The top fell off Australia’s first orbital-class rocket, delaying its launch
This was unusual
Payload fairing problems have caused a number of rocket failures, usually because they don’t jettison during launch, or only partially deploy, leaving too much extra weight on the launch vehicle for it to reach orbit.
Gilmour said it is postponing the Eris launch campaign “to fully understand what happened and make any necessary updates.” The company was founded by two brothers—Adam and James Gilmour—in 2012, and has raised approximately $90 million from venture capital firms and government funds to get the first Eris rocket to the launch pad.
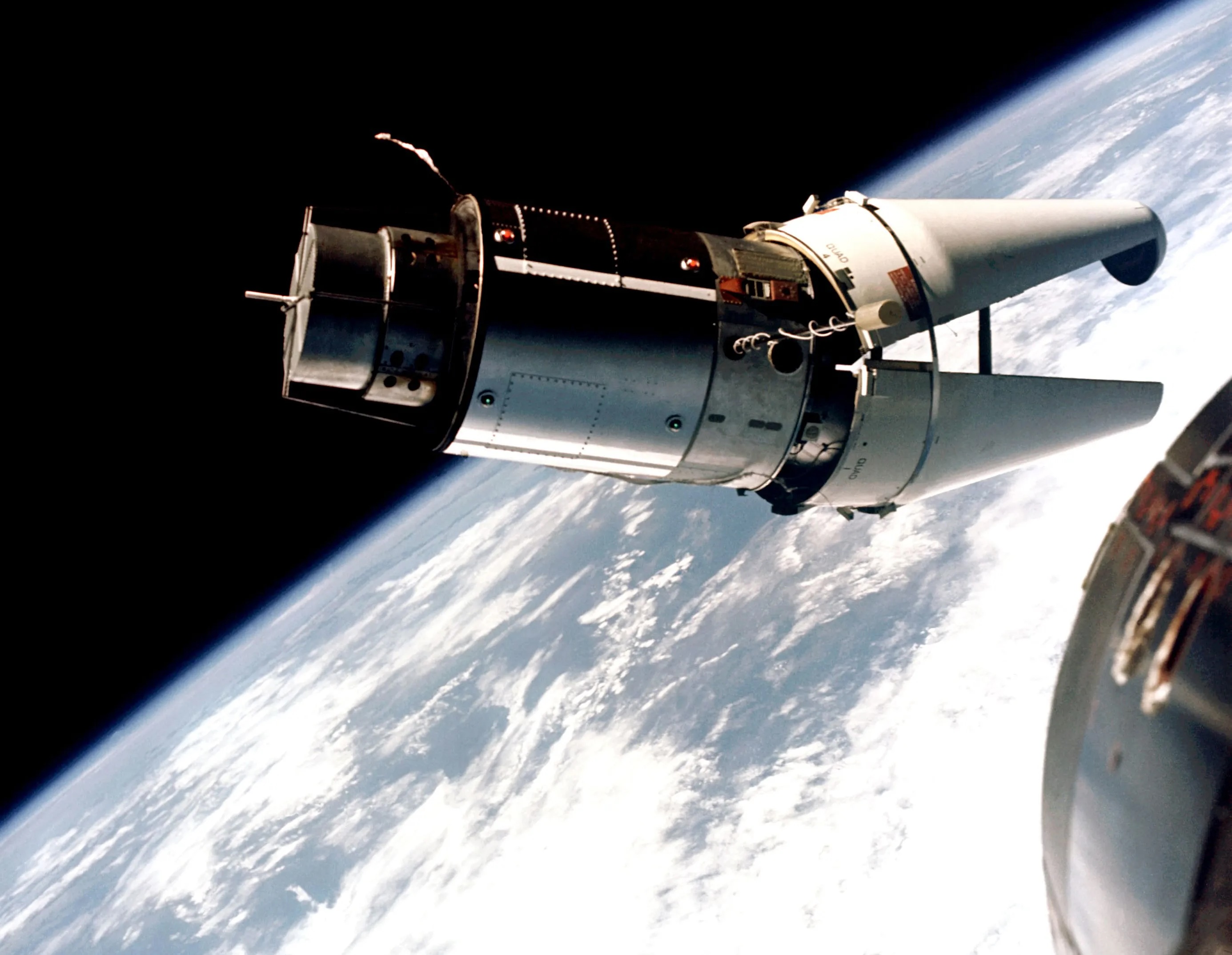
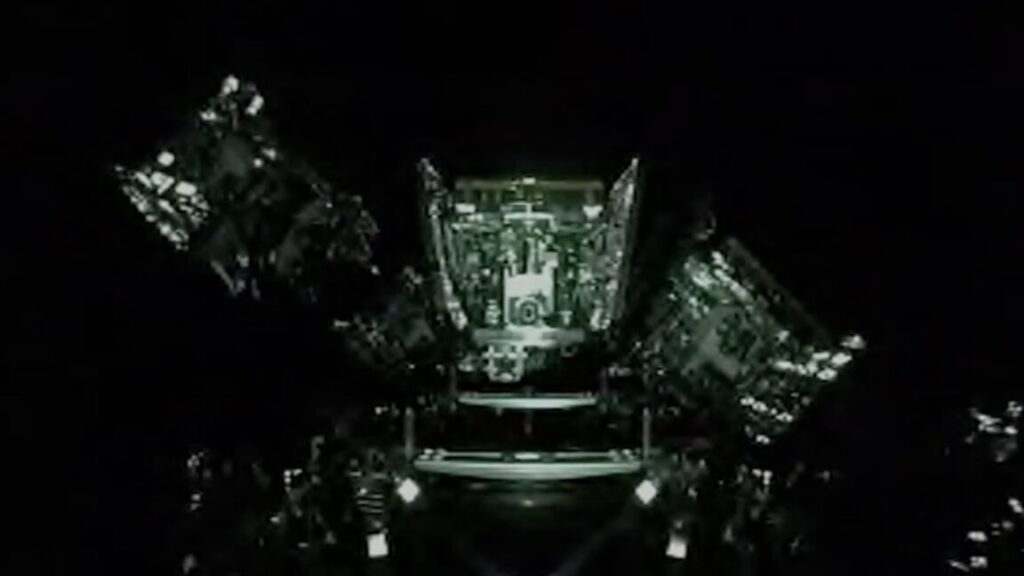
The astronauts on NASA’s Gemini 9A mission snapped this photo of a target vehicle they were supposed to dock with in orbit. But the rocket’s nose shroud only partially opened, inadvertently illustrating the method in which payload fairings are designed to jettison from their rockets in flight. Credit: NASA
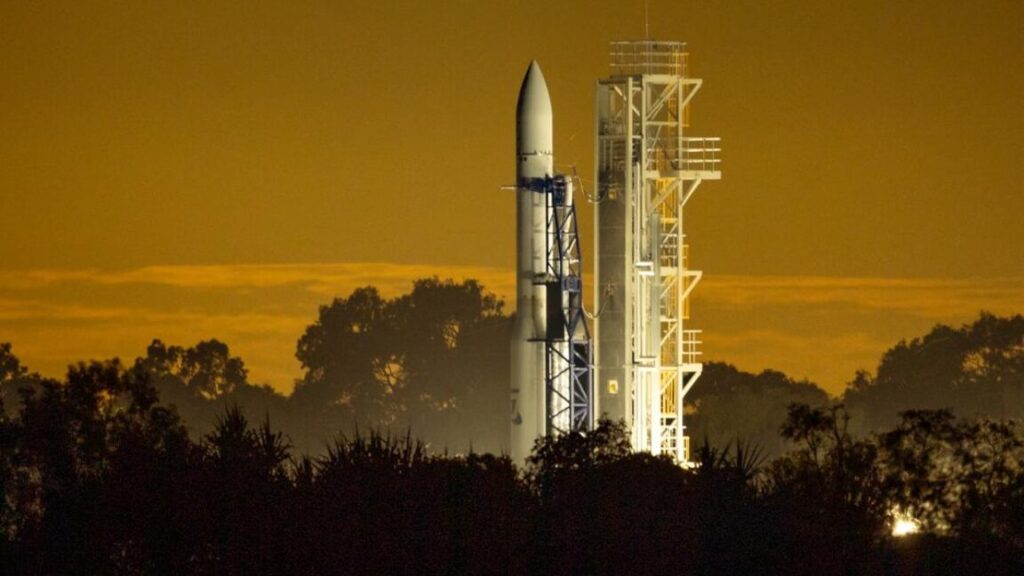
The Eris rocket was aiming to become the first all-Australian launcher to reach orbit. Australia hosted a handful of satellite launches by US and British rockets more than 50 years ago.
Gilmour is headquartered in Gold Coast, Australia, about 600 miles south of the Eris launch pad near the coastal town of Bowen. In a statement, Gilmour said it has a replacement payload fairing in its factory in Gold Coast. The company will send it to the launch site and install it on the Eris rocket after a “full investigation” into the cause of the premature fairing deployment.
“While we’re disappointed by the delay, our team is already working on a solution and we expect to be back at the pad soon,” Gilmour said.
Officials did not say how long it might take to investigate the problem, correct it, and fit a new nose cone on the Eris rocket.
This setback follows more than a year of delays Gilmour blamed primarily on holdups in receiving regulatory approval for the launch from the Australian government.
Like many rocket companies have done before, Gilmour set modest expectations for the first test flight of Eris. While the rocket has everything needed to fly to low-Earth orbit, officials said they were looking for just 10 to 20 seconds of stable flight on the first launch, enough to gather data about the performance of the rocket and its unconventional hybrid propulsion system.
The top fell off Australia’s first orbital-class rocket, delaying its launch Read More »