Why is my dog like this? Current DNA tests won’t explain it to you.
Popular genetics tests can’t tell you much about your dog’s personality, according to a recent study.
A team of geneticists recently found no connection between simple genetic variants and behavioral traits in more than 3,200 dogs, even though previous studies suggested that hundreds of genes might predict aspects of a dog’s behavior and personality. That’s despite the popularity of at-home genetic tests that claim they can tell you whether your dog’s genes contain the recipe for anxiety or a fondness for cuddles.
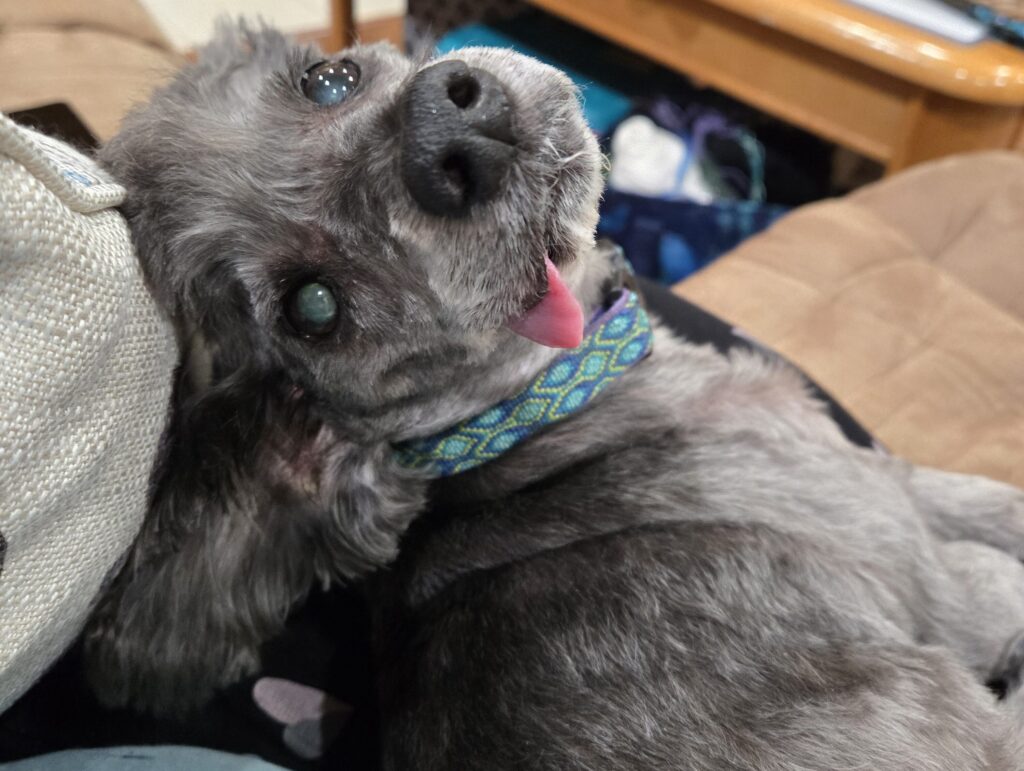

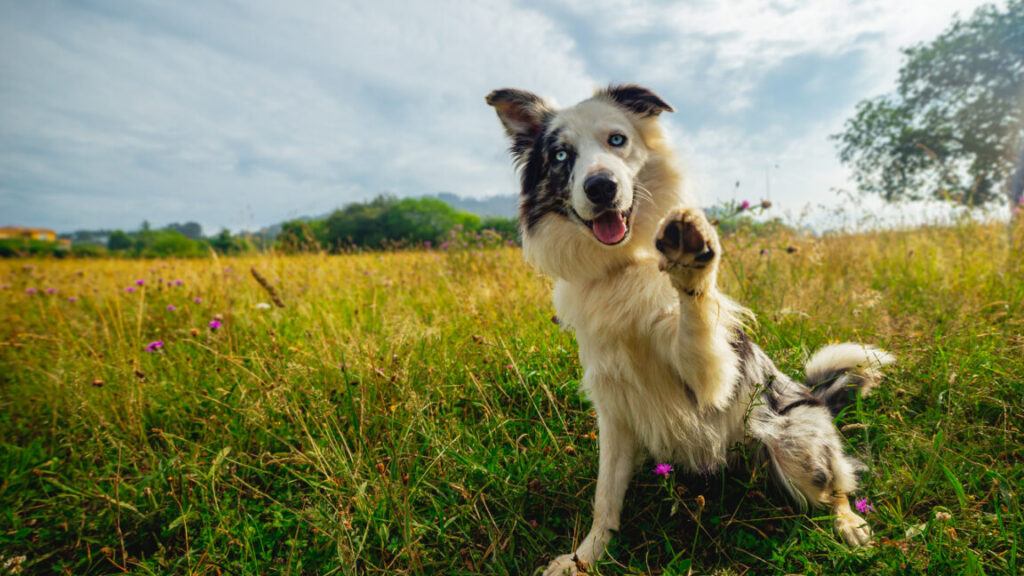
This is Max, and no single genetic variant can explain why he is the way he is. Credit: Kiona Smith
Gattaca for dogs, except it doesn’t work
University of Massachusetts genomicist Kathryn Lord and her colleagues compared DNA sequences and behavioral surveys from more than 3,000 dogs whose humans had enrolled them in the Darwin’s Ark project (and filled out the surveys). “Genetic tests for behavioral and personality traits in dogs are now being marketed to pet owners, but their predictive accuracy has not been validated,” wrote Lord and her colleagues in their recent paper.
So the team checked for relatively straightforward associations between genetic variants and personality traits such as aggression, drive, and affection. The 151 genetic variants in question all involved small changes to a single nucleotide, or “letter,” in a gene, known as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
It turns out that the answer was no: Your dog’s genes don’t predict its behavior, at least not in the simplistic way popular doggy DNA tests often claim.
And that can have serious consequences when pet owners, shelter workers, or animal rescues use these tests to make decisions about a dog’s future. “For example, if a dog is labeled as genetically predisposed to aggression, an owner might limit essential social interactions, or a shelter might decide against adoption,” Lord and her colleagues wrote.
Why is my dog like this? Current DNA tests won’t explain it to you. Read More »