Waymo leverages Genie 3 to create a world model for self-driving cars
On the road with AI
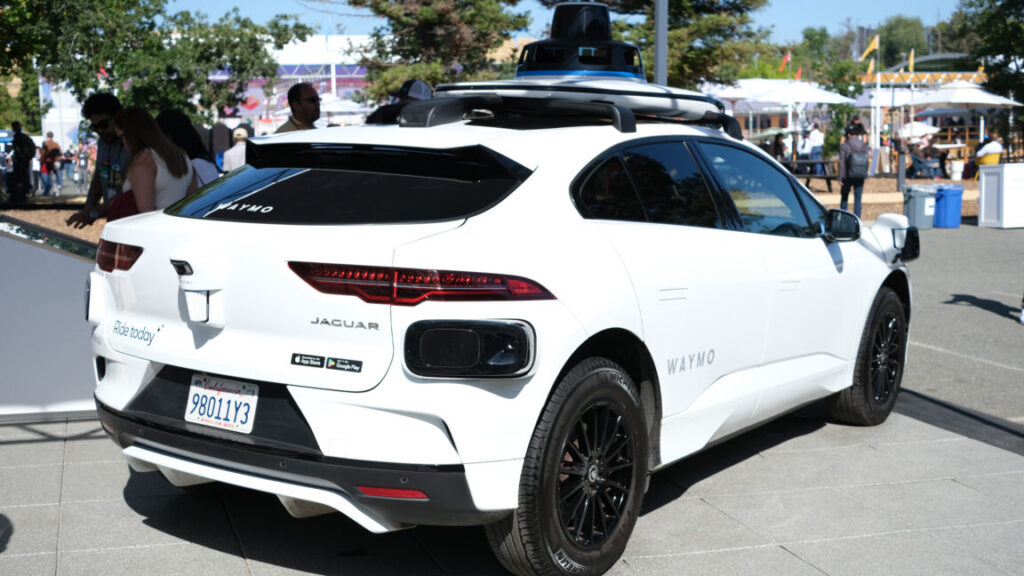
The Waymo World Model is not just a straight port of Genie 3 with dashcam videos stuffed inside. Waymo and DeepMind used a specialized post-training process to make the new model generate both 2D video and 3D lidar outputs of the same scene. While cameras are great for visualizing fine details, Waymo says lidar is necessary to add critical depth information to what a self-driving car “sees” on the road—maybe someone should tell Tesla about that.
Using a world model allows Waymo to take video from its vehicles and use prompts to change the route the vehicle takes, which it calls driving action control. These simulations, which come with lidar maps, reportedly offer greater realism and consistency than older reconstructive simulation methods.
With the world model, Waymo can see what would happen if the car took a different turn.
This model can also help improve the self-driving AI even without adding or removing everything. There are plenty of dashcam videos available for training self-driving vehicles, but they lack the multimodal sensor data of Waymo’s vehicles. Dropping such a video into the Waymo World Model generates matching sensor data, showing how the driving AI would have seen that situation.
While the Waymo World Model can create entirely synthetic scenes, the company seems mostly interested in “mutating” the conditions in real videos. The blog post contains examples of changing the time of day or weather, adding new signage, or placing vehicles in unusual places. Or, hey, why not an elephant in the road?
Waymo is ready in case an elephant shows up.
Waymo’s early test cities were consistently sunny (like Phoenix) with little inclement weather. These kinds of simulations could help the cars adapt to the more varied conditions. The new markets include places with more difficult conditions, including Boston and Washington, D.C.
Of course, the benefit of the new AI model will depend on how accurately Genie 3 can simulate the real world. The test videos we’ve seen of Genie 3 run the gamut from pretty believable to uncanny valley territory, but Waymo believes the technology has improved to the point that it can teach self-driving cars a thing or two.
Waymo leverages Genie 3 to create a world model for self-driving cars Read More »