Mpox outbreak is an international health emergency, WHO declares
PHEIC —
The declaration is “the highest level of alarm under international health law.”
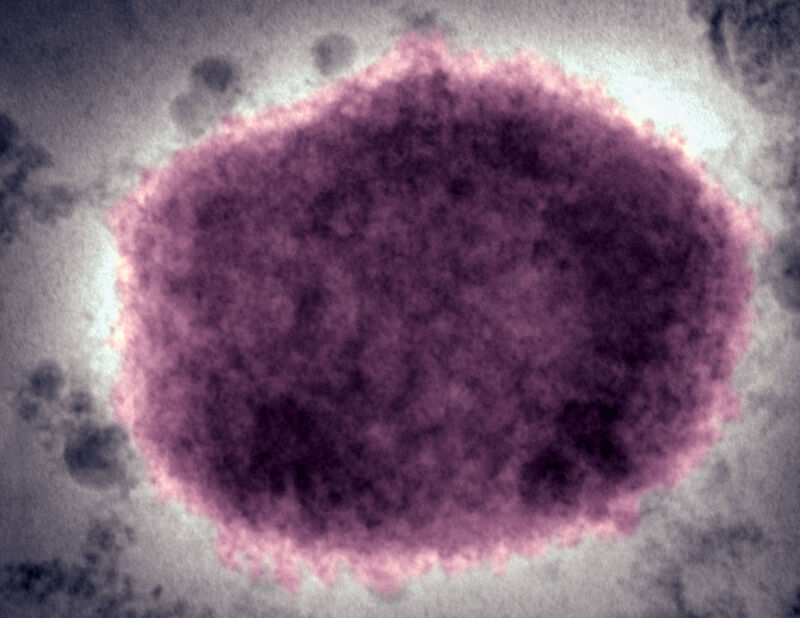
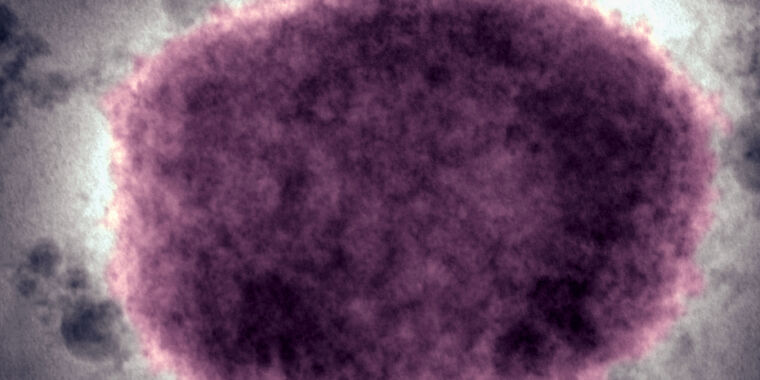
Enlarge / A negative stain electron micrograph of a mpox virus virion in human vesicular fluid.
The World Health Organization on Wednesday declared an international health emergency over a large and rapidly expanding outbreak of mpox that is spilling out of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
It is the second time in about two years that mpox’s spread has spurred the WHO to declare a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC), the highest level of alarm for the United Nations health agency. In July 2022, the WHO declared a PHEIC after mpox cases had spread across the globe, with the epicenter of the outbreak in Europe, primarily in men who have sex with men. The outbreak was caused by clade II mpox viruses, which, between the two mpox clades that exist, is the relatively mild one, causing far fewer deaths. As awareness, precautions, and vaccination increased, the outbreak subsided and was declared over in May 2023.
Unlike the 2022–2023 outbreak, the current mpox outbreak is driven by the clade II virus, the more dangerous version that causes more severe disease and more deaths. Also, while the clade I virus in the previous outbreak unexpectedly spread via sexual contact in adults, this clade II outbreak is spreading in more classic contact patterns, mostly through skin contact of household members and health care workers. A large proportion of those infected have been children.
To date, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), where the virus is endemic, has reported more than 22,000 suspect mpox cases and more than 1,200 deaths since the start of January 2023. In recent months, the outbreak has spilled out into multiple neighboring countries, including Burundi, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Kenya, and Uganda.
Earlier on Wednesday, the WHO convened an emergency committee to review the situation, in which experts from affected countries presented data to independent international experts. The committee concluded that the outbreak constituted a PHEIC, and WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus followed their recommendation.
“The emergence of a new clade of mpox, its rapid spread in eastern DRC, and the reporting of cases in several neighboring countries are very worrying,” Tedros said in a statement announcing the PHEIC. “On top of outbreaks of other mpox clades in DRC and other countries in Africa, it’s clear that a coordinated international response is needed to stop these outbreaks and save lives.”
On Tuesday, the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention declared a similar emergency. Africa CDC Director General Dr. Jean Kaseya said the declaration will “mobilize our institutions, our collective will, and our resources to act—swiftly and decisively. This empowers us to forge new partnerships, strengthen our health systems, educate our communities, and deliver life-saving interventions where they are needed most.”
For now, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assess the risk to the US public to be “very low,” given that there is limited and no direct travel between the US and the epicenter of the outbreak. So far, no clade I cases have been detected outside of central and eastern Africa.
Mpox outbreak is an international health emergency, WHO declares Read More »