AI Overviews hallucinates that Airbus, not Boeing, involved in fatal Air India crash
When major events occur, most people rush to Google to find information. Increasingly, the first thing they see is an AI Overview, a feature that already has a reputation for making glaring mistakes. In the wake of a tragic plane crash in India, Google’s AI search results are spreading misinformation claiming the incident involved an Airbus plane—it was actually a Boeing 787.
Travelers are more attuned to the airliner models these days after a spate of crashes involving Boeing’s 737 lineup several years ago. Searches for airline disasters are sure to skyrocket in the coming days, with reports that more than 200 passengers and crew lost their lives in the Air India Flight 171 crash. The way generative AI operates means some people searching for details may get the wrong impression from Google’s results page.
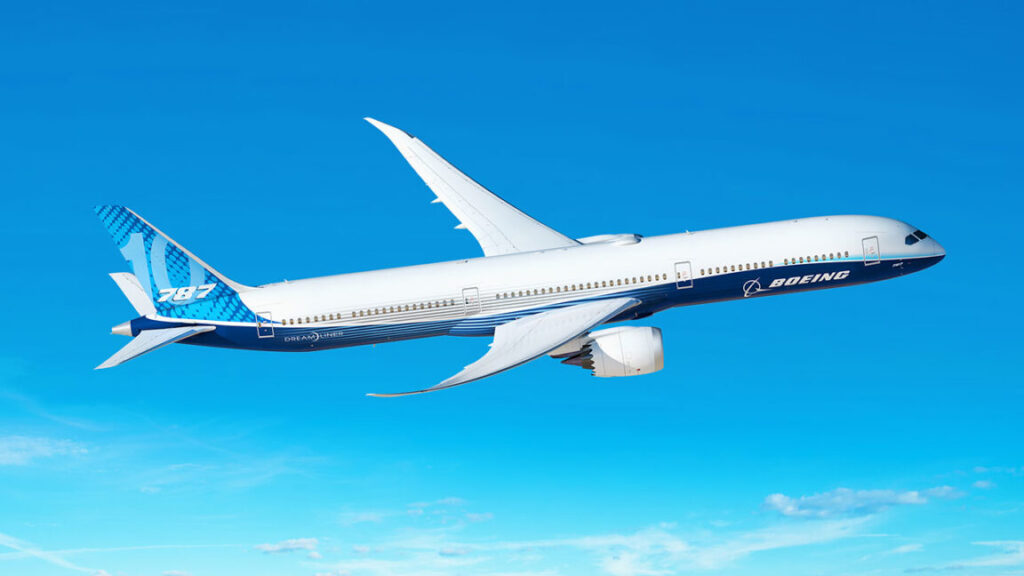
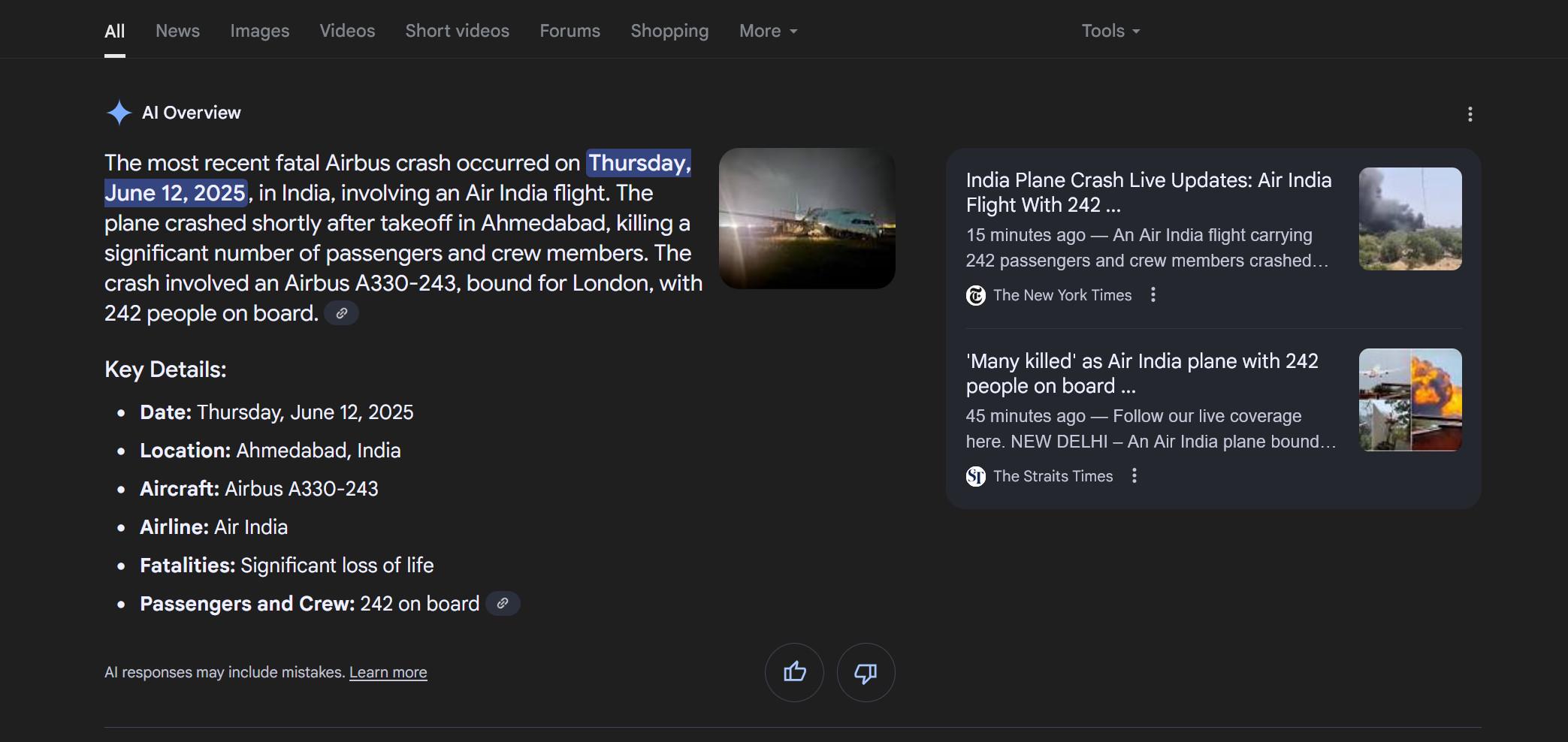
Not all searches get AI answers, but Google has been steadily expanding this feature since it debuted last year. One searcher on Reddit spotted a troubling confabulation when searching for crashes involving Airbus planes. AI Overviews, apparently overwhelmed with results reporting on the Air India crash, stated confidently (and incorrectly) that it was an Airbus A330 that fell out of the sky shortly after takeoff. We’ve run a few similar searches—some of the AI results say Boeing, some say Airbus, and some include a strange mashup of both Airbus and Boeing. It’s a mess.
In this search, Google’s AI says the crash involved an Airbus A330 instead of a Boeing 787. Credit: /u/stuckintrraffic
But why is Google bringing up the Air India crash at all in the context of Airbus? Unfortunately, it’s impossible to predict if you’ll get an AI Overview that blames Boeing or Airbus—generative AI is non-deterministic, meaning the output is different every time, even for identical inputs. Our best guess for the underlying cause is that numerous articles on the Air India crash mention Airbus as Boeing’s main competitor. AI Overviews is essentially summarizing these results, and the AI goes down the wrong path because it lacks the ability to understand what is true.
AI Overviews hallucinates that Airbus, not Boeing, involved in fatal Air India crash Read More »