Trump tries to block state AI laws himself after Congress decided not to
Trump claims state laws force AI makers to embed “ideological bias” in models.
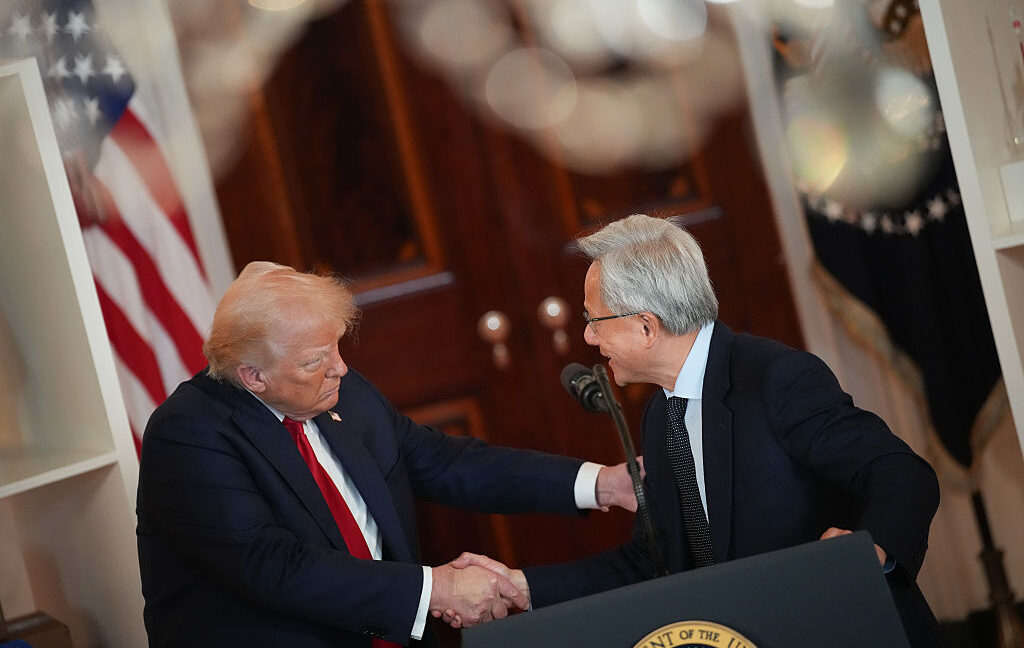
President Donald Trump talks to journalists after signing executive orders in the Oval Office at the White House on August 25, 2025 in Washington, DC. Credit: Getty Images | Chip Somodevilla
President Trump issued an executive order yesterday attempting to thwart state AI laws, saying that federal agencies must fight state laws because Congress hasn’t yet implemented a national AI standard. Trump’s executive order tells the Justice Department, Commerce Department, Federal Communications Commission, Federal Trade Commission, and other federal agencies to take a variety of actions.
“My Administration must act with the Congress to ensure that there is a minimally burdensome national standard—not 50 discordant State ones. The resulting framework must forbid State laws that conflict with the policy set forth in this order… Until such a national standard exists, however, it is imperative that my Administration takes action to check the most onerous and excessive laws emerging from the States that threaten to stymie innovation,” Trump’s order said. The order claims that state laws, such as one passed in Colorado, “are increasingly responsible for requiring entities to embed ideological bias within models.”
Congressional Republicans recently decided not to include a Trump-backed plan to block state AI laws in the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA), although it could be included in other legislation. Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) has also failed to get congressional backing for legislation that would punish states with AI laws.
“After months of failed lobbying and two defeats in Congress, Big Tech has finally received the return on its ample investment in Donald Trump,” US Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) said yesterday. “With this executive order, Trump is delivering exactly what his billionaire benefactors demanded—all at the expense of our kids, our communities, our workers, and our planet.”
Markey said that “a broad, bipartisan coalition in Congress has rejected the AI moratorium again and again.” Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Wash.) said the “executive order’s overly broad preemption threatens states with lawsuits and funding cuts for protecting their residents from AI-powered frauds, scams, and deepfakes.”
Trump orders Bondi to sue states
Sen. Brian Schatz (D-Hawaii) said that “preventing states from enacting common-sense regulation that protects people from the very real harms of AI is absurd and dangerous. Congress has a responsibility to get this technology right—and quickly—but states must be allowed to act in the public interest in the meantime. I’ll be working with my colleagues to introduce a full repeal of this order in the coming days.”
The Trump order includes a variation on Cruz’s proposal to prevent states with AI laws from accessing broadband grant funds. The executive order also includes a plan that Trump recently floated to have the federal government file lawsuits against states with AI laws.
Within 30 days of yesterday’s order, US Attorney General Pam Bondi is required to create an AI Litigation Task Force “whose sole responsibility shall be to challenge State AI laws inconsistent with the policy set forth in section 2 of this order, including on grounds that such laws unconstitutionally regulate interstate commerce, are preempted by existing Federal regulations, or are otherwise unlawful in the Attorney General’s judgment.”
Americans for Responsible Innovation, a group that lobbies for regulation of AI, said the Trump order “relies on a flimsy and overly broad interpretation of the Constitution’s Interstate Commerce Clause cooked up by venture capitalists over the last six months.”
Section 2 of Trump’s order is written vaguely to give the administration leeway to challenge many types of AI laws. “It is the policy of the United States to sustain and enhance the United States’ global AI dominance through a minimally burdensome national policy framework for AI,” the section says.
Colorado law irks Trump
The executive order specifically names a Colorado law that requires AI developers to protect consumers against “algorithmic discrimination.” It defines this type of discrimination as “any condition in which the use of an artificial intelligence system results in an unlawful differential treatment or impact that disfavors an individual or group of individuals on the basis” of age, race, sex, and other protected characteristics.
The Colorado law compels developers of “high-risk systems” to make various disclosures, implement a risk management policy and program, give consumers the right to “correct any incorrect personal data that a high-risk system processed in making a consequential decision,” and let consumers appeal any “adverse consequential decision concerning the consumer arising from the deployment of a high-risk system.”
Trump’s order alleges that the Colorado law “may even force AI models to produce false results in order to avoid a ‘differential treatment or impact’ on protected groups.” Trump’s order also says that “state laws sometimes impermissibly regulate beyond State borders, impinging on interstate commerce.”
Trump ordered the Commerce Department to evaluate existing state AI laws and identify “onerous” ones that conflict with the policy. “That evaluation of State AI laws shall, at a minimum, identify laws that require AI models to alter their truthful outputs, or that may compel AI developers or deployers to disclose or report information in a manner that would violate the First Amendment or any other provision of the Constitution,” the order said.
States would be declared ineligible for broadband funds
Under the order, states with AI laws that get flagged by the Trump administration will be deemed ineligible for “non-deployment funds” from the US government’s $42 billion Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program. The amount of non-deployment funds will be sizable because it appears that only about half of the $42 billion allocated by Congress will be used by the Trump administration to help states subsidize broadband deployment.
States with AI laws would not be blocked from receiving the deployment subsidies, but would be ineligible for the non-deployment funds that could be used for other broadband-related purposes. Beyond broadband, Trump’s order tells other federal agencies to “assess their discretionary grant programs” and consider withholding funds from states with AI laws.
Other agencies are being ordered to use whatever authority they have to preempt state laws. The order requires Federal Communications Commission Chairman Brendan Carr to “initiate a proceeding to determine whether to adopt a Federal reporting and disclosure standard for AI models that preempts conflicting State laws.” It also requires FTC Chairman Andrew Ferguson to issue a policy statement detailing “circumstances under which State laws that require alterations to the truthful outputs of AI models are preempted by the Federal Trade Commission Act’s prohibition on engaging in deceptive acts or practices affecting commerce.”
Finally, Trump’s order requires administration officials to “prepare a legislative recommendation establishing a uniform Federal policy framework for AI that preempts State AI laws that conflict with the policy set forth in this order.” The proposed ban would apply to most types of state AI laws, with exceptions for rules relating to “child safety protections; AI compute and data center infrastructure, other than generally applicable permitting reforms; [and] state government procurement and use of AI.”
It would be up to Congress to decide whether to pass the proposed legislation. But the various other components of the executive order could dissuade states from implementing AI laws even if Congress takes no action.
Trump tries to block state AI laws himself after Congress decided not to Read More »