RFK Jr.’s loathesome edits: CDC website now falsely links vaccines and autism
With ardent anti-vaccine activist Robert F. Kennedy Jr. as the country’s top health official, a federal webpage that previously laid out the ample evidence refuting the misinformation that vaccines cause autism was abruptly replaced Wednesday with an anti-vaccine screed that promotes the false link.
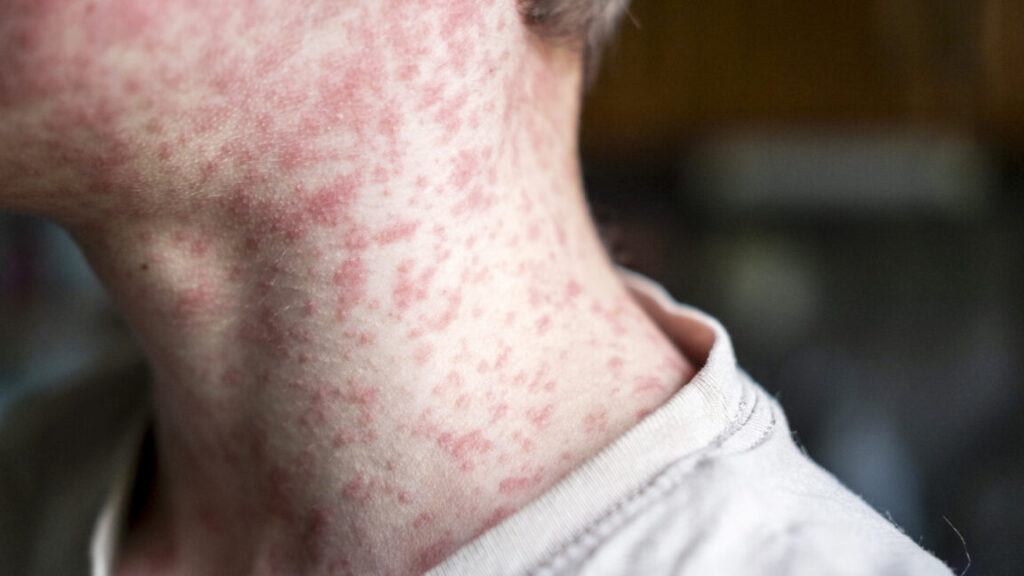
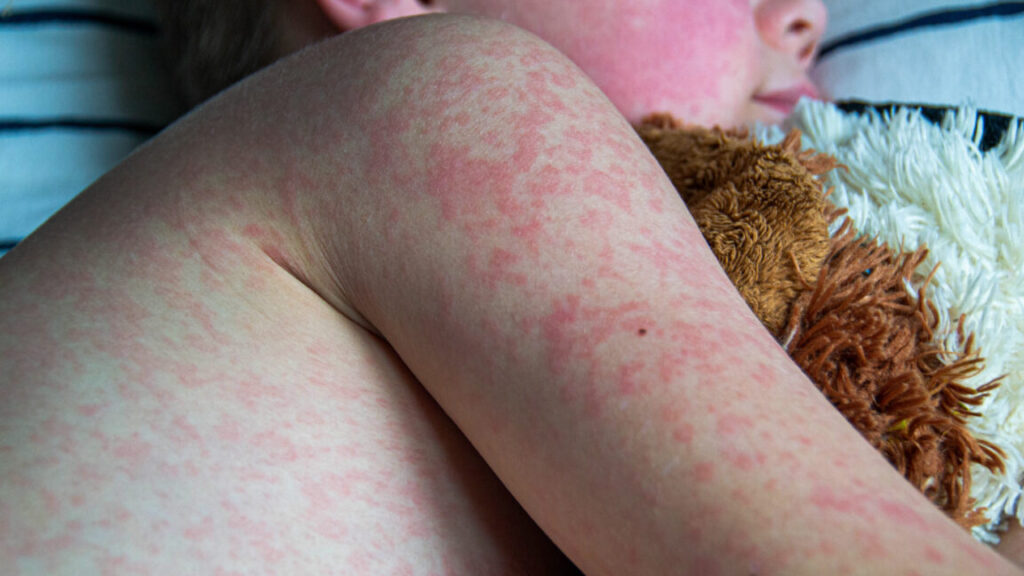
It’s a move that is sure to be celebrated by Kennedy’s fringe anti-vaccine followers, but will only sow more distrust, fear, and confusion among the public, further erode the country’s crumbling vaccination rates, and ultimately lead to more disease, suffering, and deaths from vaccine-preventable infections, particularly among children and the most vulnerable.
On the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s website titled “Autism and Vaccines,” the previous top “key point” accurately reported that: “Studies have shown that there is no link between receiving vaccines and developing autism spectrum disorder (ASD).”
But, under Kennedy, the top “key point” is now the erroneous statement: “The claim ‘vaccines do not cause autism’ is not an evidence-based claim because studies have not ruled out the possibility that infant vaccines cause autism.”
The Department of Health and Human Services, which oversees the CDC, did not respond to questions from Ars Technica about the change, including why it appears to be dismissing the substantial number of high-quality studies providing evidence that there is no association between lifesaving immunizations and the neurodevelopmental disorder. It also did not address questions of whether CDC scientists were included in the rewrite.
An emailed response attributed to HHS spokesperson Andrew Nixon said, “We are updating the CDC’s website to reflect gold standard, evidence-based science.”
RFK Jr.’s loathesome edits: CDC website now falsely links vaccines and autism Read More »