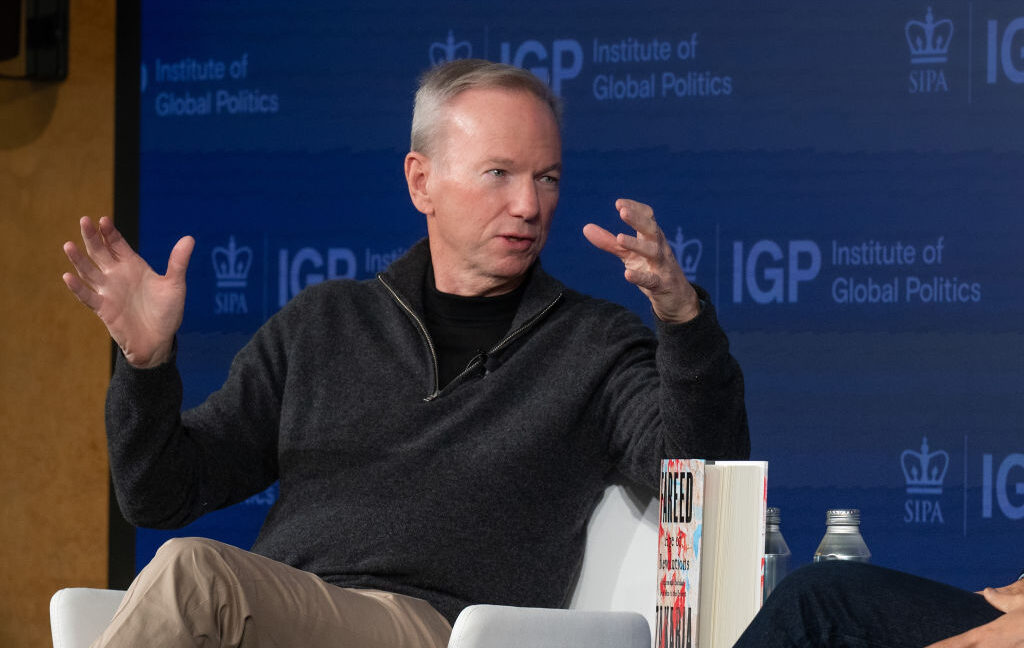
Eric Schmidt apparently bought Relativity Space to put data centers in orbit
“This probably helps explain why Schmidt bought Relativity Space,” I commented on the social media site X after Schmidt’s remarks. A day later, Schmidt replied with a single word, “Yes.”
There are relatively few US launch companies that either have large rockets or are developing them. The options for a would-be space entrepreneur who wants to control their own access to space are limited. SpaceX and Blue Origin are already owned by billionaires who have total decision-making authority. United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket is expensive, and its existing manifest is long already. Rocket Lab’s Neutron vehicle is coming soon, but it may not be large enough for Schmidt’s ambitions.
That leaves Relativity Space, which may be within a couple of years of flying the partially reusable Terran R rocket. If fully realized, Terran R would be a beastly launch vehicle capable of launching 33.5 metric tons to low-Earth orbit in expendable mode—more than a fully upgraded Vulcan Centaur—and 23.5 tons with a reusable first stage. If you were a billionaire seeking to put large data centers into space and wanted control of launch, Relativity is probably the only game in town.
As Ars has previously reported, there are some considerable flaws with Relativity’s approach to developing Terran R. However, these problems can be fixed with additional money, and Schmidt has brought that to the company over the last half-year.
Big problems, big ideas
Schmidt does not possess the wealth of an Elon Musk or Jeff Bezos. His personal fortune is roughly $20 billion, so approximately an order of magnitude less. This explains why, according to financial industry sources, Schmidt is presently seeking additional partners to bankroll a revitalized Relativity.
Solving launch is just one of the challenges this idea faces, of course. How big would these data centers be? Where would they go within an increasingly cluttered low-Earth orbit? Could space-based solar power meet their energy needs? Can all of this heat be radiated away efficiently in space? Economically, would any of this make sense?
These are not simple questions. But Schmidt is correct that the current trajectory of power and environmental demands created by AI data centers is unsustainable. It is good that someone is thinking big about solving big problems.
Eric Schmidt apparently bought Relativity Space to put data centers in orbit Read More »