RFK Jr.’s CDC panel ditches some flu shots based on anti-vaccine junk data
Flu shots with thimerosal abandoned, despite decades of data showing they’re safe.
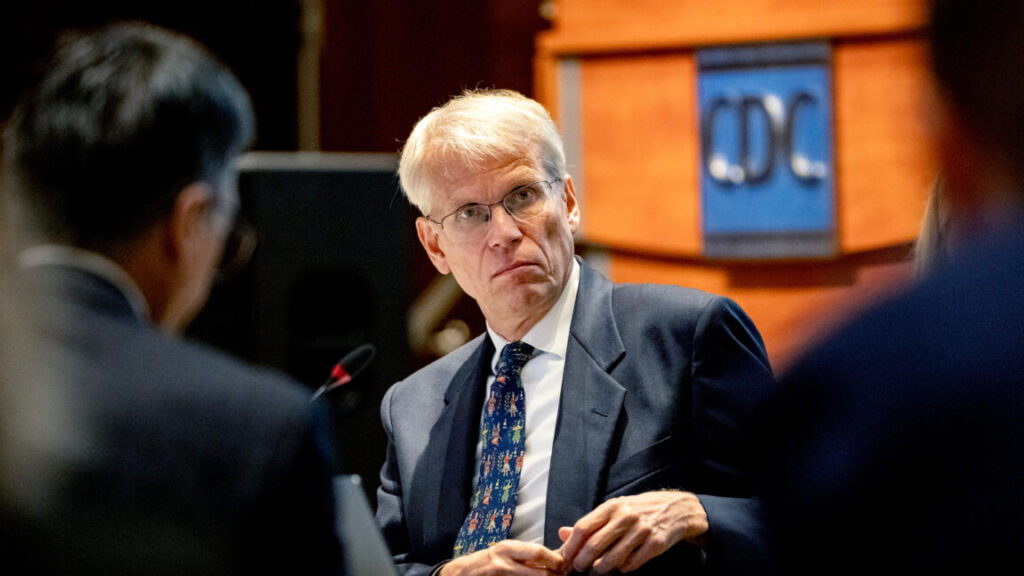
Dr. Martin Kulldorff, chair of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, during the first meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee On Immunization Practices on June 25, 2025. Credit: Getty | Bloomberg
The vaccine panel hand-selected by health secretary and anti-vaccine advocate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. on Thursday voted overwhelmingly to drop federal recommendations for seasonal flu shots that contain the ethyl-mercury containing preservative thimerosal. The panel did so after hearing a misleading and cherry-picked presentation from an anti-vaccine activist.
There is extensive data from the last quarter century proving that the antiseptic preservative is safe, with no harms identified beyond slight soreness at the injection site, but none of that data was presented during today’s meeting.
The significance of the vote is unclear for now. The vast majority of seasonal influenza vaccines currently used in the US—about 96 percent of flu shots in 2024–2025—do not contain thimerosal. The preservative is only included in multi-dose vials of seasonal flu vaccines, where it prevents the growth of bacteria and fungi potentially introduced as doses are withdrawn.
However, thimerosal is more common elsewhere in the world for various multi-dose vaccine vials, which are cheaper than the single-dose vials more commonly used in the US. If other countries follow the US’s lead and abandon thimerosal, it could increase the cost of vaccines in other countries and, in turn, lead to fewer vaccinations.
Broken process
However, it remains unclear what impact today’s vote will have—both in the US and abroad. Normally, before voting on any significant changes to vaccine recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the committee that met today—the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)— would go through an exhaustive process. That includes thoroughly reviewing and discussing the extensive safety and efficacy data of the vaccines, the balance of their benefits and harms, equity considerations, and the feasibility and resource implications of their removal.
But, instead, the committee heard a single presentation given by anti-vaccine activist, Lyn Redwood, who was once the president of the anti-vaccine organization founded by Kennedy, Children’s Health Defense.
Thimerosal has long been a target of anti-vaccine activists like Redwood, who hold fast to the false and thoroughly debunked claim that vaccines—particularly thimerosal-containing vaccines—cause autism and neurological disorders. Her presentation today was a smorgasbord of anti-vaccine talking points against thimerosal, drawing on old and fringe studies she claimed prove that thimerosal is an ineffective preservative, kills cells in petri dishes, and can be found in the brains of baby monkeys after it has been injected into them. The presentation did not appear to have gone through any vetting by the CDC, and an earlier version contained a reference to a study that does not exist.
Yesterday, CBS News reported that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is hiring Redwood to oversee vaccine safety. In response, Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.) called Redwood an “extremist,” and urged the White House to immediately reverse the decision. “We cannot allow a few truly deranged individuals to distort the plain truth and facts around vaccines so badly,” Murray said in a statement.
CDC scientists censored
Prior to the meeting, CDC scientists posted a background briefing document on thimerosal. It contained summaries of around two dozen studies that all support the safety of thimerosal and/or find no association with autism or neurological disorders. It also explained how in 1999, health experts and agencies made plans to remove thimerosal from childhood vaccines out of an abundance of caution for concern that it was adding to cumulative exposures that could hypothetically become toxic—at high doses, thimerosal can be dangerous. By 2001, it was removed from every childhood vaccine in the US and remains so to this day. But, since then, studies have found thimerosal to be perfectly safe in vaccines. All the studies listed by the CDC in support of thimerosal were published after 2001.
The document also contained a list of nearly two dozen studies claiming to find a link to autism, but where described by the CDC as having “significant methodological limitations.” The Institute of Medicine also called them “uninterpretable, and therefore, noncontributory with respect to causality.” Every single one of the studies was authored by the anti-vaccine father and son duo Mark and David Geier.
In March, it came to light that Kennedy had hired David Geier to the US health department to continue trying to prove a link between autism and vaccines. He is now working on the issue.
The CDC’s thimerosal document was removed from the ACIP’s meeting documents prior to the meeting. Robert Malone, one of the new ACIP members who holds anti-vaccine views, said during the meeting that it was taken down because it “was not authorized by the Office of the Secretary [Kennedy].” You can read it here.
Lone voice
In the meeting today, Kennedy’s hand-selected ACIP members did not ask Redwood any questions about the data or arguments she made against thimerosal. Nearly all of them readily accepted that thimerosal should be removed entirely. The only person to push back was Cody Meissner, a pediatric professor at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine who has served on ACIP in the past—arguably the most qualified and reasonable member of the new lineup.
“I’m not quite sure how to respond to this presentation,” he said after Redwood finished her slides. “This is an old issue that has been addressed in the past. … I guess one of the most important [things] to remember is that thimerosal is metabolized into ethylmercury and thiosalicylate. It’s not metabolized into methylmercury, which is in fish and shellfish. Ethylmercury is excreted much more quickly from the body. It is not associated with the high neurotoxicity that methylmercury is,” he explained.
Meissner scoffed at the committee even spending time on it. “So, of all the issues that I think we, ACIP, needs to focus on, this is not a big issue. … no study has ever indicated any harm from thimerosal. It’s been used in vaccines … since before World War II.
But he did express concern that it could be removed from the vaccine used globally.
“The recommendations the ACIP makes are followed among many countries around the world,” he said. “And removing thimerosal from all vaccines that are used in other countries, for example, is going to reduce access to these vaccines.”
Anti-vaccine agenda
In the end, the seven-member panel voted in favor of recommending only those seasonal flu vaccines that did not contain thimerosal. There were three separate votes for this, making this recommendation for children, pregnant women, and all adults each, but all with the same outcome: five ‘yes’ votes, one ‘no’ vote (Meissner), and one abstention from anti-vaccine activist and nurse Vicky Pebsworth. After the vote, Pebsworth clarified that she did not support the use of thimerosal in vaccines, but had a quibble with how the voting questions were written.
Prior to the vote, ACIP Chair Martin Kulldorff gave a brief presentation on the MMRV vaccine (measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella/chickenpox). He previewed a proposed recommendation to vote on in a future meeting that would remove the CDC’s recommendation for that vaccine as well.
Beth is Ars Technica’s Senior Health Reporter. Beth has a Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and attended the Science Communication program at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She specializes in covering infectious diseases, public health, and microbes.
RFK Jr.’s CDC panel ditches some flu shots based on anti-vaccine junk data Read More »