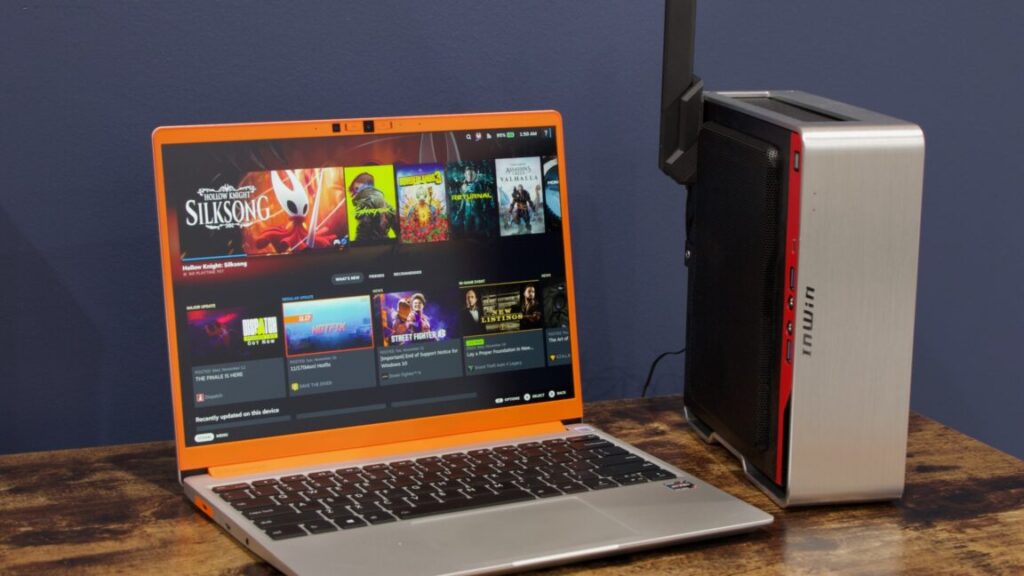
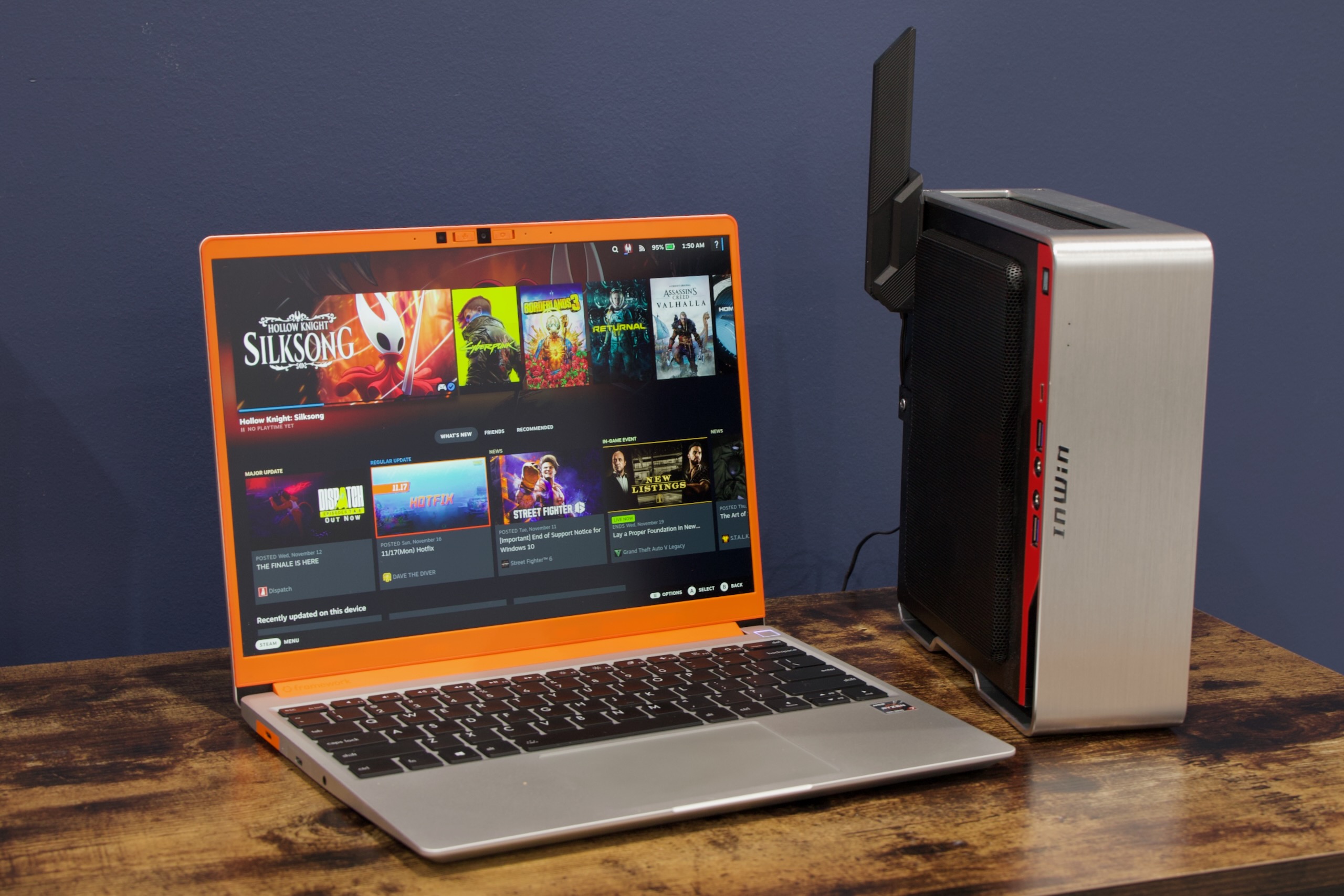
Why $700 could be a “death sentence” for the Steam Machine
Bad news for Valve in particular?
On the surface, it might seem like every company making gaming hardware would be similarly affected by increasing component costs. In practice, though, analysts suggested that Valve might be in a uniquely bad position to absorb this ongoing market disruption.
Large console makers like Sony and Microsoft “can commit to tens of millions of orders, and have strong negotiating power,” Niko Partners analyst Daniel Ahmad pointed out. The Steam Machine, on the other hand, is “a niche product that cannot benefit in the same way when it comes to procurement,” meaning Valve has to shoulder higher component cost increases.
F-Squared’s Futter echoed that Valve is “not an enormous player in the hardware space, even with the Steam Deck’s success. So they likely don’t have the same kind of priority as a Nintendo, Sony, or Microsoft when it comes to suppliers.”
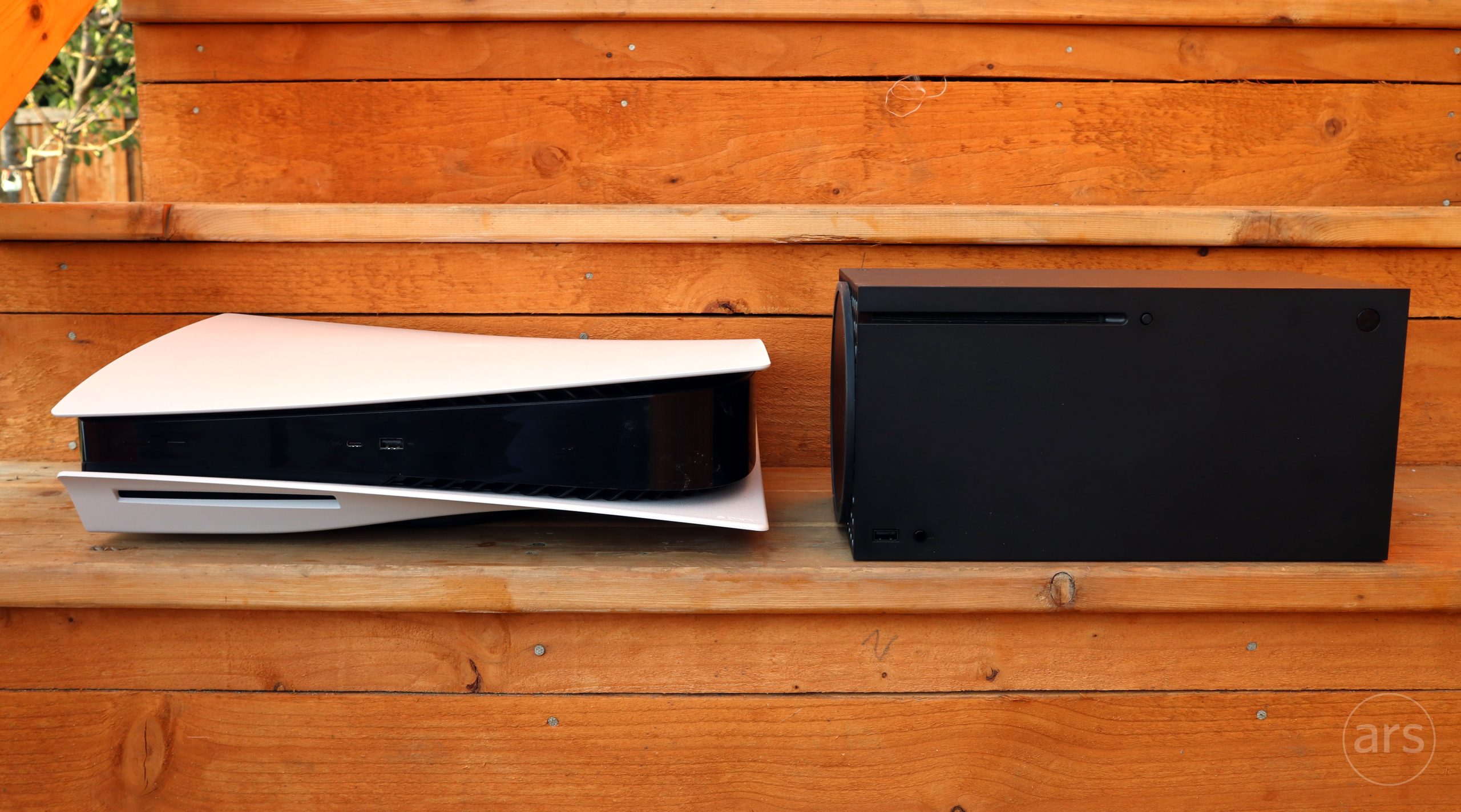
Sony and Microsoft might have an advantage when negotiating volume discounts with suppliers. Credit: Sam Machkovech
The size of the Steam Machine price adjustment also might depend on when Valve made its supply chain commitments. “It’s not clear when or if Valve locked in supply contracts for the Steam Machine, or if supply can be diverted from the Steam Deck for the new product,” Tech Insights analyst James Sanders noted. On the other hand, “Sony and Microsoft likely will have locked in more favorable component pricing before the current spike,” Van Dreunen said.
That said, some other aspects of the Steam Machine design could give Valve some greater pricing flexibility. Sanders noted that the Steam Machine’s smaller physical size could mean smaller packaging and reduced shipping costs for Valve. And selling the system primarily through direct sales via the web and Steam itself eliminates the usual retailer markups console makers have to take into account, he added.
“I think Valve was hoping for a much lower price and that the component issue would be short-term,” Cole said. “Obviously it is looking more like a long-term issue.”
Why $700 could be a “death sentence” for the Steam Machine Read More »