Just as you feel like you’re finally getting the hang of basic hiking, Baby Steps starts ramping up the terrain difficulty in a way that can feel downright trolly at time. Gentle paths of packed dirt and rock start to be replaced with narrow planks and rickety wooden bridges spanning terrifying gaps. Gentle undulating hills are replaced with sheer cliff faces that you sidle up and across with the tiniest of toe holds to precariously balance on. Firm surfaces are slowly replaced with slippery mud, sand, snow, and ice that force you to alter your rhythm and tread extremely lightly just to make incremental progress.
Grabbing that fetching hat means risking an extremely punishing fall.
And any hard-earned progress can feel incredibly fragile in Baby Steps. Literally one false step can send you sliding down a hill or tumbling down a cliff face in a way that sets you back anywhere from mere minutes to sizable chunks of an hour. There’s no “reset from checkpoint” menu option or save scumming that can limit the damage, either. When you fall in Baby Steps, it can be a very long way down.
This extremely punishing structure won’t be a surprise to anyone who has played Getting Over It With Bennett Foddy, where a single mistake can send you all the way back to the beginning of the game. Baby Steps doesn’t go quite that hard, giving players occasional major checkpoints and large, flat plains that prevent you from falling back too far. Still, this is a game that is more than happy to force you to pay for even small mistakes with huge portions of your only truly irreplaceable resource: time.
On more than one occasion during my playthrough, I audibly cursed at my monitor and quit the game in a huff rather than facing the prospect of spending ten minutes retracing my steps after a particularly damaging fall. Invariably, though, I’d come back a bit later more determined than ever to learn from my mistakes, which I usually did quickly with the benefits of time and calm on my side.
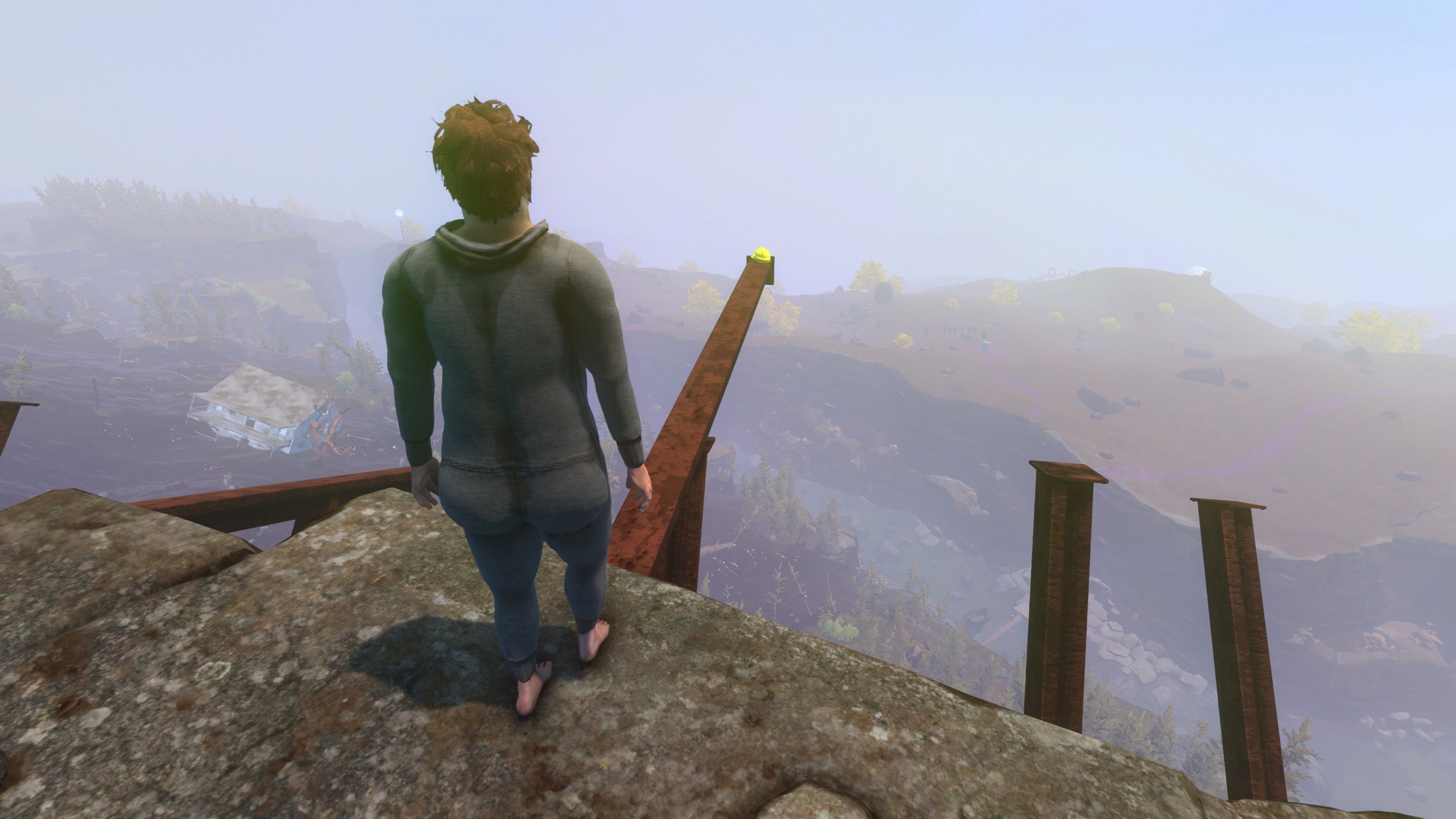
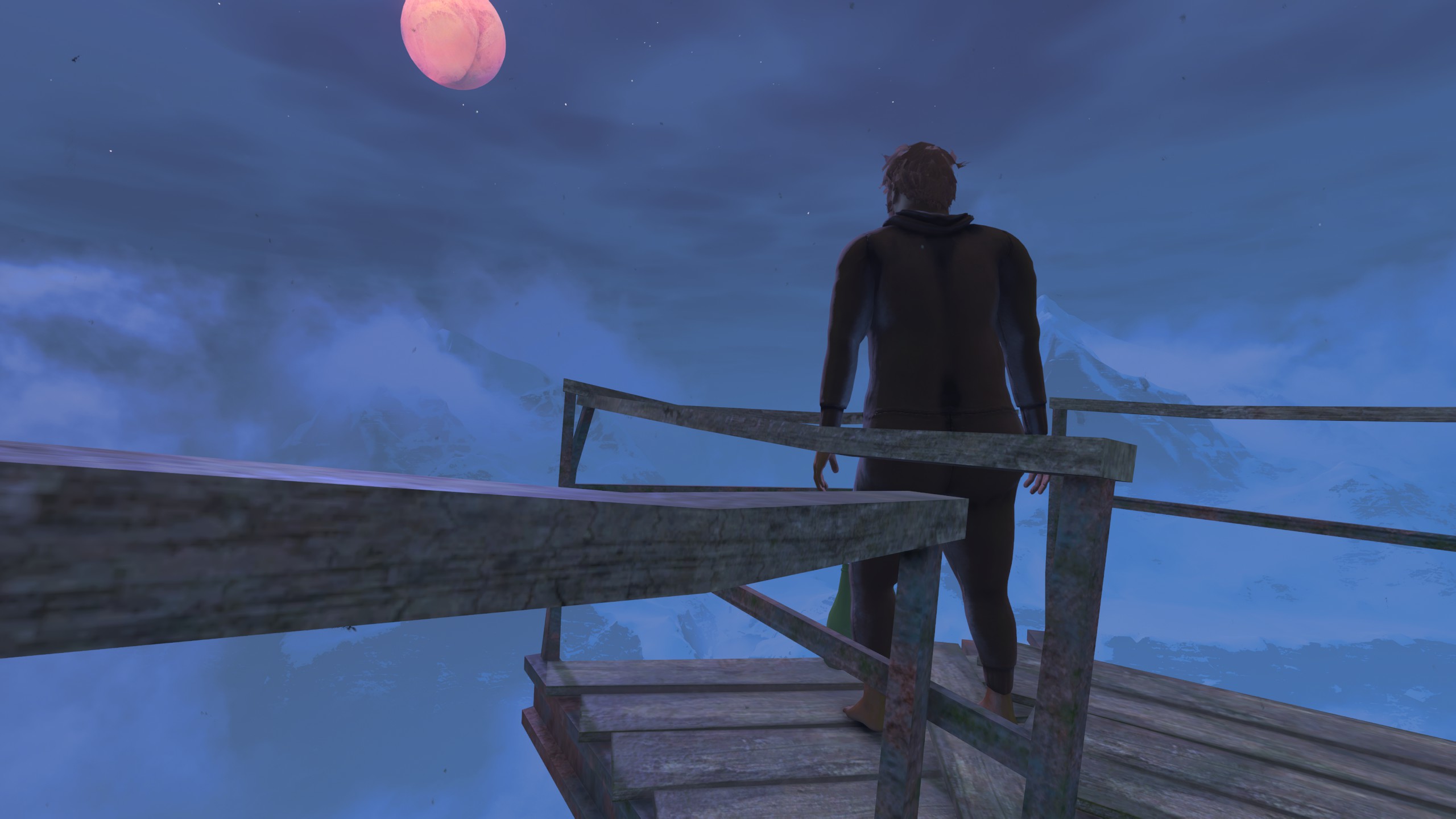
It’s frequently not entirely clear where you’re supposed to go in Baby Steps. Credit: Devolver Digital
Baby Steps is also a game that’s happy to let you wander aimlessly. There’s no in-game map to consult, and any paths and landmarks that could point you in the “intended” way up the mountain are often intentionally confusing or obscured. It can be extremely unclear which parts of the terrain are meant to be impossibly steep and which are merely designed as difficult but plausible shortcuts that simply require pinpoint timing and foot placement. But the terrain is also designed so that almost every near-impossible barrier can be avoided altogether if you’re patient and observant enough to find a way around it.
And if you wander even slightly off the lightly beaten path, you’ll stumble on many intricately designed and completely optional points of interest, from imposing architectural towers to foreboding natural outcroppings to a miniature city made of boxes. There’s no explicit in-game reward for almost all of these random digressions, and your fellow cut-scene hikers will frequently explicitly warn you that there’s no point in climbing some structure or another. Your only reward is the (often marvelous) view from the top—and the satisfaction of saying that you conquered something you didn’t need to.
Are we having fun yet?
So was playing Baby Steps any fun? Honestly, that’s not the first word I’d use to describe the experience.
To be sure, there’s a lot of humor built into the intentionally punishing designs of some sections, so much so that I often had to laugh even as I fell down yet another slippery hill that erased a huge chunk of my progress. And the promise of more wild cut scenes serves as a pretty fun and compelling carrot to get you through some of the game’s toughest sections.
I’ve earned this moment of zen. Credit: Devolver Digital
More than “fun,” though, I’d say my time with the Baby Steps felt meaningful in a way few games do. Amid all the trolly humor and intentionally obtuse design decisions is a game whose very structure forces you to consider the value of perseverance and commitment.
This is a game that stands proudly against a lot of modern game design trends. It won’t loudly and explicitly point you to the next checkpoint with a huge on-screen arrow. You can’t inexorably grind out stat points in Baby Steps until your character is powerful enough to beat the toughest boss easily. You can’t restart a Baby Steps run and hope for a lucky randomized seed that will get you past a difficult in-game wall.
Baby Steps doesn’t hand you anything. Your abilities and inventory are the same at the game’s start as they are at the end. Any progress you make is defined solely by your mastery of the obtuse movement system and your slowly increasing knowledge of how to safely traverse ever more treacherous terrain.
It’s a structure that can feel punishing, unforgiving, tedious, and enraging in turns. But it’s also a structure that leads to moments of the most genuinely satisfying sense of achievement I can remember having in modern gaming.
It’s about a miles-long journey starting with a single, halting step. It’s about putting one foot in front of the other until you can’t anymore. It’s about climbing the mountain because it’s there. It’s about falling down 1,000 times and getting up 1,001 times.
What else is there in the end?
Kyle Orland has been the Senior Gaming Editor at Ars Technica since 2012, writing primarily about the business, tech, and culture behind video games. He has journalism and computer science degrees from University of Maryland. He once wrote a whole book about Minesweeper.
Baby Steps is the most gloriously frustrating game I’ve ever struggled through Read More »