People are overdosing on off-brand weight-loss drugs, FDA warns
Dosage disarray —
Bad math and unclear directions are behind overdoses of up to 20 times the normal amount.
Enlarge / Wegovy is an injectable prescription weight-loss medicine that has helped people with obesity.
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved two injectable versions of the blockbuster weight-loss and diabetes drug, semaglutide (Wegovy and Ozempic). Both come in pre-filled pens with pre-set doses, clear instructions, and information about overdoses. But, given the drugs’ daunting prices and supply shortages, many patients are turning to imitations—and those don’t always come with the same safety guardrails.
In an alert Friday, the FDA warned that people are overdosing on off-brand injections of semaglutide, which are dispensed from compounding pharmacies in a variety of concentrations, labeled with various units of measurement, administered with improperly sized syringes, and prescribed with bad dosage math. The errors are leading some patients to take up to 20 times the amount of intended semaglutide, the FDA reports.
Though the agency doesn’t offer a tally of overdose cases that have been reported, it suggests it has received multiple reports of people sickened by dosing errors, with some requiring hospitalizations. Semaglutide overdoses cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fainting, headache, migraine, dehydration, acute pancreatitis, and gallstones, the agency reports.
Bad math
In typical situations, compounding pharmacies provide personalized formulations of FDA-approved drugs, for instance, if a patient is allergic to a specific ingredient, requires a special dosage, or needs a liquid version of a drug instead of a pill form. But, when commercially available drugs are in short supply—as semaglutide drugs currently are—then compound pharmacies can legally step in to make their own versions if certain conditions are met. However, these imitations are not FDA-approved and, as such, don’t come with the same safety, quality, and effectiveness assurances as approved drugs.
In the warning Friday, the FDA said that some patients received confusing instructions from compounding pharmacies, which indicated they inject themselves with a certain number of “units” of semaglutide—the volume of which may vary depending on the concentration—rather than milligrams or milliliters. In other instances, patients received U-100 (1-milliliter) syringes to administer 0.05-milliliter doses of the drug, or five units. The relatively large syringe size compared with the dose led some patients to administer 50 units instead of five.
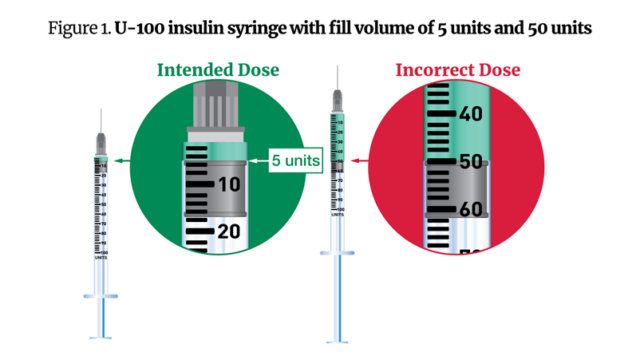
Enlarge / The figure demonstrates how syringe size could lead some to an incorrect dosage.
FDA-approved semaglutide drugs, meanwhile, are dosed in milligrams and come in standardized concentrations. The agency received several reports of health care providers incorrectly converting from milligrams to units or milliliters, leading them to calculate the wrong dosages. With these math errors, some patients administered five to 10 times more semaglutide than intended.
“FDA recognizes the substantial consumer interest in using compounded semaglutide products for weight loss,” the agency wrote. “However, compounded drugs pose a higher risk to patients than FDA-approved drugs.” The agency urged patients and prescribers to only use compounded versions when absolutely necessary.
People are overdosing on off-brand weight-loss drugs, FDA warns Read More »