DeepMind’s robotic ballet: An AI for coordinating manufacturing robots
An AI figures out how robots can get jobs done without getting in each other’s way.
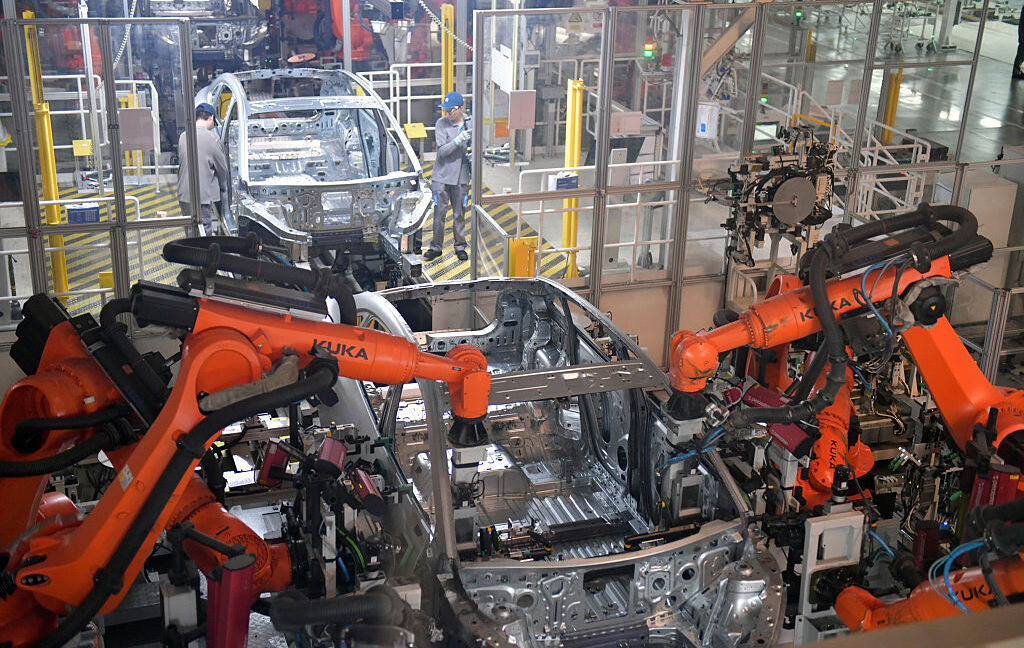
A lot of the stuff we use today is largely made by robots—arms with multiple degrees of freedom positioned along conveyor belts that move in a spectacle of precisely synchronized motions. All this motion is usually programmed by hand, which can take hundreds to thousands of hours. Google’s DeepMind team has developed an AI system called RoboBallet that lets manufacturing robots figure out what to do on their own.
Traveling salesmen
Planning what manufacturing robots should do to get their jobs done efficiently is really hard to automate. You need to solve both task allocation and scheduling—deciding which task should be done by which robot in what order. It’s like the famous traveling salesman problem on steroids. On top of that, there is the question of motion planning; you need to make sure all these robotic arms won’t collide with each other or with all the gear standing around them.
At the end, you’re facing myriad possible combinations where you’ve got to solve not one but three computationally hard problems at the same time. “There are some tools that let you automate motion planning, but task allocation and scheduling are usually done manually,” says Matthew Lai, a research engineer at Google DeepMind. “Solving all three of these problems combined is what we tackled in our work.”
Lai’s team started by generating simulated samples of what are called work cells, areas where teams of robots perform their tasks on a product being manufactured. The work cells contained something called a workpiece, a product on which the robots do work, in this case something to be constructed of aluminum struts placed on a table. Around the table, there were up to eight randomly placed Franka Panda robotic arms, each with 7 degrees of freedom, that were supposed to complete up to 40 tasks on a workpiece. Every task required a robotic arm’s end effector to get within 2.5 centimeters of the right spot on the right strut, approached from the correct angle, then stay there, frozen, for a moment. The pause simulates doing some work.
To make things harder, the team peppered every work cell with random obstacles the robots had to avoid. “We chose to work with up to eight robots, as this is around the sensible maximum for packing robots closely together without them blocking each other all the time,” Lai explains. Forcing the robots to perform 40 tasks on a workpiece was also something the team considered representative of what’s required at real factories.
A setup like this would be a nightmare to tackle using even the most powerful reinforcement-learning algorithms. Lai and his colleagues found a way around it by turning it all into graphs.
Complex relationships
Graphs in Lai’s model comprised nodes and edges. Things like robots, tasks, and obstacles were treated as nodes. Relationships between them were encoded as either one- or bi-directional edges. One-directional edges connected robots with tasks and obstacles because the robots needed information about where the obstacles were and whether the tasks were completed or not. Bidirectional edges connected the robots to each other, because each robot had to know what other robots were doing at each time step to avoid collisions or duplicating tasks.
To read and make sense of the graphs, the team used graph neural networks, a type of artificial intelligence designed to extract relationships between the nodes by passing messages along the edges of the connections among them. This decluttered the data, allowing the researchers to design a system that focused exclusively on what mattered most: finding the most efficient ways to complete tasks while navigating obstacles. After a few days of training on randomly generated work cells using a single Nvidia A100 GPU, the new industrial planning AI, called RoboBallet, could lay out seemingly viable trajectories through complex, previously unseen environments in a matter of seconds.
Most importantly, though, it scaled really well.
Economy of scale
The problem with applying traditional computational methods to complex problems like managing robots at a factory is that the challenge of computation grows exponentially with the number of items you have in your system. Computing the most optimal trajectories for one robot is relatively simple. Doing the same for two is considerably harder; when the number grows to eight, the problem becomes practically intractable.
With RoboBallet, the complexity of computation also grew with the complexity of the system, but at a far slower rate. (The computations grew linearly with the growing number of tasks and obstacles, and quadratically with the number of robots.) According to the team, these computations should make the system feasible for industrial-scale use.
The team wanted to test, however, whether the plans their AI was producing were any good. To check that, Lai and his colleagues computed the most optimal task allocations, schedules, and motions in a few simplified work cells and compared those with results delivered by RoboBallet. In terms of execution time, arguably the most important metric in manufacturing, the AI came very close to what human engineers could do. It wasn’t better than they were—it just provided an answer more quickly.
The team also tested RoboBallet plans on a real-world physical setup of four Panda robots working on an aluminum workpiece, and they worked just as well as in simulations. But Lai says it can do more than just speed up the process of programming robots.
Limping along
RoboBallet, according to DeepMind’s team, also enables us to design better work cells. “Because it works so fast, it would be possible for a designer to try different layouts and different placement or selections of robots in almost real time,” Lai says. This way, engineers at factories would be able to see exactly how much time they would save by adding another robot to a cell or choosing a robot of a different type. Another thing RoboBallet can do is reprogram the work cell on the fly, allowing other robots to fill in when one of them breaks down.
Still, there are a few things that still need ironing out before RoboBallet can come to factories. “There are several simplifications we made,” Lai admits. The first was that the obstacles were decomposed into cuboids. Even the workpiece itself was cubical. While this was somewhat representative of the obstacles and equipment in real factories, there are lots of possible workpieces with more organic shapes. “It would be better to represent those in a more flexible way, like mesh graphs or point clouds,” Lai says. This, however, would likely mean a drop in RoboBallet’s blistering speed.
Another thing is that the robots in Lai’s experiments were identical, while in a real-world work cell, robotic teams are quite often heterogeneous. “That’s why real-world applications would require additional research and engineering specific to the type of application,” Lai says. He adds, though, that the current RoboBallet is already designed with such adaptations in mind—it can be easily extended to support them. And once that’s done, his hope is that it will make factories faster and way more flexible.
“The system would have to be given work cell models, the workpiece models, as well as the list of tasks that need to be done—based on that, RoboBallet would be able to generate a complete plan,” Lai says.
Science Robotics, 2025. DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.ads1204
DeepMind’s robotic ballet: An AI for coordinating manufacturing robots Read More »