Microsoft formally deprecates the 39-year-old Windows Control Panel
losing control —
The Settings app has taken over, but Control Panels aren’t going anywhere yet.
-
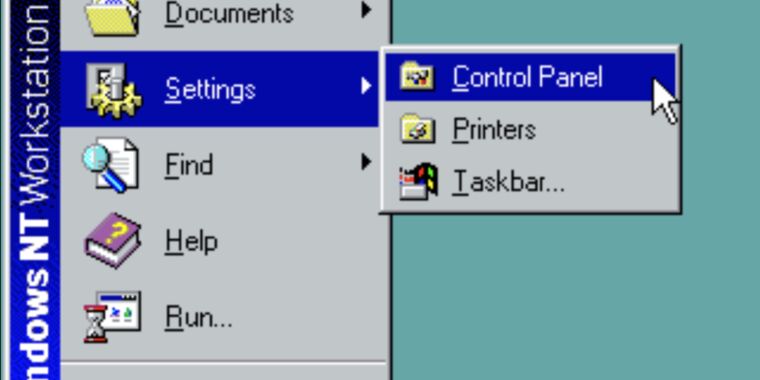
Here’s the Keyboard control panel from Windows NT 4.0.
Andrew Cunningham
-
Aside from some updated Windows Vista-era icons, the design of the modern Keyboards panel is identical.
Andrew Cunningham
-
The Mouse Pointers panel in Windows NT 4.
Andrew Cunningham
-
Again, Windows 11 hews remarkably close to the old NT-era design.
Andrew Cunningham
-
The Date & Time control panel from NT 4.
Andrew Cunningham
-
Dig a couple of menus down, and you’ll find a version of Date & Time that still looks a lot like its NT counterpart.
Andrew Cunningham
With an operating system as old as Windows, what Microsoft decides to remove is often just as (if not more) newsworthy as what it is trying to add. You may or may not care about new AI-themed MS Paint additions or the soon-to-be-reborn Recall feature, but you’ve almost certainly interacted with one of Windows’ Control Panel applets at some point in the last 39 years. And according to a note buried on Microsoft’s support site, those Control Panels’ days may be numbered (emphasis ours):
“The Control Panel is a feature that’s been part of Windows for a long time. It provides a centralized location to view and manipulate system settings and controls,” the support page explains. “Through a series of applets, you can adjust various options ranging from system time and date to hardware settings, network configurations, and more. The Control Panel is in the process of being deprecated in favor of the Settings app, which offers a more modern and streamlined experience.“
This won’t be news to anyone who has followed Windows’ development over the last decade. The Settings app was initially introduced in Windows 8 in 2012 as a touchscreen-friendly alternative for some of the Control Panel applets, but during the Windows 10 era it began picking up more and more Control Panel settings, and by the time Windows 11 rolled around it was full-featured enough to serve as a complete Control Panel replacement most of the time, with a handful of exceptions made for especially obscure changes (and those who simply prefer the Old Ways).
But while individual Control Panel applets have disappeared over the years—the Displays panel, the Add/Remove Programs screen, panels for deprecated features like Homegroups—Microsoft’s note suggests that the rest of the applets may disappear en masse in some future Windows update. That said, for now, there’s nothing that’s changing in Windows. Even the upcoming 24H2 update still has all the old Control Panels in it, and the gap between “deprecated” and “removed” can span years.
What’s incredible about some of the Control Panels at this point is how far back some of their designs go. You’re never more than a double-click away from some piece of UI that has been essentially exactly the same since 1996’s Windows NT 4.0, when Microsoft’s more-stable NT operating system was refreshed with the same user interface as Windows 95 (modern Windows versions descend from NT, and not 95 or 98). The Control Panel idea is even older, dating all the way back to Windows 1.0 in 1985.
Most of the current Control Panel designs and iconography settled down back in Windows Vista and Windows 7 in 2006 and 2009, which explains why so many of the panels still feature the rounded, glassy look that defines those versions of the operating system (check out the way the clock looks in our screenshots above). It’s one of the few areas of the operating system that hasn’t been spruced up for Windows 11, which is otherwise probably Microsoft’s most cohesive Windows design since 95 and NT 4.0; even old apps like Paint and Notepad have gotten facelifts, while other Windows 7-era holdovers like WordPad have been put out to pasture.
Microsoft formally deprecates the 39-year-old Windows Control Panel Read More »