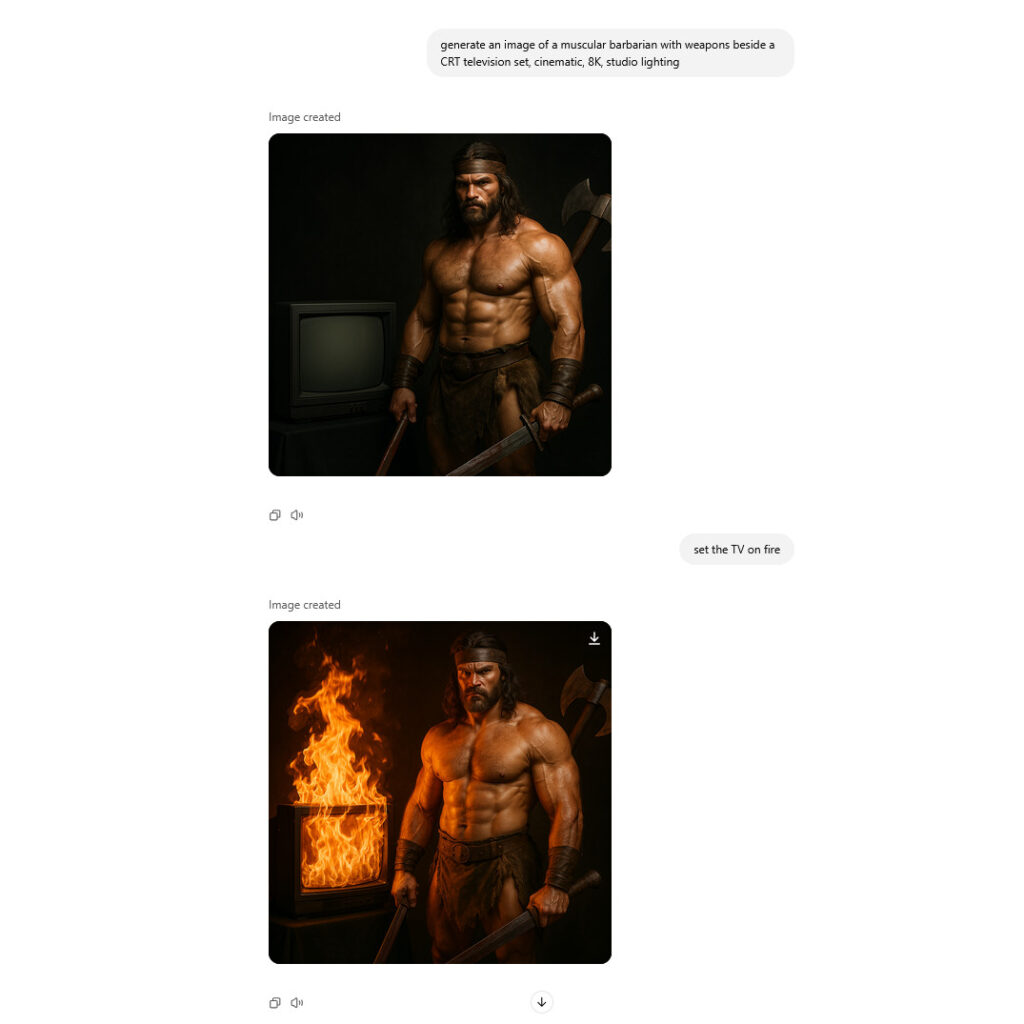
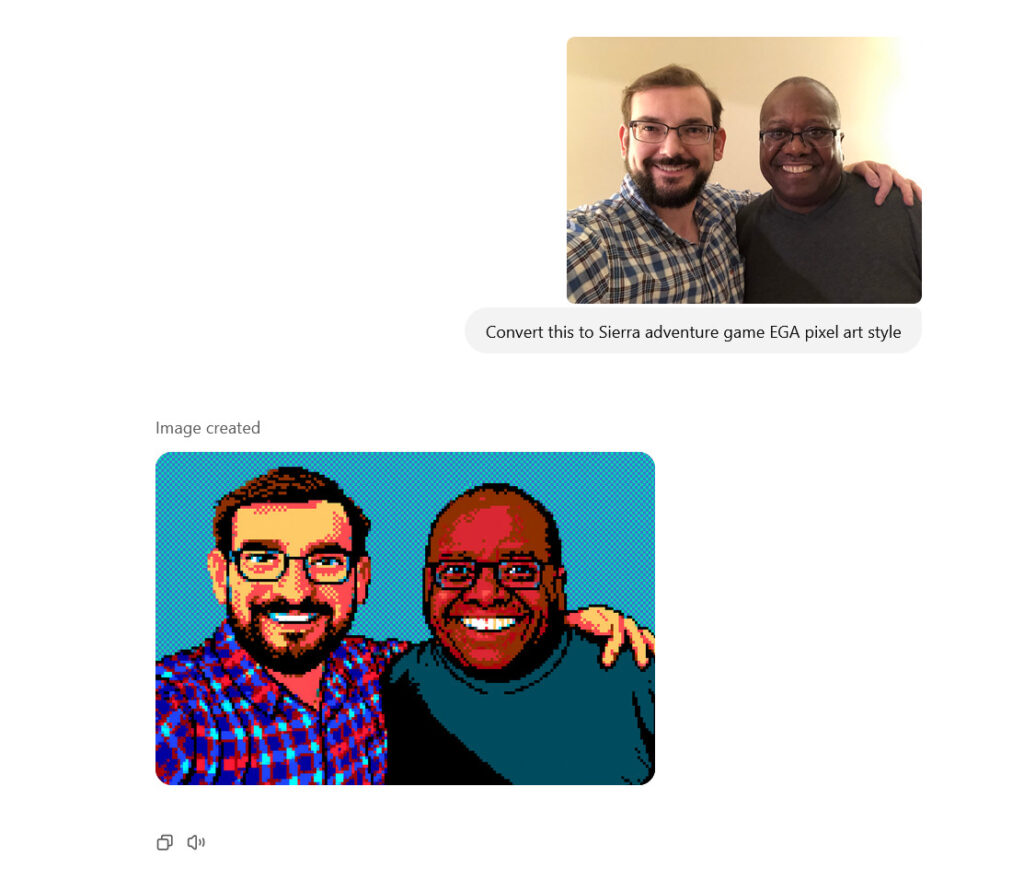
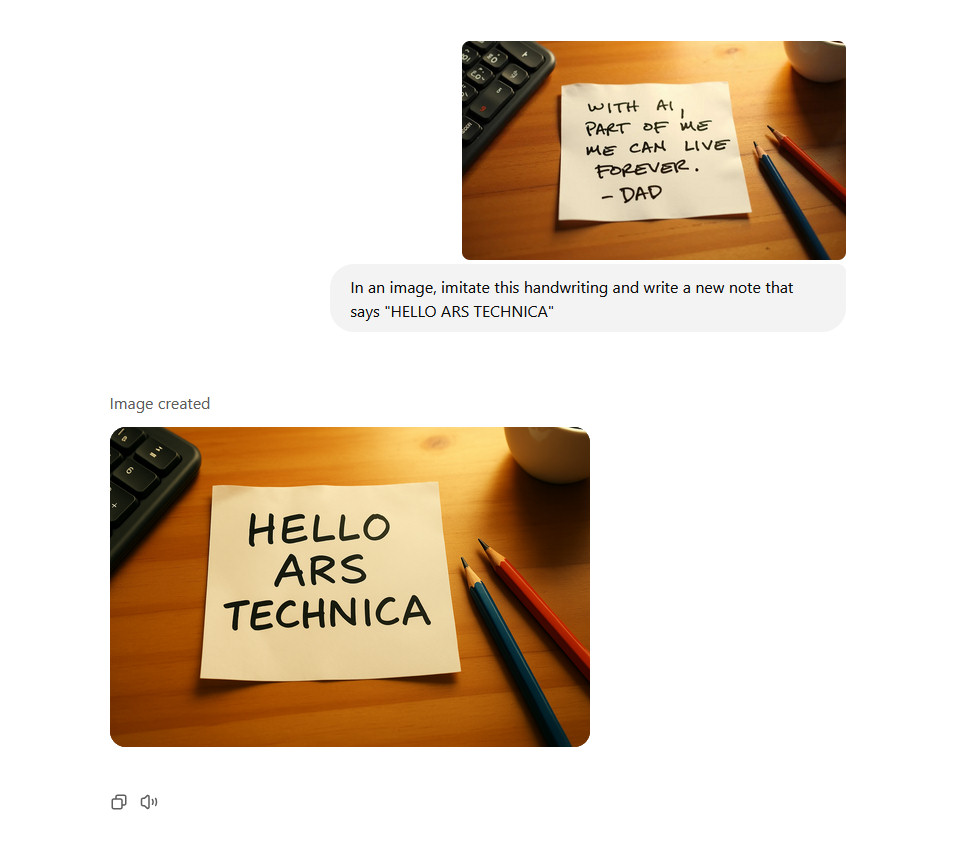
ChatGPT can now remember and reference all your previous chats
Unlike the older saved memories feature, the information saved via the chat history memory feature is not accessible or tweakable. It’s either on or it’s not.
The new approach to memory is rolling out first to ChatGPT Plus and Pro users, starting today—though it looks like it’s a gradual deployment over the next few weeks. Some countries and regions (the UK, European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland) are not included in the rollout.
OpenAI says these new features will reach Enterprise, Team, and Edu users at a later, as-yet-unannounced date. The company hasn’t mentioned any plans to bring them to free users. When you gain access to this, you’ll see a pop-up that says “Introducing new, improved memory.”
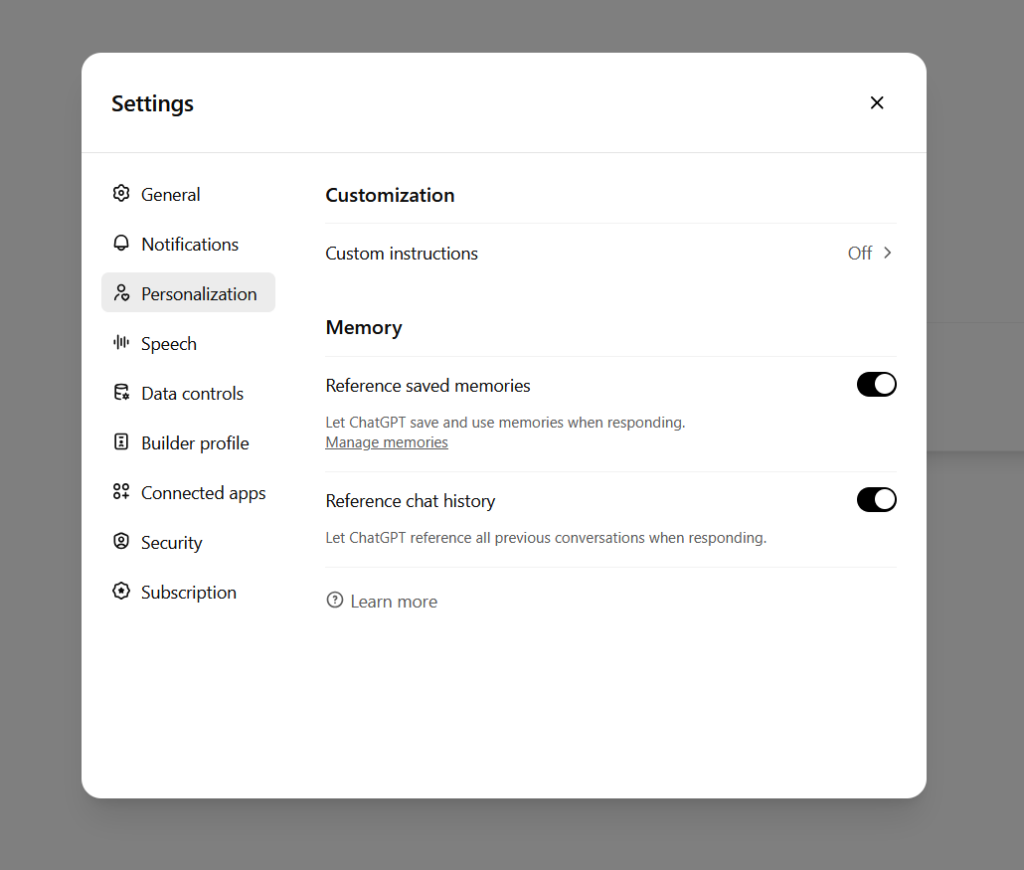
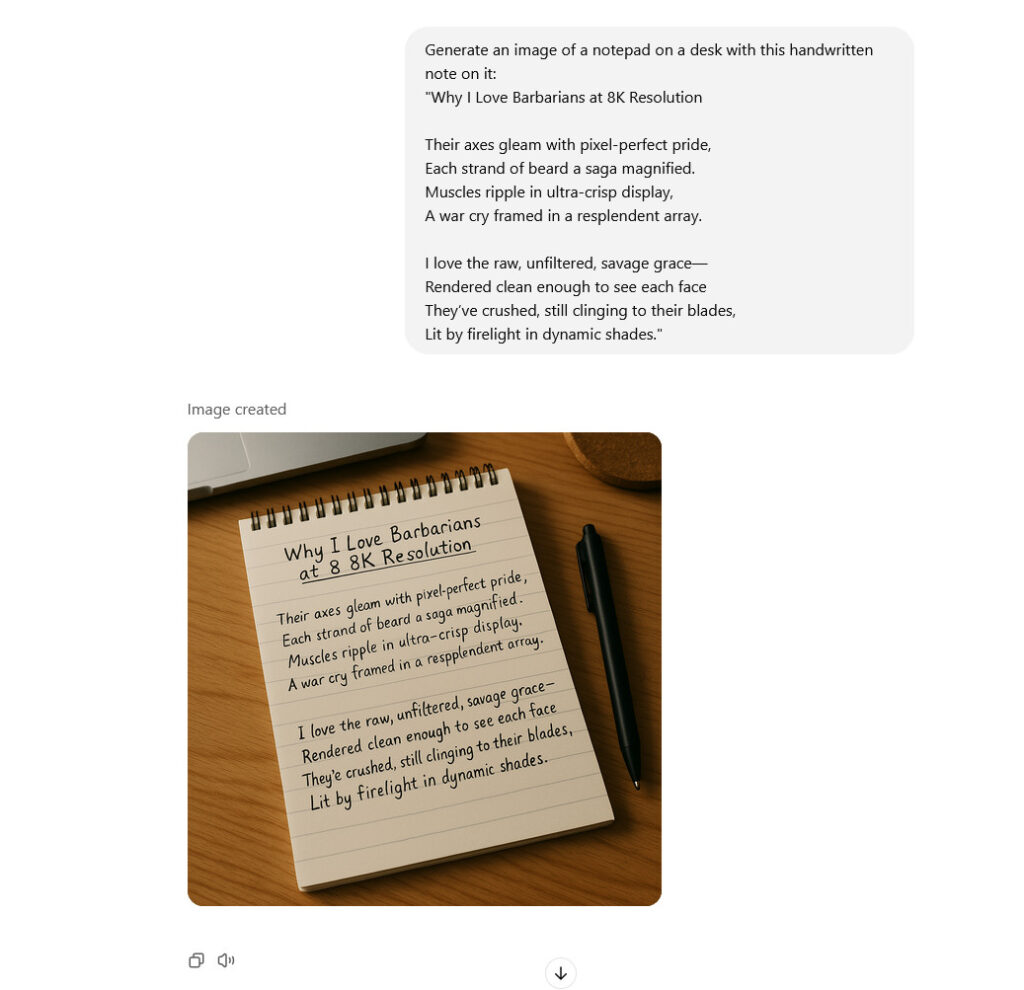
The new ChatGPT memory options. Credit: Benj Edwards
Some people will welcome this memory expansion, as it can significantly improve ChatGPT’s usefulness if you’re seeking answers tailored to your specific situation, personality, and preferences.
Others will likely be highly skeptical of a black box of chat history memory that can’t be tweaked or customized for privacy reasons. It’s important to note that even before the new memory feature, logs of conversations with ChatGPT may be saved and stored on OpenAI servers. It’s just that the chatbot didn’t fully incorporate their contents into its responses until now.
As with the old memory feature, you can click a checkbox to disable this completely, and it won’t be used for conversations with the Temporary Chat flag.
ChatGPT can now remember and reference all your previous chats Read More »